Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Jarkom CCNA Exam
Hochgeladen von
Cintia NurliyanaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Jarkom CCNA Exam
Hochgeladen von
Cintia NurliyanaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1.
What combination of IP address and wildcard mask should be used to specify only the last 8 addresses in the subnet 192.168.3.32/28? 192.168.3.32 0.0.0.7 192.168.3.32 0.0.0.15 192.168.3.40 0.0.0.7 192.168.3.40 0.0.0.15 2. Excessive broadcasts are generally a symptom of a problem at which layer? physical data link network transport 3. Refer to the exhibit. Which three pieces of information can be determined by analyzing the output shown? (Choose three.) A carrier detect signal is present. Keepalives are being received successfully. Default encapsulation is used on this serial link. Packets passing this interface cannot exceed 1 KB in size. The reliability of this link is very low. The LCP negotiation phase is complete. 4. A network administrator has received complaints that users on a local LAN can retrieve e-mail from a remote e-mail server but are unable to open web pages on the same server. Services at which two layers of the OSI model should be investigated during the troubleshooting process? (Choose two.) physical layer data link layer network layer transport layer application layer 6. Encapsulation errors from mismatched WAN protocols on a serial link between two routers indicate a problem at which OSI layer? physical data link network transport 9. Users are complaining of very long wait times to access resources on the network. The show interface command reveals collision counts far above the network baseline. At which OSI layer should the administrator begin troubleshooting? application transport network data link physical
10.
Refer to the exhibit. Users on the Internal LAN are unable to connect to the www server. The network administrator pings the server and verifies that NAT is functioning correctly. Which OSI layer should the administrator begin to troubleshoot next? physical data link network application 11. Which two statements are true concerning logical networking models? (Choose two.) TCP/IP splits the lowest layer of the OSI model into two separate layers. The top layer of the TCP/IP model combines the functions of the top three OSI layers. Troubleshooting with the TCP/IP model requires different techniques than with the OSI model. The network access layer is responsible for exchanging packets between devices on a TCP/IP network. The Internet layer provides communication between applications, such as FTP, HTTP, and SMTP on separate hosts. The TCP/IP network access layer corresponds to the OSI physical and data link layers. 13. What is one example of a physical layer problem? incorrect encapsulation incorrect STP configuration incorrect ARP mapping incorrect clock rate 17. Which two pieces of information are typically found on a logical network diagram? (Choose two.) cable types connector types interface identifiers DLCI for virtual circuits operating system versions
18.
Refer to the exhibit. Each media link is labeled. What type of cable should be used to connect the different devices? Connection 1 rollover cable Connection 2 straight-through cable Connection 3 crossover cable Connection 1 crossover cable Connection 2 rollover cable Connection 3 crossover cable Connection 1 straight-through cable Connection 2 crossover cable Connection 3 crossover cable Connection 1 straight-through cable Connection 2 crossover cable Connection 3 straight-through cable Connection 1 crossover cable Connection 2 straight-through cable Connection 3 crossover cable 5.
172.16.128.0 255.255.0.0 172.16.128.0 255.255.192.0 172.16.128.0 255.255.224.0 172.16.128.0 255.255.255.192
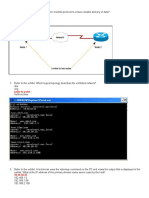
Refer to the exhibit. The command that is shown was issued on a PC. What does the IP address 192.168.33.2 represent? IP address of the host default gateway of the host IP address of the homepage for the host primary domain name server for the host IP address of the website resolver1.mooki.local 22. Which OSI layer does IP rely on to determine whether packets have been lost and to request retransmission? application presentation session transport 24. The Layer 4 header contains which type of information to aid in the delivery of data? service port number host logical address device physical address virtual connection identifier 25. As network administrator, what is the subnet mask that allows 510 hosts given the IP address 172.30.0.0? 255.255.0.0 255.255.248.0 255.255.252.0 255.255.254.0 255.255.255.0 26. Refer to the exhibit. What is required on host A for a network technician to create the initial configuration on Router1? an FTP client a Telnet client a terminal emulation program a web browser
Refer to the exhibit. What function does router RT_A need to provide to allow Internet access for hosts in this network? address translation DHCP services ftpd web server 6. When connectionless protocols are implemented at the lower layers of the OSI model, what is usually used to acknowledge that the data was received and to request the retransmission of missing data? IP UDP Ethernet a connectionless acknowledgement an upper-layer, connection-oriented protocol or service 9. What is true regarding network layer addressing? (Choose three) uses a flat structure prevent broadcasts heirarchical uniquely identifies each host 48 bits in length contains a network portion 15. Which combination of network id and subnet mask correctly identifies all IP addresses from 172.16.128.0 through 172.16.159.255? 172.16.128.0 255.255.255.224
100 Base TX 1000 Base LX
28. Refer to the exhibit. Which set of devices contains only intermediary devices? A, B, D, G A, B, E, F C, D, G, I G, H, I, J
32. Refer to the exhibit. With the router running NAT, what IP addresses can be applied to the computer to allow access to the Internet? (Choose three) 192.168.18.38 192.168.18.48 192.168.18.49 192.168.18.52 192.168.18.59 192.168.18.63
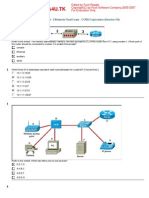
Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is trying to determine the correct IP address configuration for Host A. What is a valid configuration for Host A? IP address: 192.168.100.19; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248; Default Gateway: 192.16.1.2 IP address: 192.168.100.20; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.17 IP address: 192.168.100.21; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.18 IP address: 192.168.100.22; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 10.1.1.5 IP address: 192.168.100.30; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.1.1 IP address: 192.168.100.31; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.18 30. A routing issue has occurred in you internetwork. Which of the following type of devices should be examined to isolate this error? access point host hub router switch 31. Which type of media is immune to EMI and RFI? (Choose two.) 10 Base-T 10 Base-2 10 Base-5 100 Base-FX
33. Which three IPv4 addresses represent a broadcast for a subnet? (Choose three.) 172.16.4.63 /26 172.16.4.129 /26 172.16.4.191 /26 172.16.4.51 /27 172.16.4.95 /27 172.16.4.221 /27
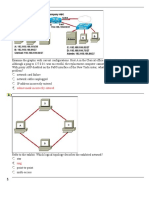
Refer to the exhibit. Assume all devices are using default configurations. How many subnets are required to address the topology that is shown? 1 3 4 5 7 35. What are three characteristics of CSMA/CD? (Choose three) Devices can be configured with a higher transmission priority. A jam signal indicates that the collision has cleared and the media is not busy. A device listens and waits until the media is not busy before transmitting. The device with the electronic token is the only one that can transmit after a collision. All of the devices on a segment see data that passes on the network medium. After detecting a collision, hosts can attempt to resume transmission after a random time delay has expired.
40. Which two functions of the OSI model occur at layer two? (Choose two.) physical addressing encoding routing cabling media access control 42. Which range of port numbers are reserved for services that are commonly used by applications that run on servers? 0 to 255 0 to 1023 1024 to 49151 49152 to 65535 43.
A GET request was sent to RouterB to retrieve data during this session.
45. Which three statements characterize the transport layer protocols? (Choose three.) TCP and UDP port numbers are used by application layer protocols. TCP uses port numbers to provide reliable transportation of IP packets. UDP uses windowing and acknowledgments for reliable transfer of data. TCP uses windowing and sequencing to provide reliable transfer of data. TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. UDP is a connectionless protocol.
46. Which of the following are the address ranges of the private IP addresses? (Choose three.) 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 200.100.50.0 to 200.100.25.255 150.150.0.0 to 150.150.255.255 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 127.16.0.0 to 127.31.255.255 47. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connectionoriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 48. Refer to the exhibit. Which logical topology best describes the exhibited network? star ring point-to-point multiaccess mesh 49. During the encapsulation process, which identifiers are added at the transport layer? two networks routing the packets two applications communicating the data two hosts at either end of the communication two nodes on the local network exchanging the frame 50. What are two characteristics of the data link layer? (Choose two.) It segments and reorders the data. It exchanges the frames between nodes. It defines the method by which network devices place data onto the media. It manages the transfer of data between the processes that run on each host.
Refer to the exhibit. What three statements are true about the IP configuration that is shown? (Choose three.) The address that is assigned to the computer represents private addressing. The computer is unable to communicate outside of the local network. The network of this computer can have 126 hosts. The prefix of the computer address is /27. The IP address that is assigned to the computer is routable on the Internet. The IP address that is assigned to the computer is a broadcast address. 44.
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator remotely accesses the CLI of RouterB from PC1 using Telnet. Which statement is true about this connection? The data is automatically encrypted. A Telnet server process is running on PC1. The connection is made through a VTY session on the router.
It retrieves signals from the media and restores them to their bit representations.
1 .Which port numbers are commonly assigned for FTP use? (Choose two.) 19 20 21 22 2 Which application layer protocol allows network devices to exchange management information? SMTP SNMP FTP TFTP EIGRP 3 FTP provides a reliable, connection-oriented service for transferring of files. Which transport layer protocol is used for data transfer when this service is being used? TFTP TCP DNS IP UDP 4 TCP is referred to as connection-oriented. What does this mean? TCP uses only LAN connections. TCP requires devices to be directly connected. TCP negotiates a session for data transfer between hosts. TCP reassembles the data steams in the order that it is received. 5 What three pieces of information does the transport layer use to manage the communication of separate data streams between hosts? (Choose three.) port numbers checksum values authentication keys sequence numbers encryption algorithms acknowledgment numbers 6 What does the http portion of the URL http://www.cisco.com/edu/ communicate to a web browser? The web browser needs to locate the www server. The address is located on a site whose name is http. The web browser is notified as to which protocol to use. The http portion represents the type of web browser that needs to be used. 7 When the receiving workstation detects an error in
the data it has received, it does not acknowledge receipt of the data. The source workstation retransmits the unacknowledged data. Which layer of the OSI model supports this process of retransmission? network application session transport 8 What are the features of the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). (Choose three.) no guaranteed delivery of datagrams connection-oriented provides reliable full-duplex data transmission reliability provided by the application layer connectionless utilizes sliding windowing techniques 9 Which Application layer protocol is widely used to support resolving host names to IP addresses? FTP SMTP SNMP DNS HTTP WWW 10 What is the purpose of TCP/UDP port numbers? indicate the beginning of a three-way handshake reassemble the segments into the correct order identify the number of data packets that may be sent without acknowledgment track different conversations crossing the network at the same time 11 If an application uses a protocol that exchanges data without using windowing or flow control and must rely on higher layer protocols for reliability, which protocol and transfer methods are being used? UDP, connection-oriented UDP, connectionless TCP, connection-oriented TCP, connectionless 12 Which protocol is used to transfer files from computer to computer but is considered connectionless? FTP TFTP SNMP TCP DHCP 13 Which layer of the OSI model can provide a connection-oriented, reliable data transfer between two hosts? Application Presentation Session
Transport 14 Which of the following are primary duties of the OSI transport layer? (Choose two.) path determination end-to-end connectivity flow control security control data representation encryption of data 15 Which protocol is used by e-mail servers to communicate with each other? FTP HTTP TFTP SMTP POP SNMP . What are two facts about how ARP resolves an IP address to a MAC address? (Choose two.) The originating host dynamically issues an arp -a command to obtain the destination MAC address. The originating host broadcasts an ARP request packet and each host in a local network receives this packet. The originating host dynamically issues an icmp echo request command to obtain the destination MAC address. The host with the specified destination IP address sends an ARP reply packet containing its MAC address back to the originating host. The host with the specified destination IP address sends an icmp echo reply packet to the originating host with its MAC address. 2. Which TCP/IP model layer supports both LAN and WAN technologies? network access layer internet layer transport layer application layer 3. What is the primary responsibility of the transport layer? allows access to the network media provides data representation and encoding selects paths through the network for data to travel defines end-to-end connectivity between host applications 4. What is the network broadcast address for a Class C address of 192.168.32.0 with the default subnet mask? 192.168.0.0 192.168.0.255 192.168.32.0 192.168.32.254 192.168.32.255 5. Which two statements correctly describe the IP address 127.0.0.1? (Choose two.) It belongs to the Class A range of addresses. It belongs to the Class B range of addresses. It belongs to the Class C range of addresses. It is reserved for loopback testing. It is reserved for multicast group testing. It is reserved for unicast testing. 6.
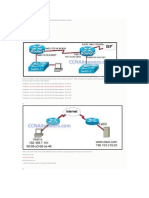
Refer to the exhibit. The small office LAN shown in the exhibit may eventually be connected to the Internet. According to Cisco best practice, which IP network addresses should be used? 12.0.0.0 172.0.0.0 172.168.0.0 192.32.17.0 192.168.67.0 225.1.5.0 7. Why is IP considered a best-effort protocol? IP detects lost packets. IP validates the content of the packets. IP does not provide acknowledgment of the data delivery. IP reorders the packet as they arrive at the destination host.
8. Which three addresses are considered to be private addresses? (Choose three.) 10.45.09.23 15.87.234.87 172.32.45.90 172.17.78.98 192.169.89.56 192.168.45.23 9.
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the information shown, which two statements are true? (Choose two.) An ARP request must be used to obtain an address that is placed in the ARP table. Frames from other hosts in the network to this host
will use a destination address of 00-06-25-25-6e-5d. The only remote locations that can be reached from this host are 192.168.1.97 and 192.168.1.254. If a packet is sent to a network device other than 192.168.1.97 and 192.168.1.254, an ARP request must be used. If the computer with the IP address of 192.168.1.94 sends a packet to the device with the IP address 192.168.1.97, no ARP request is required. 10.
14.
Refer to the exhibit. Which devices are recommended to have the IP addresses manually configured? PC1 and PC2 all servers only PC2 Laptop all hosts and all servers 11. Why were private IP addresses developed? to permit dynamic assignment of IP addresses to permit the duplication of public IP addresses to minimize the utilization of reserved IP addresses to permit public IP addresses to be used in private networks to address the issue of not enough available public IP addresses 12. Which subnet mask would be assigned to the network address of 192.168.32.0 to provide 254 useable host addresses per subnetwork? 255.255.0.0 255.255.255.0 255.255.254.0 255.255.248.0 13. When a host has an empty ARP cache, what is the next step the host will take to find the destination MAC address of a remote host? sends an ARP request as a unicast to the server sends an ARP request as a unicast to the destination sends an ARP request as a broadcast to all hosts in the local network sends an ARP request as a unicast to the default gateway
Refer to the exhibit. What is the purpose of the Obtain an IP address automatically option shown in the exhibit? to configure the computer to use ARP to configure the computer to use DHCP to configure the computer to use a routing protocol to configure the computer with a statically assigned IP address 15. How many usable hosts are available given a Class C IP address with the default subnet mask? 254 255 256 510 511 512 16. Which statement accurately describes public IP addresses? Public addresses cannot be used within a private network. Public IP addresses must be unique across the entire Internet. Public addresses can be duplicated only within a local network. Public IP addresses are only required to be unique within the local network. Network administrators are free to select any public addresses to use for network devices that access the Internet. 17. Which IPv4 class of addresses provides the most networks? Class A Class B Class C Class D Class E 18. Which IPv4 class provides the highest number of host addresses per network? Class A Class B Class C Class D Class E
19. What is the purpose of a DHCP server on a network? to resolve MAC addresses to IP addresses to resolve IP addresses to MAC addresses to resolve host names to IP addresses to assign IP addresses dynamically to hosts to assign a MAC address to a host 20.
a LAN. The number of collisions on a LAN are the same whether a hub or a switch is used. 3.
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are correct in reference to the output shown? (Choose two.) The LAN segment is subnetted to allow 254 subnets. The DNS server for this host is on the same subnet as the host. The host automatically obtained the IP addresses 192.168.1.100. The host received the IP address from the router on the local LAN segment. The host is assigned an address of 00-50-8D-F1EA-8D by the administrator. 1.What is characteristic of the operation of a Layer 2 switch? forwards data based on logical addressing duplicates the electrical signal of each frame to every port learns the port assigned to a host by examining the destination MAC address uses the destination MAC address to determine the specific interface to forward a frame 2.Two newly hired technicians are discussing the implementation of a new LAN. One technician proposes installing a hub. The other technician advises installing a switch. Which statements are true about the differences between a hub and a switch? (Choose two.) A hub operates at Layer 2 of the OSI model. A hub reduces the number of collisions on a LAN. A hub works at a higher OSI model layer than a switch. A switch provides more throughput to hosts on a LAN A switch provides a collision-free environment on
Refer to the exhibit. Forty-eight workstations are connected to a hub. The users are able to connect to the network, but access is very slow. An entry-level technician replaces the 10 Mbps hub with 100 Mbps hub but the problem still exists. What is the most economical way to correct the problem? Replace the hub with a switch. Replace the hub with a router. Replace the hub with a 1 Gbps hub. Replace the hub with a 10 Mbps fiber hub. 4.
Exhibited is a portion of ABC Company internetwork. Which of the connections can be full duplex? segments 1 and 2 segment 2 segments 3 and 4 segments 2, 3, and 4 segments 1, 2, 3, and 4 5.
Refer to the exhibit. The switch and the hub have default configurations, and the switch has built its CAM table. Which of the hosts will receive the data when workstation A sends a unicast packet to workstation C? workstation C
workstations B and C workstations B, C, and the E0 interface of the router workstations B, C, D, E, F, and the E0 interface of the router 6. An administrator would like to connect ten workstations on a 192.168.0.0/24 network. The device selected by the administrator must allow connectivity between hosts without sharing bandwidth. Which device would be appropriate? hub router switch repeater 7. Which networking devices use the MAC address to make forwarding decisions? (Choose two.) NIC bridge hub switch repeater 8. Which devices are primarily used to extend cable segments within a collision domain by regenerating the data signals? (Choose two.) switch repeater router bridge hub 9. Which devices will create multiple collision domains in an Ethernet network? (Choose two.) NIC hub switch router repeater 10.
11. A PC receives a frame. Which situation will cause the NIC on the receiving host to pass the frame contents up the OSI layers to be processed by the PC? The frame is a runt frame. The destination MAC address of the frame is FFFF.FFFF.FFFF. The transmitting host generated a jam signal during the frame transmission. The recalculated checksum for the frame does not match the FCS on the frame. 12. A network administrator has a multi-floor LAN to monitor and maintain. Through careful monitoring, the administrator has noticed a large amount of broadcast traffic slowing the network. Which device would you use to best solve this problem? bridge hub router transceiver 13. What will a bridge do if it receives a frame with a MAC address that is not within the table? discard frame ignore frame send frame to appropriate port send frame to all ports except source port 14. Which networking device reduces the size of both collision domains and broadcast domains? hub Layer 2 switch router bridge repeater 15. What is used to prevent Layer 2 switching loops? bridging segmentation Address Resolution Protocol Spanning-Tree Protocol 1.Which Ethernet standard does the IEEE 802.3 standard recommend for backbone installations? 10BASE-T 100BASE-T 100BASE-FX 1000BASE-LX
Refer to the exhibit. How many broadcast domains exist in classroom 240? 1 2 5 12 13 15
2. Which statements describe Gigabit Ethernet technology? (Choose two.) operates at 100 Mbps typically used for backbone cabling requires shielded twisted-pair cabling can be implemented over copper and fiber primarily used between workstations option
3. Which of the following are Fast Ethernet technologies? (Choose two.) 100BASE-5 100BASE2 1000BASE-F 100BASE-FX 100BASE-TX 4. To make sure timing limitations are not violated when implementing a 10 Mbps Ethernet network involving hubs or repeaters, a technician should adhere to which rule? the 4-5-3 rule the 6-4-2 rule the 3-4-5 rule the 5-4-3 rule 5. At which OSI layer do the differences between standard Ethernet, Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet occur? physical layer data link layer network layer transport layer 6. How does 1000BASE-T use the UTP wire pairs to accomplish transmission? two pairs are used to transmit and two pairs are used to receive one pair is used to transmit, one pair is used to receive, one pair is used for clocking, and one pair is used for error correction all four pairs are used in parallel by both hosts to transmit and receive simultaneously two pairs of wires are used as in 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX 7. What RJ-45 pins are unused when transmitting and receiving data in an Ethernet 100BASE-T Category 5 UTP cable? (Choose two.) 1 and 2 3 and 6 4 and 5 7 and 8 8. What is the maximum distance that 10BASE-T will transmit data before signal attenuation affects the data delivery? 100 meters 185 meters 300 meters 500 meters 9. Which media types can be used in an implementation of a 10BASE-T network? (Choose three.) Category 5 UTP Category 5e UTP Category 3 UTP
coaxial cable multi-mode fiber single mode fiber 10. Which of the following Ethernet technologies are considered legacy Ethernet? (Choose three.) 10BASE2 10BASE5 10BASE-T 100BASE-T 100BASE-FX 100BASE-TX 1. Which of the following are specified by IEEE standards as sublayers of the OSI data link layer? (Choose two.) Logical Link Control Logical Layer Control Media Access Control Logical Link Communication Media Access Communication Physical Access Communication 2.
Refer to the exhibit. Host A is communicating with host F. What happens to a frame sent from host A to host F as it travels over the Ethernet segments? The frame format is modified as it passes through each switch. The frame format remains the same across each Ethernet segment. The frame format is modified as the media speed changed at switch B and switch E. The frame format is modified as the media material changes between copper and fiber at switch C and switch D. 3. In which two layers of the OSI model does Ethernet function? (Choose two.) application session transport network data link physical 4. Where does the MAC address originate? DHCP server database configured by the administrator burned into ROM on the NIC card network configuration on the computer included in the creation of the processor chip 5. At what layer of the OSI model does a MAC address reside?
1 2 3 4 7 6. A router has an Ethernet, Token Ring, serial, and ISDN interface. Which interfaces will have a MAC address? serial and ISDN interfaces Ethernet and Token Ring interfaces Ethernet and ISDN interfaces Token Ring and serial interfaces 7. Which two devices can provide full-duplex Ethernet connections? (Choose two.) hub modem repeater NIC Layer 2
(Choose three.) A NIC connects the PC to the network media. A NIC detects collisions on the Ethernet segment. A NIC checks the formatting of data before it is transmitted. A NIC passes the contents of selected frames to the upper OSI layers. A NIC acknowledges and retransmits data that was not received properly. A NIC discards frames when the destination IP address does not match the local host. 11. In an Ethernet LAN, how does the NIC know when it can transmit data? An Ethernet NIC transmits data as soon as the frame is received. An Ethernet NIC transmits data as soon as the NIC receives a token. An Ethernet NIC transmits data when it senses a collision. An Ethernet NIC transmits data after listening for the absence of a signal on the media. 12.
Refer to the exhibit. The small office network shown in the exhibit consists of four computers connected through a hub. Which configuration would cause collisions and errors on the network? autonegotiation FastEthernet peer-to-peer shared resources administratively configured full duplex
Refer to the exhibit. All hosts are in listen mode. Host 1 and Host 4 both transmit data at the same time. How do the hosts respond on the network? (Choose two.) Hosts 1 and 4 may be operating full duplex so no collision will exist. The hub will block the port connected to Host 4 to prevent a collision. After the end of the jam signal, Hosts 1, 2, 3, and 4 invoke a backoff algorithm. When the four hosts detect the collision, Hosts 1, 2, 3, and 4 generate a jam signal. Hosts 1 and 4 are assigned shorter backoff values to provide them priority to access the media. If a host has data to transmit after the backoff period of that host, the host checks to determine if the line is idle, before transmitting. 13. Which statement describes how CSMA/CD on an Ethernet segment manages the retransmission of frames after a collision occurs? The first device to detect the collision has the priority for retransmission. The device with the lowest MAC address determines the retransmission priority. The devices on the network segment hold an election for priority to retransmit data The devices transmitting when the collision occurs DO NOT have priority for retransmission.
Refer to the exhibit. The switch and workstation are administratively configured for full-duplex operation. Which statement accurately reflects the operation of this link? No collisions will occur on this link. Only one of the devices can transmit at a time. The switch will have priority for transmitting data. The devices will default back to half duplex if excessive collisions occur. 10. What are three functions of a NIC in a PC?
14. What is the maximum distance that 10BASE-T will transmit data before signal attenuation affects the data delivery? 100 meters 185 meters 300 meters 500 meters 15. Which of the following are Fast Ethernet technologies? (Choose two.) 100BASE-5 100BASE2 1000BASE-F 100BASE-FX 100BASE-TX 16. At which OSI layer do the differences between standard Ethernet, Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet occur? physical layer data link layer network layer transport layer 17. How does 1000BASE-T use the UTP wire pairs to accomplish transmission? two pairs are used to transmit and two pairs are used to receive one pair is used to transmit, one pair is used to receive, one pair is used for clocking, and one pair is used for error correction all four pairs are used in parallel by both hosts to transmit and receive simultaneously two pairs of wires are used as in 10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX 18. Which statements describe Gigabit Ethernet technology? (Choose two.) operates at 100 Mbps typically used for backbone cabling requires shielded twisted-pair cabling can be implemented over copper and fiber primarily used between workstations option 19. Which media types can be used in an implementation of a 10BASE-T network? (Choose three.) Category 5 UTP Category 5e UTP Category 3 UTP coaxial cable multi-mode fiber single mode fiber 20. Which of the following Ethernet technologies are considered legacy Ethernet? (Choose three.) 10BASE2 10BASE5 10BASE-T
100BASE-T 100BASE-FX 100BASE-TX
Refer to the exhibit. Host A is communicating with host F. What happens to a frame sent from host A to host F as it travels over the Ethernet segments? The frame format is modified as it passes through each switch. The frame format remains the same across each Ethernet segment. The frame format is modified as the media speed changed at switch B and switch E. The frame format is modified as the media material changes between copper and fiber at switch C and switch D. 2. How many hexadecimal digits are in a MAC address? 2 8 12 16 32 3. What are three functions of a NIC in a PC? (Choose three.) A NIC connects the PC to the network media. A NIC detects collisions on the Ethernet segment. A NIC checks the formatting of data before it is transmitted. A NIC passes the contents of selected frames to the upper OSI layers. A NIC acknowledges and retransmits data that was not received properly. A NIC discards frames when the destination IP address does not match the local host. 4. At what layer of the OSI model does a MAC address reside? 1 2 3 4 7 5. A router has an Ethernet, Token Ring, serial, and ISDN interface. Which interfaces will have a MAC address? serial and ISDN interfaces Ethernet and Token Ring interfaces Ethernet and ISDN interfaces Token Ring and serial interfaces 6. In an Ethernet LAN, how does the NIC know when it can transmit data? An Ethernet NIC transmits data as soon as the
frame is received. An Ethernet NIC transmits data as soon as the NIC receives a token. An Ethernet NIC transmits data when it senses a collision. An Ethernet NIC transmits data after listening for the absence of a signal on the media. 7. Which characteristics describe carrier sense multiple access collision detect (CSMA/CD)? (Choose three.) reliable point-to-point nondeterministic connection-oriented collision environment first-come, first-served approach 8. Which two devices can provide full-duplex Ethernet connections? (Choose two.) hub modem repeater NIC Layer 2 switch 9. On a local area network, one workstation can send data on the line while it is receiving data. What type of data transfer does this describe? hybrid half duplex full duplex multilink 10.
No collisions will occur on this link. Only one of the devices can transmit at a time. The switch will have priority for transmitting data. The devices will default back to half duplex if excessive collisions occur.
12.
Refer to the exhibit. All hosts are in listen mode. Host 1 and Host 4 both transmit data at the same time. How do the hosts respond on the network? (Choose two.) Hosts 1 and 4 may be operating full duplex so no collision will exist. The hub will block the port connected to Host 4 to prevent a collision. After the end of the jam signal, Hosts 1, 2, 3, and 4 invoke a backoff algorithm. Hosts 1 and 4 are assigned shorter backoff values to provide them priority to access the media. If a host has data to transmit after the backoff period of that host, the host checks to determine if the line is idle, before transmitting. 13. When a collision occurs in a network using CSMA/CD, how do hosts with data to transmit respond after the backoff period has expired? The hosts return to a listen-before-transmit mode. The hosts creating the collision have priority to send data. The hosts creating the collision retransmit the last 16 frames. The hosts extend their delay period to allow for rapid transmission. 14. Which statement describes how CSMA/CD on an Ethernet segment manages the retransmission of frames after a collision occurs? The first device to detect the collision has the priority for retransmission. The device with the lowest MAC address determines the retransmission priority. The devices on the network segment hold an election for priority to retransmit data The devices transmitting when the collision occurs DO NOT have priority for retransmission. 15.
Refer to the exhibit. The small office network shown in the exhibit consists of four computers connected through a hub. Which configuration would cause collisions and errors on the network? autonegotiation FastEthernet peer-to-peer shared resources administratively configured full duplex 11.
Refer to the exhibit. The switch and workstation are administratively configured for full-duplex operation. Which statement accurately reflects the operation of this link?
Refer to the exhibit. A technician wants to increase the available bandwidth for the workstation by allowing the switch and the NIC on the workstation to transmit and receive simultaneously. What will permit this? CSMA/CD full-duplex FastEthernet crossover cable 16. Why do hosts on an Ethernet segment that experience a collision use a random delay before attempting to transmit a frame? A random delay is used to ensure a collision-free link. A random delay value for each device is assigned by the manufacturer. A standard delay value could not be agreed upon among networking device vendors. A random delay helps prevent the stations from experiencing another collision during the transmission. 17. In which two layers of the OSI model does Ethernet function? (Choose two.) application session transport network data link physical 18. Which of the following are specified by IEEE standards as sublayers of the OSI data link layer? (Choose two.) Logical Link Control Logical Layer Control Media Access Control Logical Link Communication Media Access Communication Physical Access Communication 19. Where does the MAC address originate? DHCP server database configured by the administrator burned into ROM on the NIC card network configuration on the computer included in the creation of the processor chip
Refer to the exhibit. What is the appropriate cable to use at each of the numbered network connections? 1-crossover; 2-straight-through; 3-crossover; 4straight-through 1-straight-through; 2-crossover; 3-straight-through; 4-straight-through 1-straight-through; 2-crossover; 3-crossover; 4straight-through 1-rollover; 2-crossover; 3-straight-through; 4straight-through 1-rollover; 2-straight-through; 3-straight-through; 4-straight-through 2. Which two devices are considered OSI Layer 1 devices? (Choose two.) hubs routers bridges switches repeaters 3. What device is used to connect hosts to an Ethernet LAN and requires a straight-through UTP cable between the hosts and this device? NIC router switch server 4. What is the most common type of cabling used in LANs? STP UTP coax fiber 5. In which situations would a crossover cable be used to connect devices in a network? (Choose two.) switch to PC switch to hub switch to router switch to server switch to switch
6. Refer to the exhibit. How many collision domains exist in the network? 1 2
4 7 8 7. What type of cable would be used to make the connection between the console port of a router and a workstation? crossover rollover straight-through patch 8.
centralized administrator not required centralized control of assets 13. Which statement is accurate about a WAN link? The link transmits data serially. The link uses a maximum distance of 100 meters. The link uses the same transmission rate as all other WAN links use. The link uses the same standardized connector style that is used for all WAN technologies. 14.
Which function is a unique responsibility of the DCE devices shown in the exhibit? transmission of data reception of data clocking for the synchronous link noise cancellation in transmitted data 9. Which address does a bridge use to make filtering and switching decisions? source MAC source IP destination MAC destination IP network IP address 10. What is characteristic of how a hub operates? A hub selectively drops packets that represent potential security risks. A hub forwards data out all interfaces except the inbound interface. A hub dynamically learns the interfaces to which all devices are attached. At start up, a hub queries the devices on all interfaces in order to learn the MAC addresses of the attached devices. A hub transmits a frame to a specific interface based on the destination MAC address. 11. Users with systems that are attached to a hub are complaining about poor response time. What device could replace the hub and provide immediate response time improvement? router switch bridge repeater 12. Which of the following are benefits of peer-topeer networks? (Choose three.) centralized security easy to create very scalable no centralized equipment required
Which items in the exhibit are DTE devices? A and B B and C C and D A and D A, B, C, and D 15. At which layer of the OSI model does the MAC address of a NIC reside? physical application network transport data link session 16.
Refer to the exhibit. A technician measured the lengths of the CAT 5e structured cable runs in the exhibit. How should the technician evaluate the cabling shown in the diagram to the network administrator? All cabling to work areas are within specifications. Station A and B may experience intermittent problems because the length exceeds the recommended standard. Station B may experience intermittent problems because the length exceeds the recommended standard. Station C may experience intermittent network connectivity because the length is less than the recommended standard.
Station A and B will have intermittent problems because the length exceeds the recommended standard. Station C will not have network connectivity because the length is less than the recommended standard. 17. Which statement describes a typical use of Gigabit Ethernet? to provide high-speed desktop connectivity for average users to provide connectivity to low to medium volume applications to provide medium volume connectivity to workgroup servers to provide high-speed connectivity for backbones and cross connects 18. Orange putih-orange-ijo putih-biru-biru putihijo-cokput-cok
1. To ensure reliable LAN communications, what should a technician be looking for when attaching connectors to the ends of UTP cable? that the white-orange/orange pair is attached first That the wire pairs remain twisted as much as possible that one end of the shield is properly ground but not the other that 50 ohm termination resistors are on both ends 2. Which of the following describes frequency? length of each wave height of each wave number of cycles each second amount of time between each wave 3. How are binary ones and zeros represented in fiber optic installations? (Choose two.) +5 volts/-5 volts 0 volts/5 volts light/no light high to low electrical transition low to high electrical transition increasing/decreasing light intensity 4. What is expected when crosstalk is present in networks with higher transmission frequencies? (Choose two.) jitter increase in crosstalk higher signal attenuation increases in cancellation effect destruction of more of the data signal 5. A small company is experiencing difficulties on its LAN. After performing some tests, a technician has determined that the copper media supporting the LAN is experiencing abnormal attenuation. What are two possible causes of the problem? (Choose two.) defective connectors excessively long cable lengths use of higher grade cabling low frequency signals used in the media network cable runs isolated from other cables 6. What factors need to be considered to limit the amount of signal attenuation in Ethernet cable runs? (Choose two.) type of users number of users length of cable type of electrical equipment installation of connectors on the cable 7. What conditions are described when transmission signals from one wire pair affects another wire pair? (Choose two.) noise resistance mismatch
The ends of a UTP cable are shown in the exhibit. Which cable configuration is shown? crossover rollover reversed-pair straight-through split-pair console 19.ijo putih-ijo-ornge putih-biru-biru putih-orangecokput-cok
The ends of a UTP cable are shown in the exhibit. Which cable configuration is shown? console crossover rollover reversed-pair split-pair straight-through 20. Which of the following are benefits of a wireless network? (Choose two.) higher data speeds better security mobility less expensive NIC cards no need to run cables to hosts
jitter crosstalk attenuation 8. What is a cause of crosstalk in UTP cable? cable pairs that are shorted cable pairs crossed during termination cabling runs installed in separate conduit cable pairs that are untwisted because of poor termination of the cable 9. Which of the following are detected by the wire map test? (Choose three.) near-end crosstalk (NEXT) opens propagation delay return loss reversed-pair faults short circuits 10. A company needs to extend the LAN to six separate buildings. To limit the amount of signal attenuation on the LAN media, what type of media would be the best to use between the buildings? air (wireless) coaxial cable fiber shielded twisted pair unshielded twisted pair 10. Which OSI layer addressing is required to route packets between two networks? Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 Layer 4 13. Which subnet mask will allow 2040 hosts per subnet on the IP network 10.0.0.0? 255.255.0.0 255.255.254.0 255.255.252.0 255.255.248.0 255.255.240.0 255.255.255.128
TCP/IP Refer to the exhibit. Which two layers of the OSI model describe the same functions as the transport and internet layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.) application layer presentation layer session layer transport layer network layer data link layer physical layer 30. What happens when a host station receives a frame that contains its own MAC address in the destination field? The Layer 2 information is removed and the frame is pushed up to Layer 3. The host station will copy the information to its buffers and send it back out. The frame originated from the host and will be ignored. The Layer 3 information is added to the frame. 32. What type of network is maintained if a server takes no dedicated role in the network? mainframe client/server peer-to-peer centralized 33. In a network design project, a network designer needs to select a device to provide collision free connections to 40 hosts on the LAN. Which device should be selected? hub router switch firewall 34. Which TCP/IP model layer creates additional overhead on network resources due to acknowledgments, tracking, and retransmission of data? internet transport application network access 35. How many host addresses may be assigned when using the 128.107.0.0 network address with a subnet mask of 255.255.248.0? 30 256 2046 2048 4094 4096
16. Refer to the exhibit. Which layered network model is shown in the diagram? Cisco IETF OSI
36. Which service is used when the nslookup command is issued on a computer? FTP DNS DHCP Telnet 37. Which process provides the means to send and receive data when running multiple applications at the same time on a computer? interleaving sequencing segmentation acknowledgement 38. Which three IPv4 addresses represent valid host addresses for a subnet? (Choose three.) 10.1.12.79/28 10.1.12.113/28 10.1.12.32/28 10.1.11.5/27 10.1.11.97/27 10.1.11.128/27 39. What is the consequence of issuing the erase startup-config command in privileged EXEC mode on a Cisco router? Data stored in RAM will be removed. Data stored in NVRAM will be erased. Information in flash memory will be removed. Flags in the configuration register will be set to 0. Both the startup-config and the running-config will be erased. 40.
IP address: 192.168.100.31; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.18
44. A routing issue has occurred in your internetwork. Which of the following type of devices should be examined to isolate this error? access point host hub router switch 45. Which statement is true about Layer 3 addresses? They are physical addresses. They are used in routing decisions. They are only used on local networks. They are altered each time a packet crosses a router. 47. Which OSI layer does IP rely on to determine whether packets have been lost and to request retransmission? application presentation session transport 50. Which option represents a point-to-point logical topology diagram?
Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is trying to determine the correct IP address configuration for Host A. What is a valid configuration for Host A? IP address: 192.168.100.19; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248; Default Gateway: 192.16.1.2 IP address: 192.168.100.20; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.17 IP address: 192.168.100.21; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.18 IP address: 192.168.100.22; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 10.1.1.5 IP address: 192.168.100.30; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.1.1
1. A router determines the path to deliver a packet. What layer of the OSI model does this fact represent? session transport network data link
physical 2.
5. Which network device creates the highest amount of latency? hub router switch bridge 6.
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured a network after subnetting the network number 192.168.0.0/28. Workstation 1 is not able to communicate with Workstation 2. What is the cause of this loss in communications? Workstation 1 and Workstation 2 are on the same subnet. The serial connections are using addresses from the LAN subnets. Workstation 1 is not on the same network that the Router 1 LAN interface is on. If routers are used in the network, IP addresses do not need to be subnetted. 3. Which physical network topology is easy to monitor and troubleshoot, easy to add new devices to as the network expands, but subject to complete failure when a central hub or switch ceases to work? bus star ring mesh 4.
Refer to the exhibit. What must be configured on Host B to allow it to communicate with the file server? (Choose three.) the MAC address of the file server the MAC address of the PADI router interface connected to Switch A the IP address of Switch A a unique host IP address the subnet mask for the LAN the default gateway address 7. A computer technician is asked to make a network cable. One end of the cable is pinned as a 568A and the other as a 568B. For what purposes can this cable be used? (Choose two.) to connect a router to a switch to connect a switch to a switch to connect a host to a switch to connect a hub to a switch to connect a router to a hub to connect a host to a hub 8. When using Category 5 UTP cable, which RJ-45 pin pairs are used to exchange data between hosts on an Ethernet network? 1 and 2; 4 and 5 1 and 2; 3 and 6 3 and 6; 7 and 8 4 and 5; 7 and 8 9. What is the correct number of usable subnetworks and hosts for the IP network address 192.168.35.0 subnetted with a /28 mask? 6 networks / 64 hosts 14 networks / 32 hosts 14 networks / 14 hosts 30 networks / 64 hosts 10. Which devices will create multiple collision domains in an Ethernet network? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit. Host A pings Host B. What can be concluded about the source and destination addresses contained in the communication sent by Router R5 when it forwards the ping out the Ethernet interface to Host B? (Choose two.) source IP address: 192.168.10.129 source MAC address: BBBB.3333.5677 source MAC address: 5555.AAAA.6666 destination IP address: 192.168.10.33 destination IP address: 192.168.10.134 destination MAC address: 9999.DADC.1234
NIC hub switch router repeater
The host sends the frame content to an upper layer protocol for error recovery.
11. What is the decimal representation of the binary number 11111000? 224 240 248 252 254 12. Which characteristics are common to both UDP and TCP? (Choose two.) provides windowing provides reliability uses port numbers acknowledges receipt of data classified as a connectionless protocol classified as a transport layer protocol 13. The ping command can be used to test connectivity between hosts. Which OSI model layers are verified by this test? Layers 1 and 2 only Layers 1 and 3 only Layers 1, 2 and 3 Layer 1 through Layer 7 Layer 4 through Layer 7 14. Why do vendors utilize the OSI model when designing networking products? It places requirements on all vendors that develop proprietary networking technologies for advance networking systems. It ensures greater compatibility and interoperability with equipment from different vendors. The International Organization for Standards develops all new products to be incorporated into the product. It is mandated by the International Organization for Standardization that network products be compliant with the OSI model. 15. An Ethernet host receives a frame, calculates the FCS, and compares the calculated FCS to the FCS received in the frame. The host finds that the two FCS values do not match. What action will be taken by the host? The host discards the frame. The host processes the data frame normally. The host initiates a request for retransmission of the frame.
16. Why would a company install a switch instead of a hub when building or expanding a corporate network? A switch manages frames faster than a hub does. A switch operates at 100 Mbps. A hub operates at a maximum of 10 Mbps. A switch modifies the Ethernet frame to remove any errors. A hub forwards the frame exactly as it arrived. A switch provides more bandwidth by sending frames only out the port to which the destination device is attached. A hub sends the frame out all ports except the source port. 17.
Refer to the exhibit. What is the order of the TCP/IP Protocol Data Units as data is moved as indicated through the OSI model? bits, segments, frames, packets, data bits, frames, packets, segments, data bits, frames, segments, packets, data bits, packets, frames, segments, data 18. After an unsuccessful ping to the local router, the technician decides to investigate the router. The technician observes that the lights and fan on the router are not operational. In which layer of the OSI model is the problem most likely occurring? transport network data link physical 19. Which of the following statements are correct about CSMA/CD? (Choose three.) It is a media access method used in LANs. It is a media access method used in FDDI WANs. When a device needs to transmit, it checks to see if the media is available. A device sends data without checking media availability because all devices have equal access.
Multiple devices can successfully transmit simultaneously. Only one device can successfully transmit at a time.
20. A network administrator has installed a 24 port switch and connected 10 computers with 10/100 NICs. If the NICs are operating at 100 Mbps, how much bandwidth is available for each computer to receive data? 0.24 Mbps 4.17 Mbps 10 Mbps 24 Mbps 100 Mbps 200 Mbps 21.
Refer to the exhibit. The connections in the exhibit are labeled A through E. Which of these indicate LAN links? (Choose two.) link A link B link C link D link E 24.
Refer to the exhibit. A newly hired technician has a task of terminating CAT 5 UTP cables. The network administrator visually examined the cables the technician terminated. Some of the cables have connectors as shown in the exhibit. What should the network administrator explain to the technician about the cables? Both cables are acceptable. The cable in Graphic A will produce more crosstalk. The cable in Graphic A should be used in the more critical network segments. The cable in Graphic A is preferred because it will be easier to crimp the connector. 22. Which technologies are considered to be LAN technologies? (Choose two.) DSL Token Ring Frame Relay ISDN Ethernet
Consider the networks shown in the exhibit. Host A is sending packets to host B. Which layer of the OSI model is being used when the router is making the calculated decision to determine which interface to send the packet out? physical data link network transport session presentation 25. What are important characteristics to consider when purchasing a network interface card? (Choose two.) security used on the network media used on the network system bus used on the computer software installed on the network diagnostic tools installed on the network 26.
255.255.255.252 29.sama 22nya
Refer to the exhibit. Which diagram represents the network topology that an administrator would prefer, and why would the administrator prefer it? Diagram A. It provides the hosts with fullduplex connections. Diagram A. It will better provide available bandwidth to the hosts. Diagram B. It extends the collision domain. Diagram B. It prevents the frames from looping. Either network will perform equally well. 27.
Refer to the exhibit. What kind of Ethernet cable is represented? rollover cable straight-through cable crossover cable console cable 30.
Based on the graphic above, which of the following occurs as each host system comes on line in the topology? Refer to the exhibit. The physical documentation shows a portion of the internetwork of the ABC Company. Which segments will be free of collisions? segments 1 and 2 segments 1, 2, and 3 segments 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 segments 2 and 3 segments 3, 4, and 5 segments 4, and 5 28. The switch sends its MAC address to each host. The switch adds MAC address to the bridge table as each host sends a frame. Each host exchanges MAC addresses with each other. The switch listens for data traffic to block since the switch lacks an IP address.
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator wants to create a subnet for the point-to-point connection between the two routers. Which subnetwork mask would provide enough addresses for the point-to-point link with the least number of wasted addresses? 255.255.255.192 255.255.255.224 255.255.255.240 255.255.255.248
31. Two peer hosts are exchanging data using TFTP. During the current session, a datagram fails to arrive at the destination. Which statement is true regarding the retransmission of the datagram? Datagram retransmission requires user authentication. Datagram retransmission is controlled by the application. Datagram retransmission relies on the acknowledgements at transport layer. Datagram retransmission occurs when the retransmission timer expires in the source host. 32. Which type of address is 192.168.170.112/28? host address subnetwork address broadcast address multicast address
33. How does a switch learn the addresses of hosts connected to its ports? All source MAC addresses must be manually configured in CAM. The switch reads the source MAC address on incoming frames and records it in CAM. The switch reads the destination MAC address on incoming frames and records it in CAM. If a switch port is full duplex, the switch reads both the source and destination MAC addresses on incoming frames and records them in CAM. 34. Which protocols are TCP/IP application layer protocols? (Choose two.) TFTP IP TCP UDP DNS 35.
establishing and managing these different FTP connections? application session transport network data link 38.
In the exhibit, the connections between the devices are labeled A, B, C, D, and E. For each connection, what is the correct UTP cable to use? A=straight, B=rollover, C=straight, D=crossover, E=crossover A=rollover, B=crossover, C=crossover, D=straight, E=straight A=rollover, B=straight, C=straight, D=crossover, E=straight A=rollover, B=straight, C=straight, D=crossover, E=crossover A=straight, B=crossover, C=rollover, D=straight, E=straight 39. sama Cuma urutan angka beda
Refer to the exhibit. How many broadcast domains are shown? three four five six eight ten 36. Which cable diagram displays the end to end pinout for a crossover cable used with Cisco devices? Cable A Cable B Cable C Cable D 40.
Refer to the exhibit. Which type of UTP cable should be used to connect Host A to Switch1? rollover console crossover straight-through 37. A user initiates three simultaneous FTP connections from the local host to the same FTP server. Which OSI layer is responsible for
Refer to the exhibit. A network associate needs to establish an Ethernet connection between Host A
and Host B. However, the distance between the two hosts is further than the cabling standards allow. Which two devices that operate at the physical layer of the OSI can be used to allow Host A and Host B to communicate? (Choose two.) switch hub bridge router repeater 41.
43. Which subnet masks could be used when subnetting a Class B IP address? (Choose two.) 255.255.255.240 255.255.192.0 255.255.0.0 255.192.0.0 240.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 44. A network administrator has added a new switch to the network. The new switch connects to an existing switch that is already installed. Which UTP cable correctly connects the new switch to the existing switch? crossover rollover straight-through console 45.
Refer to the exhibit. Workstation 1 pings the Fa0/1 interface of Router 1. Which MAC address will workstation 1 obtain during the ARP request for this communication? 00-06-5B-88-DF-C3 00-B0-D0-7F-F7-46 00-0F-24-85-75-C0 00-0B-E5-64-BD-44 00-08-A3-B6-CE-02 00-08-A3-B6-CE-03 42.
Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is trying to determine the correct IP address configuration for Host A. What is a valid configuration for Host A? IP address: 192.168.100.19; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248; Default Gateway: 192.16.1.2 IP address: 192.168.100.20; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.17 IP address: 192.168.100.21; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.18 IP address: 192.168.100.22; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 10.1.1.5 IP address: 192.168.100.30; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.1.1 IP address: 192.168.100.31; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.18
A technician is testing connectivity between the devices using the ping command. Pings between Host B and Host A were successful. The technician could not ping the R3 address 172.16.3.2 from Host A. The technician issued ipconfig from Host A and saw the information displayed in the exhibit. What is the most likely problem? The IP address of Host A is incorrect. The subnet mask of Host A is incorrect. The default gateway of Host A is incorrect. Host A is properly configured. Some other problem exists in the internetwork. 46. A router interface has been assigned an IP address of 172.16.192.166 with a mask of 255.255.255.248. To which subnet does the IP address belong? 172.16.0.0 172.16.192.0 172.16.192.128 172.16.192.160 172.16.192.168 172.16.192.176 47.
How many collision domains are shown in the diagram? three four five six seven eight 48. A large company has a network that is constantly changing. The routing tables in the routers need to be adjusted to reflect the changes in the routing paths. What type of routing would the network administrator implement? static routes dynamic routing protocols only default routes none. No routing is necessary.
4. The process of TCP on one computer marking a segment as segment 1, and the receiving computer then acknowledging the receipt of segment 1, is an example of what? a. Data encapsulation b. Same-layer interaction c. Adjacent-layer interaction d. The OSI model e. None of these answers are correct. 5. The process of a web server adding a TCP header to a web page, followed by adding an IP header, and then a data link header and trailer is an example of what? a. Data encapsulation b. Same-layer interaction c. The OSI model d. All of these answers are correct. 6. Which of the following terms is used specically to identify the entity that is created when encapsulating data inside data link layer headers and trailers? a. Data b. Chunk c. Segment d. Frame e. Packet f. None of thesethere is no encapsulation by the data link layer. 7. Which OSI layer denes the functions of logical network-wide addressing and routing? a. Layer 1 b. Layer 2 c. Layer 3 d. Layer 4 e. Layer 5 f. Layer 6 g. Layer 7 8. Which OSI layer denes the standards for cabling and connectors? a. Layer 1 b. Layer 2 c. Layer 3 d. Layer 4 e. Layer 5 f. Layer 6 g. Layer 7
1. Which of the following protocols are examples of TCP/IP transport layer protocols? a. Ethernet b. HTTP c. IP d. UDP e. SMTP f. TCP 2. Which of the following protocols are examples of TCP/IP network access layer protocols? a. Ethernet b. HTTP c. IP d. UDP e. SMTP f. TCP g. PPP 3. The process of HTTP asking TCP to send some data and make sure that it is received correctly is an example of what? a. Same-layer interaction b. Adjacent-layer interaction c. The OSI model d. All the other answers are correct.
9. Which OSI layer denes the standards for data formats and encryption? a. Layer 1 b. Layer 2 c. Layer 3 d. Layer 4 e. Layer 5 f. Layer 6 g. Layer 7 10. Which of the following terms are not valid terms for the names of the seven OSI layers? a. Application b. Data link c. Transmission d. Presentation e. Internet f. Session 1. Which of the following is true about the cabling of a typical modern Ethernet LAN? a. Connect each device in series using coaxial cabling b. Connect each device in series using UTP cabling c. Connect each device to a centralized LAN hub using UTP cabling d. Connect each device to a centralized LAN switch using UTP cabling 2. Which of the following is true about the cabling of a 10BASE2 Ethernet LAN? a. Connect each device in series using coaxial cabling b. Connect each device in series using UTP cabling c. Connect each device to a centralized LAN hub using UTP cabling d. Connect each device to a centralized LAN switch using UTP cabling 3. Which of the following is true about Ethernet crossover cables? a. Pins 1 and 2 are reversed on the other end of the cable. b. Pins 1 and 2 on one end of the cable connect to pins 3 and 6 on the other end of the cable. c. Pins 1 and 2 on one end of the cable connect to pins 3 and 4 on the other end of the cable. d. The cable can be up to 1000 meters long to cross over between buildings. e. None of the other answers is correct.
4. Each answer lists two types of devices used in a 100BASE-TX network. If these devices were connected with UTP Ethernet cables, which pairs of devices would require a straight-through cable? a. PC and router b. PC and switch c. Hub and switch d. Router and hub e. Wireless access point (Ethernet port) and switch 5. Which of the following is true about the CSMA/CD algorithm? a. The algorithm never allows collisions to occur. b. Collisions can happen, but the algorithm denes how the computers should notice a collision and how to recover. c. The algorithm works with only two devices on the same Ethernet. d. None of the other answers is correct. 6. Which of the following is a collision domain? a. All devices connected to an Ethernet hub b. All devices connected to an Ethernet switch c. Two PCs, with one cabled to a router Ethernet port with a crossover cable and the other PC cabled to another router Ethernet port with a crossover cable d. None of the other answers is correct. 7. Which of the following describe a shortcoming of using hubs that is improved by instead using switches? a. Hubs create a single electrical bus to which all devices connect, causing the devices to share the bandwidth. b. Hubs limit the maximum cable length of individual cables (relative to switches) c. Hubs allow collisions to occur when two attached devices send data at the same time. d. Hubs restrict the number of physical ports to at most eight. 8. Which of the following terms describe Ethernet addresses that can be used to communicate with more than one device at a time? a. Burned-in address b. Unicast address c. Broadcast address d. Multicast address
9. Which of the following is one of the functions of OSI Layer 2 protocols? a. Framing b. Delivery of bits from one device to another c. Error recovery d. Dening the size and shape of Ethernet cards 10. Which of the following are true about the format of Ethernet addresses? a. Each manufacturer puts a unique code into the rst 2 bytes of the address. b. Each manufacturer puts a unique code into the rst 3 bytes of the address. c. Each manufacturer puts a unique code into the rst half of the address. d. The part of the address that holds this manufacturers code is called the MAC. e. The part of the address that holds this manufacturers code is called the OUI. f. The part of the address that holds this manufacturers code has no specic name. 11. Which of the following is true about the Ethernet FCS eld? a. It is used for error recovery. b. It is 2 bytes long. c. It resides in the Ethernet trailer, not the Ethernet header. d. It is used for encryption. e. None of the other answers is correct. 1. Which of the following best describes the main function of OSI Layer 1 protocols? a. Framing b. Delivery of bits from one device to another c. Addressing d. Local Management Interface (LMI) e. DLCI 2. Which of the following typically connects to a four-wire line provided by a telco? a. Router serial interface b. CSU/DSU c. Transceiver d. Switch serial interface 3. Which of the following typically connects to a V.35 or RS-232 end of a cable when cabling a leased line? a. Router serial interface b. CSU/DSU
c. Transceiver d. Switch serial interface 4. On a point-to-point WAN link using a leased line between two routers located hundreds of miles apart, what devices are considered to be the DTE devices? a. Routers b. CSU/DSU c. The central ofce equipment d. A chip on the processor of each router e. None of these answers are correct. 5. Which of the following functions of OSI Layer 2 is specied by the protocol standard for PPP, but is implemented with a Cisco proprietary header eld for HDLC? a. Framing b. Arbitration c. Addressing d. Error detection e. Identifying the type of protocol that is inside the frame 6. Imagine that Router1 has three point-to-point serial links, one link each to three remote routers. Which of the following is true about the required HDLC addressing at Router1? a. Router1 must use HDLC addresses 1, 2, and 3. b. Router1 must use any three unique addresses between 1 and 1023. c. Router1 must use any three unique addresses between 16 and 1000. d. Router1 must use three sequential unique addresses between 1 and 1023. e. None of these answers are correct. 7. What is the name of the Frame Relay eld used to identify Frame Relay virtual circuits? a. Data-link connection identier b. Data-link circuit identier c. Data-link connection indicator d. Data-link circuit indicator e. None of these answers are correct. 8. Which of the following is true about Frame Relay virtual circuits (VCs)? a. Each VC requires a separate access link. b. Multiple VCs can share the same access link.
c. All VCs sharing the same access link must connect to the same router on the other side of the VC. d. All VCs on the same access link must use the same DLCI. 1. Which of the following are functions of OSI Layer 3 protocols? a. Logical addressing b. Physical addressing c. Path selection d. Arbitration e. Error recovery 2. Imagine that PC1 needs to send some data to PC2, and PC1 and PC2 are separated by several routers. What are the largest entities that make it from PC1 to PC2? a. Frame b. Segment c. Packet d. L5 PDU e. L3 PDU f. L1 PDU 3. Imagine a network with two routers that are connected with a point-to-point HDLC serial link. Each router has an Ethernet, with PC1 sharing the Ethernet with Router1, and PC2 sharing the Ethernet with Router2. When PC1 sends data to PC2, which of the following is true? a. Router1 strips the Ethernet header and trailer off the frame received from PC1, never to be used again. b. Router1 encapsulates the Ethernet frame inside an HDLC header and sends the frame to Router2, which extracts the Ethernet frame for forwarding to PC2. c. Router1 strips the Ethernet header and trailer off the frame received from PC1, which is exactly recreated by R2 before forwarding data to PC2. d. Router1 removes the Ethernet, IP, and TCP headers and rebuilds the appropriate headers before forwarding the packet to Router2. 4. Which of the following are valid Class C IP addresses that can be assigned to hosts? a. 1.1.1.1 b. 200.1.1.1 c. 128.128.128.128 d. 224.1.1.1 e. 223.223.223.255
5. What is the range of values for the rst octet for Class A IP networks? a. 0 to 127 b. 0 to 126 c. 1 to 127 d. 1 to 126 e. 128 to 191 f. 128 to 192 6. PC1 and PC2 are on two different Ethernets that are separated by an IP router. PC1s IP address is 10.1.1.1, and no subnetting is used. Which of the following addresses could be used for PC2? a. 10.1.1.2 b. 10.2.2.2 c. 10.200.200.1 d. 9.1.1.1 e. 225.1.1.1 f. 1.1.1.1 7. Each Class B network contains how many IP addresses that can be assigned to hosts? a. 16,777,214 b. 16,777,216 c. 65,536 d. 65,534 e. 65,532 f. 32,768 g. 32,766 8. Each Class C network contains how many IP addresses that can be assigned to hosts? a. 65,534 b. 65,532 c. 32,768 d. 32,766 e. 256 f. 254 9. Which of the following does a router normally use when making a decision about routing TCP/IP packets? a. Destination MAC address b. Source MAC address c. Destination IP address d. Source IP address e. Destination MAC and IP address 10. Which of the following are true about a LANconnected TCP/IP host and its IP routing (forwarding) choices?
a. The host always sends packets to its default gateway. b. The host sends packets to its default gateway if the destination IP address is in a different class of IP network than the host. c. The host sends packets to its default gateway if the destination IP address is in a different subnet than the host. d. The host sends packets to its default gateway if the destination IP address is in the same subnet as the host. 11. Which of the following are functions of a routing protocol? a. Advertising known routes to neighboring routers. b. Learning routes for subnets directly connected to the router. c. Learning routes, and putting those routes into the routing table, for routes adver-tised to the router by its neighboring routers. d. To forward IP packets based on a packets destination IP address. 12. Which of the following protocols allows a client PC to discover the IP address of another computer based on that other computers name? a. ARP b. RARP c. DNS d. DHCP 13. Which of the following protocols allows a client PC to request assignment of an IP address as well as learn its default gateway? a. ARP b. RARP c. DNS d. DHCP
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Serial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsVon EverandSerial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (9)
- S7 200 CommunicationDokument34 SeitenS7 200 CommunicationsyoussefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise No. 5Dokument7 SeitenExercise No. 5Stanly Mark SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Von EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Cleanroom Design in 10 Easy StepsDokument5 SeitenCleanroom Design in 10 Easy StepsWerner SchrammelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco 1 Reviewer For Final ExamDokument9 SeitenCisco 1 Reviewer For Final ExamAlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Private IP Address Ranges and Network Device ConfigurationDokument61 SeitenPrivate IP Address Ranges and Network Device ConfigurationTamer Abu-ShraikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancient Egyptian Town Planning and ArchitectureDokument18 SeitenAncient Egyptian Town Planning and ArchitectureAlok VenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamVon EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BoQ GRP Pipe Contructor 20180918Dokument8 SeitenBoQ GRP Pipe Contructor 20180918Mohammad SyeduzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 1 Final 2012 Exam AnswersDokument65 SeitenCCNA 1 Final 2012 Exam Answerserzza storeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kad2253 Hydraulic and Hydrology: CHAPTER 4: MSMA-Roof and Property DrainageDokument14 SeitenKad2253 Hydraulic and Hydrology: CHAPTER 4: MSMA-Roof and Property DrainageMuhd Farhan Bin Ibrahim100% (1)
- CCNA Cisco Network Fundamentals FINAL Exam PDFDokument14 SeitenCCNA Cisco Network Fundamentals FINAL Exam PDFLâm Quỳnh100% (1)
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVon EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Hobas Jacking PipesDokument20 Seiten02 Hobas Jacking Pipesdliu88100% (1)
- Set 1Dokument14 SeitenSet 1Engr ZynaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam V4Dokument30 SeitenCCNA 1 Practice Final Exam V4miljkoyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Cisco Network Fundamentals FINAL ExamDokument14 SeitenCCNA Cisco Network Fundamentals FINAL Examsabriel69100% (2)
- Raspunsuri Practice FinalDokument16 SeitenRaspunsuri Practice FinalViorel SeriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 2Dokument8 SeitenFinal 2arunkumardixit2Noch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 1: Final Question Answer: Thursday, July 10, 2008Dokument6 SeitenCCNA 1: Final Question Answer: Thursday, July 10, 2008Engr ZynaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA1 Final Exam Answer 2016 v5Dokument68 SeitenCCNA1 Final Exam Answer 2016 v5Maurizio PorcuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ExamDokument18 SeitenFinal ExamgenericnamezipNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers - UPDATE 2012 - Eg.1Dokument16 SeitenCCNA 1 Final Exam Answers - UPDATE 2012 - Eg.1Dobre DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Cisco Network Fundamentals Final Exam-Practice (Ver 4.0)Dokument23 SeitenCCNA Cisco Network Fundamentals Final Exam-Practice (Ver 4.0)sabriel69100% (1)
- CCNA Exploration 1: Network Fundamentals v4.0 - Final Exam Answers - Full - 2013-2014Dokument53 SeitenCCNA Exploration 1: Network Fundamentals v4.0 - Final Exam Answers - Full - 2013-2014Jinesh AhamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final PDFDokument18 SeitenFinal PDFAaron PrzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Network Fundamentals Chapter 6 Exam AnswersDokument20 SeitenCCNA Network Fundamentals Chapter 6 Exam AnswersJhanineyen Trinidad0% (1)
- CCNA1var.2 100p 12Dokument7 SeitenCCNA1var.2 100p 12tibimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Which Three Addresses Belong To The Category of Private IP AddressesDokument20 SeitenWhich Three Addresses Belong To The Category of Private IP AddressesablacadablaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enetwork FinalDokument30 SeitenEnetwork FinalKalpish SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 1 Introduction To NetworksDokument7 SeitenCCNA 1 Introduction To NetworksCharles T RingiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna Answers by AbhishekkunalDokument23 SeitenCcna Answers by AbhishekkunalAbhishek KunalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna1-Final 2 v4.0Dokument18 SeitenCcna1-Final 2 v4.0rajnox100% (6)
- Ccna1 Final v2 Jun 2009 SharedDokument24 SeitenCcna1 Final v2 Jun 2009 SharedPaulo MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Câu Hỏi Hình Tra LờiDokument6 SeitenCâu Hỏi Hình Tra LờiphoanhdongnaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna 1 Final - WWW - MediafireDokument20 SeitenCcna 1 Final - WWW - MediafireAntónio MarquesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna-4-Final Exam-Full 100% PassDokument15 SeitenCcna-4-Final Exam-Full 100% PassChristan CalvaridoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Networking Academy Program - CCNA1 3.1.1 FINAL EXAM #2Dokument16 SeitenCisco Networking Academy Program - CCNA1 3.1.1 FINAL EXAM #2Issa kandji100% (2)
- The IETF Parameter Is Missing From The Frame-Relay Map Ip 10.10.10.1 201 CommandDokument8 SeitenThe IETF Parameter Is Missing From The Frame-Relay Map Ip 10.10.10.1 201 CommandJohn QuintalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2012-2013Dokument18 SeitenCCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2012-2013miljkoyu100% (1)
- CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2011Dokument24 SeitenCCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2011funnwburbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Practice Exam v5Dokument12 SeitenCCNA Practice Exam v5pukeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prctice Final Exam Ccna1Dokument24 SeitenPrctice Final Exam Ccna1Kristo RadionNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA1 v5 + v5.02 Final Exam Answers: LAN MAN WlanDokument37 SeitenCCNA1 v5 + v5.02 Final Exam Answers: LAN MAN WlanIon CaramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- แนวข้อสอบ CCNADokument20 Seitenแนวข้อสอบ CCNASiwinee BeeverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco CCNA1 Final Answered Oct 2009 100 PercentsDokument22 SeitenCisco CCNA1 Final Answered Oct 2009 100 PercentsDiego Mogrovejo NarváezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice 100Dokument19 SeitenPractice 100ask_gabyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Take Assessment - Enetwork Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals (VERSION 4.0) - ANSWERS - 2011 - 2012Dokument6 SeitenTake Assessment - Enetwork Final Exam - Ccna Exploration: Network Fundamentals (VERSION 4.0) - ANSWERS - 2011 - 2012Juan Jose TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal CcnaDokument22 SeitenSoal CcnaArifuddin AmalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam Answers 2014Dokument22 SeitenCCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam Answers 2014jonmicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Take Assessment - Enetwork Chapter 7 - Ccna Exploration 1: Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0)Dokument40 SeitenTake Assessment - Enetwork Chapter 7 - Ccna Exploration 1: Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0)Dobre DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Login access methods and router configuration questionsDokument6 SeitenLogin access methods and router configuration questionschennai11Noch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 1 Practice Final: The Use of All Four Pairs of Wires in Full-Duplex Mode, SimultaneouslyDokument7 SeitenCCNA 1 Practice Final: The Use of All Four Pairs of Wires in Full-Duplex Mode, Simultaneouslykam-s100% (1)
- CCNA 1 v5 Pratice Final ExamDokument29 SeitenCCNA 1 v5 Pratice Final ExamDago DagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet of Things: Architectures, Protocols and StandardsVon EverandInternet of Things: Architectures, Protocols and StandardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkVon EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manajemen Operasional PelayananDokument2 SeitenManajemen Operasional PelayananCintia NurliyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of SCM-Outlines PDFDokument3 SeitenHandbook of SCM-Outlines PDFCintia NurliyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Screening-PostedDokument16 SeitenConcept Screening-PostedCintia NurliyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BWP SB Supply Chain PlanningDokument4 SeitenBWP SB Supply Chain PlanningBASITH190988Noch keine Bewertungen
- We I Bull PlottingDokument18 SeitenWe I Bull PlottingCintia NurliyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of SCM-Outlines PDFDokument3 SeitenHandbook of SCM-Outlines PDFCintia NurliyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPTV FinalDokument5 SeitenIPTV Finalamassin chhaibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Speed Counter and TimerDokument34 SeitenHigh Speed Counter and TimerpaldopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bertrand Medioni: For The Degree Master of Science in Architecture Studies at The June, 1987Dokument86 SeitenBertrand Medioni: For The Degree Master of Science in Architecture Studies at The June, 1987Đào Duy TùngNoch keine Bewertungen
- NATA 2019 Question Paper With Answer KeyDokument21 SeitenNATA 2019 Question Paper With Answer KeyssnkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Look@LAN Setup LogDokument3 SeitenLook@LAN Setup LogAlexandre Canal SabariegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Silver BridgeDokument4 SeitenThe Silver BridgeMy SaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Processing Unit (The Brain of The Computer)Dokument36 SeitenCentral Processing Unit (The Brain of The Computer)gunashekar1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- JTC Space at Tampines North AdvertorialDokument1 SeiteJTC Space at Tampines North AdvertorialPraveen AmarasuriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACP SuperCorDokument16 SeitenACP SuperCorHaryo WidodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAN Physical Layer and Termination Guide - National InstrumentsDokument3 SeitenCAN Physical Layer and Termination Guide - National InstrumentsdubimouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Profile-23.8.19Dokument15 SeitenCompany Profile-23.8.19sushilmkNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPECS 50 Innstallation ManualDokument58 SeitenIPECS 50 Innstallation ManualpeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cablofil RussiaDokument15 SeitenCablofil RussiaSourav BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of Enterprise Applications-SaaSDokument17 SeitenEvolution of Enterprise Applications-SaaSMansi DhamijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVSystem Anjay BrochureDokument4 SeitenAVSystem Anjay BrochuresdlfkjldsfNoch keine Bewertungen
- BLD-ELEC Standard Data For Electrical Items In BuildingsDokument115 SeitenBLD-ELEC Standard Data For Electrical Items In BuildingsrokiahhassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 2 Layered ArchitectureDokument8 SeitenLec 2 Layered ArchitectureRana HeshamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typical BomDokument40 SeitenTypical BomVWSSI Technical TeamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Fractal Geometry and Applications in Architecture and Civil Engineering - Anton Vrdoljak & Kristina MileticDokument14 SeitenPrinciples of Fractal Geometry and Applications in Architecture and Civil Engineering - Anton Vrdoljak & Kristina MileticMAXO44Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Steel Inspection Report PDF FreeDokument2 SeitenStructural Steel Inspection Report PDF FreeAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ServletDokument620 SeitenServletChanaka PrasannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aurora Logger Install GuideDokument25 SeitenAurora Logger Install GuideAlejandro Pedraza GiraldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Rodi Domestico 2015 2016 Pt1Dokument112 SeitenCatalogo Rodi Domestico 2015 2016 Pt1Rosa Maria Asmar UrenaNoch keine Bewertungen