Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Anaphy Renal
Hochgeladen von
Raymund Christopher Dela PeñaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anaphy Renal
Hochgeladen von
Raymund Christopher Dela PeñaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
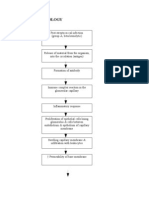
REVIEW ON THE ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OF THE RENAL SYSTEM The major role of the renal system is to maintain
n homeostasis by maintaining body fluid composition & volume. The components of the urinary system are as follows: - Kidneys - Ureters - Urinary blader - Urethra THE KIDNEYS - Two bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally at the level of the twelfth thoracic & third lumbar vertebra (costovertebral angle). - The right kidney is slightly lower than the left kidney due to the presence of the liver on the right side of the abdomen. - The kidneys are divided into renal cortex, medulla & pelvis. The medulla is composed of series of pyramids. - NEPHRONS, the functional units of the kidneys. It is composed of glumerulus & the renal tubules. - Glumerulus, a tuft of semi-permeable capillaries surrounded by the Bowmans capsule. - 3 Regions of the Renal Tubules: o Proximal Convuluted Tubules o Loop of Henle o Distal Convuluted Tubules - The primary function of the nephron is formation of urine. - About 1, 200 ml of blood flows to the kidneys per minute, which is 20 to 25% of the cardiac output. - Through the formation of urine, the kidneys remove waste products from the body, regulate fluid volume, maintain electrolyte concentration, blood pressure & pH within the body. - The glomerular filtration rate is 125 ml/min. From this, the kidneys form 0.5 ml to 1 ml of per minute, or to 30 to 60 ml per hour, or approximately 1,500 ml per day of urine. THE URETERS - Two small tubes about 25 cm long. - They transport urine from the renal pelvis to the urinary bladder. THE URINARY BLADDER - Serves as a reservoir for urine - It is composed of 3 layers of detrusor muscles. Contraction of these muscles expels urine from the bladder. - The approximate maximum capacity of the bladder is 1,000 ml of urine. THE URETHRA - Passageway of the urine into the external environment. - Female urethra: 1 -2 inches. Male urethra: 5 -6 inches. - The shorter urethra among females increase propensity to UTI.
UNP-CN|Fluids & Electrolytes| 1
RCdelaPea, RN, RM, MAN
URINE FORMATION 1. GLOMERULAR FILTRATION - Water & solutes move from the blood to the glomerular capsule. The fluid that enters the capsule is called glomerular filtrate. 2. TUBULAR REABSORPTION - It is the movement of the substances from the filtrate in the kidney tubules into the blood in the peritubular capillaries. Only 1% of the filtrate remains in the tubules & become urine. - Water & other substances that are useful to the body are reabsorbed. Water is reabsorbed by osmosis, while most solutes are reabsorbed by active transport. 3. TUBULAR SECRETION - Transport of substances from the blood into the renal tubules. Potassium & hydrogen are primarily eliminated from the body. Ammonia, uric acid, some drug metabolites are likewise eliminated.
UNP-CN|Fluids & Electrolytes|
RCdelaPea, RN, RM, MAN
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Oxygen TherapyDokument7 SeitenOxygen TherapyRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metformin Vs Insulin in The Management of Gestational Diabetes: A Meta-AnalysisDokument8 SeitenMetformin Vs Insulin in The Management of Gestational Diabetes: A Meta-AnalysisRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHN HandoutDokument4 SeitenCHN HandoutRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - Pott's Disease (Final)Dokument38 SeitenCase Study - Pott's Disease (Final)Raymund Christopher Dela Peña60% (5)
- Health Status of The Elderly in Selected Barangays of The City of ViganDokument115 SeitenHealth Status of The Elderly in Selected Barangays of The City of ViganRaymund Christopher Dela Peña100% (2)
- RevMan Nov 30 2013Dokument42 SeitenRevMan Nov 30 2013Raymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Examination and AssessmentDokument19 SeitenRespiratory Examination and AssessmentRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam in Food Hygiene 1Dokument1 SeiteFinal Exam in Food Hygiene 1Raymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Administering Medications: Raymund Christopher R. Dela Peña, RN, RM NGDokument30 SeitenAdministering Medications: Raymund Christopher R. Dela Peña, RN, RM NGRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology & Parasitology %Dokument21 SeitenMicrobiology & Parasitology %Raymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Competency StandardsDokument55 SeitenCore Competency StandardsRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts in PsychDokument26 SeitenHandouts in PsychRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Renal FailureDokument2 SeitenAcute Renal FailureRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing As A ProfessionDokument1 SeiteNursing As A ProfessionRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PsychopharmacologyDokument51 SeitenPsychopharmacologyRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head InjuryDokument46 SeitenHead InjuryRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Tracheal SuctioningDokument3 SeitenGuidelines For Tracheal SuctioningRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EcgDokument2 SeitenEcgRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Tracheal SuctioningDokument3 SeitenGuidelines For Tracheal SuctioningRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Competency StandardsDokument55 SeitenCore Competency StandardsRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurologic ExaminationsDokument4 SeitenNeurologic ExaminationsRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing As A ProfessionDokument1 SeiteNursing As A ProfessionRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen TherapyDokument7 SeitenOxygen TherapyRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing As A ProfessionDokument1 SeiteNursing As A ProfessionRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Status of The Elderly in Selected Barangays of The City of ViganDokument2 SeitenHealth Status of The Elderly in Selected Barangays of The City of ViganRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws Affecting Nursing Employment in The PhilippinesDokument114 SeitenLaws Affecting Nursing Employment in The PhilippinesRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Normal Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDokument1 SeiteOverview of Normal Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary Tract InfectionDokument3 SeitenUrinary Tract InfectionRaymund Christopher Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- NS2881 Renal Revision Worksheet 2022Dokument10 SeitenNS2881 Renal Revision Worksheet 2022Louise GeislerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretion and Coordination and Response Revision SheetDokument4 SeitenExcretion and Coordination and Response Revision SheetCamilleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah 1 Proses Pembentukan UrineDokument30 SeitenKuliah 1 Proses Pembentukan UrineImpi SusantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genitourinary SystemDokument25 SeitenGenitourinary SystemAlen Vukosavljevic100% (1)
- List of AnticoagulantsDokument9 SeitenList of Anticoagulantschristianz39100% (1)
- "Nephrotic Syndrome": Case ReportDokument30 Seiten"Nephrotic Syndrome": Case ReportRisa Maulida WidjayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strasinger AUBFDokument44 SeitenStrasinger AUBFangela tanteoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDokument14 SeitenIdentify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionCamille BaybayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proteina en Orina Spinreact AutómáticoDokument4 SeitenProteina en Orina Spinreact AutómáticojhonatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 2870 FinalDokument4 SeitenBio 2870 Finalwong1993Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Urinary SystemDokument3 SeitenThe Urinary SystemDaniel NevadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Acute GlumerulonephritisDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Acute GlumerulonephritisMASII75% (12)
- Li 1 Anatomy, Histology, PhysiologyDokument17 SeitenLi 1 Anatomy, Histology, PhysiologysandyaadindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Urinalysis Clinical MicrosDokument85 SeitenComplete Urinalysis Clinical MicrosJoshua Elbanbuena100% (1)
- Workup For ProteinuriaDokument17 SeitenWorkup For ProteinuriaSantiago ChávezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephron WTFDokument9 SeitenNephron WTFCatherine AlmarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study: Acute GlomerulonephritisDokument19 SeitenCase Study: Acute GlomerulonephritisKuruma Maricar SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PastDokument19 SeitenPastTalha Butt1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sindroma NefrotikDokument50 SeitenSindroma NefrotikMuthi'ah Ramadhani AgusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrology - Dr. Allam 2021Dokument42 SeitenNephrology - Dr. Allam 2021Alokh Saha RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excretion Worksheet 1 AnswersDokument3 SeitenExcretion Worksheet 1 Answersjjnaseem100% (3)
- Nephrology DR Osama Mahmoud PDFDokument83 SeitenNephrology DR Osama Mahmoud PDFMaria PatituNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephritic Syndrome - Armando HasudunganDokument14 SeitenNephritic Syndrome - Armando HasudunganzahraaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary SystemDokument27 SeitenUrinary SystemNicole LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toxins 13 00148 v2Dokument22 SeitenToxins 13 00148 v2Cristina BulgaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 Prep1 Key AnswerDokument16 SeitenScience 10 Prep1 Key AnswerchandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanisms of Glomerular Crescent FormationDokument19 SeitenMechanisms of Glomerular Crescent Formation_siegfried_Noch keine Bewertungen
- Glomerular Filtration: An Overview: Mary Jo HolechekDokument8 SeitenGlomerular Filtration: An Overview: Mary Jo HolechekagaasfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Semester Examination (ICM)Dokument4 SeitenI Semester Examination (ICM)Sudeep YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument17 SeitenChronic Kidney DiseaseAdelle SmithNoch keine Bewertungen