Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Organizing
Hochgeladen von
Mcmac YangoCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Organizing
Hochgeladen von
Mcmac YangoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Organizing Structuring the agency to accomplish task, setting up the organization structure, defining roles and function of every
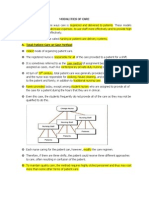
y member of organization. ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE Most often, the existing organizational structures are communicated by means of an organizational chart. This organization has a tall bureaucratic structure with many layers in the hierarchy or chain of command and a centralized formal authority in the board of trustees. It represents a formal, top-down reporting structure. EXAMPLE:
A. MATRIX STRUCTURE -designed to focus on both product and function. Function is described as all the tasks required to produce the product and the product is the end result of function. B. FLAT VERSUS TALL STRUCTURE Organizations are considered flat when there are few layers in the reporting structure. A tall organization would have many layers in the chain of command. C. DECENTRALIZED VERSUS CENTRALIZED STRUCTURE
These two refers to the degree to which an organization has spread its lines of authority, power, and communication. STAFFING Is the process of assigning competent people to fill the roles designated for the organizational structure through recruiting, selection and development, one of the major function of a nurse manager, a management activity that requires much planning it involve deciding what types of &how many personal are needed to provide adequate & quality 24 hours aday,7days a week and 52 weeks a year the process of determining and providing the acceptance number& mix of nursing personnel to produce a desired level of care CONSIDERATIONS IN DEVELOPING A STAFFING PATTERN 1. BENCHMARKING-a management tool for seeking out the best practices in ones industry so as to improve performance. 2. SKILL MIX-the percentage of RN staff to other direct care staff, LPNs, and Unlicensed Assistive Personnel. 3. STAFF SUPPORT-the supports in place for the operations of the unit or department. 4. HISTORICAL INFORMATION-this can help go identify operational issues that would not be apparent otherwise. SELECTION OF PERSONEL 1. Recruiting it is describe as the process of selecting personnel for employment, advertising, and employee recommendation
2. screeening- screen applicant who do not fit the image of the agency, try to fit the jog to a promising applicant, try to fit the applicant to the job 3. interview- to obtain further information the applicant qualifies for the position *some interview observes that the applicant a. does the applicant show genuine interesting the job, willingness to work in assumes responsibility b. is he/she has mannered?
4. Orientation- a process of becoming familiar with a new environment &adapting well to it, a part of staff development & one of your function
5. Staff development- as a nurse manager, support the program of the institution, review the
goal &provide a budget for the activity. Nurses should engage in professional education such as attending seminar ,conference in-service training program, engage in other activities that well enhance her/his competencies as a nurse &development his/her aesthetic sense &personality. PATIENT CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM To assess how many staff are needed at any given time, it is necessary to determine what the patient needs are. A measurement tool used to articulate the nursing workload for a specific patient or group of patients over a specific period of time. Classification data can be based on the patients acuity. As a patient becomes sicker, the acuity level arises, meaning the patient requires more nursing care. As a patient acuity level decreases, the patient requires less nursing care. FACTOR SYSTEM-uses units of measure that equate to nursing time. These system attempts to capture the cognitive function of assessment, planning, intervention and evaluation of patient outcome along with a written documentation process. This is the most popular of classification system of its ability to project care needs to individual patients as well as patient group. ADVANTAGES: Data are generally readily available to managers and staff for day-today operations. DISADVANTAGES: the ongoing workload for the nurse in classifying patients every day. There are also documented problems with classification creep, whereby acuity levels rise as a result of misuse classification criteria. This system does not holistically capture the patients needs for psychosocial, environmental, and health management support. PROTOTYPE SYSTEM Allocates system nursing time to large patient groups based on an average of similar patients. This model assumes that, on average, this will reflect the nursing care required and provided. The data are the news of the hospitals in determining the cost of nursing care and negotiating contracts with payers for specific patient population. ADVANTAGES: There is reduction of work for the nurse because she is not required to classify patients daily. DISADVANTAGES: There is no ongoing measure of actual nursing work required by individual patients. There are also no ongoing data to monitor the accuracy of the preassigned nursing care requirements. SCHEDULING Is the staff responsibility of the nurse manager.
She must ensure that the schedule places the appropriate staff on each day and shift for safe, effective patient care. OBJECTIVES OF SCHEDULING To assign working days and days off to individual members of the nursing staff in order to : 1. Provide adequate patient care while avoiding over staffing. 2. Treat individual members of the nursing staff fairly. 3. Achieve a desirable distribution of off days. TYPES OF SCHEDULING 1. Centralized scheduling 2. Decentralized Scheduling 3. Self-Scheduling MODALITIES OF CARE To ensure that nursing care is provided to patients, the work must be organized. A care delivery model organizes the work of caring for patients. A. CASE METHOD Oldest method of providing care to a patient. The premise is that one nurse provides total care for one patient during the entire work period. Used in Florence nightingales era when patient received total care at home. Care includes meeting the needs of the whole family like cooking TOTAL PATIENT CARE- modern day version of the case method. Nurse is responsible for the total care of her patient assignment for the shift she is working.
ADVANTAGES - Consistency of individuals in giving patient care for the entire shift. - enables the patient, nurse and family to develop a trusting relationship. -nurse has more opportunity to observe and monitor progress of the patient. DISADVANTAGES -the nurse may not have the same patients from day to day and therefore look at the patient on a shift by shift basis rather than on a continuum of care. utilize a high level of nursing hours to deliver care expensive
B. PRIMARY NURSING A care delivery model that clearly delineates the responsibility and accountability of the RN and designates the RN as the primary provider of care to patients. Primary nursing is a form of the case model that consist of four element; 1. Allocation and acceptance of individual responsibility for the decision making to one individual 2. Assignments of daily care by the case method 3. Direct person to person communications 4. And one person operationally responsible for the quality of care administered to patients on a unit 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. ADVANTAGES Patient and families are able to develop a trusting relationship with the nurse. There is a holistic approach to care which facilitates continuity of care rather than a shift to shift focus. DISADVANTAGES -High cost because there is a higher RN skill mix. The person making out the assignment s needs to b knowledgeable about the all about the patients and staffs to ensure appropriate matching of nurse to patient. -with no geographical boundaries within the unit, nursing staff may be required to travel long distances at the unit level to care for the primary patient. - Nurse-patient ratios must be realistic to ensure there is enough nursing time available to meet the patient care needs. C. TEAM NURSING Was developed after the World War II in an effort to utilize trained workers and to ease the shortage of nurses that most hospitals were experiencing. a care delivery model that assigns staff to teams that then are responsible for a group of patients. A unit maybe divided into two teams each team is lead by a registered nurse. The team leader supervises and coordinates all the care provided by those on his team. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES RN is able to get work done through others but patients often received fragmented depersonalized care. Communication in this model is complex. There is shared responsibility and accountability which can cause confusion and lack of accountability. -
D. MODULAR NURSING A delivery system is a kind of team nursing that divided as geographic space into modules of patient, with each module cared for by a team of staff led by an RN. RN is responsible for the overall care of the patient in her module. E. FUNCTIONAL NURSING Popular during world war II when there was significant shortage of nurses in the United States. Divides the nursing work into functional units that are then assigned to one of the team members. Ach care provider has specific duties or tasks they are responsible for. Decision making is usually at the level of the head nurse or the charge nurse. ADVANTAGE -care can be delivered to a large number of patients. Utilizes other types of health care workers when there is shortage of RNs. DISADVANTAGE Patients are likely to have care delivered to them in one shift by several staff members. To a patient care, care may feel disjointed. And patient become the sum of the tasks of care they require rather than an integrated whole.
Pines City Colleges Magsaysay Avenue, Baguio City COLLEGE OF NURSING
ORGANIZING
Submitted to: Mrs Buna Racal
Submitted by: Group 4
BSN 4-2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Nurse Manager Accelerator Transition from Bedside Nursing to Nurse Manager in 6 stepsVon EverandThe Nurse Manager Accelerator Transition from Bedside Nursing to Nurse Manager in 6 stepsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi FinalsDokument10 SeitenSemi FinalsMegan N. ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Along the Continuum of Care: What Every Case Manager Must Know...Von EverandAlong the Continuum of Care: What Every Case Manager Must Know...Noch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument79 SeitenAssignmentsunielgowda100% (1)
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 14, Physician LeadershipVon EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 14, Physician LeadershipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Care Delivery SystemDokument16 SeitenPatient Care Delivery Systemheba abd elazizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crunch Time Review for the Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA) ExamVon EverandCrunch Time Review for the Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA) ExamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Delivery Models in IndiaDokument14 SeitenNursing Care Delivery Models in IndiaShreyas Walvekar100% (1)
- Modalities of Nursing CareDokument4 SeitenModalities of Nursing CareRose Rebollos MaligroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staffing Group 2 ReportDokument47 SeitenStaffing Group 2 ReportDianna MV CoerbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT II Patient Care Delivery SystemDokument7 SeitenUNIT II Patient Care Delivery SystemSheila Mae ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mod Ali Ties of Care Written OutputDokument8 SeitenMod Ali Ties of Care Written OutputQharts SajiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pattern of Nursing Care Delivery in IndiaDokument14 SeitenPattern of Nursing Care Delivery in Indiamaakkan100% (3)
- Nursingcaredelivery 181011144230Dokument50 SeitenNursingcaredelivery 181011144230Nithin RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modalities of Nursing CareDokument4 SeitenModalities of Nursing CareKatherine 'Chingboo' Leonico Laud100% (5)
- Nursing Administration QuestionsDokument5 SeitenNursing Administration QuestionsmitalptNoch keine Bewertungen
- MaranDokument15 SeitenMaranmanimaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Systems For StaffingDokument4 SeitenAssignment Systems For StaffingPrincess Enolva100% (1)
- Nursing Delivery SystemsDokument9 SeitenNursing Delivery Systemsmenickel3Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Team Nursing Model?Dokument3 SeitenWhat Is The Team Nursing Model?Sofia LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignments Patterns Modalities For Delivery of Nursing CareDokument15 SeitenAssignments Patterns Modalities For Delivery of Nursing CareYnaffit Alteza UntalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module I Group WorkDokument6 SeitenModule I Group WorkNur Sanaani100% (1)
- Patient Care Delivery SystemDokument13 SeitenPatient Care Delivery Systemsimronthapa200550% (2)
- STAFFINGDokument3 SeitenSTAFFINGXnikz XnakzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Assignmen PresentationtDokument12 SeitenPatient Assignmen PresentationtSuraj Raj SubediNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCMB 419 - LM WK 2, CU2, CanvasDokument19 SeitenNCMB 419 - LM WK 2, CU2, CanvasGabriel VillegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS: Directing and ControllingDokument15 SeitenMANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS: Directing and Controllingnikki dascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care Delivery ModelDokument5 SeitenCare Delivery Modelapi-520985654100% (1)
- Chapter 21-Managing Client CareDokument4 SeitenChapter 21-Managing Client Careaderonke1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Care Delivery SystemDokument4 SeitenPatient Care Delivery SystemSheen aballeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team NursingDokument4 SeitenTeam NursingDawn NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Care Nursing and Differentiated Practice NotesDokument4 SeitenPrimary Care Nursing and Differentiated Practice NotesJohn Paolo OrioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teamwork & Collaboration in Healthcare"TITLE"Continuous Quality Improvement in Nursing" TITLE"Leadership Skills for New Nurses"TITLE"Effective Delegation & SupervisionDokument4 SeitenTeamwork & Collaboration in Healthcare"TITLE"Continuous Quality Improvement in Nursing" TITLE"Leadership Skills for New Nurses"TITLE"Effective Delegation & Supervisionclaudine padillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Nursing AssignmentDokument30 SeitenMethods of Nursing AssignmentRakersh Patidar91% (11)
- Organizing Patient Care: A Guide to Traditional and Modern ModelsDokument59 SeitenOrganizing Patient Care: A Guide to Traditional and Modern ModelsEllyn FerraterNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 119 Lesson 3 Patient Care Delivery SystemDokument66 SeitenNCM 119 Lesson 3 Patient Care Delivery Systeminno so qtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Service ManagementDokument24 SeitenNursing Service ManagementAnilkumar JaraliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Chapter VI - Patient Care Delivery SystemDokument19 Seiten6 Chapter VI - Patient Care Delivery SystemMariane DacalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Directing Nursing Service ManagementDokument13 SeitenDirecting Nursing Service ManagementAlyssa AzucenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type of and How Many: I. RecruitmentDokument5 SeitenType of and How Many: I. RecruitmentohsnapitsleiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership & Management in Nursing Unit 11 Work Load Management Define Workload ManagementDokument5 SeitenLeadership & Management in Nursing Unit 11 Work Load Management Define Workload ManagementGulfam ZamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mahoney - Organizing Patient CareDokument12 SeitenMahoney - Organizing Patient CareRica DonezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Systems For StaffingDokument10 SeitenAssignment Systems For StaffingfatmaabedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Nursing AssignmentDokument30 SeitenMethods of Nursing AssignmentJasleen Kaur100% (1)
- Staffing PatternDokument125 SeitenStaffing PatternJonah Rei BeatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Refers To The Manner in Which Nursing Care Is Organized and ProvidedDokument3 SeitenThis Refers To The Manner in Which Nursing Care Is Organized and Provided私 シャーロットNoch keine Bewertungen
- And Channel of CommunicationDokument8 SeitenAnd Channel of Communicationjennifer sampangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mod Ali Ties of Nursing CareDokument2 SeitenMod Ali Ties of Nursing CareTintin AbalosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team Nursing: DefinitionsDokument4 SeitenTeam Nursing: DefinitionsManu CvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizing Nursing Services and Patient Care: Case MethodDokument23 SeitenOrganizing Nursing Services and Patient Care: Case Methodmerin sunilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Assignment MethodDokument48 SeitenPatient Assignment Methodsathya Arunkumar100% (1)
- Assignment of PatientsDokument39 SeitenAssignment of PatientsStephy Sojan100% (1)
- Staffing Needs and Scheduling PoliciesDokument30 SeitenStaffing Needs and Scheduling PoliciesErika Mae100% (2)
- Staffing and SchedulingDokument41 SeitenStaffing and SchedulingRoy Roy100% (2)
- CHAPTER 5 FinalfinalDokument8 SeitenCHAPTER 5 FinalfinaljonilynNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING MANAGEMENT: ORGANIZINGDokument5 SeitenNURSING MANAGEMENT: ORGANIZINGheron_bayanin_15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Staffing Models and Interview TipsDokument25 SeitenStaffing Models and Interview TipsAliah BataloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roles of ICU ManagerDokument9 SeitenRoles of ICU ManagerMei ChelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Delivery Systems in IndiaDokument32 SeitenNursing Care Delivery Systems in IndiaJayarani Ashok0% (1)
- Assignment Sheet PDFDokument13 SeitenAssignment Sheet PDFعبدالرحمن علىNoch keine Bewertungen
- RanitidineDokument1 SeiteRanitidineMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolyte Imbalance May Cause HypertensionDokument1 SeiteElectrolyte Imbalance May Cause HypertensionMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plan of Activities For Head NursingDokument5 SeitenPlan of Activities For Head NursingMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENT Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenENT Drug StudyMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Jaundice PathwayDokument35 SeitenNeonatal Jaundice PathwayMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Ortho WandasDokument2 SeitenJournal Ortho WandasMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENT Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenENT Drug StudyMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For Ears Nose ThroatDokument1 SeiteNCP For Ears Nose ThroatMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENT Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenENT Drug StudyMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- By: Mr. Lord Daryll Angeles: Budgetary Leadership and ManagementDokument27 SeitenBy: Mr. Lord Daryll Angeles: Budgetary Leadership and ManagementMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- December 2012 NLE Performance of SchoolsDokument21 SeitenDecember 2012 NLE Performance of SchoolsjamieboyRNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphoma ReportDokument23 SeitenLymphoma ReportMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Odonto Genic TumorsDokument7 SeitenOdonto Genic TumorsMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PscyheDokument27 SeitenPscyheMcmac YangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- December 2012 NLE Performance of SchoolsDokument21 SeitenDecember 2012 NLE Performance of SchoolsjamieboyRNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument37 SeitenChapter 6Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision MatrixDokument12 SeitenDecision Matrixrdos14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Es E100091 Pi PDFDokument1 SeiteEs E100091 Pi PDFCarlos Humbeto Portillo MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Method For Identifying Human Factors Concerns During The HAZOP Process - Dennis AttwoodDokument5 SeitenA Method For Identifying Human Factors Concerns During The HAZOP Process - Dennis AttwoodAlvaro Andres Blanco GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plato Aristotle Virtue Theory HappinessDokument17 SeitenPlato Aristotle Virtue Theory HappinessMohd SyakirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conclusion For A Research Paper About BullyingDokument7 SeitenConclusion For A Research Paper About Bullyingafnkjuvgzjzrgl100% (3)
- Companies DatabaseDokument2 SeitenCompanies DatabaseNIRAJ KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA Study On Organisational Culture and Its Impact On Employees Behaviour - 237652089Dokument64 SeitenMBA Study On Organisational Culture and Its Impact On Employees Behaviour - 237652089sunitha kada55% (20)
- Platon Si Academia Veche de ZellerDokument680 SeitenPlaton Si Academia Veche de ZellerDan BrizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COS1512 202 - 2015 - 1 - BDokument33 SeitenCOS1512 202 - 2015 - 1 - BLina Slabbert-van Der Walt100% (1)
- Servo Magazine 01 2005Dokument84 SeitenServo Magazine 01 2005dangtq8467% (3)
- SiargaoDokument11 SeitenSiargaomalouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Significance of Vaiseshika's PragabhavaDokument5 SeitenSignificance of Vaiseshika's Pragabhavavskanchi0% (1)
- McCann MIA CredentialsDokument20 SeitenMcCann MIA CredentialsgbertainaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Basic Logical Concepts - For Students PDFDokument65 SeitenChapter 3 - Basic Logical Concepts - For Students PDFTiên Nguyễn100% (1)
- Circle Midpoint Algorithm - Modified As Cartesian CoordinatesDokument10 SeitenCircle Midpoint Algorithm - Modified As Cartesian Coordinateskamar100% (1)
- The Basics of Hacking and Pen TestingDokument30 SeitenThe Basics of Hacking and Pen TestingAnonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase Domain Modelling of Frequency Dependent Transmission Lines by Means of An Arma ModelDokument11 SeitenPhase Domain Modelling of Frequency Dependent Transmission Lines by Means of An Arma ModelMadhusudhan SrinivasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propaganda and Counterpropaganda in Film, 1933-1945: Retrospective of The 1972 ViennaleDokument16 SeitenPropaganda and Counterpropaganda in Film, 1933-1945: Retrospective of The 1972 ViennaleDanWDurningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shailesh Sharma HoroscopeDokument46 SeitenShailesh Sharma Horoscopeapi-3818255Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geo Lab Report Point LoadDokument9 SeitenGeo Lab Report Point Loaddrbrainsol50% (2)
- 8 DaysDokument337 Seiten8 Daysprakab100% (1)
- A Comparative Marketing Study of LG ElectronicsDokument131 SeitenA Comparative Marketing Study of LG ElectronicsAshish JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finance Process Optimization - Mapping The Journey To High PerformanceDokument3 SeitenFinance Process Optimization - Mapping The Journey To High PerformanceStephen G. LynchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment Baseplate DesignDokument10 SeitenMoment Baseplate DesignNeil JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inner WordDokument7 SeitenInner WordMico SavicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Logic Design: Dr. Oliver FaustDokument16 SeitenDigital Logic Design: Dr. Oliver FaustAtifMinhasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV Raman's Discovery of the Raman EffectDokument10 SeitenCV Raman's Discovery of the Raman EffectjaarthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gpredict User Manual 1.2Dokument64 SeitenGpredict User Manual 1.2Will JacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 340 Lecture 26 Avalanche Zener BreakdownDokument20 SeitenECE 340 Lecture 26 Avalanche Zener BreakdownDao ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinic Management System (24 PGS)Dokument24 SeitenClinic Management System (24 PGS)pranithNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (13)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (402)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (78)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementVon EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (40)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsVon EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (169)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesVon EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (34)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (327)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsVon EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeVon EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (253)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingVon EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (41)
- The Stress-Proof Brain: Master Your Emotional Response to Stress Using Mindfulness and NeuroplasticityVon EverandThe Stress-Proof Brain: Master Your Emotional Response to Stress Using Mindfulness and NeuroplasticityBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (109)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (33)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossVon EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (8)