Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Transfer Function of A PMDC Motor
Hochgeladen von
Kenneth Tan0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
219 Ansichten6 SeitenDynamic Modelling on electric motor winding
Originaltitel
Transfer Function of a PMDC Motor
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenDynamic Modelling on electric motor winding
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
219 Ansichten6 SeitenTransfer Function of A PMDC Motor
Hochgeladen von
Kenneth TanDynamic Modelling on electric motor winding
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
Aim
Apparatus
Student name
Signature
Date
Batch
To find the transfer function of a Permanent Magnet DC Motor.
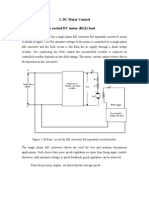
EXP-5. TRANSFER FUNCTION OF A PMDC MOTOR
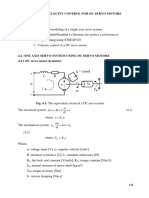
Diagram
I = i
u
R
u
+ I
d
c
dt
+ e
b (1)
e
b
= K
b
(2)
I
c
= [
do
dt
+B +I
I
(3)
T
e
= K
b
i
a
(4)
V = Applied voltage across the motor terminals.
I
a
= Current through the motor.
R
a
= Armature resistance.
L
a
= Armature inductance.
e
b
= Back emf developed.
T
e
= Electromagnetic torque developed.
= speed of the rotor.
J = moment of inertia of the rotor.
B = viscous friction coefficient.
T
l
= load torque.
K
b
= back emf constant.
Procedure
Finding armature resistance (R
a
)
When the rotor is blocked from rotation (at zero rpm) as per (2) back emf becomes
zero.
Apply very less amount of DC voltage to the motor under blocked rotor condition,
When the current reaches steady state the effect of inductance becomes zero.
Under this condition (1) becomes
V = i
a
R
a
Measure i
a
and find resistance.
Finding armature inductance (L
a
)
Apply a small AC voltage to the motor under blocked rotor condition. Measure
current passing through the motor. The ratio of the applied voltage to this
current gives impedance of the armature (Z
a
).
Z
a
= R
a
+ jX
L
From the above equation we find the value of X
L.
X
L
= 2 f L
a
Where f is the frequency of applied voltage
From above equation find the value of X
L
.
Finding back emf constant (K
b
)
Apply a DC voltage to the motor and motor starts to rotate. Allow the motor to
reach a steady state.
At the steady state inductance effect is zero. Measure current through the motor
and speed of the motor.
By solving (1) & (2) find the value of K
b
.
Finding viscous friction coefficient (B)
Under no-load condition apply a DC voltage to the motor and allow the motor to
reach a steady state or constant speed. At this condition (3) becomes
T
e
= B .
Measure speed and current through the motor. Calculate T
e
using (4)
.
From above
equation calculate the value B.
Finding the rotor moment of inertia(J)
Connect the speed sensor to DSO.
Apply a DC voltage to the motor. After a few seconds motor reaches the steady
state speed.
Observe the waveform of speed and find the time constant.
Time constant = J/B
From the above equation calculate J.
Tabulation
Armature Resistance (R
a
)
Voltage(v) Current(i
a
) Ra = v/i
a
Average
Armature inductance (L
a
)
Impedance
(Z)
Reactance
(X
L
)
Armature inductance (L
a
)
Back emf constant(K
b
) and viscous friction coefficient(B)
Applied
voltage
I
a
w K
b
T
e
B
Average value
Rotor Moment of Inertia (J)
Time
constant
Moment of Inertia
Finding transfer function
After finding all the machine constants using (1),(2),(3),(4), find the ratio of (s)/V(s).
(s)
I(s)
=
K
b
s
2
([I
u
) +s(BI
u
+ [R
u
) + (BR
u
+ K
b
2
)
Observations and Remarks
Conclusion
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- DYNA6 Manual With ExamplesDokument227 SeitenDYNA6 Manual With ExamplesDeepmalaJayesh100% (1)
- Mechanics of Wave Forces On Offshore StructuresDokument5 SeitenMechanics of Wave Forces On Offshore StructuresKenneth Tan43% (7)
- Thyristor ReportDokument9 SeitenThyristor ReportDhaval GamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual HP Photosmart C4485Dokument243 SeitenManual HP Photosmart C4485Cineva CindvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre and Post-Process Tools in Finite Element Analysis: Universitat de GironaDokument213 SeitenPre and Post-Process Tools in Finite Element Analysis: Universitat de GironaMuneer SalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fly-Ball Governor: ReferenceDokument1 SeiteFly-Ball Governor: Referencenadya novarizkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficiency Improvements in High Speed Operation Using Slotless Configuration For PMSMDokument7 SeitenEfficiency Improvements in High Speed Operation Using Slotless Configuration For PMSMAmit ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Machines: Parts of DC MachineDokument51 SeitenDC Machines: Parts of DC MachineKUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsDokument4 SeitenElectrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsPranav MenonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asynchronous Machines Tutorial Sheets (EL-208Dokument10 SeitenAsynchronous Machines Tutorial Sheets (EL-208Kushagra BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Iii Induction Motor Drives: Dept. of EEEDokument17 SeitenUnit Iii Induction Motor Drives: Dept. of EEEmanoj kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frog Leg WindingDokument9 SeitenFrog Leg WindingAbhijeet RedekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State Drives Short BookDokument48 SeitenSolid State Drives Short BookGomathi Raja MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part BDokument10 SeitenPart BVenkat ManiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dcmotors and Their RepresentationDokument61 SeitenDcmotors and Their RepresentationSoeprapto AtmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur Department of Electrical EngineeringDokument4 SeitenIndian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur Department of Electrical EngineeringKool PrashantNoch keine Bewertungen
- HV Engineering: Generation of High Frequency Ac High Voltage Using Tesla CoilDokument6 SeitenHV Engineering: Generation of High Frequency Ac High Voltage Using Tesla CoilAdnan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Link CurrentDokument8 SeitenDC Link CurrentsubbannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magenetic Chip Collector New 2Dokument27 SeitenMagenetic Chip Collector New 2Hemasundar Reddy JolluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universal Motors: Presented by Meraj WarsiDokument13 SeitenUniversal Motors: Presented by Meraj WarsiMeraj WarsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE8411 - EM 2 LabDokument6 SeitenEE8411 - EM 2 LabVengatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical ExamDokument2 SeitenPractical ExamIrfan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip TestDokument3 SeitenExperiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip Test61EEPrabhat PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load Sharing of Synchronous GeneratorDokument16 SeitenLoad Sharing of Synchronous GeneratorSalma AkterNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Motor Speed ControllerDokument22 SeitenDC Motor Speed ControllerShafqt MbrkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tut - PsocDokument2 SeitenTut - Psocfews100% (1)
- DC MachinesDokument52 SeitenDC MachinesArun Kumar100% (1)
- Unit1 EDCDokument24 SeitenUnit1 EDCKarthick Sivakumar ChellamuthuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Assignment EEE 111Dokument3 SeitenFinal Assignment EEE 111Ahmed RakibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speeed ControlDokument3 SeitenSpeeed ControlChristine GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wound-Field Synchronous Machine DrivesDokument62 SeitenWound-Field Synchronous Machine DrivesKorlpate BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 3Dokument3 SeitenSheet 3geo_bi100% (1)
- Control System Lab ManualDokument62 SeitenControl System Lab ManualVenkata Subramanian0% (1)
- Special - Electrical - Machines QBDokument25 SeitenSpecial - Electrical - Machines QBVel MuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 PDFDokument170 SeitenUnit 2 PDFSaurabh RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Single+Three) Phase Induction Motors Interview Questions SetDokument18 Seiten(Single+Three) Phase Induction Motors Interview Questions SetrajshahieeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction and Working of Brushless DC PDFDokument12 SeitenConstruction and Working of Brushless DC PDFaswardi8756Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Source InductanceDokument25 SeitenEffect of Source InductanceSriram Anil Kumar Gandham100% (1)
- Psoc Course FileDokument14 SeitenPsoc Course Filecholleti sriramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measure AC Voltages Using an AC PotentiometerDokument3 SeitenMeasure AC Voltages Using an AC PotentiometerNh Chuminda Yapa100% (1)
- HVDC Unit IIIDokument22 SeitenHVDC Unit IIISreenivas Reddy BodimallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machies Singly ExcitedDokument15 SeitenMachies Singly ExcitedMohamed ElfekyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slip Power RecoveryDokument12 SeitenSlip Power Recoverysriharidino50% (2)
- Problem Set 1Dokument9 SeitenProblem Set 1jerry tranNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE2403 Special Electrical MachinesDokument19 SeitenEE2403 Special Electrical MachinesvasanthavananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Systems Protection Course: Al-Balqa Applied UniversityDokument36 SeitenPower Systems Protection Course: Al-Balqa Applied UniversityAayush PatidarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Background On Linear Induction Motors in Transportation Jun 1970Dokument99 SeitenTechnical Background On Linear Induction Motors in Transportation Jun 1970Shantanu GaikwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC GeneratorDokument38 SeitenDC Generatoraswardi8756Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Power Systems (Eceg-3176) : Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (Aait)Dokument38 SeitenIntroduction To Power Systems (Eceg-3176) : Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (Aait)DANIEL ABERANoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial on single phase induction motor parameters and performanceDokument1 SeiteTutorial on single phase induction motor parameters and performanceHimanshu Saini0% (1)
- Induction Motor: Navigation SearchDokument8 SeitenInduction Motor: Navigation SearchSoni Mishra TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 360 Topic 6 DC MachineDokument33 Seiten360 Topic 6 DC MachineAchsan ArfandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems Chapter 5 1Dokument7 SeitenProblems Chapter 5 1Siva KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.1 Leakage Flux and Leakage InductanceDokument29 Seiten6.1 Leakage Flux and Leakage InductancePrema ElizabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinusoidal PMAC Motor - 6th AprilDokument4 SeitenSinusoidal PMAC Motor - 6th AprilSourav KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induction Generator Operation and ApplicationsDokument4 SeitenInduction Generator Operation and ApplicationsAaryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step-Down Chopper Overview and ProceduresDokument4 SeitenStep-Down Chopper Overview and ProceduresKsr AkhilNoch keine Bewertungen
- No Load and Block Rotor Tests for 3-Phase Induction MotorDokument11 SeitenNo Load and Block Rotor Tests for 3-Phase Induction MotorKsr Akhil100% (1)
- Power-system protection A Complete GuideVon EverandPower-system protection A Complete GuideBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- M4. Velocity Control For DC Servo MotorsDokument21 SeitenM4. Velocity Control For DC Servo MotorsHưng Trần ThảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Motor Control PositionDokument8 SeitenDC Motor Control Positionreynaldi adeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 2Dokument6 SeitenExp 2College ISMNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMO Sub-Committee Discusses Safe Transport of Dangerous Goods by SeaDokument99 SeitenIMO Sub-Committee Discusses Safe Transport of Dangerous Goods by SeaKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMO Sub-Committee Discusses Safe Transport of Dangerous Goods by SeaDokument99 SeitenIMO Sub-Committee Discusses Safe Transport of Dangerous Goods by SeaKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Bargain Price List 2014Dokument2 SeitenBest Bargain Price List 2014Kenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Part Price ListDokument6 SeitenComputer Part Price ListKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchor Handling VesselDokument2 SeitenAnchor Handling VesselKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Plug AbandonmentDokument20 SeitenWell Plug AbandonmentKenneth Tan100% (2)
- Ulstein Designer PX105 BrochureDokument6 SeitenUlstein Designer PX105 BrochureKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical and Electronic Installation For IACSDokument60 SeitenElectrical and Electronic Installation For IACSKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- H&S Guideline 06 - Standby Vessels (English) 29-06-2004Dokument26 SeitenH&S Guideline 06 - Standby Vessels (English) 29-06-2004awi61Noch keine Bewertungen
- Compact CIS Command Intercom SystemDokument4 SeitenCompact CIS Command Intercom SystemKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Spare Part ListDokument6 SeitenComputer Spare Part ListKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Old Supreme Court Open HouseDokument1 SeiteOld Supreme Court Open HouseKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giosan - Vortex Shedding Induced Loads On Free Standing Structures PDFDokument42 SeitenGiosan - Vortex Shedding Induced Loads On Free Standing Structures PDFmarinamoviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing Upper BodyDokument2 SeitenAssessing Upper BodyKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules For The Classification of Steel Ships Part C - Machinery Electrical Automation and Fire Protection CHP 2 - 3Dokument134 SeitenRules For The Classification of Steel Ships Part C - Machinery Electrical Automation and Fire Protection CHP 2 - 3Kenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSV Part 5 E-Jan15Dokument242 SeitenOSV Part 5 E-Jan15Kenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules For The Classification of Steel Ships Part D - Service Notations CHP 1 - 7Dokument222 SeitenRules For The Classification of Steel Ships Part D - Service Notations CHP 1 - 7Kenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enviroco Inserts Decommissioning Inde Case StudyDokument2 SeitenEnviroco Inserts Decommissioning Inde Case StudyKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Innovative Breakthrough Vessel:: Strength and DepthDokument20 SeitenOur Innovative Breakthrough Vessel:: Strength and DepthKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Store ElectricityDokument18 SeitenWhy Store ElectricityKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Fighting SystemDokument20 SeitenFire Fighting Systemanuavi93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deepstim: Advanced, Versatile Stimulation VesselsDokument4 SeitenDeepstim: Advanced, Versatile Stimulation VesselsKenneth Tan100% (1)
- IBP ShuttleBus Service (International Business Park)Dokument1 SeiteIBP ShuttleBus Service (International Business Park)Kenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resolution Msc.235Dokument11 SeitenResolution Msc.235seckin80Noch keine Bewertungen
- IBP ShuttleBus Service (International Business Park)Dokument1 SeiteIBP ShuttleBus Service (International Business Park)Kenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Geothermal Power Plants: Design, Performance and EconomicsDokument8 SeitenSmall Geothermal Power Plants: Design, Performance and EconomicsvladimirbubonjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Stimulation VesselsDokument2 SeitenWell Stimulation VesselsOscar RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warm UpDokument1 SeiteWarm UpKenneth TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torsional Response of Assymetric Multy Story Building - ThesisDokument89 SeitenTorsional Response of Assymetric Multy Story Building - Thesis폴로 쥰 차Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gravitation QuestionsDokument2 SeitenGravitation QuestionsTrilok AkhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Tunnel Notes PDFDokument173 SeitenWind Tunnel Notes PDFaeronautical rajasNoch keine Bewertungen
- P P/ V/ X X / L P F F - F: 30.4 Decay of Turbulence Downstream From A Stilling BasinDokument2 SeitenP P/ V/ X X / L P F F - F: 30.4 Decay of Turbulence Downstream From A Stilling Basinamanj2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Pull-Force in Injected PultrusionDokument28 SeitenAnalysis of Pull-Force in Injected PultrusionSabin RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2020 QP IAL Mechanics 2Dokument32 SeitenJune 2020 QP IAL Mechanics 2Daniel KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elastic and viscoelastic properties of metals and their modelingDokument11 SeitenElastic and viscoelastic properties of metals and their modelinggunapalshettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotex SpecDokument30 SeitenRotex SpecspringkimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Communication BasicsDokument164 SeitenSatellite Communication Basicsvasu100% (1)
- Orbital Mechanics: Elliptical OrbitsDokument18 SeitenOrbital Mechanics: Elliptical OrbitsDoaa KhaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMT IMP Questions NewDokument3 SeitenHMT IMP Questions NewRavi PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corbel STMDokument12 SeitenCorbel STMShishir Kumar NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creep Behavior of CMC - NASADokument20 SeitenCreep Behavior of CMC - NASAVaradhaYamunan KKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci8 Q1-M1 Laws of MotionDokument30 SeitenSci8 Q1-M1 Laws of MotionPagudpud National HSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice 2013 07 11 PDFDokument4 SeitenSimple Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice 2013 07 11 PDFYuusuf AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity, Magnetism & Electromagnetism ExplainedDokument1 SeiteElectricity, Magnetism & Electromagnetism Explainedmaxine janorasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Phenomena (Transfer Processes)Dokument38 SeitenTransport Phenomena (Transfer Processes)esiri aluyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Shallow Water Equations An Example of Hyperbolic SystemDokument32 SeitenThe Shallow Water Equations An Example of Hyperbolic SystemChibaka WarsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijcrr: A Study On Magnetorheological Fluid (MRF) DamperDokument8 SeitenIjcrr: A Study On Magnetorheological Fluid (MRF) Damperaakrit paiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rankine-Froude Model: Blade Element Momentum Theory Is A Theory That Combines BothDokument111 SeitenRankine-Froude Model: Blade Element Momentum Theory Is A Theory That Combines BothphysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluent-Intro 17.0 Module07 TurbulenceDokument50 SeitenFluent-Intro 17.0 Module07 TurbulenceSadullah TaşkınNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeworksheet-3Dokument2 SeitenHomeworksheet-3丁安磊Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric field of a uniformly charged diskDokument7 SeitenElectric field of a uniformly charged diskJay ZillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fisika - Physics For High SchoolDokument396 SeitenFisika - Physics For High SchoolZainal AbidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text Demo: Gyroscope, Tennis Racket, Old CD: Lecture 26 - Torque-Free Rotation - Body-Fixed AxesDokument5 SeitenText Demo: Gyroscope, Tennis Racket, Old CD: Lecture 26 - Torque-Free Rotation - Body-Fixed Axesabhi101010Noch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS-118 Electric Field FundamentalsDokument61 SeitenPHYS-118 Electric Field FundamentalsNavpreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Ghana: InstructionsDokument15 SeitenUniversity of Ghana: InstructionsAlexander AsonkeyNoch keine Bewertungen