Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Health Research Methodology
Hochgeladen von
lianazulakCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Health Research Methodology
Hochgeladen von
lianazulakCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
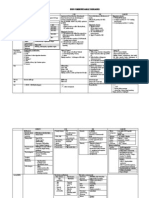
HEALTH RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research: systematic collection, analysis & interpretation of data to answer a certain question/solve problem Research experience help improve students skills in: 1. Searching & critically appraising medical literature 2. Independent continued learning 3. Writing research papers Characteristic 1. Demands a clear statement of problem 2. Requires clear obj & plan 3. Builds on existing data, using both + & - findings 4. New data should be systematically collected & analyzed to answer original research obj
Steps of conducting HR 1. Prioritizing & selecting a research topic 2. Review of literature & other existing information 3. Development of a research proposal 4. Implementation of study: i. Data collection ii. Data processing & analysis iii. Interpretation of results iv. Final report writing v. Presenting the results: scientific publication, presentation at meetings, seminar, workshops or conference, & presentation for administrators & policy makers
A. Prioritizing & selecting a research topic Criteria for select topic 1. Relevance: priority problem (magnitude of problem/public health problem, burden of problem) 2. Avoidance of duplication: no sound information 3. Urgency of data needed (timeliness): need for decisionmaking/developing intervention at various levels 4. Political acceptability of study: acceptable to high level policymakers. Interest & support of local/national authorities 5. Feasibility of study: feasible, considering available resource 6. Applicability of results: good chance of recommendations being implemented 7. Ethical acceptability: no ethical problems
1. 2. 3. 4.
Review of literature & other existing information prevent duplication work find out what other have found & reported on work bcm familiar with various types of methodology that could be use in study Provide with convincing arguments for why particular research project is needed.
B.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11.
Source text-book in libraries index medics comp-based literature bibliographies statistics collected at national, provincial, depart level opinions & belief of key informants
C. Final report writing Title/cover page Abstract (summary) Introductions Research objectives Methodology Research results (findings) Discussion Conclusions Recommendation Reference Annexes/ appendices 1.
D. Development of a research proposal 1. title 2. introduction: background info & statement of research problem (scientific justification for the study) 3. research obj 4. research hypothesis 5. methodology 6. work plan 7. plan for utilization & dissemination of research result 8. reference 9. budget preparation 10. annexes (appendices)
C. Development of a research proposal
I. Title 1. short, accurate, concise 2. central obj of study clear to reader 3. specify what population will be investigate & where it will conducted 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Introduction convince the readers of relevance of study enough background data further illustrate constitutes scientific justification for the study 1. 2. 3. III. Research objective Focus the study (narrow it down to essentials) Avoid data which not strictly necessary for understanding & solving problem Organize study in clear defined parts or phases 1. V. Methodology variables: a. independent, dependent, b. Confounding, background. c. numerical(continuous/ discrete), categorical(ordinal/nominal), d. Operational. study design: a. descriptive(cross-sectional survey), b. analytic(cohort & case-control), c. experimental/intervention strategies(clinical & preventive trials) study population, selection criteria, sample selection & size, sampling method study setting proposed intervention (if applicable) data collection procedure, data collection tools: questionnaire/interview schedule, clinical examination, laboratory test, screening procedure, records plan of data processing & analysis: by manual or computer ethical considerations: a. equitable selection of subj b. informed consent form c. confidentially d. compulsion e. enhance benefit & eliminate harm pre-testing methodology (pilot study) a. reactions of respondent to research procedures & to questions related to sensitive issues b. appropriateness of study type & research tools selected for purpose of study c. appropriateness of format & wording of questionnaires & interview schedule & accuracy of translations d. time needed to carry out interview, observation or measurement e. feasibility of designed sampling procedures f. feasibility of designed procedure for data processing & analysis
-Properly formulated, specific objectives facilitate dvlpmnt of research methodology orient the collection analysis, interpretation, utilization data Characteristic 1. state obj in questions, positive sentences, hypothesis 2. must be SMART 3. logical & coherent 4. feasible 5. realistic, considering local conditions 6. defined in operational terms that can be measured (precise indicator that to measure the variable) 7. phrase to be clearly meet the purpose of the study Formulation General obj Study states that research except to achieve by the study in general term Eg: to assess factor influencing utilization of maternal services in district X Systemically address various aspect of problem. what, where, what purpose eg: to assess , identify, determine (positive sentences)
2.
Logical sequence 1. Magnitude, frequency & distribution 2. Probable causes of problem 3. Possible solution 4. Unanswered question IV. Research hypothesis = prediction/ explanation of relationship btwn 1 or more independent variable (PREDISPOSING/RISK FACTOR) & 1 dependent variable (OUTCOME/CONDITION FACTOR) eg: health education involving active participation by mothers will produce more positive changes in child feeding than health education based on lecture independent v: types of health dependnt v: changes in child feeding
3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
Specific obj
9.
: VI. Work plan : = is schedule that summarizes in clear fashion, various components of research project & how they fit together 1. Various tasks to be performed 2. When the tasks will be performed 3. Who will perform the tasks VII. Plan for utilization & dissemination of research results - indicate what reports / other means of disseminating research findings are planned 1. progress report 2. final report 3. publications 4. seminars, workshop & conferences 5. discussion with policymakers & program managers
VIII. -
References
IX. Annexes interview schedule/questionnaire informed consent form institutional/ethical approval for the study
D. Final report writing
Title/cover page 1. research title 2. Name of author with title & positions 3. institutions that publishing report 4. challenging statement/question 5. informative subtitle covering the content of study & indicating area where the study was implemented Abstract (summary) 300 words written after final draft of report completed 1. what: very brief description of problem 2. why: main objective 3. where: place of study 4. how: types of study & methods used 5. major findings & conclusions 6. major recommendations Introductions contain relevant background data related to problem follow statement of problem contain paragraph what hoped to achieve with result if study justify study not to display ability to read literature Research objectives - If necessary, just adjust slightly for style & sequence. Not change their basic nature - If not meet some objectives, state in methodology section & in discussion of findings Methodology should include: 1. study type 2. major study variable on which data was collected 3. study population, sampling methods & size of sample 4. data collection techniques used 5. how data was collected & by whom 6. Procedure used for data analysis. statistical test Methodological limitations if deviated from original study design presented in research proposal, should explain to what extent you did so & why. 'Limitations of study' Research results (findings) systematic presentations of findings in relation to research objectives description of findings may be complemented by a limited no of tables / graphs that summarized the findings Discussion - by objective or by cluster of related variables - include finding from other related studies that support or contradict your own present & discuss limitations of the study - some general conclusions Conclusions: logically from discussion of findings Recommendation logically from discussion of the findings & supportive information from other sources must summarize according to grp toward which they are directed. Most important section: action-oriented grps eg: 1. policy-makers 2. health & health-related managers at different levels 3. health & health-related staff who could implement activities 4. potential clients 5. community at large Reference Vancouver style citing references 1. no reference in order 2. dont include reference in abstract. identify references in text, tables & legends by numerals in parenthesis 3. some journal require references to be indicated in superscript which makes typing more difficult 4. dont abstract as your source information. Must consult full text of article b4 using if as cited reference 5. Acknowledge only 1st author where there are 3 or more authors. Reference at end of sentence is included before the period 6. list of reference must begin on a new page & recited by no & sequenced by order of citation. Include all authors in list of references. Annexes/ appendices Contain additional information needed to enable professional to follow your research procedure & data analysis 1. Table referred to in text but not included in order to keep report short 2. interview schedule/questionnaires 3. flowchart-steps in dvlpmt of HRP
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Non Communicable DsDokument3 SeitenNon Communicable DslianazulakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Tahun 5 IkhwahDokument3 SeitenTahun 5 Ikhwahlianazulak0% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Sexual OffencesDokument52 SeitenSexual Offenceslianazulak100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- 5th and 6th WeekDokument3 Seiten5th and 6th WeeklianazulakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Assignment Groups For Cardiovascular Module International)Dokument2 SeitenAssignment Groups For Cardiovascular Module International)lianazulakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- 4th Week 2nd Year IumpDokument3 Seiten4th Week 2nd Year IumplianazulakNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- 3rd Week 2nd Year IumpDokument3 Seiten3rd Week 2nd Year IumplianazulakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- 2nd Week 2nd Year IumpDokument2 Seiten2nd Week 2nd Year IumplianazulakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Final Exam ILODokument3 SeitenPharmacology Final Exam ILOIqbal BearNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Introduction To Medical Mycology: by Prof Ashraf MOGAHEDDokument61 SeitenIntroduction To Medical Mycology: by Prof Ashraf MOGAHEDlianazulak100% (2)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Experiment and The Foundations of Quantum Physics: Anton ZeilingerDokument10 SeitenExperiment and The Foundations of Quantum Physics: Anton ZeilingerMansoor MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- CH 1 Introduction To Chemistry Form 4 KSSM (1) StudentDokument43 SeitenCH 1 Introduction To Chemistry Form 4 KSSM (1) StudentJASON CHONG CHIA HANG Moe100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Unit I: Introduction To Chemistry: LEARNING OUTCOMES: After Successful Completion of This Unit, You Should Be Able ToDokument23 SeitenUnit I: Introduction To Chemistry: LEARNING OUTCOMES: After Successful Completion of This Unit, You Should Be Able ToMabale, Joyce Danielle H.Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Research PhilosophyDokument12 SeitenResearch PhilosophyJarhan Azeem92% (12)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Research in Daily Life 1 - ReviewerDokument6 SeitenResearch in Daily Life 1 - Reviewerdivinegrace.cruz.mnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Case Study 2Dokument9 SeitenCase Study 2HàMềm100% (2)
- Student Name: Gaurav Raut University ID: 2038584: 6CS012 Workshop 4Dokument48 SeitenStudent Name: Gaurav Raut University ID: 2038584: 6CS012 Workshop 4Gaurav RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantization (Physics)Dokument19 SeitenQuantization (Physics)praveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- MATERI Mixed Method (SAZ)Dokument18 SeitenMATERI Mixed Method (SAZ)Siti Azizah - FAPETNoch keine Bewertungen
- TG Science 11Dokument13 SeitenTG Science 11Barcs UbarcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4: Random Variables and Probability Distributions: Solve The ProblemDokument4 SeitenChapter 4: Random Variables and Probability Distributions: Solve The ProblemEunice WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Linear Distance MeasurementDokument47 SeitenLinear Distance MeasurementRahim GenesisNoch keine Bewertungen
- (1996) The Rasch Model As A Foundation For The Lexile Framework-DikonversiDokument23 Seiten(1996) The Rasch Model As A Foundation For The Lexile Framework-Dikonversianon_506896902Noch keine Bewertungen
- UoSOutline MKTG1001 2011Dokument11 SeitenUoSOutline MKTG1001 2011michael_todd_44Noch keine Bewertungen
- English SkillsDokument133 SeitenEnglish SkillsRamachandra Rao Jayanthi100% (2)
- OM End KNSDokument2 SeitenOM End KNSSakshi BahetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Role of Business ResearchDokument7 SeitenThe Role of Business Researchgrincha2183% (6)
- PROJECT Advanced StatisticsDokument58 SeitenPROJECT Advanced StatisticsBhagyaSree JNoch keine Bewertungen
- DDD NDD DND DDN DNN NDN NND NNN S N Denotes "Non-Defective" andDokument3 SeitenDDD NDD DND DDN DNN NDN NND NNN S N Denotes "Non-Defective" andLabonnoAkterLabonnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of InstallationDokument5 SeitenCertificate of InstallationtyasdwiarumNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSUnit IV Lesson 3 Confidence Intervals For The Population Mean When Is UnknownDokument18 SeitenPSUnit IV Lesson 3 Confidence Intervals For The Population Mean When Is UnknownJaneth MarcelinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Longitudinal Vs LatitudinalDokument1 SeiteLongitudinal Vs LatitudinalAbdul Ghaffar BhattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regression Modeling Strategies - With Applications To Linear Models by Frank E. HarrellDokument598 SeitenRegression Modeling Strategies - With Applications To Linear Models by Frank E. HarrellApoorva100% (3)
- MMW Activity 6Dokument5 SeitenMMW Activity 6Jolly S. SendinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 008 SHORT QUIZ - Audit Sampling - ACTG411 Assurance Principles, Professional Ethics & Good GovDokument2 Seiten008 SHORT QUIZ - Audit Sampling - ACTG411 Assurance Principles, Professional Ethics & Good GovMarilou PanisalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- M2L2 CLRM & Simple Linear Regression AnalysisDokument13 SeitenM2L2 CLRM & Simple Linear Regression AnalysisQueenie Marie Obial AlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arzu IN: Analisis Penggunaan Media Pembelajaran Papan Pecahan Kelas Tinggi Di SD Negeri Periuk Jaya Permai TangerangDokument9 SeitenArzu IN: Analisis Penggunaan Media Pembelajaran Papan Pecahan Kelas Tinggi Di SD Negeri Periuk Jaya Permai TangerangPutri Nur PermataNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Fact, Value and ObjectivityDokument8 Seiten3 Fact, Value and ObjectivityAnkur RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- VariablesDokument6 SeitenVariablesJosephine GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stock Watson 3U ExerciseSolutions Chapter7 InstructorsDokument12 SeitenStock Watson 3U ExerciseSolutions Chapter7 Instructorsaspendos68100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)