Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Laboratory Test. Lyks
Hochgeladen von
Kiyla92Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Laboratory Test. Lyks
Hochgeladen von
Kiyla92Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
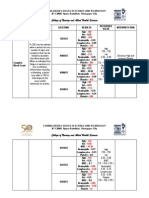
LABORATORY EXAMINATIONS Hematology Hematology- the diagnostic tests of the blood and its constituent parts.
Date: 1/9/13
PARAMETERS Hemoglobin Hematocrit RBC Count
ACTUAL FINDINGS 150 0.46 4.87
WBC Count Neutrophils
11.4 87
NORMAL FINDINGS M: 140-180 g/L F: 120-160 g/L M: 0.40-0.54 F: 0.37-0.47 M: 4.6-6.5 x10 ^12L F: 3.9-5.6 x 10 ^12L 5-10 x 10 g/L 50-70%
INTERPRETATION Normal Normal Normal
ANALYSIS
increased increased
Lymphocytes
12
25-40%
decreased
Indicates infection. Indicates infection, gonorrhea, osteomyelitis, otitis media, Metabolic Disorders; diabetic acidosis, eclampsia, uremia, thyrotoxicosis, Stress Response; due to acute hemorrhage, surgery, emotional distress &others Severe debilitating illness; congestive heart failure, renal failure, advanced tuberculosis Others; Defective lymphatic circulation, high levels of adrenal Corticosteriods, others
Eosinophils Bleeding Time Clotting Time
1 2 30 6 9
1-4% 1-3 minutes 3-5 minutes
Normal Normal
Chemistry Blood chemistry - defined simply as identifying the numerous chemical substances found in the blood.
Date: 1/9/13
PARAMETERS FBS HGT
ACTUAL FINDINGS 6.90 10.1
NORMAL FINDINGS 4.2-6.4 mmo/L 4.4-7.7 mmo/L
INTERPRETATION increased increased
ANALYSIS May indicate diabetes. May indicate high sugar level in the blood that may result to diabetes.
CREATININE (Male)
116.3
47-159umol/L
Normal
Date: 1/10/13
PARAMETERS Sodium Potassium
ACTUAL FINDINGS 142.1 3.49
NORMAL FINDINGS 135-148mmol/L 3.6-5.4 mmol/L
INTERPRETATION Normal decreased
ANALYSIS
Hypokalemia can be caused by decreased intake, protracted vomiting, renal loss, cirrhosis and others.
Chemistry Blood chemistry - defined simply as identifying the numerous chemical substances found in the blood.
Date: 1/13/13
PARAMETERS Creatinine (Male) Blood Urea Nitrogen
ACTUAL FINDINGS 86.4 3.32
NORMAL FINDINGS 47-159 umol/L 2.88-8.21mmol/L
INTERPRETATION Normal Normal
ANALYSIS
Date:1/14/13 PARAMETERS Sodium Potassium Chloride ACTUAL FINDINGS 146.5 3.60 117.5 NORMAL FINDINGS 135148mmol/L 3.6-5.4 mmol/L 96-100 mmol/L INTERPRETATION Normal Normal increased An increased level of blood chloride (called hyperchloremia) usually indicates dehydration, but can also occur with other problems that cause high blood sodium, such as Cushing syndrome or kidney disease. ANALYSIS
URINALYSIS Urinalysis- is the physical, chemical & microscopic examinations of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect & measure various compounds that pass through the urine.
DATE: 1/9/13
PARAMETERS Color
ACTUAL FINDINGS Dark Yellow
NORMAL FINDINGS Pale yellow
INTERPRETATION abnormal
ANALYSIS dark yellow to orange indicates some liver disorder. Excess turbidity results from the presence of suspended particles in the urine. Common causes of abnormal turbidity include increased cells (RBC, WBC), numerous crystals, bacteria, lipiduria (lipids often rise to the surface), mucus (especially in horses), semen, fecal contamination. High specific gravity indicates diabetes mellitus or acute kidney infection. Presence of albumin in the urine may indicate onset of kidney dysfunction. acidic Increase level of pus cells indicates urinary tract infection or non infectious condition such as fever, stress,
Transparency
Turbid
Clear to slightly turbid
abnormal
Specific Gravity
1.030
1.015-1.025
increased
Albumin
Positive
negative
abnormal
Sugar pH Pus cells
Negative 5.0 6-8/ hpf
negative 7.35-7.45 2-3 hpf
normal decreased increased
dehydration irritation to urethra, bladder or urethra. RBC Epithelial Cells Bacteria 1-3/ hpf Few Few 2-4 hpf few Absent normal normal abnormal
Presence of bacteria indicates infection. Too much crystals in the urine is an indication of having kidney stones. calcium oxalate and/or hippurate crystals may suggest ethylene glycol (antifreeze) ingestion. Neurological abnormalities, appearance of drunkenness, hypertension, and a high anion gap acidosis are usually accompanied with the antifreeze toxicity. The crystals are best seen with a polarized (yellow lens). Large numbers of calcium oxalate crystals occur, as well, with acute renal failure following methoxyflurane (Metophane) anesthesia. Urine is usually supersaturated in calcium oxalate, often in calcium phosphate, and acid urine is often saturated in uric acid.
Amorphous Materials Crystals
Moderate
few
abnormal
CALCIUM OXALATES: Few
few
normal
ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS Arterial blood gases (ABGs)- are diagnostic tests performed on blood taken from an artery which contains oxygen and carbon dioxide. Date/Time: 1/13/13 ( 1:19pm)
PARAMETERS RESULT NORMAL VALUES INTERPRETATION pH 7.434 7.35-7.45 Normal PCO2 31.1 mmHg 35-45 mmHg Alkalosis PO2 69.3 mmHg 80-100 mmHg Moderate Hypoxemia HCO3 20.8 mmol/L 22-26 mmol/L Acidosis RESULT: PARTIALLY COMPENSATED RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS WITH MODERATE HYPOXEMIA O2 SAT 94.4% 95-100% May indicate low blood oxygen. Base Excess -1.7 mmol/L 2 reduced
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Nursing: Lab Values: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideVon EverandNursing: Lab Values: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Exam Results SummaryDokument11 SeitenLab Exam Results SummaryKiyla92100% (1)
- Date Procedure Results IndicationDokument6 SeitenDate Procedure Results Indicationcharedj0yNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory and Diagnostic Worksheet For ClinicalDokument4 SeitenLaboratory and Diagnostic Worksheet For ClinicalTee Wood100% (1)
- Viii - Diagnostics Date Procedure Description Purpose/ Significance Normal Ranges Result Indication/Impr EssionDokument9 SeitenViii - Diagnostics Date Procedure Description Purpose/ Significance Normal Ranges Result Indication/Impr EssionChristian Karl B. LlanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iii. Laboratory and Diagnostic Examinations Hematology October 24, 2014 Examination Result Normal Values InterpretationDokument22 SeitenIii. Laboratory and Diagnostic Examinations Hematology October 24, 2014 Examination Result Normal Values InterpretationDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIAGNOSTIC TESTS GUIDEDokument56 SeitenDIAGNOSTIC TESTS GUIDEJay BolivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- UrinalysisDokument2 SeitenUrinalysisNniqui C Fitero100% (1)
- Acute Liver Failure 2012Dokument47 SeitenAcute Liver Failure 2012nancy voraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SampssDokument18 SeitenSampssRochelle Anne Herradura PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HyponatremiaDokument6 SeitenHyponatremiaJaymart Saclolo CostillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- AST Normal Results: CirrhosisDokument7 SeitenAST Normal Results: CirrhosisVijay RajaindranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytology of Body FluidDokument68 SeitenCytology of Body FluidZeeshan YousufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Diseases ReviewDokument45 SeitenRenal Diseases ReviewRaheelNoch keine Bewertungen
- LaboratoryDokument7 SeitenLaboratoryWindy Barrio RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serum ElectrolytesDokument2 SeitenSerum ElectrolytesKervin CablaidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Pathology Fecalysis and UrnalysisDokument16 SeitenClinical Pathology Fecalysis and UrnalysisRem Alfelor100% (3)
- CKDDokument48 SeitenCKDJuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Cirrhosis: Causes, Complications and ManagementDokument55 SeitenLiver Cirrhosis: Causes, Complications and ManagementAnonymous vUEDx8100% (1)
- MINI ReviewDokument10 SeitenMINI ReviewShamila KaruthuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 9th July 2021Dokument2 SeitenCase Study 9th July 2021sivakamasundari pichaipillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft To LabDokument5 SeitenDraft To LabvelascomhaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nusing Assessment Guide: Kidney Failure (CKD) Area: CCUDokument15 SeitenNusing Assessment Guide: Kidney Failure (CKD) Area: CCUAbbas AwfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Interpretation Made Easy: Diana Tamondong-Lachica, MD, FPCPDokument41 SeitenLaboratory Interpretation Made Easy: Diana Tamondong-Lachica, MD, FPCPmarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nusing Assessment Guide: Kidney Failure (CKD) Area: CCUDokument15 SeitenNusing Assessment Guide: Kidney Failure (CKD) Area: CCUAbbas AwfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transudate vs. Exudate OverviewDokument4 SeitenTransudate vs. Exudate OverviewAdam LechnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Clinical ManifestationsDokument17 SeitenGeneral Clinical ManifestationsYohannis AsefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver function tests, ultrasound, biopsy guide to interpreting resultsDokument14 SeitenLiver function tests, ultrasound, biopsy guide to interpreting resultsshihochan100% (2)
- College of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesDokument8 SeitenCollege of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesAileen Jennifer FelipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- In The Name of God, Most Gracious, Most MercifulDokument22 SeitenIn The Name of God, Most Gracious, Most MercifulMohammad Sadiq AzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hyponatremic Patient: A Systematic Approach To Laboratory DiagnosisDokument7 SeitenThe Hyponatremic Patient: A Systematic Approach To Laboratory DiagnosisJuen LohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrology & Urology: Archer Online USMLE ReviewsDokument107 SeitenNephrology & Urology: Archer Online USMLE ReviewsBeerappaJanpetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Somaville University Faculty of Medicine Urology &Nephrology Lecturer: Dr.Osman Urine Analyze Presentation By Group ADokument49 SeitenSomaville University Faculty of Medicine Urology &Nephrology Lecturer: Dr.Osman Urine Analyze Presentation By Group ALayla CabduqaadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peripheral Oedema (Assessment Of) - Diagnosis - Approach - Best Practice - EspañolDokument4 SeitenPeripheral Oedema (Assessment Of) - Diagnosis - Approach - Best Practice - EspañolOscar Castro CuaquiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Renal FailureDokument33 SeitenAcute Renal FailureAqsa Akbar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Patient With Pancytopenia: Section I: HistoryDokument12 SeitenA Patient With Pancytopenia: Section I: HistoryHadia AamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Pathology MedadTeam WWW EgydrDokument4 SeitenClinical Pathology MedadTeam WWW EgydrOmar SiagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Kidney Failure OverviewDokument5 SeitenAcute Kidney Failure OverviewNiña CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 BodyDokument35 Seiten4 Bodysinte beyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory StudyDokument3 SeitenLaboratory StudyGely LacsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematologic DisordersDokument108 SeitenHematologic DisordersEmma IntiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Failure: Symptoms, Causes, Tests & TreatmentDokument7 SeitenRenal Failure: Symptoms, Causes, Tests & TreatmentAndrelyn Balangui LumingisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Am Fam Physician. 2003 Jan 1 67 (1) :67-74.: January 1, 2003 Table of ContentsDokument13 SeitenAm Fam Physician. 2003 Jan 1 67 (1) :67-74.: January 1, 2003 Table of ContentsaanyogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYPERALDOSTERONISMDokument7 SeitenHYPERALDOSTERONISMMarnee Justine ColladoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS) : Inayatur Rosyidah., S.Kep - NsDokument62 SeitenMultiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS) : Inayatur Rosyidah., S.Kep - Nsmahendra-kurniahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading A Lab ReportDokument4 SeitenReading A Lab ReportsohaibsindhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jasmin O. Dingle BSN-4y1-3CDokument6 SeitenJasmin O. Dingle BSN-4y1-3CJasmn DingleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment or Acute Renal Failure SymptomsDokument6 SeitenAssessment or Acute Renal Failure SymptomsRifa Aprillia CahyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purpose: Alanine AminotransferaseDokument3 SeitenPurpose: Alanine AminotransferaseRona PieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Values: Test Value StudiedDokument31 SeitenLaboratory Values: Test Value Studiedanila_dhukkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management: DiagnosisDokument6 SeitenManagement: DiagnosisAhmed El-MalkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generally, the prognosis is better for prerenal and postrenal causes compared to intrinsic renal injury. Early recognition and treatment also improves prognosisDokument23 SeitenGenerally, the prognosis is better for prerenal and postrenal causes compared to intrinsic renal injury. Early recognition and treatment also improves prognosisrjfeeleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For The Management of HyponatraemiaDokument8 SeitenGuidelines For The Management of HyponatraemiaMuhammad Amiro RasheeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof Emma-Edit Endocrine Hypertension Meet The ExpertsDokument32 SeitenProf Emma-Edit Endocrine Hypertension Meet The ExpertsJames KomalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Urinalysis 2004Dokument50 Seiten05 Urinalysis 2004ali_mirjaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary AldosteronismDokument31 SeitenPrimary AldosteronismSteph100% (1)
- Abg, FB, FBC, Buse, GXMDokument20 SeitenAbg, FB, FBC, Buse, GXMeden_kampungboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: WIDYA AULIA C014182261 Siti Azreen Azira Binti Adzhar C014182197Dokument35 SeitenCase Report Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: WIDYA AULIA C014182261 Siti Azreen Azira Binti Adzhar C014182197ghaisani humairahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Askep HipertensiDokument23 SeitenAskep HipertensiTikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Art Therapy FatherDokument1 SeiteArt Therapy FatherKiyla92Noch keine Bewertungen
- V. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenV. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationLyka Milo AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Art Therapy BikeDokument1 SeiteArt Therapy BikeKiyla92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Test. LyksDokument6 SeitenLaboratory Test. LyksKiyla92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan. LyksDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan. LyksKiyla92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Test. LyksDokument6 SeitenLaboratory Test. LyksKiyla92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal & Fetal Assessment During LaborDokument2 SeitenMaternal & Fetal Assessment During LaborAnthony JenkinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Gastroenteritis Case StudyDokument6 SeitenAcute Gastroenteritis Case StudyKiyla920% (1)
- Acute Gastroenteritis Case StudyDokument6 SeitenAcute Gastroenteritis Case StudyKiyla920% (1)
- Laboratory Test. LyksDokument6 SeitenLaboratory Test. LyksKiyla92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On AGEDokument28 SeitenCase Study On AGEzyxert100% (19)
- V. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenV. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationLyka Milo AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- V. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenV. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationLyka Milo AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy, PathophysiologyDokument7 SeitenAnatomy, PathophysiologyKiyla92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal & Fetal Assessment During LaborDokument2 SeitenMaternal & Fetal Assessment During LaborAnthony JenkinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument40 SeitenDrug StudyLyka Milo AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal & Fetal Assessment During LaborDokument2 SeitenMaternal & Fetal Assessment During LaborAnthony JenkinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument40 SeitenDrug StudyLyka Milo AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen