Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
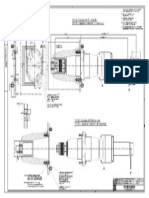
Current Transformer
Hochgeladen von
renjithas2005Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Current Transformer
Hochgeladen von
renjithas2005Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
current transformer an instrument transformer in which the secondary current, in normal conditions of use, is substantially proportional to the primary
current and differs in phase from it by an angle which is approximately zero for an appropriate direction of the connections bushing type current transformer a current transformer without primary conductor and primary insulation of its own which can be fitted directly over an insulated bushing or conductor bus type current transformer a current transformer without primary conductor, but with primary insulation, which can be fitted directly over a conductor or busbar cable type current transformer a current transformer without primary conductor and primary insulation of its own, which can be mounted over an insulated cable split core type current transformer a current transformer without primary conductor, and primary insulation of its own, the magnetic circuit of which can be hinged open (or otherwise separated into two parts) and then closed around the insulated conductor carrying the current to be measured bar primary type current transformer a transformer in which the primary conductor is made up of a bar or a set of bars in parallel bar primary bushing type current transformer a current transformer so constructed that it can be used as a bushing support type current transformer a current transformer so arranged that it acts as a support for the conductor in the primary circuit wound primary type current transformer a current transformer in which the primary winding consists of a single or multiturn coil fully insulated current transformer a current transformer having as an integral part of its construction, insulation suitable for its rated insulation level extended rating type current transformer a current transformer having a rated continuous thermal current higher than rated primary current and for which accuracy requirements are prescribed at that current single-core type current transformer a current transformer in which only one magnetic core with one secondary winding and one primary winding are provided
multi-core type current transformer a current transformer comprising a number of magnetically separated cores with individual secondary windings and a common primary winding compound-wound current transformer a current transformer having an auxiliary winding with an independent supply especially intended to reduce the phase displacement between the primary and secondary currents auto-compound current transformer a current transformer having an auxiliary winding in series with the secondary of the transformer, especially intended to reduce the phase displacement between the primary and secondary currents summation current transformer a transformer for the measurement of the sum of the instantaneous values of currents having the same frequency within a power system current matching transformer a current transformer for matching the rated secondary current of the main current transformer to the rated current of the burden, or for reducing the instrument security factor measuring current transformer a current transformer intended to transmit an information signal to measuring instruments and meters protective current transformer a current transformer intended to transmit an information signal to protective and control devices NOTE The accuracy class of a protective current transformer is designated by its class index followed by the letter P (standing for "Protection"). The class index gives the limit of the absolute value of composite error at the rated accuracy limit primary current for the class concerned, as a percentage of this current. residual current the sum of the instantaneous values of all three line currents, in a three-phase system residual current transformer a single, or a group of three, current transformer(s) so connected as to transform only the residual current rated short time thermal current the maximum value of the primary current which a transformer will withstand for a specified short time without suffering harmful effects, the secondary winding being short-circuited extended rating current the highest value of the primary current, expressed as a percentage of primary rated current, at which an extended rating type current transformer complies with the temperature rise and accuracy requirements
rated dynamic current the maximum peak value of the primary current which a transformer will withstand without being damaged electrically or mechanically by the resulting electromagnetic forces, the secondary winding being short-circuited rated continuous thermal current the value of the current which can be permitted to flow continuously in the primary winding, the secondary winding being connected to the rated burden, without the temperature rise exceeding the values specified composite error under steady-state conditions, the r.m.s. value of the difference between: a) the instantaneous values of the primary current, and b) the instantaneous values of the actual secondary current multiplied by the rated transformation ratio, the positive signs of the primary and secondary currents corresponding to the convention for terminal markings NOTE The composite error is generally expressed as a percentage of the r.m.s. value of the primary current. rated instrument limit primary current (IPL) the value of the minimum primary current at which the composite error of the measuring current transformer is equal to or greater than 10%, the secondary burden being equal to the rated burden instrument security factor (FS) the ratio of rated instrument limit primary current to the rated primary current rated accuracy limit primary current (of a protective current transformer) the value of primary current up to which the current transformer will comply with the requirements for composite error accuracy limit factor (of a protective current transformer) the ratio of the rated accuracy limit primary current to the rated primary current secondary limiting e.m.f. the product of the instrument security factor, the rated secondary current and the vectorial sum of the rated burden and the impedance of the secondary winding exciting current the r.m.s. value of the current taken by the secondary winding of a current transformer, when a sinusoidal voltage of rated frequency is applied to the secondary terminals, the primary and any other windings being opencircuited
internal burden (of a current transformer) the impedance of the secondary winding knee point voltage the r.m.s. value of the sinusoidal voltage at rated frequency applied to the secondary terminals of the transformer, all other windings being open circuited, which when increased by 10% causes the r.m.s. value of the exciting current to increase by 50% turns correction a design feature of a current transformer in which the turns ratio differs from the rated transformation ratio
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Automotive Controls Algorithm Engineer 1Dokument3 SeitenAutomotive Controls Algorithm Engineer 1renjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Control Systems EngineerDokument1 SeiteControl Systems Engineerrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Central Maintenance SupervisorDokument2 SeitenCentral Maintenance Supervisorrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Central Maintenance SupervisorDokument2 SeitenCentral Maintenance Supervisorrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Education:: Date Posted Location Country Degree Required Job Type Min Experience Position Id Job DescriptionDokument2 SeitenEducation:: Date Posted Location Country Degree Required Job Type Min Experience Position Id Job Descriptionrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial Electricians NeededDokument1 SeiteCommercial Electricians Neededrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Factory Test Procedure For AccessoriesDokument7 SeitenFactory Test Procedure For Accessoriesrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Class Stationary Engineer OperationDokument2 Seiten2nd Class Stationary Engineer Operationrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Apprentice Electrician - Required Immediately!: Job Order #: 5159923Dokument1 SeiteApprentice Electrician - Required Immediately!: Job Order #: 5159923renjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Power System Protection and CoordinationDokument54 SeitenFundamentals of Power System Protection and Coordinationrenjithas2005100% (1)
- Saskatchewan: Toddler/Preschool Social ResumeDokument3 SeitenSaskatchewan: Toddler/Preschool Social Resumerenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short CT Calc ForCu Tube 1000 SQ MM Cable JointDokument1 SeiteShort CT Calc ForCu Tube 1000 SQ MM Cable Jointrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Apprentice ElectricianDokument2 SeitenApprentice Electricianrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- FAT For 132 KV Accesories MTSBDokument7 SeitenFAT For 132 KV Accesories MTSBrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- 05 - 4 - 00 - SIE - 18 - 4038 Install Inst Outdoor S EndDokument21 Seiten05 - 4 - 00 - SIE - 18 - 4038 Install Inst Outdoor S Endrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- DTS - 1924 - 170906 - 2 PageDokument2 SeitenDTS - 1924 - 170906 - 2 Pagerenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- CONSORTIUM - GTC/5/2004: Sie-Gtc5/Dts/ Document Transmittal SheetDokument1 SeiteCONSORTIUM - GTC/5/2004: Sie-Gtc5/Dts/ Document Transmittal Sheetrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5051 Inst Instr HV-Bushings.E GR 5sDokument2 Seiten5051 Inst Instr HV-Bushings.E GR 5srenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3039 Type Test 66 KV 500sqmm Rev1 20060913Dokument8 Seiten3039 Type Test 66 KV 500sqmm Rev1 20060913renjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clarification To DTA 1062 Dated 21 Aug 2006Dokument2 SeitenClarification To DTA 1062 Dated 21 Aug 2006renjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short CT Calc ForCu Tube 500 SQ MM Cable JointDokument1 SeiteShort CT Calc ForCu Tube 500 SQ MM Cable Jointrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short CT Calc ForCu Tube 1000 SQ MM Cable JointDokument1 SeiteShort CT Calc ForCu Tube 1000 SQ MM Cable Jointrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short CT Calc ForCu Tube 1000 SQ MM Cable JointDokument1 SeiteShort CT Calc ForCu Tube 1000 SQ MM Cable Jointrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- DTS 1924 Cover - SheetsDokument11 SeitenDTS 1924 Cover - Sheetsrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- 0049 Plug in Size 4 For 500sqmm-828104aDokument1 Seite0049 Plug in Size 4 For 500sqmm-828104arenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short CT Calc ForCu Tube 1000 SQ MM Cable JointDokument1 SeiteShort CT Calc ForCu Tube 1000 SQ MM Cable Jointrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short CT Calc ForCu Tube 1000 SQ MM Cable JointDokument1 SeiteShort CT Calc ForCu Tube 1000 SQ MM Cable Jointrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4022 Insulated Joint 1000sqmm 20060818Dokument1 Seite4022 Insulated Joint 1000sqmm 20060818renjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short CT Calc ForCu Tube 500 SQ MM Cable JointDokument1 SeiteShort CT Calc ForCu Tube 500 SQ MM Cable Jointrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short CT Calc Cu Tube 500 and 1000sqmmDokument2 SeitenShort CT Calc Cu Tube 500 and 1000sqmmrenjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Acupuncture System and The Liquid Crystalline Collagen Fibres of The Connective TissuesDokument17 SeitenThe Acupuncture System and The Liquid Crystalline Collagen Fibres of The Connective Tissuesmkljhrguyt100% (2)
- O Revision E&MDokument9 SeitenO Revision E&MAlmas TalibNoch keine Bewertungen
- EASA Module 13 All Q AsDokument8 SeitenEASA Module 13 All Q AssomeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 74 HC 4538Dokument11 Seiten74 HC 4538vagitusNoch keine Bewertungen
- TempRise IEC61439 07112018Dokument7 SeitenTempRise IEC61439 07112018Anonymous JDWNC4ZDMUNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Giant Step Towards Solving The Energy & Pollution CrisesDokument2 SeitenA Giant Step Towards Solving The Energy & Pollution CrisesJa Moje100% (1)
- DC Motor: F Bli NewtonDokument35 SeitenDC Motor: F Bli NewtonMuhammad TausiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical InjuryDokument5 SeitenElectrical InjuryCandilicious10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Compilation 2Dokument42 SeitenCompilation 2api-26570979100% (1)
- Introduction To ElectricityDokument37 SeitenIntroduction To Electricityhazreen othman100% (4)
- IB Physics Revision NotesDokument31 SeitenIB Physics Revision NotesBig Long67% (3)
- Physics ProjectDokument17 SeitenPhysics ProjectKalpa Barman100% (1)
- What Is Electromagnetism? Introduction in Pictures: Branislav K. NikolićDokument14 SeitenWhat Is Electromagnetism? Introduction in Pictures: Branislav K. NikolićGINNO OSMILLONoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermoelectric Technical ReferenceDokument54 SeitenThermoelectric Technical ReferenceVikram BorkhediyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tertiary Winding of TransformerDokument2 SeitenTertiary Winding of TransformerHamayoun MurtazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of High Voltages and High CurrentsDokument3 SeitenMeasurement of High Voltages and High CurrentspriyadarshniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Green House Monitoring SystemDokument39 SeitenAutomated Green House Monitoring SystemSaiKrishna86% (14)
- 14-37 Arc Electron AvalancheDokument5 Seiten14-37 Arc Electron AvalancheDrazen Dan MijacikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Lesson Plan Subject: PHYSICS: P S P S P P S SDokument11 SeitenDaily Lesson Plan Subject: PHYSICS: P S P S P P S SFauziati Ab WahabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ect ReviewerDokument7 SeitenEct ReviewerDannahcaye Api PalcesNoch keine Bewertungen
- JVL High Quality, High Torque AC Servo Motors MSE400, 800, 1K5 and 3K0Dokument4 SeitenJVL High Quality, High Torque AC Servo Motors MSE400, 800, 1K5 and 3K0ElectromateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 11 Year End Review Package - New Curriculum - UseDokument11 SeitenPhysics 11 Year End Review Package - New Curriculum - UseCarmen JuranovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Non Destructive Testing (NDT)Dokument26 SeitenIntroduction To Non Destructive Testing (NDT)Engr Arfan Ali DhamrahoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suresh Main Project of ExcitationDokument68 SeitenSuresh Main Project of Excitationvenkeyharish0% (1)
- Automotive Electrical DisturbancesDokument40 SeitenAutomotive Electrical DisturbancesNirmala Ranawat100% (1)
- Technical CatalogueDokument62 SeitenTechnical CatalogueYanuar Ardian PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project of English: Electricity and RecycleDokument12 SeitenProject of English: Electricity and RecycleAlejandra RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSC Pc4020cfsp ManualDokument58 SeitenDSC Pc4020cfsp ManualGreta BonthuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centurion Eddy Current Ed520Dokument6 SeitenCenturion Eddy Current Ed520mgmqroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrochemistry Chemistry - 5070 Electrochemistry in ThisDokument9 SeitenElectrochemistry Chemistry - 5070 Electrochemistry in ThisTopikHamdanNoch keine Bewertungen