Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
MI0036 SLM Unit 14
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous bTh744z7E6Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MI0036 SLM Unit 14
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous bTh744z7E6Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
Unit 14
Structure 14.1
Business Intelligence Strategy and Road Map
Introduction Objectives 14.2 Planning to implement a Business Intelligence Solution 14.3 Understand Limitations of Business Intelligence 14.4 Business Intelligence Usage How to make the best use of Business Intelligence? The Advantages of BI with Sales How can BI be used for the rescue? 14.5 Organisation Culture 14.6 Managing Total Cost of Ownership for Business Intelligence Total Cost of Ownership and Business Intelligence Managing the TCO of the Business Intelligence 14.7 Factors that Affect Total Cost of Ownership 14.8 Summary 14.9 Case Study 14.10 Terminal Questions 14.11 Answers 14.12 Glossary
14.1
Introduction
By now you must be familiar with the challenges to build a successful BI. In this unit, you will learn about the strategies involved in a BI solution. We will discuss various factors that need to be taken in to account while devising a plan for a BI. Business Intelligence can be planned by analysing the requirements so that the one appropriate to the company can be chosen. Before implementing the Business Intelligence to the organisation, there is need for real-time integration tools which comes with the real time data replication engine. Planning to implement a Business Intelligence in the company, may also have graphic visuals so that the overall view of the desired function can be obtained. Analytic dashboards have now become a necessity and can also supplement the statistical and the numeric information.
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 285
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
BI can enhance the overall performance of the company.. The data is often considered as the second most important resource a company can have where the companys most important asset is considered to be its people. BI also expedites the decision-making, by acting quickly and correctly on the information before competing businesses can often result in competitively better performance. BI allows firms to gather the data on the trends in the marketplace and come up with modern products or services in prediction of the customer's changing demands. The TCO management gives one set of measures which will help to understand the value of BI. Learning Objectives After studying this unit, you will be able to: Identify the limitations of BI. Define the values of requirements of BI end users. Explain strategies to manage total cost of ownership. Analyse the factors affecting cost of ownership.
14.2 Planning to Implement a Business Intelligence Solution
The companies are relying more and more on the timely and accurate information so that they can stay in todays competitive market. The Business Intelligence solutions and the real time data charts are highly efficient in getting the correct kind of information at the ideal time. The implementation of the Business Intelligence can be planned by analysing the requirements appropriate to the company can be chosen. Planning to implement the Business Intelligence solutions is more than implementing technologies and tools related to the solution. It has to be ensured that the system gives the necessary results and at the same time be able to refresh the real time data marts. There will be need to access fast the real time information. For example, a bank might require responses within milliseconds while the other settings may accept it in few minutes. The time to update data has to be analysed and based on which the near real time solution for the business has to be chosen. All the users in the organisation should be educated about the capacities of the system. Before implementing the Business Intelligence to the
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 286
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
organisation, there is need for real-time integration tools which comes with the real time data replication engine. The cost of this kind of system is quite high and an alternative to this is the database native replicator. The database triggers can also be used in the place of real time systems. These are easy to afford and requires low maintenance. The changes captured are then posted into a separate area of staging from where the real time integration engine will be able to read it continuously. Planning to implement a Business Intelligence in the company, may also have graphic visuals, so that the overall view of the desired function can be obtained. Analytic dashboards have now become a necessity and can also supplement the statistical and the numeric information. The real time information obtained through the Business Intelligence system should be delivered to almost any place. In the market, there are several gadgets which will route exception alerts and the dashboard reports to the webenabled devices like the PDAs1. While implementing the Business Intelligence solutions all these things should be kept in mind for the business needs to be met effectively. The system should be planned and designed and the application should be given to qualified and experienced solutions providers. This way the benefits of the business can be reaped. While choosing BI the companies will have to first analyse the way the decisions are made and also consider the information that the executives require to facilitate more confident and more rapid decision making as well as how the information should be presented. Decision making discussions will tell the information companies to what needs to be collected, analysed, and published in the BI systems. Good BI systems will give the context. It is not sufficient to report the sales were X was done yesterday and Y was done a year ago the same day. Like other technologies, BI will not give returns if the users feel threatened or doubtful about the technology and hence will refuse to use it as a result. The seven steps to be followed while rolling out the BI solutions are: 1. Make sure that the data is clean. 2. Train the users effectively.
1
Personal Digital Assistant is a handheld computer for managing contacts, appointments and tasks.
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No.: 287
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
3. Quickly deploy and adjust while progressing. Huge amount of time up front developing the perfect reports should not be spent because the needs evolve as the business evolves. Deliver the reports which provide the most value quickly and then tweak them. 4. An integrated approach should be considered while building the data warehouse from the starting. Getting into unwanted data strategy must be avoided. 5. The ROI should be clearly defined before starting. The specific benefits that have to be achieved should be outlined and then a reality check has to be done every quarter or six months. 6. There should be focus on the business objectives. 7. Business Intelligence software should not be bought just because there is a need. Deploy the BI with the idea that there are numbers which has to be found and roughly understood where it is required.
14.3 Understand Limitations of Business Intelligence
Data warehouses, that the BI systems attach to, generally do not contain all the necessary data to generate the revenue from the existing company data. The data present in the data warehouse may not be in the right format for sales. The relationships in the data warehouse may not be optimised for the revenue generating user community. Data warehouses usually do not store old data to allow the formation of trended information. The final data quality is questionable. The queries can take a long time to run that is more than 10mins. The IT departments will have data warehouses but only experts can access them. The sales representative will not or may not use the BI tools. The queries solved out of the BI systems can be burdensome and time consuming for the end users. The data analysts and the business intelligence tools do not have to directly generate the revenue but there should be more effective and productive sales representatives. Activity 1: HSV is a packed food chain company. It has branches all over the world. It has to maintain the huge data about all the products sold by the company. How should it plan to implement the Business Intelligence solutions?
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 288
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
Self 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Assessment Questions There are seven steps in rolling out BI solutions.(True/False) Good _____ systems will give the context. _________ can be used in place of real systems. BI solutions should not focus on the business objectives.(True/False) _______ should be trained effectively.
14.4 Business Intelligence Usage
The companies using BI have many benefits. BI can remove a lot of the guesswork within the organisation, enhance the communication among the departments while coordinating the activities, and also allow the companies to respond quickly to the changes in the financial conditions, the customer choices and the supply chain operations. BI can enhance the overall performance of the company by using it. The data is often considered as the second most important resource a company can have where the companys most important asset is considered to be its people. So, when a company makes decisions based on the timely and correct data, the company can enhance its performance. BI also expedites the decision-making, by acting quickly and correctly on the information before competing businesses can often result in competitively better performance. It can also improve the customer experience, allowing for the timely and suitable reply to the customer problems and priorities. The firms have recognised the importance of business intelligence for the masses and some of them are as follows: Analysing the click-stream data to improve the e-commerce plans. Quickly detecting the warranty-related problems to minimise the impact of the product design deficiencies. Discovering the money-laundering criminal activities. Analysing the potential growth of the customer profitability and minimises the risk of exposure through more correct financial credit scoring of the customers. Determining what are the combinations of the products and service lines the customers are likely to purchase and when. Analysing the clinical tests for experimental drugs. Setting more gainable rates for the insurance premiums.
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No.: 289
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
Minimising the equipment downtime by applying the predictive maintenance. Identifying and preventing the fraudulent activities, such as from the usage spikes when the credit or phone cards are stolen. Converting the business knowledge through the analytical intelligence to solve the business issues can be easily done by the employees using the BI superior tools like increasing the response rates from the direct mail, telephone, e-mail and internet delivered marketing campaigns. Recognising the loyalty of firms most profitable customers and the future customers can be done with the help of BI.
Customers are the most important feature to a company's success. Without them the company cannot survive. So, it is very crucial that the firms have data on their preferences. Firms must quickly adjust to the changing demands. Business Intelligence allows firms to gather the data on the trends in the marketplace and come up with modern products or services in prediction of the customer's changing demands. Competitors can be a big obstacle on the firms way to success. The objectives are the same as the firms where the profits and customer satisfaction has to be maximised. To be successful the firms should stay one step ahead of the competitors. Business Intelligence tells the actions the competitors are taking, so that one can make better informed decisions. The Business intelligence usage can be grouped into the following categories: Business operations reporting: The most general form of business intelligence is the business operations reporting. This includes the actual and how the actual stack up against the aims. This type of business intelligence often manifests itself in the regular weekly or monthly reports that have to be produced. Forecasting: Forecasting is both a science and art. It is an art because the future cannot be predicted. What if the competitors decide to spend a huge amount of money in advertising? What if the price of oil goes up to Rs.2000 a barrel? And at the same time it is a science because it can be generalised from the historical data.
Page No.: 290
Sikkim Manipal University
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
Dashboard: The main use of a dashboard is to communicate the data at a glimpse. For this there is little necessity for drilling down the data. At the same time, presentation and ease of use are very vital for a dashboard to be useful. Multidimensional analysis: The multidimensional analysis refers to the "slicing and dicing" of the data. It gives a good insight into the numbers at the more granular level which requires a solid data warehouse / data mart backend, as well as a business-savvy analyst to get to the required data. Finding correlation among various factors: This is going very deep into the business intelligence. Questions like, "How the different factors are associated to one another?" and "Are there important time trends that can be furnished/anticipated?"
14.4.1 How to make the best use of Business Intelligence? It is not a big secret that todays businesses rely greatly on the data and the information it gives about the companies. Whether it is for the reason of the customer acquisition, improving the operational performance, or understanding the competitors, all of the data has to be showed in the form of complex and large amounts of data. Presently, the data that comes into the modernised organisations has to be reproduced several hundred times then looked at in association with the types of data which were already available for the analysis in the previous decade. Also the different kinds of sources of data have increased thoroughly, calling for the vigorous Business Intelligence solutions for data integration, storage and analysis to increase the effective decision making. Due to the technological progress made over the last few years it has become even easier to capture the data and is less costly to store the data than before. Where as the Business Intelligence tools of the past were most generally used for no more than a one time analysis, but today there are improved Business Intelligence tools which are being used as an integral feature of on going and continuous enhancement of the way in which the organisations work with and for their customers. After all of the data has been exhausted one of the things that have changed considerably over the years is the cost at which the Business
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 291
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
Intelligence tools can be obtained. Due to the different types of vendors, those concerned in investing in a Business Intelligence solution now have more option as far as the price and complexity are concerned. With the various tools offered by the Business Intelligence solutions unimaginable possibilities can happen. The applications within the Business Intelligence software allow the organisations to check the competitor data, providing the additional edge necessary to stay ahead. These tools can help the leaders of a company to guess the future outcomes based on the historical and the current date which will in turn give sufficient time to prepare for what may lie ahead. 14.4.2 The Advantages of BI with Sales Profits can be built by recognising the useful ventures. Often there are sales and marketing issues which can behave as road blocks to increase the profitability. In order to efficiently overcome these road blocks the organisation will need the data that will make them to direct the work towards the most gain-able targets. The very same data also makes the organisation to steer its products towards significantly increasing the gain. If the organisation is well equipped with the intelligence that is required then they can enable mainly the profit-based compensation and also encourage the sales or marketing teams in the direction of a more profitable outcome. Next the Business Intelligence allows an organisation to increase the sales by using the fact bases of selling tools. There are always issues which will slow down the selling process and still some of the issues can be over come in advance. How can these obstacles be over come? The obstacles can be overcome with the help of Business Intelligence tools which will help an organisation to analyse why a product or service sells in one account and not in another similar one. The organisation can pin point inventory issues in a particular store and suggest moving the overstock to another location. Also the Business Intelligence data allows the organisation to recognise and bring to attention the cross selling opportunities. The sales representatives with the computer access to the facts given by the Business Intelligence system are better equipped to make convincing sale offers in real time. This sometimes means helping a customer to make product or service quality decision by using on the spot analysis of the
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 292
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
similar accounts. It is good to note that the successful companies are building the customer loyalty by providing the internet access to the data. 14.4.3 How can BI be used for the rescue? BI means the IT platform and tools which can be used to gather, give access to, and analyse the data about the organisation operations and the activities. The platform consists of a set of information technologies which are represented as a stack that is one technology set on top of another. Starting at the base the stack is as follows: Infrastructure: It is the organisation's servers, operating systems, workstations, and networks. Data acquisition: The main transaction systems for example payroll, accounts receivable, outpatient registration, and the electronic health record are the sources of data which are used by BI analyses software. Data integration: The software is used to extract the data from the source systems, clean the data, and link data from different systems. Data aggregation and storage: The repository of data that results from the data integration process which can keep both the complete data and data summaries. Data analyses: The analytic software is used to query the repository, run reports, and perform data modelling and "what if" scenarios which are often called BI by the software vendors. Portal: The interface is used by the managers and the IT analysts to work with the BI stack.
Though the technology is an important part of BI, efficient management of the BI is just as necessary.
14.5 Organisation Culture
Organisation culture relates to the general culture within a company or organisation, and is often referred to as the corporate culture, though it is not the best description since a big non-profit organisation or charity could also have its own organisational culture although they are definitely not corporations. Here are some of the many definitions of the organisational culture which can be found.
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 293
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
The organisation culture can be defined as: "The set of the beliefs, values, and norms, along with the symbols like the dramatised events and personalities that represent the unique character of an organisation, and give the context for action in it and by it." Beliefs and values are words which will pop up regularly in other definitions also. The norms may be described as the traditions, the structure of authority, or the routines. Organisation culture can also be defined as: "The pattern of common basic assumptions that the group learned as it solved its problems has worked well enough to be assumed valid and is passed on to the new members as the correct way to comprehend, think, and feel in relation to those problems." Though the words are different, the two definitions are almost the same in terms of content. Another more simple way of looking at the organisation culture is to view it as a group's common reaction to the stimulus. An organisation culture is a group of people who have been trained, or who have learned by those around them, how to perform in any given condition. In this way, the corporate culture will function just as any social learning will do. The other feature of the organisation culture that is often correct is that it becomes very deeply rooted. It is the identity of the company and in some ways which gets an identity of those who work there, as well. This is important as the culture becomes like a circular argument. This will result in people affecting the culture as much as the culture is affecting them. Because the culture is so deeply rooted in an organisations history of success or failure, and because of its collective experience, any organisation that will have to work to change it will be face an uphill battle and a huge investment in time, resources, and work. In such a situation, it is often good to find get professional outsiders to at least help out, people who have not been exposed and sucked into the bad habits of a dysfunctional organisation culture. So when there are many definitions of organisation culture, all of them aim on the same points: collective experience, routine, beliefs, values, goals, and system which are learned and re-learned, passed on to the new employees, and continue on as part of a company's core identity.
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No.: 294
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
Organisation culture is a plan in the field of organisational studies and management which states the psychology, attitudes, experiences, beliefs and values like the personal and cultural values of an organisation. It has been defined as "the particular collection of the values and the norms that have to be shared by people and groups in an organisation and that control the way they interact with each other and with the stakeholders outside the organisation." The organisation values are also known as "the beliefs and ideas about what types of aims the members of an organisation should follow and also the ideas about the suitable kinds or standards of behaviour the organisational members should use to achieve the aims. From the organisational values the organisational norms, guidelines or expectations are developed that put the suitable kinds of behaviour by the employees in a specific situations and control the behaviour of the organisational members towards one another." Organisation culture is not the same as the corporate culture. It is the broader and the deeper concepts, something that an organisation 'is' rather than what it 'has'. Corporate culture is the total sum of the values, the customs, the traditions and the meanings that will make a company different. The corporate culture is frequently called "the character of an organisation" as it embodies the idea of the companys founders. The values of a corporate culture can influence the moral standards within a corporation. The senior management can try to decide a corporate culture. They may also wish to apply the corporate values and standards of the behaviour that can specifically tell the objectives of the organisation. In addition, there will also be an existing internal culture within the workforce. The work groups within the organisation can have their own behavioural quirks and interactions which can affect the whole system. Unlike organisation culture, the corporate culture can be 'imported'. For example, a computer technician will have the expertise, language and behaviours obtained independently of the organisation, but their presence can affect the culture of the organisation as a whole. Persistent, deep, largely subconscious, and implied code will give the 'feel' of an organisation and determine what is considered to be right or wrong,
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 295
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
important or unimportant, workable or unworkable in it, and how it can respond to the unexpected crises, the jolts, and the sudden change. All the new employees must incorporate the code to know the right way to behave and what to expect from other employees. Organisation culture is the sum total of an organisation's past and current assumptions, experiences, philosophy, and values which can hold it together, and are expressed in its self-image, inner workings, interactions with the outside world, and the future expectations. It is based on the shared attitudes, beliefs and customs, express or implied contracts, and written and unwritten rules which the organisation develops over time and which have worked well enough to be considered suitable. The corporate culture demonstrates: The way the organisation conducts its business, treats its employees, customers, and the broader community. The level to which the autonomy and the freedom is allowed in decision making, developing new ideas, and personal expression. The process of power and the data flows through its hierarchy. The strength of the employee commitment towards the collective objectives.
It is termed as 'strong' or 'weak' to the extent it is diffused through the organisation. It affects the organisation's productivity and performance, and gives guidelines on the customer care and service; the product quality and safety; the attendance and punctuality; and anxiety for the environment. It also extends to the production methods, marketing and the advertising practices in the new product creation. This is commonly expressed as "It's how we do things here," which is unique for every organisation and also one of the hardest thing to change.
14.6 Managing Total Cost of Ownership for Business Intelligence
The economy has definitely seen better days. The budgets used to be larger during the bull market. The Fiscal optimism nurtured independence among the company departments, groups, and divisions seeking changes and encouraging technology purchases to encourage growth. Acquiring the bestof-breed and grow-at-any-cost attitudes persisted.
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No.: 296
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
The present moderate business the climate and the renewed importance on the corporate accountability have encouraged an assessment of the overall purchases. Today, the businesses cannot pay for the independent expenditures that do not add the value in a coordinated fashion for the entire enterprise. Organisations realised, for example, that many of the business intelligence tools are present throughout the enterprise but produce little or nothing of value together, except for the information. The maintenance and licensing fees on each of the BI tool are important as well. 14.6.1 Total Cost of Ownership and Business Intelligence The financial analysis of the enterprise costs, such as the technology investments and expenses have be done annually to evaluate the affect of any changes that might affect the business. It is important to compute the overall cost of ownership with business drivers, such as enterprise efficiencies, productivity enhancements, and customer satisfaction. When an organisation struggles to reduce its Total Cost of Ownership (TOC), it should first plan a cohesive enterprise strategy meeting discouraging the challenges such as business units with their own technology standards, applications, and tools; along with products that do not work successfully together or with the already existing data; too many server licenses; and the cost prohibitive support requirements. While using the TOC specific to the Business Intelligence, all the costs and benefits should be valuated to make sure that the users are authorised properly to access, to transform, and to make better or faster decisions using the most important asset: which is information. Business intelligence potentially gives the highest ROI of any technical investment. As the size of the applications grows, it becomes even more important for the organisations to better manage the TCO in order to maximise the ROI. The business intelligence software with the lowest TCO will cost-effectively scale within the enterprise and beyond, and will not need moving the data and populating the data marts or cubes, or buying the unwanted hardware, which are all the very expensive. 14.6.2 Managing the TCO of the Business Intelligence As the companies continue to prioritise the Business Intelligence (BI) initiatives, they are becoming more concerned about the related costs and the impact that the costs can have on the final success or failure of the BI
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 297
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
projects. Many executives become wary of the hidden costs based on the previous experiences with the data warehousing and other enterprise application initiatives, and are putting the BI vendors to the test to reveal as much information as possible about the expected costs related with the solutions. The report has to be written to give the end-user organisations with an understanding of all of the cost factors related with the BI initiatives, and how the Best-in-Class organisations those which have attained the highest performance in managing the Total Cost of Ownership.
14.7 Factors that Affect Total Cost of Ownership
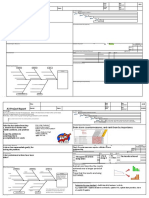
Concentrating entirely on the price while evaluate the costs and the reductions is risky. The methodology behind the BIs TOC is complicated. The following figure 14.1 shows the factors that contribute in finding the TOC of an enterprises BI strategy.
Hardware Cost Data Architecture
Software Cost Software Functionality
TOC
Support and Maintenance User Training Software Architecture and Scalability Time to Implementation
Figure 14.1: Factors of Total Cost of Ownership
Each of the factors shown in the figure 14.1 is interrelated and reliant upon the others. Even one should not be removed without taking into account how it could affect the others. A BI approach will have to: Support all the user needs Let the development of custom the BI applications Work with the data
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 298
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
Run on the platforms Need minimal support
The costs related with supporting and giving each metric may become very expensive as the business grows or the demand for more data increases. If there are plans to deploy the applications publicly may be to the customers then it would be a direct reflection of the organisation and the application is reliable and efficient Costs of the Hardware and the Software Think about all of the costs associated with the hardware and the software located throughout the enterprise and all of the people trying to access the applications concurrently. Buying more processors, maintaining multiple server licenses, and deploying expensive personnel to support the products and tools got over the years only increases the wasteful spending especially if many of the products do not effectively work together. To significantly reduce the expenses related with a BI strategy, the organisation must increase the ROI with a cost-effective solution that scales up to meet the growing demands for information. The best solution can be Web-based, without per user client licensing fees, and should not need any additional software on the client end. Software Functionality The enterprise has many types of users: casual users, more sophisticated users who make their own reports and analysts or power users who drill down to do Online Analytical Processing (OLAP). The functionality is vital and the entire enterprise has to be empowered to quickly and easily create all kinds of ad hoc reports, complicated queries, and in-depth analysis with nothing more than a Web browser. Rolling out a BI solution at the lowest TCO cannot be done if the solution has tools that need extensive training. Instead, the solution should consist of an intuitive environment that does not need plug-ins and is straightforward to learn and easy to use. Software Architecture and Scalability The vendor that gives significantly less software prices and is also good with the hardware specifications should be located. To make sure of the best
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No.: 299
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
performance, the BI solution will have to use the Internet as the vehicle to drive data to and from all the levels of the users. Buying more hardware processors will not resolve the bigger issue of how to put up with the growing number of users which requires the accurate information immediately. A truly scalable BI solution needs less hardware and maintenance while addressing the needs of all the information consumers. When users will become self-sufficient, the costly IT resources can be redeployed from reacting to the many sudden business requests to implementing and integrating the strategic enterprise initiatives. The idea was to calculate the price related with the purchase, the deployment and the operation of BI solutions. Finally, choosing the least cost vendor in the biggest category of Business Intelligence with parameterised reporting and user defined reporting on both the Windows and UNIX platforms is an extremely cost-effective solution for large-scale environments. In some scenarios, it is even possible to save hundreds of thousands of rupees, for example, in the categories of 1,000 and 10,000 users, by choosing the least-cost vendor. Time to Implement The developer resources are expensive and the users will have to immediately access the information. Hence, the developers need flexible tools to quickly build and deploy the complicated BI applications throughout the enterprise which can meet different user preferences for greater ease of use and maximum productivity. Choose the BI solution with an open and intuitive environment which will allow the quick development of almost any type of Web based report or information system. User Training The users should be ready to access the right information to do the analysis and also to create reports. But are they prepared? Keep the time and costs related with training the diverse groups of users at a minimum in order to make sure the lowest total cost of ownership. Empower the organisation to immediately access and analyse the data in a way that is best suited to get results and also meets the needs of executives, partners, customers, and sophisticated analysts. Next is to make sure that the people can easily manage and share information throughout the enterprise and the results can be saved, viewed, printed, and taken offline for additional analysis. As the
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 300
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
usability increases, the BI solution becomes more valuable, thereby increasing the Return On Investment2. Support and Maintenance Maintaining an environment where the valuable IT talent can handle every simple user request which will increase the TCO. Reducing the amount of maintenance and support required throughout the organisation by increasing the user self-sufficiency. Choose a reliable and manageable BI solution in which the users can instinctively help themselves to the right information, perform simple queries, and create or change the reports. Then, the IT resources can be deployed to solve more complicated problems. Data Architecture Throughout the organisation there are important business intelligence investments that should be leveraged. Rather than haphazardly removing these assets, particularly based only on the price, the focus should be first on removing the unwanted data and the overlapping technologies. Then minimise the difficulty of systems and consolidate the server resources to make sure the interoperability. The main objective is to increase the operations by empowering users to ably access and manipulate the information, at the cost of very old or duplicate tools. Using the information intelligently throughout an enterprise will improve the performance, propel the productivity, and reduce the costs. A fragmented BI strategy is regularly the result of having multiple tools deployed and working independently of each other. The studies have shown that the approach is very expensive and can create problems such as stovepiped views and data inconsistencies among the departments or groups. Control the assets already owned and choose the BI solution that interoperates with the assets and the data to lower the TCO. Managing the total cost of ownership TOC is used to recognise the costs associated with developing and operating the BI programs and components. The TCO gives valuable data
Is a measure of a corporation's profitability, which is equal to a fiscal year's income divided by the common stock and preferred to stock equity plus long-term debt. ROI will measure how effectively the firm uses its capital to generate profit; the higher the ROI, the better.
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No.: 301
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
which can be used to decide the Return Of Investment (ROI) of the program. The conventional TCO approach addresses the visible costs related with the BI, which means that it usually focuses on the hardware, the software, the telecommunications and the development and the support of personnel expenses. This approach leaves out an extremely important component, and many clients have struggled to validate moving to an enterprise data warehouse because the component was deleted. The missing feature is the time and hence the price of the business analysts who can use the information. Instead of using the traditional approach, the companies should emphasise the TCO management of the information delivery. This slight change in the terminology expands the scope from the technical environment to the business environment and indicates that with the addition of the term management action should be taken based on the cost data that is captured. To understand the affect of including the business analysts time the example of the company trying to rationalise the passage from a data mart environment to an enterprise data warehouse or to the development of conformed dimensions. If it calculates the TCO using the tradition approach, the enterprise data warehouse conformed dimensions appear to be more costly. Without exceptionally strong executive support, such a project would not be perceived as being cost justified. With the proposed approach, the time business analysts spent in capturing, validating, recording, and correcting the data should be included. It is not uncommon for these analysts to spend a main portion of the time on such activities, leaving only a little portion of the time to actually use the information. The enterprises approach the information capture and reconciliation by combining it into one source and the information validation and correction by treating data quality in Extract, Transform and Load processes. Measuring the components of the TCO is crucial if we are to manage it. Ideally, capturing the actual time spent by the business analysts on the information delivery activities, and also the information, cost components would be available. In most of the companies, this is not practical. Hence, there should be another approach for capturing these costs.
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No.: 302
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
This can be achieved through the periodic survey, which will include questions such as: What is the percentage of the time spent searching for the information? What is the specific data which is difficult to find? How many sources of information have to be used to capture the information for the most common analysis and reporting activities? What kind of data has the most sources, and what are the sources to be used? What percentage of the time is spent reconciling the data obtained from the multiple sources? Which data is the most difficult or time consuming to reconcile? What percentage of the time is spent reworking on the analysis because of the data errors that may be discovered? Which data is most prone to such errors? What is the percentage of the information analysis and delivery time which could be saved if accurate, reconcile, trust worthy information were available from a single source? What improvement if any has been experienced since the last survey? The first survey has to be conducted in the BI program as early as possible, with the successive surveys have to be performed following the incremental deployments. The primary and the secondary sets of questions have to be included. The primary questions are designed to give the predictable cost information for the inclusion in the TCO calculation. While not specific, the information is and will become meaningful if it is tracked over the time or used as the base for projecting the savings. The answers to the secondary questions indicate the specific areas which are troublesome. This is helps in establishing the BI priorities and can actually recognise some of the short term measures which can give the dramatic improvements. In addition, the improvements in particular areas has to become more visible as the areas which create problems will have to shift over time The TCO management gives one set of measures which will help to understand the value of BI. Other success measures which are both objective and subjective should also be tracked. Some of the success measures to be considered include the usage levels, user satisfaction, observable data quality issues, the reuse levels and, eventually the business value obtained.
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 303
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
Managing the TCO for information delivery is an important success factor for a BI program. This consists of the costs necessary to go beyond the traditional visible expenses and should address the effort people spend while changing the data received into useful information which can be applied to the business value. Activity 2: You are working for a sporting goods retail company called PSD. It has to report all the sales details. For this they have asked you prepare a report on the goods sold using the Bi software. How will it help in the TCO estimation? Self 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Assessment Questions TCO stands for____________________. _______________ is a plan in the field of organisational studies OLAP stands for ____________. _____________ is the total sum of the values. Business intelligence potentially gives the highest _______of any technical investment.
14.8 Summary
Business Intelligence system should be delivered to almost any place. Good BI systems will give the context. The data present in the data warehouse may not be in the right format for sales. The relationships in the data warehouse may not be optimised for the revenue generating user community. Data warehouses usually do not store old data to allow the formation of trended information. BI also expedites the decision-making, by acting quickly and correctly on the information before competing businesses can often result in competitively better performance. It can also improve the customer experience, allowing for the timely and suitable reply to the customer problems and priorities. Today, the businesses cannot pay for the independent expenditures that do not add the value in a coordinated fashion for the entire enterprise. Measuring the components of the TCO is crucial if we are to manage it. Business Intelligence allows firms to gather the data on the trends in the marketplace and come up with modern products or services in prediction of the customer's changing demands.
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No.: 304
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
14.9 Case Study
DGB is a sporting goods retail company. The overall sales of the company have been declining rapidly in the last three quarters and the management was very concerned about this. The retail stores have their own specific data bases which would keep track of the sales for particular items. Still at the overall management level only the sales figures for each store is reported for example the brand X and model Y running shoes and by categories of sales items such as all the running shoes so that the decisions on which product lines to drop and to reduce the overall inventory costs. The BI specialist came up with the procedure to obtain the data from each individual database, reconcile the data formats and types, aggregate all the data into a data repository and develop queries based on the management requests. They have to communicate and work closely with the management representatives to make sure that the data repository is created and that the report meets their needs. This is basically involves a series of back and forth discussions during which both the sides can ask question and answers. The BI specialist along with his team developed and deployed the software. However, there were many limitations that the company had to face. What are the limitations that the company had to face? List them.
14.10 Terminal Questions
1. How to implement Business Intelligence solutions? 2. What are the limitations of BI solutions? 3. What are the advantages of BI sales? 4. Define Organisational culture. 5. What are the factors the affect Total Cost of Ownership?
14.11 Answers
Answers to Self Assessment Questions 1. True 2. BI 3. Database triggers 4. False
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 305
Business Intelligence and Tools
Unit 14
5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Users Total Cost of Ownership Organisational culture Online Analytical Processing Corporate culture ROI
Answers to Terminal Questions 1. Refer Section 14.2 2. Refer Section 14.3 3. Refer Section 14.4.2 4. Refer Section 14.5 5. Refer Section 14.7
14.12 Glossary
Terms Database Triggers Description A trigger is a stored PL/SQL code block attached and executed by an event which occurs to a database table A company which supplies parts or services to another company. also called supplier. A server is a software program, or the computer on which the program runs, that gives a particular kind of service to client software running on the same computer or other computers on a network. A repository is a collection of resources which can be accessed to retrieve information. Repositories often consist of many databases tied together by a common search engine.
Vendors Servers
Repository
References 1. http://www.informationmanagement.com/specialreports/2009_145/open_source_business_inte lligence_bi_management_decision_making-10015500-1.html 2. Business Intelligence Roadmap by: Larissa T. Moss and Shaku Atre 3. Business Intelligence for Dummies (Paperback) Swain Scheps 4. Business Intelligence Roadmap: The Complete Project Lifecycle for Decision-Support Applications with CDROM-by Larissa T. Moss
Sikkim Manipal University Page No.: 306
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Business Intelligence Assignment 2 Version 2Dokument30 SeitenBusiness Intelligence Assignment 2 Version 2jonathan mottleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Process Engineering A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandBusiness Process Engineering A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.tech CS S8 Client Server Computing Notes Module 1Dokument13 SeitenB.tech CS S8 Client Server Computing Notes Module 1Jisha ShajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04-DDD.Assignment 1 frontsheet 2018-2019-đã chuyển đổi PDFDokument13 Seiten04-DDD.Assignment 1 frontsheet 2018-2019-đã chuyển đổi PDFl1111c1anh-5Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Unit 19 - Assignment 1 FrontsheetDokument24 Seiten1 - Unit 19 - Assignment 1 FrontsheetBui Hoang Bao Anh (FGW DN)Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1649 GCS0605 HuynhTanPhat ASM2Dokument20 Seiten1649 GCS0605 HuynhTanPhat ASM2RaishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 8 Research Project InformationDokument3 SeitenUnit 8 Research Project InformationAngel YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICON College of Technology and ManagementDokument20 SeitenICON College of Technology and ManagementClaudiu IordanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit Number and Title Submission DateDokument27 SeitenAssignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in Computing Unit Number and Title Submission DateHuynh Nhat Nam (FGW HCM)Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1639 GCS210462 NguyenQuangHuyASM1 BriefDokument19 Seiten1639 GCS210462 NguyenQuangHuyASM1 BriefLão Rùa OfficialNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1639 GCS18741 TranVuLinh Assignment1Dokument57 Seiten1639 GCS18741 TranVuLinh Assignment1Trần Vũ LinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- AD Coursework2 - RawinduDokument77 SeitenAD Coursework2 - RawinduAvishka Ravindu ImiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business IntelligenceDokument28 SeitenBusiness IntelligenceAaron ⎝⏠⏝⏠⎠ Ah Woon100% (1)
- 1639 GCS1005A NguyenNgocPhu GCS210331 Assignment1Dokument21 Seiten1639 GCS1005A NguyenNgocPhu GCS210331 Assignment10367712902phuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structures and AlgorithmDokument159 SeitenData Structures and Algorithmanon_655179541Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business Intelligance Nabin SirDokument5 SeitenBusiness Intelligance Nabin SirSusmita DhitalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Computing For Term 1 PGP 18 Mohammed Shahid Abdulla IT and Systems Area, IIMK Room 2/16, Ext 254, Office Hours: 2-3.30PM Mon-FriDokument37 SeitenBusiness Computing For Term 1 PGP 18 Mohammed Shahid Abdulla IT and Systems Area, IIMK Room 2/16, Ext 254, Office Hours: 2-3.30PM Mon-FriAbhilash BhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1missjojo89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 20 - Assignment Brief 1Dokument2 SeitenUnit 20 - Assignment Brief 1Võ Ngọc HùngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 19 - Assignment Brief 1Dokument15 SeitenUnit 19 - Assignment Brief 1Chuan Do100% (2)
- Data StructureDokument25 SeitenData StructureClaudiu IordanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABC Assignment PDFDokument64 SeitenABC Assignment PDFRaishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Video Library Management System Project ReportDokument118 SeitenVideo Library Management System Project ReportAkash ModakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dad Assignment - EsoftDokument11 SeitenDad Assignment - Esoftsheran2333% (3)
- INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Assignment #8 Submitted By: Mustafa DEĞERLİDokument2 SeitenINTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Assignment #8 Submitted By: Mustafa DEĞERLİMustafa Degerli0% (1)
- Jonathan Mottley - Business Intelligence Assignment 1Dokument17 SeitenJonathan Mottley - Business Intelligence Assignment 1jonathan mottleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 17 Project Planning With ITDokument11 SeitenUnit 17 Project Planning With ITDaniel BellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Project CompletDokument48 SeitenAssignment Project CompletArturo HernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample EndDokument120 SeitenSample Endairjaffna.lk100% (1)
- NTDokument77 SeitenNTRajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java - 16 - 001Dokument12 SeitenJava - 16 - 001Sudharaka SanjeewaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAND6211: Lu1: Textual AnalysisDokument27 SeitenSAND6211: Lu1: Textual AnalysisAkilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 13 Computing Research Project (Fall 2022)Dokument6 SeitenUnit 13 Computing Research Project (Fall 2022)Exremely FastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Verification of Assessment Decisions - Btec (RQF) : Jghigher NationalsDokument32 SeitenInternal Verification of Assessment Decisions - Btec (RQF) : Jghigher NationalsSusira MednisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1649 - GCS200888 - Vo Nguyen Duy Nam - Assignment 2 FullDokument40 Seiten1649 - GCS200888 - Vo Nguyen Duy Nam - Assignment 2 FullDuy Nam Võ NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- AD Assingment Guidlines1Dokument5 SeitenAD Assingment Guidlines1Madara NirmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- IDM/HND/System Analysis Page 1 of 5Dokument5 SeitenIDM/HND/System Analysis Page 1 of 5ChiranSJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data AnalysisDokument25 SeitenData AnalysisSrinivasan Manavalan100% (1)
- Data Mining - ASSIGNMENTDokument3 SeitenData Mining - ASSIGNMENTKim QuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 38 DatabaseManagementSystem-RoshanSirDokument5 SeitenUnit 38 DatabaseManagementSystem-RoshanSirManzu PokharelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Management Unit I Mba Anna UniversityDokument62 SeitenInformation Management Unit I Mba Anna UniversityViswanath T KNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Introduction To Data ScienceDokument33 Seiten1-Introduction To Data ScienceMenna SaedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corp Presentation 20160829Dokument17 SeitenCorp Presentation 20160829harigopaldasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Assignment On Professional Wider Services - Instant Assignment HelpDokument11 SeitenSample Assignment On Professional Wider Services - Instant Assignment HelpInstant Assignment HelpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Routing Protocol AssignmentDokument17 SeitenRouting Protocol AssignmentronicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Computer in Enhancing BankingDokument10 SeitenThe Role of Computer in Enhancing Bankinghibbuh100% (1)
- Literature Review Cloud ComputingDokument3 SeitenLiterature Review Cloud ComputingFarhan Sarwar100% (1)
- Cloud Gcd191295 PhananhlylyDokument22 SeitenCloud Gcd191295 PhananhlylyLy Phan anhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Information System and E-Business NotesDokument25 SeitenManagement Information System and E-Business NotesUwihoroye JosephineNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Evolving Role of IS/IT in Organizations: A Strategic PerspectiveDokument72 SeitenThe Evolving Role of IS/IT in Organizations: A Strategic PerspectiveAllesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Save A Snap Survey To Google DocsDokument5 SeitenSave A Snap Survey To Google DocsJames AndersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1: Business IntelligenceDokument40 SeitenAssignment 1: Business IntelligenceThanh TaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 Brief: Introduction To ThemeDokument3 SeitenAssignment 1 Brief: Introduction To ThemeKiên ĐỗNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 Excel Spreadsheet 2 3Dokument20 SeitenAssignment 1 Excel Spreadsheet 2 3api-360416081Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Activity Front Sheet: ASSIGNMENT 10.02Dokument9 SeitenAssessment Activity Front Sheet: ASSIGNMENT 10.02api-550884439Noch keine Bewertungen
- Soft Etro Ampus: Assignment Submission FormDokument68 SeitenSoft Etro Ampus: Assignment Submission Formronica100% (1)
- Chapter One Introduction To SADDokument26 SeitenChapter One Introduction To SADCali Cali100% (1)
- Week Five Assignment Database Modeling and NormalizationDokument9 SeitenWeek Five Assignment Database Modeling and NormalizationEvans OduorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 27 Health and Nutrition Tips That Are Actually Evidence-BasedDokument7 Seiten27 Health and Nutrition Tips That Are Actually Evidence-BasedAnonymous bTh744z7E6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One General Introduction 1.1background of The StudyDokument58 SeitenChapter One General Introduction 1.1background of The StudyAnonymous bTh744z7E6Noch keine Bewertungen
- IR Sensor Interface With PIC18F4550Dokument8 SeitenIR Sensor Interface With PIC18F4550Anonymous bTh744z7E6Noch keine Bewertungen
- About The Presentations: 1 E-Business, Ninth EditionDokument69 SeitenAbout The Presentations: 1 E-Business, Ninth EditionAnonymous bTh744z7E6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4final PDFDokument20 SeitenUnit 4final PDFAnonymous bTh744z7E6Noch keine Bewertungen
- ISA Topic 10Dokument8 SeitenISA Topic 10Anonymous bTh744z7E6Noch keine Bewertungen
- ISA Topic 6Dokument10 SeitenISA Topic 6Anonymous bTh744z7E6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Setting Advertising Objectives and Formulating Advertising StrategiesDokument12 SeitenUnit 2 Setting Advertising Objectives and Formulating Advertising StrategiesAnonymous bTh744z7E6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data, Digital Demand, and Decision-MakingDokument24 SeitenBig Data, Digital Demand, and Decision-MakingAbdulGhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment For First Sem CMDokument4 SeitenAssignment For First Sem CMnishant khadkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mg1401 Total Quality Management 3 0 0 100Dokument1 SeiteMg1401 Total Quality Management 3 0 0 100ganku001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tap GasDokument24 SeitenTap GasAnonymous iI88LtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 - MarketingDokument27 SeitenUnit 4 - MarketingSorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParcoDokument42 SeitenParcoHaris Ali KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Management AccountingDokument32 SeitenChapter 1 - Introduction To Management Accountingyến lêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acct Statement XX5398 17062023Dokument4 SeitenAcct Statement XX5398 17062023paras rawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMECS 2016 Full PapersDokument779 SeitenIMECS 2016 Full PapersCristin PasatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtusa Pegasystems Engagement Success StoriesDokument20 SeitenVirtusa Pegasystems Engagement Success StoriesEnugukonda UshasreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ferrari Case StudyDokument2 SeitenFerrari Case StudyjamesngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vijaychandran R 9629869676 Deputy Manager: May2019 - Aug 2019Dokument2 SeitenVijaychandran R 9629869676 Deputy Manager: May2019 - Aug 2019vijayfs2Noch keine Bewertungen
- A3 Problem-Solving: Title: A3 # Owner: TeamDokument2 SeitenA3 Problem-Solving: Title: A3 # Owner: TeamMayra HernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Chapter 2 - Purchasing StrategyDokument52 Seiten2 Chapter 2 - Purchasing StrategyMuhammad Arif FarhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ardra - MBA FINAL PROJECTDokument90 SeitenArdra - MBA FINAL PROJECTKochuthresia JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) MCQ With Answers PDFDokument4 SeitenEnterprise Performance Management (EPM) MCQ With Answers PDFMijanur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Supply Chain Management Concept 1aDokument20 SeitenThe Supply Chain Management Concept 1aMRK466100% (1)
- Design and Development 1Dokument4 SeitenDesign and Development 1asderbvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questionnaire FormDokument2 SeitenQuestionnaire FormChaudhry Waqar ZafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Packaging On Generation Y's Consumer BehaviourDokument76 SeitenImpact of Packaging On Generation Y's Consumer BehaviourRohith Thampi100% (3)
- Mankiw10e Lecture Slides Ch04Dokument43 SeitenMankiw10e Lecture Slides Ch04Anggi YudhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ey Cafta Case Championship 2022 Chapter 2Dokument17 SeitenEy Cafta Case Championship 2022 Chapter 2Wavare YashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tradesphere Industrial Commodities, Inc.: Chua, Kelvin Uy, Rachel Wu, Ziling Exprodu Te001 (Midterm)Dokument18 SeitenTradesphere Industrial Commodities, Inc.: Chua, Kelvin Uy, Rachel Wu, Ziling Exprodu Te001 (Midterm)Kim UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- RICS Course Guide BIMDokument6 SeitenRICS Course Guide BIMjode2213100% (1)
- IBC Chap 2Dokument28 SeitenIBC Chap 2Chilapalli SaikiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swiggy Refine - AswathyUdhayDokument6 SeitenSwiggy Refine - AswathyUdhayAswathy UdhayakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PWC Insurtechs Transforming ReinsurersDokument7 SeitenPWC Insurtechs Transforming ReinsurersRezky Naufal PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAMEL NCP Tuesday FinalDokument83 SeitenCAMEL NCP Tuesday FinalJoel LampteyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 2 9 Coping With Piracy in ChinaDokument3 SeitenCase 2 9 Coping With Piracy in ChinaChin Kit YeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- UTI - Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) New Editable Application FormDokument4 SeitenUTI - Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) New Editable Application FormAnilmohan SreedharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon's Journey into the AfterlifeVon EverandProof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon's Journey into the AfterlifeBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (165)
- Secrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthVon EverandSecrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (197)
- The Game: Penetrating the Secret Society of Pickup ArtistsVon EverandThe Game: Penetrating the Secret Society of Pickup ArtistsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (131)
- New Zealand Adventure Travel GuideVon EverandNew Zealand Adventure Travel GuideBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (14)
- Coastal Alaska & the Inside Passage Adventure Travel GuideVon EverandCoastal Alaska & the Inside Passage Adventure Travel GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jamaica: A Guide to the Food & RestaurantsVon EverandJamaica: A Guide to the Food & RestaurantsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Geneva, Lausanne, Fribourg & Western Switzerland Travel AdventuresVon EverandGeneva, Lausanne, Fribourg & Western Switzerland Travel AdventuresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adventure Travel Guide to the Georgia & Carolina CoastsVon EverandAdventure Travel Guide to the Georgia & Carolina CoastsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Hollywood & the Best of Los Angeles Travel GuideVon EverandHollywood & the Best of Los Angeles Travel GuideBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)