Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Automatic Alarm System (Lifting Air Detector)
Hochgeladen von
rmaffireschoolOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Automatic Alarm System (Lifting Air Detector)
Hochgeladen von
rmaffireschoolCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
FT 39 AUTOMATIC ALARM SYS
AUTOMATIC FIRE DETECTORS
(Lifting Air Detector)
OBJECTIVE 1. To explain the fundamentals of lifting air detectors their function and operation.
REFERENCE 2. a. b. Manual of Fireman ship Book 9. Fire College Notes.
CONTENTS
3.
Modern Development of Detectors: a. Lifting Air Detectors.
Combined Heat and Smoke Detector 4. A laser produces a beam light which does not spread out. It travels throughout its path as a narrow pencil beam. Special gallium arsenide lamps produce a suitable beam for fire detection purposes although not a proper laser beam. 5. The detector projects a light beam across the detected space just below the ceiling. It is then reflected back by a corner cube mirror on to a suitable photo-electric cell. A fire below the beam produces air turbulence which causes the reflected beam to dance and produce an alternating current output from the PE cell. Certain output frequencies can be identified as being caused by a fire situation and the alarm is caused to sound. 6. Smoke reduces the light falling on the PE cell and this also can be caused to sound the alarm. 7. It has now been found possible to employ the same detection technique without using a laser beam or a corner cube reflector. The Beam Master detector produced by Chubb uses an infra-red beam to sense both the absorption effect of smoke and air turbulence produced by a fire.
229
8.
Detectors Using Thermo-electric Effects: a. Thermo-Electric Voltage Detector.
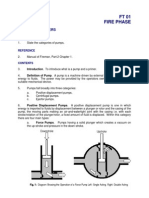
If two metals are joined and alternate junctions are maintained at different temperature electric pressure is generated. This can be used to operate an alarm system when a particular temperature is reached. b. Resistance/Temperature Detector. When a metallic conductor is heated its resistance increases. By means of a wheatstone bridge circuit this resistance change can be used to operate an alarm. The principle employed is similar to that used in a gas detector. A bridge circuit is shown in Fig. Thermostats are semi-conducting circuit elements whose resistance changes quickly once a particular temperature has been reached. These can be used like ordinary resistors to operate an alarm system. c. Electrical Line Detectors.
The insulation of the wiring used may be made to serve as a heat detector. This may be achieved by either: (1) Using insulation which melts at a specific temperature causing a short which operates the alarm. (2) Using insulation whose resistance capacitance or inductance varies with temperature leading to an alarm being sounded. d. Tagushi Type. Certain special materials have an electrical resistance varies with specific stimuli for instance a temperature change, light or heat radiation. Such materials are called semi-conductors.
230
e. One such semi-conductor responds to the oxygen content. Any situation which affects this content will cause a resistance change. The presence of a flammable atmosphere will reduce this oxygen content and by connecting the Tagushi detectors are less reliable than the catalysis type but can be very much cheaper. Their tack of reliability arises from the fact that smoke or steam may cause a reduction in the oxygen content and therefore excite a response. f. Particular situation in which a gas detector could have application are mines, flammable gas and liquid storage areas, mobile home and for the protection of engine rooms in ships and similar installations where ventilation may be restricted.
231
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Automatic Alarm System (Detector Circuit)Dokument3 SeitenAutomatic Alarm System (Detector Circuit)rmaffireschool100% (1)
- Fix Installation (Foam)Dokument4 SeitenFix Installation (Foam)rmaffireschool100% (1)
- Automatic Alarm System (Beam Master)Dokument26 SeitenAutomatic Alarm System (Beam Master)rmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Alarm System (Design Principle)Dokument6 SeitenAutomatic Alarm System (Design Principle)rmaffireschool100% (2)
- Automatic Alarm System (Heat Detector)Dokument7 SeitenAutomatic Alarm System (Heat Detector)rmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hosereel SystemDokument5 SeitenHosereel Systemrmaffireschool100% (3)
- Fix Installation (CO2)Dokument10 SeitenFix Installation (CO2)rmaffireschool100% (1)
- Means of Escape Part IIDokument6 SeitenMeans of Escape Part IIrmaffireschool100% (2)
- Fix Installation (Dry Chemical Powder)Dokument5 SeitenFix Installation (Dry Chemical Powder)rmaffireschool100% (1)
- Rising MainDokument3 SeitenRising Mainrmaffireschool100% (3)
- Automatic Sprinkler (Drenchers)Dokument2 SeitenAutomatic Sprinkler (Drenchers)rmaffireschool89% (9)
- Automatic Sprinkler (Control, Gauges & Alarms)Dokument6 SeitenAutomatic Sprinkler (Control, Gauges & Alarms)rmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatik Sprinkler (Sprinkler Head)Dokument5 SeitenAutomatik Sprinkler (Sprinkler Head)rmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Sprinkler (Water Supply & Hazards)Dokument7 SeitenAutomatic Sprinkler (Water Supply & Hazards)rmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Sprinkler (Types)Dokument8 SeitenAutomatic Sprinkler (Types)rmaffireschool100% (1)
- Means of Escape Part IVDokument6 SeitenMeans of Escape Part IVrmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic SprinklerDokument3 SeitenAutomatic SprinklerrmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire ResistanceDokument5 SeitenFire Resistancermaffireschool100% (1)
- Runway Vacuum Sweeperr Ak 445Dokument9 SeitenRunway Vacuum Sweeperr Ak 445rmaffireschool100% (1)
- Means of Escape Part 1Dokument1 SeiteMeans of Escape Part 1rmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Foam Making EquipmentsDokument10 SeitenMechanical Foam Making EquipmentsrmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire PumpsDokument14 SeitenFire Pumpsrmaffireschool100% (4)
- Primary Foam Tender (PFT)Dokument7 SeitenPrimary Foam Tender (PFT)rmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building ConstructionDokument6 SeitenBuilding ConstructionrmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- CME Model RIT 3500 SATDokument6 SeitenCME Model RIT 3500 SATrmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump & PrimerDokument16 SeitenPump & Primerrmaffireschool100% (12)
- Hose Binding MachineDokument2 SeitenHose Binding MachinermaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fafa Hydrostatic PumpDokument1 SeiteFafa Hydrostatic PumprmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poseidon High Pressure Compressor (P 135)Dokument5 SeitenPoseidon High Pressure Compressor (P 135)rmaffireschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting ProceduresDokument6 SeitenAircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting Proceduresrmaffireschool86% (7)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- ASSH Company - ProfileDokument33 SeitenASSH Company - ProfileOmar FarukNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS7240V2 User GuideDokument64 SeitenDS7240V2 User GuideVasile MesesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ficha-EN R001 SIGA-OSD Intelligent Photoelectric Smoke Detector Installation SheetDokument2 SeitenFicha-EN R001 SIGA-OSD Intelligent Photoelectric Smoke Detector Installation SheetYin VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 08Dokument112 SeitenModule 08eshet chafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elevator Operation Rescue SOPProposed 1Dokument6 SeitenElevator Operation Rescue SOPProposed 1vhlactaotaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 054581ATG0 Fire Alarm Product Catalog 2017Dokument247 Seiten054581ATG0 Fire Alarm Product Catalog 2017yunusbarkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC5020 V3.1 - Manual Instalare PDFDokument53 SeitenPC5020 V3.1 - Manual Instalare PDFDarie SilviuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft PowerPoint - 2015 IRC IBC IEBC Update ABM SV 2Dokument40 SeitenMicrosoft PowerPoint - 2015 IRC IBC IEBC Update ABM SV 2Abhishek ChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silent Knight Beam Spec IntelliknightDokument2 SeitenSilent Knight Beam Spec Intelliknightmatt12manyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSC Pc4020cfsp ManualDokument58 SeitenDSC Pc4020cfsp ManualGreta BonthuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Basis For Fire Fighting SystemDokument10 SeitenDesign Basis For Fire Fighting Systemsripriya01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crisis Management - Sample CPP Exam QuestionsDokument82 SeitenCrisis Management - Sample CPP Exam Questionskaleem ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Packet Tracer in Learning Wireless Networks and PDFDokument4 SeitenThe Role of Packet Tracer in Learning Wireless Networks and PDFReza AdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Risk AssessmentDokument13 SeitenFire Risk Assessmentteuku zulfikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7th Sem ProjectDokument12 Seiten7th Sem ProjectAyash KatangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BC8002+ Operating ManualDokument44 SeitenBC8002+ Operating Manualarmand isakhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maxsys PC4020 V3.5 - Manual Instalare PDFDokument80 SeitenMaxsys PC4020 V3.5 - Manual Instalare PDFDarie SilviuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Al Fall Protection Program For Adults NFPADokument34 SeitenFire Al Fall Protection Program For Adults NFPAjulio_92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thrust Ventilation System Description: Novenco Car ParkDokument16 SeitenThrust Ventilation System Description: Novenco Car ParkOtelea StefanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pearl of Scandinavia Fire Report-AFFDokument6 SeitenPearl of Scandinavia Fire Report-AFFsimNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT-2052 SD Series Photoelectric Smoke DetectorsDokument2 SeitenCAT-2052 SD Series Photoelectric Smoke DetectorsJonathan EscobedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installation Instructions Model HZM: Remote Conventional Zone ModuleDokument6 SeitenInstallation Instructions Model HZM: Remote Conventional Zone ModuleGabriel BarrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tyco DatasheetDokument4 SeitenTyco DatasheetPCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fsi 851 PDFDokument2 SeitenFsi 851 PDFPARIETALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Inspection For 102 Pindar CrescentDokument57 SeitenHome Inspection For 102 Pindar CrescentStacy MurphyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Division 8. Places of Assembly: Requiremen T FdasDokument10 SeitenDivision 8. Places of Assembly: Requiremen T FdasEli NaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Alarm Control Panel SFP-2402 & SFP-2404 SFP-2402E & SFP-2404E ManualDokument56 SeitenFire Alarm Control Panel SFP-2402 & SFP-2404 SFP-2402E & SFP-2404E Manualeka suputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- QCS 2014 - Section 23-Fire Fighting and Fire Alarm SystemsDokument61 SeitenQCS 2014 - Section 23-Fire Fighting and Fire Alarm SystemsEng. JamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dop6001 PDFDokument14 SeitenDop6001 PDFLORIUNEANoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam1224 Beam1224s Datasheet Bmds755Dokument2 SeitenBeam1224 Beam1224s Datasheet Bmds755KVSureshkumarNoch keine Bewertungen