Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chap 4 Bio
Hochgeladen von
Sper BacenaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chap 4 Bio
Hochgeladen von
Sper BacenaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cell - smallest unit of life, has plasma membrane, has cytoplasm and DNA.
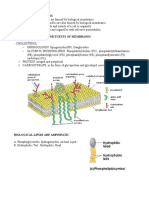
Traits common to all cells 1. Plasma membrane - separates its contents from the environment. - selectively permeable - consist mainly of lipids. 2. Cytoplasm - mixture of water, sugars, ions, and proteins. -Where cell metabolism occur. 3. Organelles - found in the Cytoplasm. - carry out specific metabolic processes in the cell. 4. Nucleus (eukaryotic cells) - where DNA is found Constraints on Cell Size -surface to volume ratio Cell Theory Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek -invented the first microscope. -coined "animalcules" -coined "cellae" for tiny compartments on sliced cork Robert Brown - identified cell nucleus Matthias Schleiden -plant cells are independent living unit even when being apart from the plant itself. Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann -animal and plant cells are composed of cells and their products. -cell have a life of their own even when apart from the cell. Robert Hooke - cells come from division of preexisting cells. Cell Theory (first articulated by Schleiden and Schwann) 1. Every living organism consists of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the structural and functional unit of all organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life, individually alive even as a part of a multicelled organism. 3. All living cells come from division of preexisting cells. 4. Cells contain hereditary material, which they pass to their offspring during division. MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Phospholipids lipid bilayer - structural foundation of cell membranes; double layer of lipids arranged tail to tail.
fluid mosaic - model of a cell membrane as a two dimensional fluid of mixed composition (lipids and proteins). MEMBRANE PROTEINS 1. Adhesion protein - membrane protein that helps cells stick together in tissues. e.g. Integrins, cadherins 2. Recognition protein - Plasma membrane protein that identifies a cell as belonging to self (one's own body). e.g. MHC molecules 3. Receptor protein - Plasma membrane protein that binds to a particular substance outside of the cell. e.g. Insulin receptor, B cell receptor 4. Transport protein - Protein that passively or actively assists specific ions or molecule across a membrane. a) Passive transporters - allows ions or small molecules to cross a membrane to the side of less concentration e.g. Porins, glucose transporter b) Active transporters - pump ions or molecule through membranes to the side where they are more concentrated. Require energy input, as from ATP. e.g. Calcium pump, serotonin transporter 5.Enzyme - speeds a specific reaction. e.g. Cytochrome c oxydase of mitochondria. BACTERIA AND ARCHAEANS ribosome - organelle of protein synthesis (polypeptides). plasmid - small circle of DNA in some bacteria and archaeans. nucleoid - region of cytoplasm where the DNA is concentrated inside a bacterium or archaean. flagellum - long, slender cellular structure used for motility. pilus - a protein filament that projects from the surface of some bacterial cells. cell wall - semirigid but permeable structure that surrounds the plasma membrane of some cells. biofilm - community of microorganisms living within a shared mass of slime. EUKARYOTIC CELLS Organelles with membranes Nucleus - protecting and controlling access to DNA. Endoplasmic Reticulum - routing, modifying new polypeptide chains, synthesizing lipids. Golgi Body - modifying new polypeptide chains, sorting, shipping proteins and lipids. Vesicles - transporting, storing, or digesting substances in a cell. Mitochondrion - making ATP by glucose breakdown.
Chloroplast - making sugars into plants, some protists. Lysosome - intracellular digestion. Peroxisome - inactivating toxins. Vacuole - storage ORGANELLES WITHOUT MEMBRANES Ribosomes - assembling polypeptide chains Centriole - anchor for cytoskeleton OTHER COMPONENTS Cytoskeleton - contributes to cell shape, internal organization, and movement. THE NUCLEUS nuclear envelope a double membrane that constitutes the outer boundary of the nucleus. nucleoplasm viscous fluid enclosed by the nuclear envelope. nucleolus in the cell nucleus, a dense, irregularly shaped region where ribosomal subunits are assembled. THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM - series of interacting organelles between the nucles and the plasma membrane. Endoplasmic reticulum organelle that is a continuous system of sacs and tubes; extension of the nuclear envelope. Rough ER is studded with ribosomes; smooth ER is not. vesicle small, membrane-enclosed, saclike organelle; different kinds store, transport, or degrade their contents. vacuole a fluid-filled organelle that isolates or disposes of waste, debris, or toxic materials. central vacuole fluid-filled vesicle in many plant cells. lysosome enzyme-filled vesicle that functions in intracellular digestion. peroxisome enzyme-filled vesicle that breaks down amino acids, fatty acids, and toxic substances. Goldgi body organelle that modifies polypeptides and lipids; also sorts and packages the finished products into vesicles.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 4 Significance of The Events IndustryDokument12 SeitenChapter 4 Significance of The Events IndustrySper BacenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pointers For Prelims Mt13110Dokument1 SeitePointers For Prelims Mt13110Sper BacenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrient-Rich Avocado GuideDokument8 SeitenNutrient-Rich Avocado GuideSper BacenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cursive Practice A ZDokument26 SeitenCursive Practice A Zavabhyankar9393Noch keine Bewertungen
- Locomotor and NonlocomotorDokument1 SeiteLocomotor and NonlocomotorSper BacenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masao Takahashi and Family. Mastering Judo PDFDokument225 SeitenMasao Takahashi and Family. Mastering Judo PDFMario Bertoluci100% (3)
- Willyoustillloveme PDFDokument2 SeitenWillyoustillloveme PDFSper BacenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Locomotor and NonlocomotorDokument1 SeiteLocomotor and NonlocomotorSper BacenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO1 DNA, cells, organismsDokument1 SeiteBIO1 DNA, cells, organismsSper BacenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmbryologyDokument4 SeitenEmbryologySper BacenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Sim BiomoleculesDokument18 SeitenSim BiomoleculesJose Mari100% (5)
- Ebook Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7Th Edition Karp Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDokument68 SeitenEbook Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7Th Edition Karp Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDavidLeekemt100% (11)
- Protien ASDokument25 SeitenProtien ASRabia RafiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIT Biophysics Undergrad 2015Dokument1 SeiteMIT Biophysics Undergrad 2015Kadir OzcanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Crystallography AhmadhDokument12 SeitenAssignment Crystallography AhmadhAhmadhAzharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of the Plasma Membrane and Fluid Mosaic ModelDokument19 SeitenFunctions of the Plasma Membrane and Fluid Mosaic ModelKrystin DiamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7 KeyDokument4 SeitenCH 7 KeyJa'mia100% (1)
- Crystalline Structures AssignmentDokument6 SeitenCrystalline Structures AssignmentNouman1203Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quaternary StructureDokument19 SeitenQuaternary StructureChiku MteghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 08 LipidDokument10 SeitenChapter 08 Lipid楊畯凱Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Two, The Structure of Crystalline Solids PDFDokument23 SeitenChapter Two, The Structure of Crystalline Solids PDFOmar Abu MahfouthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qdoc - Tips Biology Project On Immunity For Class 12thDokument25 SeitenQdoc - Tips Biology Project On Immunity For Class 12thPadma VsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bche 111 Chemistry For Engineers - Lets Analyze - 1538 - Dominic John D. AmbidDokument3 SeitenBche 111 Chemistry For Engineers - Lets Analyze - 1538 - Dominic John D. AmbidDominic John AmbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipid Movement BiochemDokument9 SeitenLipid Movement BiochemCrowNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPLEMENT SYSTEM NoteDokument6 SeitenCOMPLEMENT SYSTEM NoteKaren AgbaegbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membrane Transport Practice QuestionsDokument2 SeitenMembrane Transport Practice QuestionsLogan ParkisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science SHS 8.1 ProteinsDokument21 SeitenPhysical Science SHS 8.1 ProteinsjouselleduayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane and Transport ColoringDokument3 SeitenCell Membrane and Transport ColoringTeresa GonzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio NoteDokument5 SeitenBio NoteErikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ion Channels as Drug TargetsDokument71 SeitenIon Channels as Drug TargetsQonita NitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 006 Animal-Immune-SystemDokument13 SeitenWeek 006 Animal-Immune-SystemMark Lorens StaanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nelson Biology Answers 1Dokument2 SeitenNelson Biology Answers 1ritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helix Coil TheoryDokument13 SeitenHelix Coil TheoryJaime Sarmiento ZegarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Leukocyte Antigens: Dr. B.Vijayasree 1 Year Post-Graduate Department of MicrobiologyDokument30 SeitenHuman Leukocyte Antigens: Dr. B.Vijayasree 1 Year Post-Graduate Department of Microbiologyvijayasree bavireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Crystal StructureDokument32 SeitenOn Crystal StructureDeathEaterReturnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicotine Spectra IRDokument8 SeitenNicotine Spectra IRYohanNugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action Potential - The Resting Membrane Potential - Generation of Action Potentials - TeachMePhysiologAyDokument4 SeitenAction Potential - The Resting Membrane Potential - Generation of Action Potentials - TeachMePhysiologAymohammed awolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Klaus - Juergen Schleifer LectureDokument20 SeitenKlaus - Juergen Schleifer Lectureapi-3787547Noch keine Bewertungen
- VASP Workshop Band Structure Lecture NotesDokument15 SeitenVASP Workshop Band Structure Lecture Notesabhinav jangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 PHAR0004 9 7 ReceptorStructure NSM 2018 NotesDokument3 Seiten2 PHAR0004 9 7 ReceptorStructure NSM 2018 NotesArthi ArumukasamyNoch keine Bewertungen