Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet Key
Hochgeladen von
Ewen AriolaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet Key
Hochgeladen von
Ewen AriolaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Intermolecular Force Worksheet Key 1.
Identify the strongest intermolecular force present in pure samples of the following substances: SO2 dipole-dipole forces SCO dipole-dipole forces H2O hydrogen bonds PCl3 dipole-dipole forces CH2Cl2 dipole-dipole forces SO3 London dispersion forces
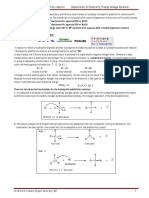
2. Identify the strongest intermolecular force operating in the condensed phases of the following substances. Fully explain how you determined this. a. Cl2 London dispersion forces The Cl-Cl bond is nonpolar so the molecule is nonpolar. Non polar molecules have only London dispersion forces operating in the substance. c. SO2 Dipole-dipole forces SO2 is a bent, polar molecule. The strongest intermolecular force in a polar molecule is the dipole-dipole force e. HF Hydrogen bonding forces Molecules that have hydrogen attached to an O, N, or F can form hydrogen bonds. These are the strongest of the intermolecular forces. b. CO Dipole-dipole forces The C-O bond is polar so the molecule is polar. Polar molecules have dipole-dipole forces. They also have London dispersion forces, but dipole-dipole forces are stronger. d. CH2Cl2 Dipole-dipole forces The strongest intermolecular force in a polar molecule that cannot form hydrogen bonds is the dipole-dipole force g. CH3-O-CH3 Dipole-dipole forces The hydrogen atoms are not bonded to the oxygen, so this molecule cannot form hydrogen bonds. It is polar, so it will have dipole-dipole forces.
3. Based on the intermolecular forces present, predict the relative boiling points of each of the substances below. Arrange each series of substances in order of increasing boiling point. State your reasons for the order you use (identify the forces and explain how they affect the boiling point). a. dimethyl ether (CH3OCH3), ethanol (CH3CH2OH), and propane (CH3CH2CH3) lowest bp: propane (CH3CH2CH3) < dimethyl ether (CH3OCH3)< ethanol (CH3CH2OH) highest bp Dimethyl ether cannot form hydrogen bonds (no O-H bond), but is polar and has dipole-dipole forces. Ethanol can form hydrogen bonds. propane is nonpolar, so it has only London dispersion forces. The boiling point increases as the strength of the intermolecular forces increase: London dispersion < dipole-dipole forces < hydrogen bonds
[All have similar molar masses: 46.07g/mol, 46.07g/mol and 44.09g/mol respectively.] b. Br2, Cl2, I2 lowest bp: Cl2 < Br2 < I2 highest bp All are nonpolar molecules so only London dispersion forces are present. London dispersion forces get stronger as molar mass increases. 4. For each pair of substance identify the substance that is likely to have the higher vapor pressure. Explain your reasoning. a. CO2 or SO2 CO2 will have the higher vapor pressure. Vapor pressure tends to decrease as the strength of the intermolecular forces increase. Carbon dioxide is non-polar (dispersion forces only). Sulfur dioxide is polar (dipole-dipole forces are present). b. CH3OH or CH3-O-CH3 CH3OCH3 will have the higher vapor pressure. Vapor pressure tends to decrease as the strength of the intermolecular forces increase. CH3OH can hydrogen bond. CH3OCH3 is polar (bent shape around the oxygen), so dipole-dipole forces are the strongest forces in this compound.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet KeyDokument2 Seiten115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet Keyada wangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermolecular Force Worksheet KeyDokument3 SeitenIntermolecular Force Worksheet KeyBill alfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early Theories of Acids and BasesDokument12 SeitenEarly Theories of Acids and Basesapi-242798587Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cis and TransDokument23 SeitenCis and TransIrvandar NurviandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Formulae and Equations - Part 1Dokument22 SeitenChemical Formulae and Equations - Part 1zkn 86Noch keine Bewertungen
- 110 Oxidation NumberDokument3 Seiten110 Oxidation NumberTerry100% (1)
- Balancing Chemical EquationsDokument13 SeitenBalancing Chemical EquationsShouq Merza Al KathairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions: John A. Schreifels Chemistry 211-Notes 1Dokument22 SeitenChemical Reactions: John A. Schreifels Chemistry 211-Notes 1Hayan LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interhalogen Compounds: Smt. Edna Richard Asst. Professor Department of ChemistryDokument14 SeitenInterhalogen Compounds: Smt. Edna Richard Asst. Professor Department of ChemistryAndriati RahayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Soal GasDokument1 SeiteLatihan Soal GasnajmahsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming of Ionic CompoundsDokument24 SeitenNaming of Ionic CompoundsDr. Ghulam Fareed100% (1)
- Lab Alkaline Earth MetalsDokument6 SeitenLab Alkaline Earth MetalsMatt HallNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Chem Review 3Dokument36 Seiten04 Chem Review 3Khizra Abdul shakoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4b Evidence For Chemical Reactions LabDokument3 Seiten4b Evidence For Chemical Reactions Labapi-369690183100% (1)
- 7 4 Solution ConcentrationsDokument20 Seiten7 4 Solution ConcentrationsAstrid María PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Octahedral vs. Tetrahedral GeometriesDokument3 SeitenOctahedral vs. Tetrahedral GeometriesMa'arif A. SyafiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test BanksDokument21 SeitenTest Banksalex_flutistNoch keine Bewertungen
- OxidationreductionDokument40 SeitenOxidationreductionMohamad HanifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming CompoundsDokument27 SeitenNaming CompoundsAtulya BharadwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - CALCULATIONS WITH CHEMICAL FORMULASDokument24 SeitenChapter 3 - CALCULATIONS WITH CHEMICAL FORMULASSai RaghavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Oxygen Family (Chalcogens)Dokument31 SeitenThe Oxygen Family (Chalcogens)faridatul jannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Standard Cell PotentialDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan: Lesson: Standard Cell PotentialMarcTnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehyde and Ketone ReactionsDokument21 SeitenAldehyde and Ketone ReactionsAinsssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid and Base TheoryDokument25 SeitenAcid and Base TheoryPtrick MahnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical ReactionsDokument26 SeitenChemical ReactionsEvernim Ompacan100% (1)
- Lab Titration of VinegarDokument5 SeitenLab Titration of Vinegardesree07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lattive EnergyDokument44 SeitenLattive EnergyClarize Soo HooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility and Simultaneous Equilibria: Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6EDokument59 SeitenSolubility and Simultaneous Equilibria: Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6EEriani WulandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Introduction To Practical ChemistryDokument11 SeitenReport Introduction To Practical Chemistrykat tunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Work For PHD in Chemistry From VtuDokument71 SeitenCourse Work For PHD in Chemistry From Vtufarooq_bagbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 3 (Partial Pressures)Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet 3 (Partial Pressures)Jose Ruben SortoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical FormulaDokument35 SeitenChemical FormulaKim Clauwie AnchetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry WorksheetDokument3 SeitenOrganic Chemistry WorksheetOrane CassanovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 19H NotesDokument40 SeitenCH 19H NotesHello HelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions From Previous Chemistry 116 ExamsDokument21 SeitenQuestions From Previous Chemistry 116 ExamsBindu JayachandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- MolarityDokument26 SeitenMolarityAmanah WatiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Lecture Notes - 0Dokument44 SeitenChapter 2 Lecture Notes - 0KirilKocevskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 1 - Covalent Bonding and Shapes of MoleculesDokument10 SeitenCHAPTER 1 - Covalent Bonding and Shapes of MoleculeslorrainebarandonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming Coordination CompoundsDokument18 SeitenNaming Coordination CompoundsPedro SuyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energi Kisi Dan Born HaberDokument31 SeitenEnergi Kisi Dan Born HaberNovi CherlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCH 102: Organic Chemistry IDokument152 SeitenSCH 102: Organic Chemistry IH to O ChemistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titration Sample ProblemDokument8 SeitenTitration Sample ProblemPaulAcademicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9halogens Group PresentationDokument31 Seiten9halogens Group PresentationQueen GeminiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absolute Configuration RSDokument13 SeitenAbsolute Configuration RSSubhasish SauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Johniya Cochran - Ionic and Covalent Bonds ActivityDokument4 SeitenJohniya Cochran - Ionic and Covalent Bonds ActivityJohniya CochranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redox ReactionsDokument4 SeitenRedox Reactionsmahika gaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raoult's Law PDFDokument12 SeitenRaoult's Law PDFKeshav JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical ReactionsDokument190 SeitenChemical ReactionsAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- Chapter 12 PDFDokument35 SeitenChapter 12 PDFTamara M KaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid-Base Practice Problems-Answers PDFDokument5 SeitenAcid-Base Practice Problems-Answers PDFSuci PrameswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Introduction To Physical Chemistry QuestionsDokument2 Seiten1.1 Introduction To Physical Chemistry QuestionsWrl RossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem M12 Chemical NomenclatureDokument19 SeitenChem M12 Chemical NomenclatureToh YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam 40% Exams 45% Report 5% Homework 10%Dokument74 SeitenFinal Exam 40% Exams 45% Report 5% Homework 10%kaleijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment RedoxDokument6 SeitenExperiment RedoxJaaizah JaafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan 2016-2017 Term 3Dokument9 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan 2016-2017 Term 3Fazliawati Mahayuddin50% (2)
- Oxides Summary WorksheetDokument2 SeitenOxides Summary WorksheetMaoga2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lewis Dot Structures of Atoms and Ions: Valence Electrons Noble Gas StabilityDokument6 SeitenLewis Dot Structures of Atoms and Ions: Valence Electrons Noble Gas StabilityAndrew CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet KeyDokument2 Seiten115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet Keytharanga100% (2)
- Practice Problems 16 AnswersDokument4 SeitenPractice Problems 16 Answersedward_1711100% (1)
- Flame Spray Synthesis and Characterisation PHD Thesis MBDokument171 SeitenFlame Spray Synthesis and Characterisation PHD Thesis MBKoorosh IraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms, Molecules, and IonsDokument68 SeitenAtoms, Molecules, and Ions張婷昀Noch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To Design, Modelling and Simulation of Multiple Effect EvaporatorsDokument7 SeitenApproach To Design, Modelling and Simulation of Multiple Effect Evaporatorscemal gümrükçüoğluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benson BoilerDokument21 SeitenBenson BoilerDr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ans GP-Spec Heat WSDokument4 SeitenAns GP-Spec Heat WSOthello64Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Problem SolvingDokument53 SeitenBiochem Problem SolvingNasser Gemina PantaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells 106 FinalDokument66 SeitenChapter 5 Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells 106 FinalAhmed Fouad MusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 8 - Q3 - Las 4 RTPDokument4 SeitenScience 8 - Q3 - Las 4 RTPAprilyn CollanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uniheat - Transfer Thermal Unitst II Convective Heat Transfer Thermal UnitsDokument33 SeitenUniheat - Transfer Thermal Unitst II Convective Heat Transfer Thermal Unitsaerosanth100% (1)
- Nam28 DHLV2Dokument1 SeiteNam28 DHLV2Madara_uchiha13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter:-Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction Department of Chemistry, Pratap College, AmalnerDokument12 SeitenChapter:-Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction Department of Chemistry, Pratap College, Amalnermilindthakare75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 05 Catalytic Tubular Reactor (TFR)Dokument8 SeitenModule 05 Catalytic Tubular Reactor (TFR)Farizal RahmatNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXP 7 Simultaneous Determination of Caffeine and Acetylsalicylic Acid in An Analgesic by Ultraviolet SpectrosDokument8 SeitenEXP 7 Simultaneous Determination of Caffeine and Acetylsalicylic Acid in An Analgesic by Ultraviolet Spectroslebogang100% (3)
- Annamalai University: Degree ExaminationsDokument28 SeitenAnnamalai University: Degree ExaminationsHarish PuttarajaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution ChemistryDokument27 SeitenSolution ChemistryZarahbeth Claire G. ArcederaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iwa 281 Lab 2Dokument28 SeitenIwa 281 Lab 2Lp NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Insulation and Mechanical Properties Ofpolylactic Acid (PLA) at DifferentProcessing ConditionsDokument16 SeitenThermal Insulation and Mechanical Properties Ofpolylactic Acid (PLA) at DifferentProcessing Conditionsmohamed elhaddajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Some Exercises With SolutionsDokument6 Seiten02 Some Exercises With SolutionsANGIE PAOLA RODELO PANZANoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 Chemistry PartDokument2 SeitenClass 10 Chemistry PartVicky Singh100% (3)
- Parametric and Kinetic Studies On The Decolorization of Aqueous Methyl Red Solution Using Electrolyzed WaterDokument88 SeitenParametric and Kinetic Studies On The Decolorization of Aqueous Methyl Red Solution Using Electrolyzed WaterJoyce EdrozoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Point of Petroleum Products (Constant Cooling Rate Method)Dokument7 SeitenCloud Point of Petroleum Products (Constant Cooling Rate Method)Muhammad Syarif HidayatullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Figure Shows A 20 KG Rod AB Used To Main - Tain...Dokument4 SeitenThe Figure Shows A 20 KG Rod AB Used To Main - Tain...Amir PskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiphase Flow in PipesDokument23 SeitenMultiphase Flow in Pipes000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Transfer: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Emel AKYOLDokument16 SeitenMass Transfer: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Emel AKYOLesra göçenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 194 2427 194 T Tot H H : Input OutputDokument19 Seiten194 2427 194 T Tot H H : Input Outputxuankhoi doanvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPSA MEG CalculationDokument3 SeitenGPSA MEG CalculationChitu Ionut-LaurentiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outlook: Ucr Where Ucr. The Brinkman-Rice Scenario For The MIT Predicts Ucr - 0, and The Gap Ucr 0Dokument1 SeiteOutlook: Ucr Where Ucr. The Brinkman-Rice Scenario For The MIT Predicts Ucr - 0, and The Gap Ucr 0SupriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculate The Relieving Temperature & Latent Heat of Vaporization For Fire Case PSV Sizing by Shell DEP MethodDokument3 SeitenCalculate The Relieving Temperature & Latent Heat of Vaporization For Fire Case PSV Sizing by Shell DEP Methodrohitkush80% (5)
- Lab 6 Reflection Refraction OnlineDokument12 SeitenLab 6 Reflection Refraction OnlineOmar El ErakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffraction: Diffraction Refers To Various Phenomena That Occur When ADokument5 SeitenDiffraction: Diffraction Refers To Various Phenomena That Occur When AshohobiNoch keine Bewertungen