Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sample Assignment Analysis HSIB AZRB
Hochgeladen von
haznawiOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sample Assignment Analysis HSIB AZRB
Hochgeladen von
haznawiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sample of Good Assignment
FACULTY OF BUSINESS AND MANAGEMENT
JANUARI 2012 BBPW 3103 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT 1
SAMPLE
MATRICULATION NO IDENTITY CARD NO. TELEPHONE NO. E-MAIL LEARNING CENTRE : : : : :
Sample of Good Assignment
Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction ..................................................................................................................3 1.1 Company Background ................................................................................................3 1.1.1 Hup Seng Industries Bhd ............................................................................................3 1.1.2 Ahmad Zaki Resources Bhd .......................................................................................5 2.0 The Liquidity and Leverage Ratio Calculations .......................................................7 Hup Seng Industries Bhd .....................................................................................................9 Ahmad Zaki Resources Bhd ..............................................................................................11 3.0 The Analysis of Companies Financial Position .......................................................13 3.1 Detail Analysis of HSIB Liquidity and Leverage Ratio ..............................................15 3.2 Detail Analysis of AZRB Liquidity and Leverage Ratio.............................................20 4.0 The Differences of Companies Financial Position ..................................................25 5.0 Conclusion ..................................................................................................................27 APPENDIX .......................................................................................................................29 6.0 References ...................................................................................................................35
Sample of Good Assignment
1.0 Introduction One way to evaluating company financial position or performance is by calculating financial ratios. Ratios are simply relationships between two financial balances or financial calculations. These relationships establish for company references to manage and performing appropriately. Since the purpose of this assignment is to evaluate and analyze the liquidity and leverage position of Bursa Malaysia listed companies, Ive choose a company which involves in consumer product and construction sector. The names of the companies are Hup Seng Industries Bhd. and Ahmad Zaki Resources Bhd. The background and details are as explain below; 1.1 Company Background 1.1.1 Hup Seng Industries Bhd. The Hup Seng Industries Bhd. (HSIB) was incorporated on 04 October 1991 under Company Act 1965(Company No: 226098-P). The principal activities are manufacture and sales of biscuits and coffee mix, and dealers in biscuits, confectionery, and other foodstuff. HSIB are leading manufacture in consumer sector have been honour with numerous awards such as MS ISO 9002 Quality System Certification, MS ISO 9001:2000 Quality System Certification, HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points) and BRC (British Retail Consortium) Certification. Furthermore, the summary of company important information as stated in as stated in Table 1.0.
Elements Company Legal Address
Details Suite 6.1a Level 6, Menara Pelangi, Jalan Kuning, Taman Pelangi, Johor Bahru 80400 JOHOR DARUL TAKZIM
Type Incorporation Date Manufacture and Sales Financial Auditors
Public Limited Company 4 October 1991 Cream Crackers, Crackers, Marie Biscuits, Sandwiches, Cookies and Assorted Biscuits Ernst & Young (2011)
Sample of Good Assignment
Financial Information
Turnover, Profit After Tax And Net Earnings Per Share (Sen.) For The Year 2005 Until 2009.
Vision
To establish an integrity and profitable business for our customers, shareholders and suppliers.
Mission
Create products that signify good quality, service, & management for the benefits & pleasures of our customers. To build a range of products known for its competitive pricing. Build a brand one product at a time based on ISO 9002. Some of the product manufacture by HSIB:
Products
Sample of Good Assignment
1.1.2 Ahmad Zaki Resources Bhd. The Ahmad Zaki Resources Bhd. (AZRB) was incorporated on 26 May 1997 under Company Act 1965(Company No: 432768-X). The principal activities are contractors of civil and structural contract. At beginning, AZRB contracting job was landscaping works for a housing project owned by Terengganu State Economic Development Corporation in Kemaman, Terengganu. AZRB obtained licensing a Class 'A' contractor and now approximately 2 (two) Billion Ringgit worth of projects, consisting of various types of buildings and civil engineering works successfully completed. AZRB also have 3 overseas projects need complete in year 2015 such as in Chennai, India and two in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Furthermore, the summary of company important information as stated in as stated in Table 1.1.
Sample of Good Assignment
Elements Company Legal Address
Details 6 Jalan Bangsar Utama 9, Bangsar Utama, Kuala Lumpur, 59000 WILAYAH PERSEKUTUAN
Type Incorporation Date Manufacture and Sales Financial Auditors Financial Information
Non-Liability Limited Company 26 May 1997 Contractors Of Civil And Structural Contract
Moore Stephens AC (2010) Revenue,Shareholder Funds, Profit/(Loss) before Taxation and Net Tangible Assets Per Share for The Year 2005 Until 2009.
Vision
Trusted industry leader in delivering commitment with excellence and value.
Sample of Good Assignment
Mission
Smart partnership with customers, employees and stakeholders. Institutionalize the virtues of honesty and trust. Setting and maintaining high standards; striving for superior performance in all undertakings. Being pro-active through continuous research and development in meeting challenges.
Products
Some of the completed projects of AZRB:
Indoor Stadium, Kuala Terengganu
Mosque, Jalan Duta
2.0 The Liquidity and Leverage Ratio Calculations The calculation of liquidity and leverage financial ratio for Hup Seng Industries Bhd. (consumer) and Ahmad Zaki Resources Bhd. (construction) computed based on values taken from statement of Financial Position and statement of Comprehensive Income. The summary of HSIB and AZRB companies financial statement and income statement year 2005 until 2009 stated in Appendix 1.0. The detail workings and performance indicator result shows in Table 1.2 Hup Seng Industries Bhd. (consumer) and Table 1.3 Ahmad Zaki Resources Bhd. (construction). To measure companies liquidity and leverage level, calculated a few ratios as stated Chart 1.0 and Chart 1.1.
Sample of Good Assignment
Chart 1.0 Account Receivables Turnover Average Collection Period
Quick Ratio
Current Ratio
Net Working Capital
Liquidity
Inventory Turnover
Chart 1.1
Equity Multiplier
Debt to Equity Ratio
Debt Ratio Leverage
Interest Coverage Ratio
Sample of Good Assignment
Table 1.2 The Calculation of Liquidity and Leverage Ratio for Company Hup Seng Industries Bhd.
Sample of Good Assignment
Sample of Good Assignment
Table 1.3 The Calculation of Liquidity and Leverage Ratio for Company Ahmad Zaki Resources Bhd.
Sample of Good Assignment
Sample of Good Assignment
3.0 The Analysis of Companies Financial Position In order to measure those companies financial position, liquidity and leverage ratios are applied. Liquidity ratio determines ability companies to repay short-term creditors out of its total cash. The liquidity ratio is the result of dividing the total cash by short-term borrowings. It shows the number of times short-term liabilities are covered by cash. Apart from this, leverage ratio allows companies to increase the potential gains or losses on a position or investment beyond what would be possible through a direct investment of its own funds. The compliance summary liquidity and leverage ratio analysis for Hup Seng Industries Bhd. and Ahmad Zaki Resources Berhad. as stated in Table 1.4 and Table 1.5.
Sample of Good Assignment
Sample of Good Assignment
3.1 Detail Analysis of Hup Seng Industries Bhd. Liquidity and Leverage Ratios Graph 1.0 Net Working Capital Trend
70 60 50 RM (Mil) 40 30 20 10 0 Net Working Capital
2005 35.52
2006 37.97
2007 32.97
2008 43.47
2009 63.76
Graph above showing Net Working Capital and average RM42.74 million indicate HSIB higher than industry average (RM42, 700) for the year 2005 until 2009. The company able to settle its short-term debts and maintained or expand day-to-day operation.
Sample of Good Assignment
Graph 1.1 The Trend of Current, Quick, Account Receivables Turnover and Inventory Ratio
9 8 7 6 Times 5 4 3 2 1 0 Current Ratio Quick Ratio Account Receivables Turnover Inventory Turnover 2005 2.73 1.96 6.82 5.92 2006 2.31 1.54 6.94 7.92 2007 1.98 1.19 6.36 6.95 Year Current Ratio Quick Ratio Account Receivables Turnover Inventory Turnover 2008 1.99 1.32 7.39 6.3 2009 2.25 1.42 7.1 7.01
Based on the graph, HSIB decrease the current ratio for the past 5 years but still compliance with industry average. This shows that company short term assets have managed to meet their short term creditors and obligations. Besides, they also managed to achieve a good current ratio flow after year of 2008. In overall from year 2005-2009. Quick Ratio for HSIB was at highest in the year 2009 (at a ratio of 4.94) and they were at lowest in the year 2006 (at a ratio of 1.54). The company achieved a best positioning in the current year of 2009 as they were able to meet their short term obligations with their most liquid assets. In overall, the company maintained a good quick ratio with an average ratio of 1.49 from year 2005-2009 (industry average 1.43). the company maintained a good liquidity performance for current ratio with an average ratio of 2.25 achieved for the last 5 years
Sample of Good Assignment
Account Receivables Turnover for HSIB is unsatisfactory level compared the industry average which is less than 8.24 times. This may shows the company unable to manage credit collection in order to collect all the revenues. In overall, the company maintained a business inefficiency with an average ratio of 6.92 times from year 2005-2009. Inventory Turnover for HSIB maintained much better with average 6.82times (industry average 6.6 times) from year 2005-2009 which means company does not keep any surplus of inventory. Graph 1.2 The Trend of Average Collection Turnover
58 56 54 52 50 48 46 44 Average Collection Period
Days
2005 50.7
2006 48.71
2007 56.6
2008 51.87
2009 52.79
Average collection turnover for HSIB is unsatisfactory with average 52.13 days (industry average 44.3 days) which means company takes longer time to collect debts from their customers.
Sample of Good Assignment
Graph 1.3 The Trend of Equity Multiplier and Interest Coverage Ratio
60000
50000
40000 Times
30000
20000
10000
0 Equity Multiplier Interest Coverage Ratio
2005 1.33 63.21
2006 1.44 7972.44
2007 1.37 997.45 Year
2008 1.34 2987.04
2009 1.32 57098.07
Equity Multiplier
Interest Coverage Ratio
Average Equity Multiplier for HSIB is satisfactory with average 1.36 times (industry average less than1.67) from year 2005-2009. This shows that company assets via equity is higher compared other constructions companies. Interest coverage ratio for HSIB is satisfactory with average 13,823.64 times (industry average more than 4.3 times) from year 2005-2009. This shows company has higher ability to make interest payment regularly by using operation income.
Sample of Good Assignment
Graph 1.4 The Trend of Debt Ratio and Debt to Equity Ratio
35.00% 30.00% 25.00% Percentage (%) 20.00% 15.00% 10.00% 5.00% 0.00% Debt Ratio Debt to Equity Ratio
2005 25.62% 8.77%
2006 29.10% 8.57%
2007 27.02% 8.08% Year
2008 25.21% 7.28%
2009 24.30% 6.15%
Debt Ratio
Debt to Equity Ratio
Debt Ratio for HSIB is satisfactory with average 26.25 % (industry average less than 40%) from year 2005-2009. This means company able to settle off interest and principal loans. Debt to Equity Ratio for HSIB is satisfactory with average 7.77 % (industry average less than 50%) from year 2005-2009. This means companies not rely on long-term creditor supplied fund than owner supplied funds.
Sample of Good Assignment
3.2 Detail Analysis of Ahmad Zaki Resources Berhad. Liquidity and Leverage Ratios Graph 1.5 Net Working Capital Trend
200 180 160 140 RM (Mil) 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Net Working Capital 2005 136.1 2006 130.57 2007 153.22 2008 176.1 2009 108.39
Graph above showing Net Working Capital and average RM140.88 million indicate AZRB higher than industry average (RM42, 700) for the year 2005 until 2009. The company able to settle its short-term debts and maintained or expand day-to-day operation.
Sample of Good Assignment
Graph 1.6 The Trend of Current, Quick, Account Receivables Turnover and Inventory Ratio
50 45 40 35 30 Times 25 20 15 10 5 0 Current Ratio Quick Ratio Account Receivables Turnover Inventory Turnover 2005 1.7 1.62 7.1 12.86 2006 1.48 1.4 1.8 36 2007 1.42 1.37 1.82 36.54 Year Current Ratio Quick Ratio Account Receivables Turnover Inventory Turnover 2008 1.52 1.46 2.16 45.43 2009 1.28 1.23 1.44 32.61
Based on the graph, AZRB decrease the current ratio for the past 5 years and shows company not compliance with industry average (2.05> times). This shows that company short term assets not able to meet their short term creditors and obligations. In overall the company maintained a bad liquidity performance for current ratio with an average ratio of 1.48 times for the last 5 years from year 2005-2009. Quick Ratio for AZRB was at highest in the year 2005 (at a ratio of 1.62) and they were at lowest in the year 2009 (at a ratio of 1.23). The company not positioning good in the current year of 2009 as they were not able to meet their short term obligations with their most liquid assets. In overall, the company maintained a bad quick ratio with an average ratio of 1.41 from year 2005-2009 (industry average 1.43).
Sample of Good Assignment
Account Receivables Turnover for AZRB is unsatisfactory level compared the industry average which is less than 8.24 times. This may shows the company unable to manage credit collection in order to collect all the revenues. In overall, the company maintained a business inefficiency with an average ratio of 2.86 times from year 2005-2009. Inventory Turnover for AZRB maintained much better with average 32.69 times (industry average 6.6 times) from year 2005-2009 which means company does not keep any surplus of inventory. Graph 1.7 The Trend of Average Collection Turnover
300 250 200 Days 150 100 50 0 Average Collection Period
2005 50.7
2006 200
2007 198
2008 166
2009 250
Average collection turnover for AZRB is unsatisfactory with average 172.94 days (industry average 44.3 days) which means company takes longer time to collect debts from their customers.
Sample of Good Assignment
Graph 1.8 The Trend of Equity Multiplier and Interest Coverage Ratio
12
10
8 Times
0 Equity Multiplier Interest Coverage Ratio
2005 2.01 10.35
2006 2.37 8.7
2007 3.24 5.4 Year
2008 2.34 2.48
2009 2.1 2.25
Equity Multiplier
Interest Coverage Ratio
Average Equity Multiplier for AZRB is unsatisfactory with average 2.41 times (industry average less than1.67) from year 2005-2009. This shows that company assets via equity is lower compared other constructions companies. Interest coverage ratio for AZRB is satisfactory with average 5.84 times (industry average more than 4.3 times) from year 2005-2009. This shows company has higher ability to make interest payment regularly by using operation income.
Sample of Good Assignment
Graph 1.9 The Trend of Debt Ratio and Debt to Equity Ratio
120.00%
100.00%
80.00% Percentage (%)
60.00%
40.00%
20.00%
0.00% Debt Ratio Debt to Equity Ratio
2005 66.83% 44.19%
2006 70.33% 40.49%
2007 76.44% 77.15% Year
2008 70.00% 102.51%
2009 67.76% 46.45%
Debt Ratio
Debt to Equity Ratio
Debt Ratio for AZRB is satisfactory with average 70.26 % (industry average less than 40%) from year 2005-2009. This means company has difficulties to settle off interest and principal loans. Debt to Equity Ratio for AZRB is satisfactory with average 62.16 % (industry average less than 50%) from year 2005-2009. This means companies rely on long-term creditor supplied fund than owner supplied funds.
Sample of Good Assignment
4.0 The Differences of Companies Financial Position Based on Liquidity and Leverage Ratio Analysis Stated in Table 1.6. Comparison Elements Net Working Capital Hup Seng Industries Berhad (Consumer) Ahmad Zaki Resources Berhad. (Construction)
Comparison from 2005 until 2009 on Net Comparison from 2005 until 2009 on Net Working Capital shows significant Working Capital shows significant decreased increase around 44% throughout the year. around 25% throughout the year. This happen This happen when total current liabilities when total current liabilities keep on increased decrease and increased current assets. Conclusion: Consumer industries are stronger in cable of liquid assets that are available to sustain and build business by measuring your companys efficiency and short-term financial health. and total current assets remain the same.
Current Ratio There are 0.48 times increased on current There are 0.42 times decreased on current ratio ratio throughout year 2005 until 2009 throughout year 2005 until 2009 because the because the total current assets of company total current assets of company drop and total dramatically increased and makes total liabilities dramatically increased. liabilities drop. Conclusion: Consumer industries are positioning in ideal number of cash to be converted from current assets in order to pay debts that come due during every year. Quick Ratio There are 0.55 times increased on current There are 0.39 times decreased on current ratio ratio throughout year 2005 until 2009 throughout year 2005 until 2009 because the because company. Conclusion: Consumer industries and construction sector are in good positioning but the trend construction sector decreasing and afraid in future the firm would not be able to meet its current obligations. the total current assets of total liabilities dramatically increased.
Sample of Good Assignment
Account Receivables Turnover/ Average Collection Period
There are 0.28 times and 2.09 days There are 5.66 times and 199.30 days increased increased on Account Receivables on Account Receivables Turnover Ratio and Turnover Ratio and Average Collection Average Collection Period throughout the year Period throughout the year 2005 until 2005 until 2009. 2009. Conclusion: Both companies indicate having trouble collecting on sales it provided customers on credit. Construction sector have extremely have higher risk on revenue collection because the completion projects takes longer time to recognized actual sales.
Inventory Turnover
Inventory turnover drops 1.09 times from Inventory turnover increased 19.75 times from year 2005 until 2009. Conclusion: Construction sector indicates favorable and fastest inventory can be sold in a year comparing consumer industries. This situation happen because cost of goods sold higher than inventory in a company. year 2005 until 2009.
Debt Ratio
Debt Ratio drops 1.32% from year 2005 Debt Ratio increased 0.93% from year 2005 until 2009. Conclusion: Consumer industries most likely facing less debt because amount of liabilities are less compare construction sector debt ratio reach until 67.76 %( Industry Average 40%) and indicate higher risks. until 2009.
Debt To Equity Ratio
Debt to equity Ratio drops 2.62% from Debt Ratio increased 2.26% from year 2005 year 2005 until 2009. Conclusion: Consumer industries consider less satisfactory level because does not take efforts to expand Its sales and earnings even though company meets the requirement every year (2009 -6.19% industry average 50%). Construction satisfactory result because maintain debt on 46.45% and take a lot of efforts to expand their business. until 2009.
Sample of Good Assignment
Equity Multiplier
Equity Multiplier Ratio drops 0.01% from Equity Multiplier Ratio increased 0.09% from year 2005 until 2009. Conclusion: Construction sector relies more on debt to finance its assets and higher than the industry average compare consumer industries ideal figure throughout the year. year 2005 until 2009.
Interest Coverage Ratio
Interest 2009.
coverage
ratio
increased
to Interest coverage ratio decreased to 8.1 times
57,034.86 times from year 2005 until from year 2005 until 2009.
Conclusion: Consumer industries shows excellent result compared construction sector on ability to pay the interest charges on its debt. This happen when interest paying buy consumer industries lesser than construction sector.
5.0 Conclusion Based on the evaluation of consumer industry (Hup Seng Industries Bhd.) and construction sector (Ahmad Zaki Resources Bhd.) financial position, tells the actual condition of the company financial management. The analysis of liquidity and leverage ratio on two separate groups of companies indentify the satisfactory or unsatisfactory result in total performance. In order to measure the total performance of both companies for the year 2005 until 2009, percentage of marks scale used such as 0-50% (insufficient), 51-63% (sufficient), 64-79% (satisfactory), 8089% (Good), 90-100% (excellent). The calculation stated below: Hup Seng Liquidity Ratio Measurement Industries Leverage Ratio Measurement Bhd. (HSIB) Total Year 2005 -2009 Total Analysis Done (34/50 100%) 6 4 +
10 5 50
Total Performance Based on Satisfactory Result Average Industry 68%
Sample of Good Assignment
Ahmad Zaki Bhd. (AZRB)
Liquidity Ratio Measurement Leverage Ratio Measurement
6 4 +
Resources Total Year 2005 -2009 Total Analysis Done (18/50 100%)
10 5 50
Total Performance Based on Satisfactory Result Average Industry 36%
As a summary of total performance report, clearly shown HSIB satisfactory (68%) result and AZRB insufficient (36%) result. The percentage able to visualize the future, initiates changes and achieves the purpose of companies under highly dynamic conditions. HSIB has potential to grow much better to reach excellent status but AZRB must lessen the liability or borrowings and make collection period faster to reach excellent level. (2768 words)
Thank You Dear Sir/Madam for Allocate your Precious Time to Marking My Assignment
Sample of Good Assignment
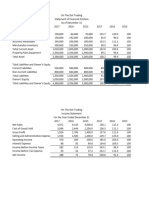
Appendix SUMMARY HUP SENG INDUSTRIES BHD. The Statement of Financial Position For The Year 2005 until 2009 2009 (RM) Non-Current Assets Property, Plant and Equipment Investment Properties Prepaid Payments Goodwill Deferred Tax Assets 66,074,493 1,865,671 4,959,874 13,227,508 483,543 86,611,089 Current Assets Inventories Trade and Other Receivables Tax Recoverable Cash and Bank Balances Total Assets Equity Attribute to Owners of Company: Share Capital Share Premium Other Reserves Retain Earnings Total Equity 60,000,000 14,333,133 2,621,865 64,706,562 141,661,560 60,000,000 14,333,133 741,468 50,691,989 60,000,000 14,333,133 796,374 39,076,700 60,000,000 14,333,133 42,983 40,889,315 115,265,431 60,000,000 14,333,133 42,983 38,402,464 112,778,580 23,418,474 32,727,914 2,153,919 42,219,598 100,519,905 187,130,994 20,282,491 33,504,972 1,688,218 21,224,792 76,700,473 21,438,292 26,970,184 1,342,882 15,634,694 65,386,052 22,004,531 31,972,951 1,157,978 21,222,356 76,357,816 165,901,179 20,013,925 28,411,531 549,268 14,950,315 63,925,039 149,474,452 70,653,265 1,882,526 5,085,565 13,227,508 610,170 91,459,034 70,283,151 1,899,726 4,651,831 13,227,508 1,050,966 91,113,182 69,163,153 1,915,808 3,803,261 13,227,508 1,433,633 89,543,363 65,487,549 1,935,186 3,910,102 13,227,508 983,068 85,549,413 2008 (RM) 2007 (RM) 2006 (RM) 2005 (RM)
168,159,507 156,499,234
125,766,590 114,206,207
Sample of Good Assignment
Non-Current Liabilities Deferred Tax Liabilities Current Liabilities Trade and Other Payables Tax Payable Borrowings Total Liabilities Total Equity and Liabilities 33,423,934 3,333,252 36,757,186 45,469,434 187,130,994 31,376,270 1,857,168 33,233,438 42,392,917 32,794,782 263,000 33,057,782 42,293,027 36,219,272 2,164,321 38,383,593 48,258,142 163,910,573 27,878,114 165,367 361,521 28,405,002 38,299,478 151,465,058 8,712,248 9,159,479 9,235,245 9,874,549 9,894,476
168,159,507 156,499,234
Sample of Good Assignment
SUMMARY HUP SENG INDUSTRIES BHD. The Statement of Comprehensive Income For The Year 2005 until 2009 2009 (RM) Revenue Cost of Sales Gross Profit Other Operating Income Selling and Marketing Expenses Administrative Expenses Operating Profit Finance Cost Profit before Tax Tax Expenses Profit for the Year Turnover (17,120,606) 35,800,492 (627) 35,799,865 (8,919,368) 26,880,497 213,405,000 (15,526,004) 21,348,342 (7,147) 21,341,195 (5,270,394) 16,070,801 220,329,000 (15,483,201) 6,131,309 (6,147) 6,125,162 (1,367,152) 4,758,010 193,115,000 (16,516,238) 9,965,555 (1,250) 9,964,305 (3,157,454) 6,806,851 188,338,000 (13,092,073) 7,603,386 (120,293) 7,483,093 (2,385,295) 5,097,798 180,968,000 213,405,132 74,674,219 1,866,323 (23,619,444) 2008 (RM) 220,329,264 59,495,444 1,883,155 (24,504,253) 2007 (RM) 193,115,141 44,061,976 1,572,200 (24,019,666) 2006 (RM) 188,338,321 49,616,354 1,384,413 (24,518,974) 2005 (RM) 180,967,603 40,718,525 1,650,768 (21,673,834)
(138,730,913) (160,833,820) (149,053,165) (138,721,967) (140,249,078)
Sample of Good Assignment
SUMMARY AHMAD ZAKI RESOURCES BERHAD The Statement of Financial Position For The Year 2005 until 2009 2009 (RM) Non-Current Assets Property, Plant and Equipment Prepaid Land Lease Payment Investment Properties Investment in Associated Company Investment in Joint Venture New Planting Expenditures Other Investment Deferred Tax Assets Goodwill 49,932,707 7,902,103 19,500,000 95,679,500 (28,637,206) 82,011,852 2,615,500 3,744,605 232,749,061 Current Assets Inventories Property Development Cost Trade Receivables Tax Assets Cash and Bank Balances Total Assets 12,045,447 1,459,535 319,274,486 4,268,175 152,619,459 489,667,102 722,416,163 12,927,339 5,831,594 306,258,522 3,931,817 185,642,625 514,591,897 721,144,257 12,142,953 2,531,332 289,351,747 2,514,749 207,990,592 514,531,373 689,961,887 10,521,722 1,784,567 246,063,818 737,035 145,004,720 404,111,862 469,108,800 15,513,481 1,642,492 156,200,474 2,850,925 154,096,042 330,303,414 372,261,303 48,408,426 8,242,056 19,500,000 89,784,333 (28,698,666) 62,956,106 2,615,500 3,744,605 206,552,360 41,644,699 8,582,009 25,000,000 84,762,385 (28,873,164) 31,954,480 8,615,500 3,744,605 175,430,514 37,748,620 10,017,557 24,550,000 59,875 (28,601,943) 12,862,724 4,615,500 3,744,605 64,996,938 35,418,056 24,200,000 63,120 (28,407,817) 2,293,598 4,615,500 30,827 3,744,605 41,957,889 2008 (RM) 2007 (RM) 2006 (RM) 2005 (RM)
Sample of Good Assignment
Equity Attribute to Owners of Company: Share Capital Reserves Treasury Shares Minority Shares Total Equity Non-Current Liabilities Other Borrowings Deferred Tax Liabilities Current Liabilities Trade Payables Other Borrowings Bank Overdrafts Tax Liabilities Total Liabilities Total Equity and Liabilities 279,892,669 83,895,648 16,696,378 795,281 489,485,402 722,416,163 288,922,481 37,723,565 9,865,602 2,006,458 505,148,352 721,144,257 300,207,725 53,039,168 3,497,348 4,568,845 527,405,911 689,961,887 254,826,555 12,640,669 3,687,933 2,382,075 329,927,268 469,108,800 185,382,323 2,916,026 5,361,355 552,322 248,776,662 372,261,303 103,931,069 4,274,357 108,205,426 161,476,632 5,153,614 166,630,246 161,001,406 5,091,419 166,092,825 51,350,526 5,039,510 56,390,036 50,582,645 3,981,991 54,564,636 138,317,965 90,497,764 (1,004,622) 5,119,654 232,930,761 138,265,800 74,073,128 (1,004,622) 4,661,599 215,995,905 69,132,900 89,819,619 3,603,457 162,555,976 66,710,400 69,710,468 2,760,664 139,181,532 66,710,400 54,249,887 2,524,354 123,484,641
Sample of Good Assignment
SUMMARY AHMAD ZAKI RESOURCES BERHAD The Statement of Comprehensive Income For The Year 2005 until 2009 2009 (RM) Operating Revenue Direct Operating Cost Gross Profit Other Operating Revenue Administrative Cost Other Operating Cost Profit from Operation Finance Cost Share of Joint Venture Share of Associated Company Profit before Tax Taxation 459,400,393 66,654,685 7,919,874 (30,702,170) (4,216,374) 39,656,010 (17,599,297) 1,481,090 8,952,617 32,490,420 (10,892,791) 2008 (RM) 662,676,939 75,356,838 7,427,952 (34,142,268) (9,299,426) 39,343,096 (15,833,047) 865,580 4,667,242 29,042,871 (12,596,576) 2007 (RM) 525,770,666 82,082,096 5,770,502 (32,183,205) (5,690,637) 49,978,756 (9,248,152) (271,221) 1,699,879 42,129,262 (14,991,475) 2006 (RM) 442,600,300 63,928,773 5,018,843 (22,609,156) (5,022,555) 41,315,905 (4,751,830) (194,126) (3,245) 36,366,704 (11,975,443) 2005 (RM) 249,124,615 49,602,202 4,012,515 (19,391,174) (2,471,975) 31,751,568 (3,067,938) (561,846) (3,899) 28,117,885 (9,249,362)
(392,745,708) (587,320,101) (443,688,570) (378,671,527) (199,522,413)
Profit for the Year
21,597,629
16,446,295
27,137,787
24,391,261
18,868,523
Sample of Good Assignment
6.0 References 1. Paramasivan, C. S. (2009). Financial Management. India: New Age International. 2. Ramagopal, C. (2008). Financial Management. India: New Age International. 3. Satyaprasad, B.G. Raghu, G.A. (2010). Advanced Financial Management. India: Global Media 4. Helfert, E. (2001). Financial Analysis Tools and Techniques. United States of America: McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing. 5. Jewell, J., & Mankin, J. (2009). Standardizing financial statement analysis across the business curriculum: An interdisciplinary approach. Allied Academies International Conference. Academy of Educational Leadership. Proceedings, 14(2), 15-19. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/192405168?accountid=48462 6. Hup Seng Industries Bhd. (2012). The Company Annual Report. [ONLINE]. Available:
http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com/HUPSENG-AnnualReport2010.pdf http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com/HUPSENG-AnnualReport2009.pdf http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com/HUPSENG-AnnualReport2008.pdf http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com/HUPSENG-AnnualReport2007.pdf http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com/HUPSENG-AnnualReport2006.pdf http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com/HUPSENG-AnnualReport2005.pdf
7. Ahmad Zaki Resources Bhd. (2012). The Company Annual Report. [ONLINE]. Available:
http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com /AZRB-AnnualReport2010.pdf http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com /AZRB-AnnualReport2009.pdf http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com /AZRB-AnnualReport2008.pdf http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com /AZRB-AnnualReport2007.pdf http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com /AZRB-AnnualReport2006.pdf http://announcements.bursamalaysia.com /AZRB-AnnualReport2005.pdf
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PESTEL Analysis AssignmentDokument4 SeitenPESTEL Analysis AssignmentLeza smithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement 31 December 2014Dokument52 SeitenFinancial Statement 31 December 2014Riyas KalpettaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlmaraiDokument4 SeitenAlmaraiShruthiJangitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Operations IssuesDokument20 SeitenStrategic Operations IssuesMichael YuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINANCIAL ANALYSIS FOR MANAGERSDokument40 SeitenFINANCIAL ANALYSIS FOR MANAGERSSumant KhetanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.5.3 Zenith Bank PLC HistoryDokument3 Seiten2.5.3 Zenith Bank PLC HistoryOyeleye TofunmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internship Saudi Pak Investment CompanyDokument39 SeitenInternship Saudi Pak Investment Companyikhan5100% (2)
- Assignment ECGDokument13 SeitenAssignment ECGsaitteyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Management Assignement On Green Supply ChainDokument10 SeitenSupply Chain Management Assignement On Green Supply ChainL-a DerricksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Analysis For Eastman KodakDokument4 SeitenFinancial Analysis For Eastman KodakJacquelyn AlegriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Analysis in Mergers AcquisitionsDokument27 SeitenFinancial Analysis in Mergers AcquisitionsJas KainthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Corporate Responsibility in The Wider Business EnvironmentDokument2 SeitenManaging Corporate Responsibility in The Wider Business EnvironmentUnknwn NouwnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On Mercantile Bank Limited, Dhaka, Bangladesh.Dokument6 SeitenAssignment On Mercantile Bank Limited, Dhaka, Bangladesh.নিশীথিনী কুহুরানীNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 UK Corporate Governance Code FINAL PDFDokument20 Seiten2018 UK Corporate Governance Code FINAL PDFMichał TomczykNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abbott Financial Report Analysis 2012Dokument85 SeitenAbbott Financial Report Analysis 2012Muhammad Zubair50% (2)
- BSc Business Administration Integrating ManagementDokument1 SeiteBSc Business Administration Integrating ManagementShaikh Ghassan AbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet MarketingDokument5 SeitenInternet MarketingAssignmentLab.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Management in Health Servic PDFDokument7 SeitenSupply Chain Management in Health Servic PDFSa Be MirNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF A VALID CONTRACTDokument21 SeitenESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF A VALID CONTRACTMegha NadhNoch keine Bewertungen
- #@$ Finance Investing The Islamic Way Verdell WalkerDokument194 Seiten#@$ Finance Investing The Islamic Way Verdell WalkerIcas PhilsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Drivers ObstaclesDokument22 SeitenSupply Chain Drivers ObstaclesRikudo Akyoshi0% (1)
- Human Resource Management - AssignmentDokument16 SeitenHuman Resource Management - AssignmentLazy FrogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership AssignmentDokument12 SeitenLeadership AssignmentFoad AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Report - International Marketing: Institute of Management Technology Nagpur Trimester V / PGDM (2008-10) / IMDokument6 SeitenFinal Report - International Marketing: Institute of Management Technology Nagpur Trimester V / PGDM (2008-10) / IMHemant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics Assign Mba 9Dokument34 SeitenEconomics Assign Mba 9Dickson MdhlaloseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On AccountingDokument5 SeitenAssignment On AccountingRodney ProcopioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leading in Organisations: Chapter SummaryDokument24 SeitenLeading in Organisations: Chapter SummaryMD FAISALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avari Towers, Fatima Jinnah Road, Karachi 75530, Pakistan Uan: +92-21-5660100 - Fax: +92-21-5680310 Uan: +92-21-111-Avaris (282747)Dokument44 SeitenAvari Towers, Fatima Jinnah Road, Karachi 75530, Pakistan Uan: +92-21-5660100 - Fax: +92-21-5680310 Uan: +92-21-111-Avaris (282747)ocean519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Management of Print MediaDokument39 SeitenSupply Chain Management of Print MediaHector MoodyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enterprise SystemsDokument11 SeitenEnterprise SystemsumairaleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medd's Cafe - Group Assignment DraftDokument20 SeitenMedd's Cafe - Group Assignment DraftB UNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Summer Training Project Report On Country ClubDokument64 SeitenA Summer Training Project Report On Country ClubPrabhakar GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Supply Chain Management Assignment 1Dokument6 SeitenInternational Supply Chain Management Assignment 1Mudit GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations Management b2bDokument23 SeitenOperations Management b2bmsulgadleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment: Strategic Financial ManagementDokument7 SeitenAssignment: Strategic Financial ManagementVinod BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dutch Lady Malaysia's History and Organizational StructureDokument10 SeitenDutch Lady Malaysia's History and Organizational StructureKah Weii100% (1)
- H&M: The Challenges of Global Expansion and The Move To Adopt International Financial Reporting StandardsDokument6 SeitenH&M: The Challenges of Global Expansion and The Move To Adopt International Financial Reporting StandardsSami KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coca-Cola's BCG MatrixDokument28 SeitenCoca-Cola's BCG MatrixDhairya Parekh100% (1)
- Assesment 1strategic Financial Management R1812D7073086Dokument17 SeitenAssesment 1strategic Financial Management R1812D7073086Oluwadare AkinyeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Supply Chain Management True/False & Multiple ChoiceDokument11 SeitenChapter 1 Supply Chain Management True/False & Multiple ChoicePunit Tilani100% (1)
- Organizational Structures Used by UK Supermarkets PDFDokument10 SeitenOrganizational Structures Used by UK Supermarkets PDFIbrahim IrshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limitations of Balance SheetDokument6 SeitenLimitations of Balance Sheetshoms_007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Services: Key Concepts and ClassificationsDokument9 SeitenManagement of Services: Key Concepts and ClassificationsPRABHUDEVANoch keine Bewertungen
- CBCS Guidelines For B.comh Sem VI Paper No - BCH 6.1 Auditing and Corporate GovernanceDokument2 SeitenCBCS Guidelines For B.comh Sem VI Paper No - BCH 6.1 Auditing and Corporate GovernanceJoel DinicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventory Management in Supply ChainDokument11 SeitenInventory Management in Supply Chainparadise AngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation and Supply Chain ManagementDokument22 SeitenOperation and Supply Chain ManagementTyrone WaltersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kedai Rakyat 1Malaysia: Low-Cost Grocery InitiativeDokument12 SeitenKedai Rakyat 1Malaysia: Low-Cost Grocery InitiativeJamilah EdwardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rainforest Seafoods Supply Chain ExcellenceDokument18 SeitenRainforest Seafoods Supply Chain ExcellenceNordia BarrettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ob Final AssignmentDokument38 SeitenOb Final AssignmentmenonshyaminiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CorporateFraudinNigeria ATwo CaseStudyDokument10 SeitenCorporateFraudinNigeria ATwo CaseStudyonyekachukwu0% (1)
- Financial Analysis of A CompanyDokument10 SeitenFinancial Analysis of A CompanyRupesh PuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Performance AppraisalDokument7 SeitenA Study On Performance AppraisalMohanreddy AllamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Porter's Five Forces ModelDokument3 SeitenPorter's Five Forces ModelDokte Baulu Bangkit100% (1)
- Organisations and Leadership during Covid-19: Studies using Systems Leadership TheoryVon EverandOrganisations and Leadership during Covid-19: Studies using Systems Leadership TheoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Improvement Districts: An Introduction to 3 P CitizenshipVon EverandBusiness Improvement Districts: An Introduction to 3 P CitizenshipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Value Chain Management Capability A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandValue Chain Management Capability A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human in Human ResourceVon EverandThe Human in Human ResourceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simplex Example 3.3Dokument4 SeitenSimplex Example 3.3haznawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODI VAM methods transportation problems tutorialDokument10 SeitenMODI VAM methods transportation problems tutorialVivek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAW CasesDokument21 SeitenLAW CaseshaznawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPM Problem - Critical Path Method Questions AnsweredDokument2 SeitenCPM Problem - Critical Path Method Questions Answeredhaznawi100% (2)
- KFC Marketing Plan For PakistanDokument26 SeitenKFC Marketing Plan For PakistanReader100% (4)
- CPM Problem - Critical Path Method Questions AnsweredDokument2 SeitenCPM Problem - Critical Path Method Questions Answeredhaznawi100% (2)
- Project Plan: Critical Path Method: STEP 1: Identify The Logic NetworkDokument5 SeitenProject Plan: Critical Path Method: STEP 1: Identify The Logic Networkhaznawi100% (1)
- Asgmt StatistikDokument4 SeitenAsgmt StatistikhaznawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20111004120509sample Answer EBTQ3103Dokument8 Seiten20111004120509sample Answer EBTQ3103haznawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Make Me A M'sia1Dokument10 SeitenWhat Make Me A M'sia1haznawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PWC Loyalty Analytics ExposedDokument13 SeitenPWC Loyalty Analytics ExposedUmang GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HAND OUT No. 3 FABM The Accounting EquationDokument9 SeitenHAND OUT No. 3 FABM The Accounting Equationnatalie clyde matesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Earnings ChecklistDokument7 SeitenQuality Earnings ChecklistKevin SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Office and BranchDokument9 SeitenHome Office and BranchLive LoveNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1989 NY Poultry Farm Business SummaryDokument30 Seiten1989 NY Poultry Farm Business SummarysuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCAOB Auditing Standards Chapter 5Dokument35 SeitenPCAOB Auditing Standards Chapter 5Daniel John Cañares Legaspi100% (1)
- BADM 2001 - Fall 2019 - Assignment 3Dokument2 SeitenBADM 2001 - Fall 2019 - Assignment 3Vanessa M. EzzatNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1Dokument85 SeitenCH 1EmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tipton Ice Cream Financial ForecastingDokument10 SeitenTipton Ice Cream Financial ForecastingFD ReynosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Reaction and Valuation of IFRS Reconciliation Adjustments First Evidence From The UK by Joanne Horton and George SerafeimDokument55 SeitenMarket Reaction and Valuation of IFRS Reconciliation Adjustments First Evidence From The UK by Joanne Horton and George SerafeimAlexandra NarcisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studi Kelayakan Investasi Pada Proyek Peningkatan JalanDokument18 SeitenStudi Kelayakan Investasi Pada Proyek Peningkatan JalanIrma MartaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biwheels Excel SheetDokument18 SeitenBiwheels Excel SheetSREEDIP GHOSHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring and Reporting Cash FlowDokument11 SeitenMeasuring and Reporting Cash Flowtom willetsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trend AnalysisDokument1 SeiteTrend Analysisangel caoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intangible Assets & Impairments of AssetsDokument72 SeitenIntangible Assets & Impairments of AssetsMuthia Khairani100% (2)
- Mega Quiz File Mgt101Dokument199 SeitenMega Quiz File Mgt101Azhar NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Informe Anual CECA Cuentas Consolidadas 2019 - EngDokument181 SeitenInforme Anual CECA Cuentas Consolidadas 2019 - Engjosecente123321Noch keine Bewertungen
- Water StationDokument14 SeitenWater StationPrincess TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement Analysis TechniquesDokument51 SeitenFinancial Statement Analysis TechniquesSumit Rp100% (4)
- Chapter 1 Financial AccountingDokument47 SeitenChapter 1 Financial Accountingslipns1ideNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21.understanding Retail ViabilityDokument23 Seiten21.understanding Retail ViabilitySai Abhishek TataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kebijakan Modal Kerja Dalam Keuangan Syariah.Dokument11 SeitenKebijakan Modal Kerja Dalam Keuangan Syariah.shivakarlina273Noch keine Bewertungen
- ACCA Dec 2011 F7 Mock PaperDokument10 SeitenACCA Dec 2011 F7 Mock PaperCharles AdontengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Accounting Final ExamDokument4 SeitenManagement Accounting Final Examacctg2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Standards ChartsDokument26 SeitenAccounting Standards ChartsEdu 4 AllNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Training Report Final 1Dokument65 SeitenSummer Training Report Final 1Nipun ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Analysis - Molycorp, Inc. Produces Rare Earth Minerals. the Company Produces Rare Earth Products, Including Oxides, Metals, Alloys and Magnets for a Variety of Applications Including Clean Energy TechnologiesDokument8 SeitenFinancial Analysis - Molycorp, Inc. Produces Rare Earth Minerals. the Company Produces Rare Earth Products, Including Oxides, Metals, Alloys and Magnets for a Variety of Applications Including Clean Energy TechnologiesQ.M.S Advisors LLCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation of Project Cash Flows: Centre For Financial Management, BangaloreDokument14 SeitenEstimation of Project Cash Flows: Centre For Financial Management, BangaloreNic KnightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maini - Blueprint - Fi - 100 - Main Document - Ver - 3.0 PDFDokument69 SeitenMaini - Blueprint - Fi - 100 - Main Document - Ver - 3.0 PDFBhaskarChakraborty0% (2)
- Ifrs Edition: Prepared by Coby Harmon University of California, Santa Barbara Westmont CollegeDokument56 SeitenIfrs Edition: Prepared by Coby Harmon University of California, Santa Barbara Westmont Collegemartinus linggoNoch keine Bewertungen