Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Experiment Da Te
Hochgeladen von
humbleaviOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Experiment Da Te
Hochgeladen von
humbleaviCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Experiment Date; Submission Date;
Experiment No. 2
DETERMINATION OF VISCOSITY OF LIQUIDS
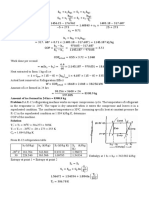
Aim: To fjnd out the kinematic viscosity of a fluid, Apparatus: Redwood Viscometer Theory: Viscosity is defined a:* that property of a fluid by which one layer of the liquid offers resistance to other layer's movement. It is primarily due to the force of cohesion between liquid molecules and molecular momentum exchange between them. Coefficient of dynamic viscosity: By Newton's law of viscosity the stress on a layer of a fluid is directly proportional to the rat~ i.e.a where, r is the shearing stress Therefore Here. is the coefficient of dynamic viscosity, SI unit is N-s/m2
Coefficient of Kinematic Viscosity: It is defined as ratio between the dynamic viscosity and the mass, density of the fluid. It is denoted by . Where 29 /p = (dynamic viscosity/mass density). The SI unit of kinematic viscosity is m2/s. 1 Stoke = 1 cm2/s - 10Hm2/s Factors affecting coefficient of viscosity: 1. The cohesion between the molecules of the fluid. 2. Momentum transfer of the molecules. 3. The temperature of the fluid. Methods to determine viscosity: 1. Newton's law of viscosity. 2. Hagen-Poiseuille equation. 3. Stake's law. Common Viscometers used: 1. Capillary tube viscometer: A capillary tube viscometer consists of a horizontal capillary tube through which, the given fluid is made to flow. Pressure in the capillary is estimated and discharge is measured. Hagen-Poiseuille's equation is applied. = -(dpgh)/128Q1)
2. Coaxial Rotating cylinder viscometer: This consists of two concentric cylinders of radius R1 and R2 with a narrow space left in between. Liquid of which viscosity is to be measured is filled between the gap and outer cylinder is rotated with known speed. The inner cylinder, which is attached to the torsion spring, also rotates when outer cylinder is rotated. Thus knowing torque on the inner cyfinder shear stress can be computed arid hence the viscosity. = -(aT)/(2R12 R2 wH) a =-radial space R2R1 H = submerged height of inner cylinder T = Torque generated. 3.Redwood viscontetcr. Hagen
Poiseuille's equation is used to find kinematic viscometer viscosity. does not This actually
measure viscosity but it facilitates comparison between viscosities of different fluids. The working is based on calculating the time of flow in seconds for a definite quantity of oil {50 ml) under definite conditions of temperature and pressure. Components: a) Oil cup: The oil cup is cylindrical brass vessel open from top and concave at bottom. It has a tapered control hole in which a jet can be fitted in with a hole, at the centre. b) Heating Bath :. It is a cylindrical water bath made out of copper and surrounds the oil cup. c) d) slirrer it is metallic ball attached to the end of a stiff wire. Oil valve it in the form of a metallic ball attached to the end of a stiff wire.
e) Oil collecting flask: A special type jet to collect thekolharush flask is place below the jet to collect the outgoing oil of volume 0.05liter Procedure: 1. Adjust the instrument with the screws. 2. 3. 4. Fill the oil in the oil cup up to the mark shown by the tip of wire. Place the 50 ml flask below the jet. Close the jet by keeping the valve rod in position. .
5. Fill the water in a water bath and heat slowly.
6. Stir the water for uniform transmission of heat. Heat oil up to 80c and then cool it. Take the readings of temperature and time taken for filling 50ml oil into flask at regular intervals. Precautions: 1. The viscometer should be thoroughly cleaned with alcohol before starting the experiment. 2. Viscometer should be properly adjusted and levelled. 3. The ball valve should be lifted gently. Liquid should be free from particles and suspended impurities. Observation Table: Sr. No. Temperature Time for 50ml V Kinematic Viscosity v W/s' 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 80 75 70 65 60 91.40 110.50 148 170.57 203.47 181.10-4 0.0226x10-4 0.0313x10-4 0.364x10-4 0.438x10-4 Dynamic viscosity p. 'N-s/mJ 0.1704 0.2128 0.2947 0.3428 0.4124
Sample Calculations:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- IIT JEE 2015 Test Schedule: Date Day Time Subject TopicsDokument1 SeiteIIT JEE 2015 Test Schedule: Date Day Time Subject TopicshumbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions: A) B) D) E) Will WillDokument3 SeitenQuestions: A) B) D) E) Will WillhumbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Dates For PHD and Mtech (Research) Programmes: Sardar Vallabhbhai National Institute of Technology, SuratDokument1 SeiteImportant Dates For PHD and Mtech (Research) Programmes: Sardar Vallabhbhai National Institute of Technology, SurathumbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPE Teaching PlanDokument5 SeitenPPE Teaching PlanhumbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac No No Serial No Surname Name Father/Husband Name Age Sex Id Card No Polling Station Name Polling Station LocationDokument1 SeiteAc No No Serial No Surname Name Father/Husband Name Age Sex Id Card No Polling Station Name Polling Station LocationhumbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODIFIEDSchedule PHD 2013 14 PDFDokument1 SeiteMODIFIEDSchedule PHD 2013 14 PDFhumbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amrutvahini College of Engineering, SangamnerDokument3 SeitenAmrutvahini College of Engineering, SangamnerhumbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Strategies To Improve Your Presentation Skills : TodayDokument1 SeiteSimple Strategies To Improve Your Presentation Skills : TodayhumbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM UiiDokument4 SeitenFM UiihumbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Auditing: Do Not Estimate When You Can Calculate! Do Not Calculate When You Can Measure!!Dokument70 SeitenEnergy Auditing: Do Not Estimate When You Can Calculate! Do Not Calculate When You Can Measure!!humbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- IITJEE2012 Papar II SolutionDokument34 SeitenIITJEE2012 Papar II SolutionhumbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gdkjsgdjhdklhelke Cgoheocfhdlhcioed CdgcoldhdcvhdiodDokument1 SeiteGdkjsgdjhdklhelke Cgoheocfhdlhcioed CdgcoldhdcvhdiodhumbleaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument6 SeitenUnit 2humbleavi100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Objective Type QuestionsDokument151 SeitenFluid Mechanics Objective Type Questionshumbleavi100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Main ISM Ch07Dokument14 SeitenMain ISM Ch07Shoja Sammy RahimianNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Chapter 13 MC Practice Questions With MC AnswersDokument9 SeitenAP Chapter 13 MC Practice Questions With MC AnswersapantollanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RACNOTESVCRSDokument2 SeitenRACNOTESVCRSAnonymous 5HYsyrddpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mekanik Bendalir - Venturi MeterDokument17 SeitenMekanik Bendalir - Venturi MeterMohd_Razif_Aje_5747Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lectuer-11 EvaporatorDokument41 SeitenLectuer-11 EvaporatorAurenio RibeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reservoir Types. Classification MethodologyDokument2 SeitenReservoir Types. Classification MethodologyMukhtarov PgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiphase Systems PDFDokument11 SeitenMultiphase Systems PDFDicky HartantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consider Practical Conditions For Vacuum Unit ModelingDokument6 SeitenConsider Practical Conditions For Vacuum Unit ModelingstudyendlessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Sheet 4Dokument2 SeitenTutorial Sheet 4Syed YousufuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- N2 Regulator and Gauges DatasheetDokument4 SeitenN2 Regulator and Gauges DatasheetpavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNG 520 - Course On Phase RelationsDokument172 SeitenPNG 520 - Course On Phase RelationsDenstar Ricardo SilalahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan ScienceDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan ScienceChi Chi CarbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Bond Formation: General ChemistryDokument20 SeitenIonic Bond Formation: General Chemistryyoona stewartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated NGL Recovery and LNG LiquefactionDokument59 SeitenIntegrated NGL Recovery and LNG Liquefactionsea_wave100% (1)
- Buoyancy Forces in CT ApplicationsDokument3 SeitenBuoyancy Forces in CT ApplicationsQazi WaqasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Pedro Julio Villegas AguilarDokument48 SeitenDr. Pedro Julio Villegas AguilarCt0% (1)
- Vle of Hcl-WaterDokument6 SeitenVle of Hcl-WaterYaqoob Ali0% (1)
- CHEMISTRY-19-11 - 11th (J-Batch) SpaceDokument21 SeitenCHEMISTRY-19-11 - 11th (J-Batch) SpaceRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Force & Pressure (Teacher)Dokument23 SeitenChapter 3 Force & Pressure (Teacher)ima_1806Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dimensionamiento Tuberías Con Coolselector (Webinar)Dokument52 SeitenDimensionamiento Tuberías Con Coolselector (Webinar)Robier Triana GüisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiling Assignment Part 1Dokument9 SeitenBoiling Assignment Part 1BrianRungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line SizingDokument17 SeitenLine SizingAllyssa Jane ErcillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT BitsDokument12 SeitenMT BitsKundan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example Problem RBI PSV - Rev1Dokument17 SeitenExample Problem RBI PSV - Rev1RizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poster TemplateDokument1 SeitePoster TemplateEndurance BillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 Properties of Liquids and IMFDokument47 SeitenLesson 3 Properties of Liquids and IMFHillary Faith GregoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multifunction ExtractionDokument7 SeitenMultifunction ExtractionSiraj AL sharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- PVT Analysis For OilDokument27 SeitenPVT Analysis For Oilel hadi100% (1)
- A-A 59503A (Nitrogen)Dokument6 SeitenA-A 59503A (Nitrogen)mtcengineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Pipeline HydraulicsDokument35 Seiten2 Pipeline HydraulicsRahul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen