Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Torsion constant calculation methods
Hochgeladen von
Hossam T BadranOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Torsion constant calculation methods
Hochgeladen von
Hossam T BadranCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
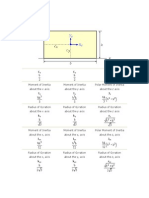
Torsion constant
Torsion constant
The torsion constant is a geometrical property of a beam's cross-section which is involved in the relationship between angle of twist and applied torque along the axis of the bar, for a homogeneous linear-elastic bar. That is, the torsion constant describes a beam's torsional stiffness.
History
In 1820, the French engineer A. Duleau derived analytically that the torsion constant of a beam is identical to the second moment of area normal to the section Jzz, which has an exact analytic equation, by assuming that a plane section before twisting remains plane after twisting, and a diameter remains a straight line. Unfortunately, that assumption is correct only in beams with circular cross-sections, and is incorrect for any other shape.[1] For non-circular cross-sections, there are no exact analytical equations for finding the torsion constant. However approximate solutions have been found for many shapes. Non-circular cross-section always have warping deformations that require numerical methods to allow the exact calculation of the torsion constant.[2]
Partial Derivation
For a beam of uniform cross-section along its length:
where is the angle of twist in radians T is the applied torque L is the beam length J is the 2nd Polar Moment of Area G is the Modulus of rigidity (shear modulus) of the material
Torsion constant
Examples for specific uniform cross-sectional shapes
Circle
[3]
where r is the radius This is identical to the second moment of area Jzz and is exact. alternatively write: D is the Diameter s
[3]
where
Ellipse
[4][5]
where a is the major radius b is the minor radius
Square
[6]
where 2a is the side length
Rectangle
where a is the length of the long side b is the length of the short side is found from the following table:
a/b 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 0.141 0.196 0.229 0.249 0.263 0.281 0.291 0.299
10.0 0.312
Torsion constant
3
0.333
[7]
Alternatively the following equation can be used with an error of not greater than 4%:
[4]
Thin walled closed tube of uniform thickness
[8]
A is the mean of the areas enclosed by the inner and outer boundaries t is the wall thickness U is the length of the median boundary
Thin walled open tube of uniform thickness
[9]
t is the wall thickness U is the length of the median boundary (perimeter of median cross section)
Circular thin walled open tube of uniform thickness
This is a tube with a slit cut longitudinally through its wall.
[8]
t is the wall thickness r is the mean radius This is derived from the above equation for an arbitrary thin walled open tube of uniform thickness.
Commercial Products
There are a number specialized software tools to calculate the torsion constant using the finite element method. ShapeDesigner [10] by Mechatools Technologies [11] ShapeBuilder [12] by IES Web [13] STAAD SectionWizard [14] by Bentley [15] SectionAnalyzer [16] by Fornamagic Ltd [17] Strand7 BXS Generator [18] by Strand7 Pty Limited [19]
Torsion constant
References
[1] Archie Higdon et al. "Mechanics of Materials, 4th edition". [2] Advanced structural mechanics, 2nd Edition, David Johnson [3] "Area Moment of Inertia." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http:/ / mathworld. wolfram. com/ AreaMomentofInertia. html [4] Roark's Formulas for stress & Strain, 7th Edition, Warren C. Young & Richard G. Budynas [5] Continuum Mechanics, Fridtjov Irjens, Springer 2008, p238, ISBN 978-3-540-74297-5 [6] Torsion Equations, Roy Beardmore, http:/ / www. roymech. co. uk/ Useful_Tables/ Torsion/ Torsion. html [7] Advanced Strength and Applied Elasticity, Ugural & Fenster, Elsevier, ISBN 0-444-00160-3 [8] Roark's Formulas for stress & Strain, 6th Edition, Warren C. Young [9] Advanced Mechanics of Materials, Boresi, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 0-471-55157-0 [10] http:/ / www. mechatools. com/ en/ shapedesigner. html [11] http:/ / www. mechatools. com [12] http:/ / www. iesweb. com/ products/ shapebuilder/ index. htm [13] http:/ / www. iesweb. com [14] http:/ / www. bentley. com/ en-US/ Products/ STAAD. Pro/ Section-wizard. htm [15] http:/ / www. bentley. com [16] http:/ / fornamagic. com/ download. php?view. 15 [17] http:/ / www. fornamagic. com [18] http:/ / strand7. com [19] http:/ / www. strand7. com
Article Sources and Contributors
Article Sources and Contributors
Torsion constant Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?oldid=563815380 Contributors: Bassplr19, BenFrantzDale, Bradv, Closedmouth, Davius, GTi16V, Greglocock, Kallog, Lockley, RockMagnetist, Suffusion of Yellow, The wub, Zerodamage, 58 anonymous edits
Image Sources, Licenses and Contributors
File:TorsionConstantBar.svg Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:TorsionConstantBar.svg License: Creative Commons Attribution-Sharealike 3.0 Contributors: TorsionConstantBar.png: Kallog (talk). derivative work: Zerodamage
License
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported //creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Tubular Profiles For Telecom Structures PDFDokument8 SeitenTubular Profiles For Telecom Structures PDFJitendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timber Purlin ChecksDokument1 SeiteTimber Purlin ChecksNeil SonNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEPOC 150dpiDokument6 SeitenSTEPOC 150dpinick8081Noch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Steel Roof DesignDokument31 Seiten03 Steel Roof DesignvarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- HCF PDFDokument68 SeitenHCF PDFSushmit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- StaircaseDokument9 SeitenStaircaseNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handrail StandardsDokument4 SeitenHandrail StandardsSachin SithikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Platipus Anchors - Sheet Pile Tieback Specifications and Submittal Package PDFDokument13 SeitenPlatipus Anchors - Sheet Pile Tieback Specifications and Submittal Package PDFDIEGO TUNARROSANoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Dissertation Structure GuideDokument0 SeitenMaster Dissertation Structure Guideess_kayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combined Footing Design Guide with ExamplesDokument2 SeitenCombined Footing Design Guide with ExamplesNick GeneseNoch keine Bewertungen
- RC Stair Design (EN1992)Dokument7 SeitenRC Stair Design (EN1992)Win ThanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branz Advisory Trower PartitionsDokument6 SeitenBranz Advisory Trower PartitionsMatt Stubbins100% (1)
- UB5 Steel Beam Analysis & Design (BS5950Dokument4 SeitenUB5 Steel Beam Analysis & Design (BS5950yambalaoingjrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Calculations Fully FramelessDokument13 SeitenStructural Calculations Fully FramelessasdasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Wind Load Procedures ASCE 7 05 PDFDokument13 Seiten2 Wind Load Procedures ASCE 7 05 PDFLeah AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Calculations For Metal Structure and Fence Legalization PlansDokument34 SeitenStructural Calculations For Metal Structure and Fence Legalization PlansAlejandro MorelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4Dokument55 Seiten4ManishaCharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometrical Properties Material Properties: Design of Helicoidal StairDokument5 SeitenGeometrical Properties Material Properties: Design of Helicoidal StairPrashant Verma100% (1)
- Two Way Slab Design SpreadsheetDokument4 SeitenTwo Way Slab Design SpreadsheetLikhon Biswas0% (1)
- Design and Analysis of Seismic Resistant Apartment BuildingDokument12 SeitenDesign and Analysis of Seismic Resistant Apartment BuildingMunzuara AktherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 - ExamplesDokument15 SeitenTopic 1 - ExamplesnurulselangorNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS-5950-90 Example 001Dokument7 SeitenBS-5950-90 Example 001Maribel Isaura Cunurana YapuchuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Steel Structures BS 5950: Eng. Chamara Yapa Arachchi Civil EngineerDokument60 SeitenDesign of Steel Structures BS 5950: Eng. Chamara Yapa Arachchi Civil Engineerpareen9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vertical Loads On Building Frames: Assumptions For The Analysis of Girders Using Approximate AnalysisDokument10 SeitenVertical Loads On Building Frames: Assumptions For The Analysis of Girders Using Approximate AnalysisNeven Ahmed HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opening in Slab and BeamDokument13 SeitenOpening in Slab and BeamYohan LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temporary StructuresDokument65 SeitenTemporary StructuresnisfibolahenkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Design and Analysis Proposed Three Storey Commercial ResidenceDokument79 SeitenStructural Design and Analysis Proposed Three Storey Commercial ResidenceGEREMY SANTIAGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Columns in Multi-Storey FramesDokument4 SeitenDesign of Columns in Multi-Storey FramesXet FatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fink TrussDokument4 SeitenFink TrussJommel GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASI Design Guide 10 - Bolted Moment End Plate Beam Splice Connections 21Dokument1 SeiteASI Design Guide 10 - Bolted Moment End Plate Beam Splice Connections 21Anonymous 0x2pwMCWgjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Steel BeamDokument19 SeitenDesign of Steel BeamAnonymous tBhJoH5wgMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project PDFDokument36 SeitenProject PDFMable MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culvert Design (1-Barrel 1x1.5m)Dokument7 SeitenCulvert Design (1-Barrel 1x1.5m)Waqas AnjumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Today: Proceedings: Mohan Sai Gaddam, Aravindan AchuthanDokument5 SeitenMaterials Today: Proceedings: Mohan Sai Gaddam, Aravindan AchuthanAshutosh BorageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab With and Without OpeningDokument17 SeitenSlab With and Without Openingstructure123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structure Engineer CertificateDokument1 SeiteStructure Engineer CertificateSantosh100% (2)
- Design Guidelines For Timber Ceiling Structures With Asbestos Cement Sheets or Light Timber Planks by Prof. S.R. de S. Chandrakeerthy 2005Dokument8 SeitenDesign Guidelines For Timber Ceiling Structures With Asbestos Cement Sheets or Light Timber Planks by Prof. S.R. de S. Chandrakeerthy 2005ishanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PF2Dokument4 SeitenPF2nhulugallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bondek I - Calculation Note - 1 Row of SupportDokument7 SeitenBondek I - Calculation Note - 1 Row of Supporttrung1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- ASCE7-10 Wind Load CalculationDokument17 SeitenASCE7-10 Wind Load Calculationhala94Noch keine Bewertungen
- RCC Beam With Different Choice of Design WSD For Singly & Doubly ReinforcementDokument5 SeitenRCC Beam With Different Choice of Design WSD For Singly & Doubly ReinforcementdsanandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cop On Access For External Maintenance 2021Dokument34 SeitenCop On Access For External Maintenance 2021Ck ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masonry Reinforcement Product SelectorDokument8 SeitenMasonry Reinforcement Product Selectorkakarock79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spiral StaircaseDokument48 SeitenSpiral StaircaseUbani Obinna RanksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toaz - Info Design Calculation Skylight Structure PRDokument7 SeitenToaz - Info Design Calculation Skylight Structure PRAbdul khaliquNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purlin DESIGNDokument10 SeitenPurlin DESIGNMohamed NkNoch keine Bewertungen
- A184 PDFDokument3 SeitenA184 PDFluisNoch keine Bewertungen
- GF SlabDokument8 SeitenGF Slabcheligp1981Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Example of Reinforce Concrete BeamsDokument60 SeitenDesign Example of Reinforce Concrete BeamsMario FrankistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WIND LOAD CALCULATION FOR FLAT ROOF BUILDINGDokument5 SeitenWIND LOAD CALCULATION FOR FLAT ROOF BUILDINGAboalmaail AlaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prayer Room & Guard Room Structure With CalculationDokument42 SeitenPrayer Room & Guard Room Structure With CalculationNazrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectangular Water Tank DesignDokument61 SeitenRectangular Water Tank DesignChinkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Level Enrollment InformationDokument2 SeitenA-Level Enrollment InformationTalitha Cumi MatamboNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS6399:Part2:1995 Code of Practice for Wind LoadsDokument14 SeitenBS6399:Part2:1995 Code of Practice for Wind LoadsAreeb Ahmed100% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Design Manual IntroductionDokument7 SeitenReinforced Concrete Design Manual IntroductionLim Wee BengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Lanka National Annex Euro Code1Dokument26 SeitenSri Lanka National Annex Euro Code1Sahan100% (1)
- W-Sections Metric UnitsDokument13 SeitenW-Sections Metric UnitskennethcyinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Actions SummaryDokument7 SeitenWind Actions Summaryliam daviesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Flexure and Shear Design of Corbel (Bracket)Dokument12 SeitenThe Flexure and Shear Design of Corbel (Bracket)Girum MindayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Vibration of Cracked BeamDokument12 SeitenFree Vibration of Cracked BeamMaheswaran MuthaiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helicopter SlidesDokument133 SeitenHelicopter SlidesRyan Nguyễn100% (3)
- Modern Helicopter AerodynamicsDokument53 SeitenModern Helicopter AerodynamicsAulia®100% (1)
- Analysis of Composite Laminate Beams Using Coupling Cross-Section Finite Element MethodDokument10 SeitenAnalysis of Composite Laminate Beams Using Coupling Cross-Section Finite Element MethodHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- NR - Numerical Model of Single Main Rotor Helicopter DynamicsDokument10 SeitenNR - Numerical Model of Single Main Rotor Helicopter DynamicsHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flutter of Subsonic WingDokument11 SeitenFlutter of Subsonic WingmamalilariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vortex Lattice MethodDokument4 SeitenVortex Lattice MethodHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To MATLAB - Lesson2Dokument19 SeitenAn Introduction To MATLAB - Lesson2Lava SatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Flutter Control of A Smart FinDokument12 SeitenActive Flutter Control of A Smart FinHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 789882013062467849649Dokument12 Seiten789882013062467849649Hossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Vibration of Cracked BeamDokument12 SeitenFree Vibration of Cracked BeamMaheswaran MuthaiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Conceptual Design of Joined-WingDokument62 SeitenIntegrated Conceptual Design of Joined-WingHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonlinear Systems 2Dokument14 SeitenNonlinear Systems 2Jérôme KyabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- DerivativesDokument32 SeitenDerivativesHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 08Dokument39 SeitenChapter 08Nimra_Jalali_9220Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 08Dokument39 SeitenChapter 08Nimra_Jalali_9220Noch keine Bewertungen
- WIKI Lifting-Line TheoryDokument8 SeitenWIKI Lifting-Line TheoryHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- AOE 5104 Assignment 6 Solution: GroundDokument7 SeitenAOE 5104 Assignment 6 Solution: GroundHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 789882013062467849649Dokument12 Seiten789882013062467849649Hossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech BeamDokument31 SeitenMech BeamHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Frequencies of RotatingDokument8 SeitenNatural Frequencies of RotatingHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB programs for aeroelastic flutter and controlDokument8 SeitenMATLAB programs for aeroelastic flutter and controlcrimelife6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration of Continuous SystemsDokument21 SeitenVibration of Continuous SystemsHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explicit Frequency Equation and Mode Shapes of A Cantilever Beam Coupled in Bending and Torsion PDFDokument15 SeitenExplicit Frequency Equation and Mode Shapes of A Cantilever Beam Coupled in Bending and Torsion PDFHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surfaces - User Manual - Vortex Lattice ModuleDokument136 SeitenSurfaces - User Manual - Vortex Lattice ModulehkhouaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bending Induced StressesDokument33 SeitenBending Induced StressesHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area Moment of InertiaDokument10 SeitenArea Moment of InertiaHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical and Continuum Analysis2 - ContinuousDokument30 SeitenNumerical and Continuum Analysis2 - ContinuousHossam T BadranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aeromatrix MethodsDokument24 SeitenAeromatrix MethodsManoj ManoharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torsional PropertiesDokument19 SeitenTorsional PropertiesAndrés Felipe HernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phytochemical and antioxidant potential of Martynia annua fruit oilDokument7 SeitenPhytochemical and antioxidant potential of Martynia annua fruit oilRam SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe ForgeDokument6 SeitenPipe ForgePierre799esNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Planner - Chemistry PDF OnlyDokument1 SeiteLecture Planner - Chemistry PDF OnlyJai ChandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shear Friction MattockDokument10 SeitenShear Friction MattockSisina Anish100% (1)
- Amines PDFDokument1 SeiteAmines PDF최승원Noch keine Bewertungen
- QCMDokument2 SeitenQCMmanish_keswani01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clean Light-Colored Bricks SafelyDokument1 SeiteClean Light-Colored Bricks SafelymutazsalihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quinine Hydrochloride 0018eDokument2 SeitenQuinine Hydrochloride 0018eMark GoldbergNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Mössbauer Spectroscopy To Study Reaction Products of Polyphenols and Iron CompoundsDokument11 SeitenUse of Mössbauer Spectroscopy To Study Reaction Products of Polyphenols and Iron CompoundsOmar MorteoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardsurfacing HandbookDokument24 SeitenHardsurfacing HandbookscribdphinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRC and Pro-Seal: Aerospace Sealants Application GuideDokument4 SeitenPRC and Pro-Seal: Aerospace Sealants Application GuidefloreiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 1Dokument14 SeitenLab Report 1Amirah100% (1)
- Steerable AntennaDokument44 SeitenSteerable AntennaKenNediaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility of Titanium Dioxide in Cosmetic FormulationsDokument10 SeitenSolubility of Titanium Dioxide in Cosmetic FormulationsMeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sulfur and Nirogen IndustriesDokument58 SeitenSulfur and Nirogen IndustriesSarah SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Herramientas CaterpillarDokument112 SeitenCatalogo Herramientas CaterpillarJorge Perez100% (2)
- LL0220AA Linear Low Density Polyethylene Film PropertiesDokument1 SeiteLL0220AA Linear Low Density Polyethylene Film PropertiesXuân Giang NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrate Planck's Function Using Gamma FunctionDokument14 SeitenIntegrate Planck's Function Using Gamma FunctionMaxtron Evelyn MoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAILMA Steel Grades & SheetsDokument2 SeitenSAILMA Steel Grades & SheetsElumalai SrinivasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RaceDokument3 SeitenRaceapi-3769525100% (5)
- Ans No. 4-Conservation of Mass Equation-: + Known As Continuity EquationDokument4 SeitenAns No. 4-Conservation of Mass Equation-: + Known As Continuity EquationHimanshu TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- D Block ElementDokument48 SeitenD Block ElementPrabhakar BandaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equal Percentage Control Valves and Applications - Control NotesDokument6 SeitenEqual Percentage Control Valves and Applications - Control NotesShubham PisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Physics 2023-2025 ATP TipsDokument7 SeitenO Level Physics 2023-2025 ATP TipsAmy WolmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1400 10MDokument5 Seiten1400 10MAngelia WileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Studies in Boiler FailuresDokument14 SeitenCase Studies in Boiler Failuresparthi2006576880% (5)
- Underground Pipe Stress Check CalculationsDokument6 SeitenUnderground Pipe Stress Check Calculationsani_datNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors of Safety for Cuttings in Normally Consolidated ClaysDokument5 SeitenFactors of Safety for Cuttings in Normally Consolidated ClaysAnonymous GnfGTwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternative-Refrigerants R22 GBDokument12 SeitenAlternative-Refrigerants R22 GBMon PerezNoch keine Bewertungen