Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
NCP For Eclampsia
Hochgeladen von
Fatma Nor Aljanna MacogOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
NCP For Eclampsia
Hochgeladen von
Fatma Nor Aljanna MacogCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Among the most fatal part of pregnancy-induced hypertension is eclampsia.
The status of having an eclampsia is an introductory phase for having convulsions when the case is not managed properly. Previous researchers attempted to cite out the cause of hypertension but until now they could not point it out. Only contributing factors are sited such as heredity, lifestyle and supporting vessels. Previously, eclampsia is called toxaemia since researchers thought a certain toxin may cause the hypertensive episodes on mothers. In diagnosing pregnant mothers in the pre-eclamptic stage, a triad of signs and symptoms are observed: 1. Intense Vasospasm 2. Local or disseminated intravascular coagulation 3. Plasma volume contraction
Eclampsia can only be squared down when the following signs and symptoms are present:
hypertension proteinuria edema
Predisposing factors: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Multiparity Being pregnant under 20 years old Being pregnant more than 30 years old Being in a low socio-economic status Previous diagnosed illness such as heart disease, diabetes mellitus and essential hypertension
Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan-Altered tissue perfusion
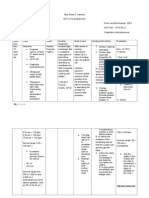
Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Nursing Actions 1. Monitor vital signs, palpate peripheral pulses and note capillary refill, assess 1. Rationale Rationale Indicators of adequacy of systemic perfusion, fluid/ blood, needs, and Evaluation Outcome Criteria: Clients blood pressure is below 140/90mmHg
Goals/ Nursing Diagnosis: Objectives: Altered tissue perfusion (Cerebral, peripheral and renal) Short term goal: Possible Etiologies: (Related to) Client will demonstrate
Arterial adequate vasospam/ perfusion, constriction of as blood vessels evidenced Decreased by stable prostaglandin vital signs, levels palpable Sensitivity to pulses, and angiotensin II alert and Impaired oriented, glomerular absence of perfusion seizure Decreased episodes, uteroplacental balanced perfusion intake and Increased output, cardiac decrease in workload presence of Vascular edema and damage good fetal Red blood cell status damage evaluation Alteration in within a liver function in week. severe cases Unusual Long term sensitivity to goal: blood loss probably Client will because of demonstrate leakage of blood readiness components into during the the postpartal extravascular period in space. monitoring ones health Defining and characteristics: involving (Evidenced by) oneself to dietary Elevated blood restrictions pressure and medical Edema, follow up especially of the checkups hands and face and Sudden weight intervention
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
urinary output, weigh client daily and evaluate changes in mentation. Place client on left recumbent position.Moni tor maternal well- being periodically. Administer oxygen as prescribed. Ensure safety by putting the side rails always up and monitor client for tonicclonic convulsions. Insert foley catheter as indicated by the physician and monitor urine output. Administer Magnesium Sulfate as ordered by the physician and monitor for signs for toxicity. Administer fluids as prescribed. Assist in the delivery of the baby.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
developing , urine output complications. of above This is to avoid 30ml/hour, uterine pressure fetal heart on the vena rate is cava and between 120prevent supine 160 beats per hypotension min, absence syndrome. of seizure Womans BP episodes, should be taken decrease in at least every 4 presence of hours to detect edema. for increase which is a Client warning of verbalizes worsening; if plans upon fluctuating, it discharge, should be done participates hourly. during To ensure lecturesupply of discussion oxygen to both sessions, and the mother and demonstrates the fetus. willingness to Convulsions perform are evident in monitoring Eclampsia so it measures. should be watched out and monitored. Urine output should be in congruence with fluid intake. This drug is usually given to control the blood pressure of clients with pregnancy induced hypertension. Replacement of fluids maintains
gain . Proteinuria (1+ up to 4+) Hyperreflexia Headache Visual disturbances Epigastric pain Fetal status Decreased urine output Rales, if pulmonary edema is present Elevated BUN, creatinine, uric acid Decreased hematocrit and haemoglobin Seizure
circulating volume and tissue perfusion.Deliv ery of the baby is considered the only cure for Eclampsia.
References: Maternal and Child Health Nursing: Care of the Childbearing and Childrearing Family Philippine Edition of Pillitteri, A.(1992) Phantom Notes in Nursing: Maternal Newborn 1st Edition of Glickman Jr., J. (1995).
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Normal Hemodynamic Parameters and Laboratory Values PDFDokument3 SeitenNormal Hemodynamic Parameters and Laboratory Values PDFKenNiyaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEE in Congenital Heart DiseaseDokument249 SeitenTEE in Congenital Heart DiseaseAdriana VasilicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- St. Paul School Science Exam PrepDokument3 SeitenSt. Paul School Science Exam PrepIrish Jhaizel Kaye FuentesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Internal Medicine PDFDokument388 Seiten1-Internal Medicine PDFAbdulaziz AlQahtani100% (1)
- Chapter 27 - Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and ConductionDokument8 SeitenChapter 27 - Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and ConductionMichael Boado100% (1)
- Understanding HELLP SyndromeDokument21 SeitenUnderstanding HELLP Syndromearebe29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Process For A Client With Molar Pregnancy (H-Mole)Dokument24 SeitenNursing Process For A Client With Molar Pregnancy (H-Mole)api-370148995% (19)
- Friendhip QuotesDokument5 SeitenFriendhip QuotesFatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friendhip QuotesDokument5 SeitenFriendhip QuotesFatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- AngiographyDokument15 SeitenAngiographyladylyn santosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abruptio PlacentaDokument13 SeitenAbruptio Placentamiss RN92% (12)
- Case Study of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDokument12 SeitenCase Study of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionJamaica Leslie Noveno100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenNursing Care PlanBhie DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASESTUDY EclampsiaDokument39 SeitenCASESTUDY EclampsiayasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionVincent Paul SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abruptio Placentae (Case Presentation)Dokument46 SeitenAbruptio Placentae (Case Presentation)Bansot Baltaken100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDokument9 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionMurugham DineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Copy For Pre-EclampsiaDokument60 SeitenFinal Copy For Pre-EclampsiaSheena ClaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurse's Pocket Guide, 2010Dokument2 SeitenNurse's Pocket Guide, 2010YUBarom67% (3)
- NCP For EclampsiaDokument6 SeitenNCP For EclampsiaXtine Soliman Zamora100% (3)
- Uterine AtonyDokument3 SeitenUterine AtonyArsheina Paradji100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta PathophysiologyDokument4 SeitenAbruptio Placenta Pathophysiologyjamie carpioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDokument45 SeitenCongenital Heart DiseaseBrandedlovers OnlineshopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic Pregnancy Nursing Care PlansDokument27 SeitenEctopic Pregnancy Nursing Care Plansviper7967880% (20)
- Pre Eclampsia Case StudyDokument38 SeitenPre Eclampsia Case StudyFelmerPolancoRodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gestational HypertensionDokument6 SeitenGestational HypertensionDimitrisSoulisNoch keine Bewertungen
- EclampsiaDokument24 SeitenEclampsiaHengky HanggaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Preeclampsia and EclampsiaDokument14 SeitenNCP Preeclampsia and EclampsiaBiway RegalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Premature Rupture of MembranesDokument4 SeitenPremature Rupture of MembranesNikko Pabico67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan PIHDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan PIHLei Ortega100% (7)
- Hydatidiform MoleDokument28 SeitenHydatidiform MoleRitamaria100% (7)
- Preeclampsia Nursing Care PlanDokument8 SeitenPreeclampsia Nursing Care PlanElli SuñgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP: Gestational HTN - Preeclampsiaeclampsia - Hellp SyndromeDokument23 SeitenNCP: Gestational HTN - Preeclampsiaeclampsia - Hellp SyndromeKath100% (2)
- Pih Case Study For PrintDokument17 SeitenPih Case Study For Printfoxrivergate100% (1)
- Assessing and managing decreased cardiac output due to pregnancy induced hypertensionDokument2 SeitenAssessing and managing decreased cardiac output due to pregnancy induced hypertensionThesa FedericoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adenomyosis NCPDokument2 SeitenAdenomyosis NCPBrainan Aquino100% (2)
- Case Study Placenta Previa This Is It 1Dokument71 SeitenCase Study Placenta Previa This Is It 1Homework Ping100% (1)
- Nursing Care Management of a Client with Eclampsia: A Case StudyDokument72 SeitenNursing Care Management of a Client with Eclampsia: A Case StudyMauren Daza100% (4)
- Normal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryDokument35 SeitenNormal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryJohn Edward EscoteNoch keine Bewertungen
- EclampsiaDokument45 SeitenEclampsiarekhamol100% (1)
- Eclampsia: A Pregnancy Disorder Characterized by ConvulsionsDokument22 SeitenEclampsia: A Pregnancy Disorder Characterized by ConvulsionsDr-Fouad ElmaadawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMelDred Cajes BolandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Born NCPDokument8 SeitenNew Born NCPCarl Vincent Marrion Rejuso100% (1)
- Pre Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan by Maria Amabelles SorianoDokument39 SeitenPre Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan by Maria Amabelles SorianoLei Santillan0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan AbortionDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan AbortionJane Casiquin100% (1)
- CP Hydatidiform MoleDokument13 SeitenCP Hydatidiform Molesweetheart_joannieNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP Preeclampsia RevisedDokument32 SeitenCP Preeclampsia RevisedTessa Grace PugonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Umbilical Cord ProlapseDokument6 SeitenUmbilical Cord ProlapseJules Cantal100% (3)
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Case StudyDokument75 SeitenPregnancy Induced Hypertension Case StudyJing CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care With EclampsiaDokument40 SeitenNursing Care With EclampsiaNadia DesyerianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDokument51 SeitenAmniotic Fluid EmbolismDenyse Mayer Atutubo100% (2)
- Case StudyDokument19 SeitenCase Studywella goNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeWann WannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erceflora Antidiarrheal ClassDokument1 SeiteErceflora Antidiarrheal ClassfLOR_ZIANE_MAENoch keine Bewertungen
- CA - Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDokument13 SeitenCA - Amniotic Fluid EmbolismRodelen Maraño100% (2)
- Po No Breast RationaleDokument4 SeitenPo No Breast Rationalearnold john boniteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Premature Rupture of MembranesDokument3 SeitenPremature Rupture of MembranesSheena Kunkel100% (2)
- Case Study PIHDokument26 SeitenCase Study PIHChen OmbrosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionDokument2 SeitenNursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionJustin PasaronNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Presentation On Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDokument7 SeitenA Case Presentation On Pregnancy Induced Hypertensionzygote_23100% (1)
- HELLP Syndrome: A Variant of Severe PreeclampsiaDokument29 SeitenHELLP Syndrome: A Variant of Severe PreeclampsiaNona Saudale100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta FullDokument10 SeitenAbruptio Placenta FullChester ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE ANALYSIS Ectopic Pregnancy Part 1Dokument10 SeitenCASE ANALYSIS Ectopic Pregnancy Part 1Diane Celine SantianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retained Placental FragmentsDokument9 SeitenRetained Placental FragmentsHannah Laput100% (2)
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDokument19 SeitenAbnormal Uterine BleedingDelphy Varghese100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument20 SeitenNursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElaine Grace Timbol-Babasa100% (1)
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Dokument6 SeitenPlacenta Previa NCP 1Nicole ArandingNoch keine Bewertungen
- MaeDokument9 SeitenMaeCharmaigne Mae Padilla Sotelo100% (1)
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum AnemiaDokument10 SeitenHyperemesis Gravidarum AnemiaKate SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyDokument20 SeitenHypertensive Disorders in PregnancyemeyyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic NameDokument1 SeiteGeneric NameFatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Leon - Corporation Code.2010Dokument1.114 SeitenDe Leon - Corporation Code.2010Fatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Art SubjectsDokument3 SeitenTypes of Art SubjectsFatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patients Bill of RightsDokument4 SeitenPatients Bill of RightsFatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA (Finals)Dokument1 SeiteCA (Finals)Fatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- State of The Nation Address 2013Dokument1 SeiteState of The Nation Address 2013Fatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspiring Mother's Day Quotes CollectionDokument8 SeitenInspiring Mother's Day Quotes CollectionFatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA (Finals)Dokument1 SeiteCA (Finals)Fatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Invasive Procedure For CancerDokument11 SeitenNon-Invasive Procedure For CancerFatma Nor Aljanna Macog100% (1)
- 9 Steps To Safe Food HandlingDokument2 Seiten9 Steps To Safe Food HandlingFatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine National SymbolsDokument10 SeitenPhilippine National SymbolsFatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article On Diabetes Mellitus and CADokument3 SeitenArticle On Diabetes Mellitus and CAFatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- BoracayDokument2 SeitenBoracayFatma Nor Aljanna MacogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predictor Scale of Delayed Cerebral Ischemic in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Case Series: What A Radiologist Should KnowDokument5 SeitenPredictor Scale of Delayed Cerebral Ischemic in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Case Series: What A Radiologist Should KnowPopy TheresiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study For Cardiorespiratory PhysiotherapyDokument3 SeitenCase Study For Cardiorespiratory Physiotherapypp ssNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Human Anatomy & PhysiologyDokument36 SeitenThe Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Human Anatomy & PhysiologymalisalukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DKD and Sglt2iDokument61 SeitenDKD and Sglt2iماكريلا المصريNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2: GASES EXCHANGE IN ANIMALSDokument6 SeitenExperiment 2: GASES EXCHANGE IN ANIMALSDiana NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improvements in Cardiac Patients Through Exercise TrainingDokument41 SeitenImprovements in Cardiac Patients Through Exercise Trainingifan zulfantriNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2009 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelDokument24 SeitenJune 2009 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelAyse KerimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calcification AorticDokument28 SeitenCalcification AorticGaal PinNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS-EP data collection worksheetDokument2 SeitenCS-EP data collection worksheetNnaemeka NwobodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogenesis of AtherosclerosisDokument21 SeitenPathogenesis of Atherosclerosishakky gamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook Egans Fundamentals of Respiratory Care 11Th Edition Kacmarek Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument40 SeitenEbook Egans Fundamentals of Respiratory Care 11Th Edition Kacmarek Test Bank Full Chapter PDFalexandercampbelldkcnzafgtw100% (10)
- Chest Physical Examination: Paltep, Rashell Anne C. Family Medicine PGI September, 2020Dokument23 SeitenChest Physical Examination: Paltep, Rashell Anne C. Family Medicine PGI September, 2020Rash PaltepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventricular Aneurysm: PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenVentricular Aneurysm: PathophysiologyMegan N. ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDL Cholesterol KitDokument2 SeitenHDL Cholesterol KitZumaira AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Different Doses of Omega-3 Fatty Acids On Cardiovascular Outcomes, A Pairwise and Network Meta-AnalysisDokument10 SeitenImpact of Different Doses of Omega-3 Fatty Acids On Cardiovascular Outcomes, A Pairwise and Network Meta-Analysisadam shingeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal Resuscitation DrillDokument23 SeitenMaternal Resuscitation Drillapi-219741636100% (2)
- Patient anticoagulation trackingDokument2 SeitenPatient anticoagulation trackingbrendacoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Guide, Volume 1 - 453562006191b - en-US PDFDokument82 SeitenQuick Guide, Volume 1 - 453562006191b - en-US PDFIvan CvasniucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burger Allen Exercises PDFDokument122 SeitenBurger Allen Exercises PDFlucky 116Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ventricular FibrillationDokument3 SeitenVentricular FibrillationsundarirakhmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentor: John Hommer E. Dy M.D. Moderator: Joy Marchadesch M.DDokument57 SeitenPresentor: John Hommer E. Dy M.D. Moderator: Joy Marchadesch M.DJohn Hommer DyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carson LiberalvsRestrictiveTransfusionforSymptomaticCAD AmHeartJ 2013 PDFDokument9 SeitenCarson LiberalvsRestrictiveTransfusionforSymptomaticCAD AmHeartJ 2013 PDFDio AlexanderNoch keine Bewertungen