Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
TASK 1 (P1) 1. Compare and Contrast The Structure of The DNA With The Structure of The RNA
Hochgeladen von
Fatmata Haja KamaraOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TASK 1 (P1) 1. Compare and Contrast The Structure of The DNA With The Structure of The RNA
Hochgeladen von
Fatmata Haja KamaraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
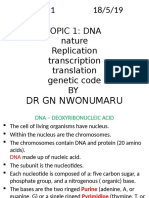
TASK 1 (P1) 1.
Compare and contrast the structure of the DNA with the structure of the RNA
DNA RNA
DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid and contains the 5 carbon sugar deoxyribose.
RNA is ribonucleic acid and contains the 5 carbon sugar ribose.
DNA is a double stranded molecule. DNA contains 4 bases Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) and Thymine (T).
RNA is single stranded. In RNA Thymine is replaced by Uracil(U) but also contains A, C and G.
Both DNA and RNA are composed of sub units called nucleotides. A nucleotide has 3 sub units: A 5 carbon sugar, An inorganic phosphate and one of four bases. The nucleotides in both DNA and RNA are linked by chemical bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the Phosphate of the next to form a 'sugar- phosphate backbone'.
TASK 2 (M1) How a length of DNA contains coded information DNA contains the four bases, Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine. The four bases will base complimentary pair in one of four ways A-T, T-A, G-C, C-G. Chromosomes are made up of DNA and chromosomes contain genes- hereditary units of coded information passed from parent to offspring. Each gene has its own specific sequence of bases- often containing 100/1000's of nucleotides and each gene codes for one protein/ polypeptide chain. Proteins are created during protein synthesis which occurs in the ribosomes ( out of the nucleus) for the DNA code to travel out of the nucleus mRNA is necessary, which contains the nucleotide Uracil rather than Thymine, the mRNA complimentary base Pairs with the DNA and then leaves the nucleus, into the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. Each molecule of mRNA contains a codon which codes for one amino acid. The tRNA brings the amino acid to the correct mRNA molecule as it has a anti-codon which complimentary base pairs with the codon on the mRNA. The amino acids join together with poly-peptide bonds forming a polypeptide chain- protein.
Proteins are coded for by sequences of three bases on the nucleic acid strands. A series of three bases on DNA is called a Triplet. On mRNA a sequence of three bases is called a codon and on tRNA it is called an anticodon. mRNA is copied from one strand of DNA by a process called Transcription. DNA, being double stranded is too large to pass out of the nuclear pores and so is confined to the nucleus. mRNA being single stranded can pass out of the nucleus to carry the genetic code to the ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum for translation into sequences of amino acids. (Called Translation) DNA can undergo self-replication, RNA can't. The base pairing rule in DNA is A with T and C with G. In RNA the base pairing rule is A with U and C with G.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Nucleic AcidsDokument46 SeitenNucleic AcidsM. MalonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Cheat Sheet For EllaDokument3 SeitenBiology Cheat Sheet For EllaJay EdwardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna and Rna: Molecule of HeredityDokument74 SeitenDna and Rna: Molecule of Heredityalfani wahyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- As A Level BiologyDokument10 SeitenAs A Level BiologykeosotepyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Auto Saved)Dokument7 SeitenGenetics Auto Saved)natseeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Overview Central DogmaDokument56 SeitenDNA Overview Central DogmaBukhari DiangkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument11 SeitenUntitledAnisur Rahman ZihadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Possible QuestionsDokument6 SeitenBiochem Possible QuestionsAbegail Bautista DoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein SynthesisDokument32 SeitenProtein SynthesisJosefina JerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCH 305 (Chemistry & Metabolism of Nucleic Acids)Dokument30 SeitenBCH 305 (Chemistry & Metabolism of Nucleic Acids)ihebunnaogochukwu24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic AcidsDokument23 SeitenNucleic Acidsglenn johnstonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acids: Adopted From: Francine Williams Excelsior Community CollegeDokument46 SeitenNucleic Acids: Adopted From: Francine Williams Excelsior Community CollegeGarnetNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Rep and RNA StructureDokument30 SeitenDNA Rep and RNA Structurekoromamoses235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Function of Dna and Rna: Jon Paul M. Reyes, RMT, MBA, MSMLS Program Chair College of Medical TechnologyDokument21 SeitenStructure and Function of Dna and Rna: Jon Paul M. Reyes, RMT, MBA, MSMLS Program Chair College of Medical TechnologyRich Darlene Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDokument6 Seiten1 The Central Dogma of Molecular Biologydeladestianiaji2490100% (1)
- Biology Unit-2Dokument16 SeitenBiology Unit-2Uttam NeelapureddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENETICSDokument37 SeitenGENETICSJohn KennedyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA, RNA and ProteinsDokument47 SeitenDNA, RNA and ProteinsShanice RhuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFDokument55 SeitenNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFAleine Leilanie Oro0% (1)
- Nucleic Acids Store, Transmit and Help Express Hereditary InformationDokument6 SeitenNucleic Acids Store, Transmit and Help Express Hereditary InformationDanielle GuerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4A Key Concepts - Nucleic Acids 2023Dokument1 SeiteWeek 4A Key Concepts - Nucleic Acids 2023Natalie UrquhartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Function of DNADokument29 SeitenStructure and Function of DNAMatthew Justin Villanueva GozoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiDokument14 SeitenGenetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiYasmine HadiastrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rna Protein Synthesis VocabDokument1 SeiteRna Protein Synthesis VocabChastity MiddlebrooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Function of DNADokument27 SeitenStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Biology: DNA Replication, Transcription, and TranslationDokument8 SeitenDNA Biology: DNA Replication, Transcription, and TranslationEva Mayte GuadarramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA and RNA PracticeDokument4 SeitenDNA and RNA PracticeLaya ShrbagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 8 - Nucleic Acids and Central DogmaDokument52 SeitenModule 8 - Nucleic Acids and Central DogmaPauline Grace CadusaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Part 1Dokument26 SeitenChapter 7 Part 1coolsuernameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aw Protein SynthesisDokument18 SeitenAw Protein SynthesisOCRChemistrySaltersNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Quarter W4 LECTURE On Protein Synthesis in DNA and MutationDokument53 Seiten3rd Quarter W4 LECTURE On Protein Synthesis in DNA and MutationMorante GeraldineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dogma SentraDokument46 SeitenDogma SentraindahonlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna StructureDokument42 SeitenDna StructureCedric BaldozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- In-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDokument21 SeitenIn-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisGbenga AjaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Nucleic AcidsDokument8 SeitenStructure of Nucleic Acidsplayandhavefun23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acids and NucleotidesDokument4 SeitenNucleic Acids and NucleotidesWolverineInZenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 471 - BCH 201-Lecture Note On WebDokument10 Seiten471 - BCH 201-Lecture Note On WebShaikh SalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ribonucleic Acid: DescriptionDokument3 SeitenRibonucleic Acid: DescriptionMira LutfianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic AcidDokument4 SeitenNucleic AcidrcwxnNoch keine Bewertungen
- (C) and Uracil (U) - The Five-Carbon (Pentose) Sugar in RNA Is RiboseDokument5 Seiten(C) and Uracil (U) - The Five-Carbon (Pentose) Sugar in RNA Is RiboseRishikesh BhintadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- RNA Ribonucleic Acid (English Pronunciation: /raɪbɵ - Nju Kleɪ - Ɨk Æsɪd/), or RNA, Is One of The Three MajorDokument1 SeiteRNA Ribonucleic Acid (English Pronunciation: /raɪbɵ - Nju Kleɪ - Ɨk Æsɪd/), or RNA, Is One of The Three MajorPRINTDESK by DanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mechanism of TranslationDokument68 SeitenThe Mechanism of TranslationRama KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 4Dokument8 SeitenDay 4Kinberly AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromosomes, Genes and Nucleic AcidsDokument23 SeitenChromosomes, Genes and Nucleic AcidsDANIELLA LOMA CAPONPONNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006 CHM6108 L9L10 SlidesDokument40 Seiten2006 CHM6108 L9L10 Slidesaidar.seralinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Ribonucleic AcidDokument9 Seiten3 Ribonucleic Acidmichael.quinn729Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDokument29 SeitenProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade - 12 Biology: Oromia Education Bureau in Collaboration WithDokument79 SeitenGrade - 12 Biology: Oromia Education Bureau in Collaboration Withmmree yyttNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry - Biosynthesis of Protein & Protein ChemistryDokument113 SeitenBiochemistry - Biosynthesis of Protein & Protein ChemistryAdella AnggrainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1 HeredityDokument9 SeitenActivity 1 HeredityAnonymous SpjVHfNpqNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO G12 Unit 3 Short NotesDokument12 SeitenBIO G12 Unit 3 Short NotesAmanuel AyalewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna Rna FinalDokument52 SeitenDna Rna Final4tqpxmts7zNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDokument13 SeitenSemi-Conservative DNA ReplicationMohd JunaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dianne D. Mariano BSN 101Dokument9 SeitenDianne D. Mariano BSN 101Dianne MarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RNA Transcription and TranslationDokument11 SeitenRNA Transcription and TranslationMaiSakurajimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RNAProtein Synthesis VocabDokument2 SeitenRNAProtein Synthesis VocabdherSZN ツNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.10 Protein-SynthesisDokument20 Seiten3.10 Protein-SynthesisPratika MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical Engineering Class 6Dokument3 SeitenBiochemical Engineering Class 6Vittal PiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory LegislationDokument1 SeiteLaboratory LegislationFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy of FuelsDokument1 SeiteEnergy of FuelsFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collecting ConkersDokument4 SeitenCollecting ConkersFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerobic and Anaerobic RespirationDokument7 SeitenAerobic and Anaerobic RespirationFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- TASK 1 (D3) A. Safety Devices That Are in The Lab To Protect Against Electric ShockDokument1 SeiteTASK 1 (D3) A. Safety Devices That Are in The Lab To Protect Against Electric ShockFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure and Radioactivity 2Dokument3 SeitenAtomic Structure and Radioactivity 2Fatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drunkard of The VillageDokument1 SeiteDrunkard of The VillageFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure and Radioactivity 2Dokument3 SeitenAtomic Structure and Radioactivity 2Fatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnzymesDokument1 SeiteEnzymesFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic ReactionsDokument3 SeitenOrganic ReactionsFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- TASK 2 (M4) The Importance of Chirality in Drug SynthesisDokument1 SeiteTASK 2 (M4) The Importance of Chirality in Drug SynthesisFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantities Advantages Disadvantages: Cumulative Frequency Less Than 19.995Dokument3 SeitenQuantities Advantages Disadvantages: Cumulative Frequency Less Than 19.995Fatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control and Coordination-Nervous and Endocrine SystemDokument1 SeiteControl and Coordination-Nervous and Endocrine SystemFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionizing RadiationDokument2 SeitenIonizing RadiationFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Region Is Rice Grown inDokument1 SeiteWhat Region Is Rice Grown inFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Are Savoiur Siblings Morally JustifiedDokument1 SeiteAre Savoiur Siblings Morally JustifiedFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy ChangesDokument1 SeiteEnergy ChangesFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument2 SeitenPhysicsFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases and Infection (Unit 43)Dokument6 SeitenDiseases and Infection (Unit 43)Fatmata Haja Kamara50% (2)
- CholeraDokument1 SeiteCholeraFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy ChangesDokument1 SeiteEnergy ChangesFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Are Savoiur Siblings Morally JustifiedDokument1 SeiteAre Savoiur Siblings Morally JustifiedFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control and Coordination-Nervous and Endocrine SystemDokument1 SeiteControl and Coordination-Nervous and Endocrine SystemFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic ReactionsDokument3 SeitenOrganic ReactionsFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Displacement ReactionDokument3 SeitenDisplacement ReactionFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rates of ReactionDokument3 SeitenRates of ReactionFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical IssuesDokument1 SeiteEthical IssuesFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Computer Viru1Dokument2 SeitenWhat Is A Computer Viru1Fatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CholeraDokument1 SeiteCholeraFatmata Haja KamaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior Project RiceberryDokument76 SeitenSenior Project RiceberryIttisak PrommaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Quick Guide PDFDokument1 SeiteChemical Quick Guide PDFAndrejs ZundaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6Dokument2 Seiten6Min Hsuan HsianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 41 Assignment Worksheets For SchoolDokument26 Seiten41 Assignment Worksheets For Schoolsoinarana456Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A VolcanoDokument2 SeitenWhat Is A VolcanonatachaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sustainable Development at British Petroleum: Presented by Amardeep Kulshrestha 09BS0000172 Section-EDokument20 SeitenSustainable Development at British Petroleum: Presented by Amardeep Kulshrestha 09BS0000172 Section-EAmar KulshresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 204-04B - Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)Dokument23 Seiten204-04B - Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)Sofia AltuzarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Kuliah Liver CirrhosisDokument55 Seiten6 Kuliah Liver CirrhosisAnonymous vUEDx8100% (1)
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) : SRS PrecautionsDokument1 SeiteHVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) : SRS PrecautionssoftallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Education in America: The Dumbing Down of The U.S. Education SystemDokument4 SeitenEducation in America: The Dumbing Down of The U.S. Education SystemmiichaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SanMilan Inigo Cycling Physiology and Physiological TestingDokument67 SeitenSanMilan Inigo Cycling Physiology and Physiological Testingjesus.clemente.90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cargador de BateríaDokument34 SeitenCargador de BateríaBenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe 3 Syllabus - GymnasticsDokument7 SeitenPe 3 Syllabus - GymnasticsLOUISE DOROTHY PARAISO100% (1)
- Join Our Telegram Channel: @AJITLULLA: To Get Daily Question Papers & SolutionsDokument24 SeitenJoin Our Telegram Channel: @AJITLULLA: To Get Daily Question Papers & SolutionsNaveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALL102-Walker Shirley-Unemployed at Last-The Monkeys Mask and The Poetics of Excision-Pp72-85Dokument15 SeitenALL102-Walker Shirley-Unemployed at Last-The Monkeys Mask and The Poetics of Excision-Pp72-85PNoch keine Bewertungen
- EV Hammer Impact Crusher - ENDokument8 SeitenEV Hammer Impact Crusher - ENKeshav NandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACF5950 - Assignment # 7 Semester 2 2015: The Business Has The Following Opening Balances: Additional InformationDokument2 SeitenACF5950 - Assignment # 7 Semester 2 2015: The Business Has The Following Opening Balances: Additional InformationkietNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Speech ActDokument1 SeiteClassification of Speech ActDarwin SawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behavior Specific Praise Statements HandoutDokument3 SeitenBehavior Specific Praise Statements HandoutDaniel BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doctors ListDokument212 SeitenDoctors ListSaranya Chandrasekar33% (3)
- Soal UAS Bahasa Inggris 2015/2016: Read The Text Carefully! Cold Comfort TeaDokument5 SeitenSoal UAS Bahasa Inggris 2015/2016: Read The Text Carefully! Cold Comfort TeaAstrid AlifkalailaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 107 2021 High Speed Rail Corridor RegDokument3 Seiten107 2021 High Speed Rail Corridor Rega siva sankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Cold ChainDokument22 SeitenLaboratory Cold ChainEmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scope: Procter and GambleDokument30 SeitenScope: Procter and GambleIrshad AhamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gender, Slum Poverty and Climate Change in Flooded River Lines in Metro ManilaDokument53 SeitenGender, Slum Poverty and Climate Change in Flooded River Lines in Metro ManilaADBGADNoch keine Bewertungen
- G1 Series User Manual Ver. 1.2Dokument101 SeitenG1 Series User Manual Ver. 1.2unedo parhusip100% (1)
- Lichens - Naturally Scottish (Gilbert 2004) PDFDokument46 SeitenLichens - Naturally Scottish (Gilbert 2004) PDF18Delta100% (1)
- How To Import Medical Devices Into The USDokument16 SeitenHow To Import Medical Devices Into The USliviustitusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entitlement Cure SampleDokument34 SeitenEntitlement Cure SampleZondervan100% (1)
- Guideline On Smacna Through Penetration Fire StoppingDokument48 SeitenGuideline On Smacna Through Penetration Fire Stoppingwguindy70Noch keine Bewertungen