Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tooth-Mucosa Borne (Extension Base) Partial Denture Design: Force Resultant Movements Counteracted by Longitudinal Axis
Hochgeladen von
Oday Noa'manOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tooth-Mucosa Borne (Extension Base) Partial Denture Design: Force Resultant Movements Counteracted by Longitudinal Axis
Hochgeladen von
Oday Noa'manCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
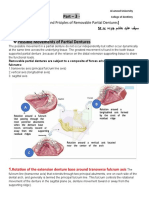
Tooth-mucosa borne (extension base) partial denture design The extension base or toothe-mucosa borne partial denture derives
support from the dento-alveolar and mucosa-osseuo segments. Movements of a distal extention base in response to forces force Mastication (unilateral) Parafunction (clenching) Resultant movements Tissueward movement of the extension base on the loaded side Rotation around a longitudinal axis formed by the ridge crest Dislodging (lifting) of the denture base on the opposite side Tissueward movement of the extension base bilaterally Rotation around the fulcrum line axis Buccolingual movement of the partial denture Rotating around vertical axis near center of arch Movement of extention base away from the ridge Rotation around the retentive fulcrum line axis .the axis passes through the two retentive clasp terminals when direc retention is absent Counteracted by Denture base Maxillary major connector Minor connectors Clasp assemblies Artificial tooth placement Rests
Longitudinal axis
Fulcrum line axis
Mastication (bilateral) Parafunction (clenching) swallowing
Denture base Maxillary major connector Non-stress directing Clasp assemblies rests Denture base Maxillary major connector Minor connectors Clasp bracing components
Vertical axis
Retentive fulcrum line axis
Mastication loading forces may appear obliquely generating horizontal components of force Parafunctional (bruxing) Mastication (sticky foods) Muscles of lips,tongue and cheeks
Direct retainers Indirect retainers Guiding planes and minor connectors Gravity (mandibular)
Diagnostic considerations Evaluate dento-aleveolar support potential ( teeth , periodontium and alveolar bone )
Evaluate muco-osseous support potential (mucosa,submucosa and basal bone ) Evaluate potential of applied forces (opposing occlusion,muscular force potential,parafunctional habits ,length of edentulous span,history of prosthesis failure and histore of poor tissue tolerance ) Design consideration Optimum muco-osseous support ,Optimum dento-alveolar support,Equitable distribution of forces and Reduction of forces applied to the extension base
Factors determining the selection of majer connectors Support Location of dentulous area Anticipater loss of natural teeth Functional depth of the lingual vestibule Inclination of the remating teeth Tissue restrictions Patient preference
Factors determining the selection of denture bases Support adjusments
Factor determining the selection clasp assemblies Distribution of forces Location of undercuts Minimal tooth and minimal gingival Esthetics Clasps on previous removable partial denture
Comparative movments of clasps during function Clasp with mesial rests , clasp with distal rests Mechanics of commonly used clasp assemblies that do not provide stress release Circlet clasp assembly (akers) and embrasure clasp assembly Mechanics of commonly used clasp assemblies that provide strees release RPI clasp assembly , RPC clasp assembly ,cast circumferntial and wrought wire circumferential clasp ,back action clasp and additional clasp designs )
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Orthodontically Driven Corticotomy: Tissue Engineering to Enhance Orthodontic and Multidisciplinary TreatmentVon EverandOrthodontically Driven Corticotomy: Tissue Engineering to Enhance Orthodontic and Multidisciplinary TreatmentFederico BrugnamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distal ExtensionDokument110 SeitenDistal ExtensionParmod GuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchorage in Orthodontic: Shah A, Phulari BSDokument38 SeitenAnchorage in Orthodontic: Shah A, Phulari BSرهف عمرNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ortho Intro #5 - Anchorage and HeadgearDokument5 SeitenOrtho Intro #5 - Anchorage and HeadgearOrion KongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stresses Induced by Removoble Partial DentureDokument85 SeitenStresses Induced by Removoble Partial DentureSimran Sahni100% (2)
- Occulasl Consideration For Implant Supported Prostehsi / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDokument117 SeitenOcculasl Consideration For Implant Supported Prostehsi / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academy100% (2)
- RPD DesigenDokument112 SeitenRPD DesigenMohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supporting Structures For RPDDokument5 SeitenSupporting Structures For RPDLWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of Removable Partial DentureDokument22 SeitenComponents of Removable Partial DentureDanus Jambaksos100% (1)
- Biomechanics of Removable Partial DenturesDokument31 SeitenBiomechanics of Removable Partial DenturesDepressed CowNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAB II (McCracken's Removable Partial Prostodontics)Dokument3 SeitenBAB II (McCracken's Removable Partial Prostodontics)Cattleya TanosseloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Direct Retainer (DR VikasDokument128 SeitenDirect Retainer (DR VikasVikas Aggarwal50% (2)
- Anchorage in Orthodontics Part 1Dokument75 SeitenAnchorage in Orthodontics Part 1Andrei Busmachiu0% (1)
- Part IIDokument129 SeitenPart IIrohan23augNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distal ExtentionDokument33 SeitenDistal ExtentionMohammed HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchorage in OrthodonticsDokument64 SeitenAnchorage in Orthodonticsmanishpankaj1230% (1)
- Nikitha AnchorageDokument116 SeitenNikitha AnchorageMounika S100% (1)
- Occlusal Appliance TherapyDokument32 SeitenOcclusal Appliance TherapyZakria Al-HadadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ortho M6 TO 9Dokument70 SeitenOrtho M6 TO 9JEVELYN D. TUMBAGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cantliver SeminarDokument94 SeitenCantliver Seminarفاطمه شبانهNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchorage: By, Ayesha Khan Ambreen ThobaniDokument33 SeitenAnchorage: By, Ayesha Khan Ambreen ThobaniMaira HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Partial Denture Design FayadDokument53 Seiten2 Partial Denture Design FayadMostafa Fayad100% (3)
- Al-Anbar University, Dental Faculty, Prosthodontics Unit Dr. Salah Kh. Al-Rawi 3 Year/ 1 LecDokument3 SeitenAl-Anbar University, Dental Faculty, Prosthodontics Unit Dr. Salah Kh. Al-Rawi 3 Year/ 1 LecSamer AlRefaayNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioMechanics of Canine RetractionDokument113 SeitenBioMechanics of Canine Retractionarshabharata100% (5)
- Presented By: Satyam Mehta Bds Iv YrDokument29 SeitenPresented By: Satyam Mehta Bds Iv YrGurdeep SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balanced OcclusionDokument120 SeitenBalanced Occlusionrahel sukma100% (5)
- Esthetic Consideration in Gingival Tissue ManagementDokument24 SeitenEsthetic Consideration in Gingival Tissue Managementviva_33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pros FullDokument249 SeitenPros FullAsem Debris100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Occlusion: Reference: Shillingburg Funamentals of Fixed Prosthodontics, Third Edition Chapter TwoDokument44 SeitenFundamentals of Occlusion: Reference: Shillingburg Funamentals of Fixed Prosthodontics, Third Edition Chapter Twoوا إسلاماه100% (2)
- Concepts of Occlusion2010finalfDokument100 SeitenConcepts of Occlusion2010finalfYuchen The HuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchorage in OrthodonticsDokument33 SeitenAnchorage in OrthodonticsMini RobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wishing You All A Very Good MorningDokument34 SeitenWishing You All A Very Good MorningAnisha Mandavia DoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchorage in OrthodonticsDokument49 SeitenAnchorage in OrthodonticsKamal Shanto100% (2)
- Fixed Appliance Design, Function and ConstructionDokument14 SeitenFixed Appliance Design, Function and Constructionsp vumbunu100% (1)
- 4.2 Direct RetainerDokument38 Seiten4.2 Direct RetainerMujtaba AlsalehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canine Impaction Different MethodsDokument11 SeitenCanine Impaction Different MethodsMSHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prostho Sheet 2Dokument31 SeitenProstho Sheet 2Yomna NimerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stresses Induced by CPD-FinalDokument26 SeitenStresses Induced by CPD-FinalNikita AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Considerations in RPD For Control of StressDokument7 SeitenDesign Considerations in RPD For Control of StressSahana RangarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson - 1-Dental Prosthetics and DentistryDokument35 SeitenLesson - 1-Dental Prosthetics and DentistryDuncan MakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penjangkaran: Yenny Yustisia Bag. Ortodonsia FKG UnejDokument47 SeitenPenjangkaran: Yenny Yustisia Bag. Ortodonsia FKG UnejPrima D AndriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec.9 Ortho. MovementDokument10 SeitenLec.9 Ortho. MovementSaid SaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- OsteotomyDokument4 SeitenOsteotomyMihai DuduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attachment5th ClassDokument10 SeitenAttachment5th ClasswxmdkhbyvkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Restoration of Edentulous Maxillae With OverdenturesDokument29 SeitenRestoration of Edentulous Maxillae With OverdenturesCostina BolboriciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress BreakersDokument7 SeitenStress BreakerssavyasachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space Closing Mechanics - DIFFERENT LOOPSDokument147 SeitenSpace Closing Mechanics - DIFFERENT LOOPSdrarjunvedvyas100% (18)
- Hiral Abutment Selection Part 2Dokument46 SeitenHiral Abutment Selection Part 2khushbu samaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- GTC 1 - Introduction To Fixed Prosthodontics (PPSG Lectures)Dokument52 SeitenGTC 1 - Introduction To Fixed Prosthodontics (PPSG Lectures)rositadewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPT 9Dokument37 SeitenGPT 9MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar 13Dokument60 SeitenSeminar 13radhikamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of RPD DesignDokument59 SeitenPrinciples of RPD DesignanushiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part - - (: St.n: هدوج مشاه دياع فيس Possible Movements of Partial DenturesDokument4 SeitenPart - - (: St.n: هدوج مشاه دياع فيس Possible Movements of Partial DenturesSaif AyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Dental Implantology: Dr. Nigam Sattar KhanDokument49 SeitenIntroduction To Dental Implantology: Dr. Nigam Sattar KhanNigam SattarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Distal Extension Base Denture.1 PDFDokument5 SeitenThe Distal Extension Base Denture.1 PDFenlighten070% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Evaluation of Available BoneDokument24 SeitenChapter 3 - Evaluation of Available BoneKomal TalrejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- R.P.I ConceptDokument6 SeitenR.P.I ConceptVikas AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Locating The Center of Resistance of Maxillary AnteriorDokument17 SeitenLocating The Center of Resistance of Maxillary AnteriorMoniek GuoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory 4 Dental Waxes and Investment Materials Answer The Following Questions and Hand in Your Report As A Group (Typed Not Hand Written)Dokument3 SeitenLaboratory 4 Dental Waxes and Investment Materials Answer The Following Questions and Hand in Your Report As A Group (Typed Not Hand Written)Oday Noa'manNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3 Assignment 2012Dokument2 SeitenLab 3 Assignment 2012Abdallah Essam Al-ZireeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2 Assignment 2012Dokument2 SeitenLab 2 Assignment 2012Ismail Bazly ZarirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 5. Microbial DiversityDokument34 SeitenBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 5. Microbial DiversityOday Noa'manNoch keine Bewertungen
- D 7752Dokument6 SeitenD 7752Asep TheaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eliasmith2012-Large-scale Model of The BrainDokument5 SeitenEliasmith2012-Large-scale Model of The Brainiulia andreeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 Front SheetDokument9 SeitenAssignment 1 Front SheetBách PhạmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reduce, Reuse, RecycleDokument9 SeitenReduce, Reuse, RecyclemarieangeluNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual: Samsung Medison Diagnostic Ultrasound SystemDokument686 SeitenUser Manual: Samsung Medison Diagnostic Ultrasound SystemHuế Trần100% (1)
- Foundations of Group BehaviorDokument31 SeitenFoundations of Group BehaviorRaunakNoch keine Bewertungen
- XII Biology Practicals 2020-21 Without ReadingDokument32 SeitenXII Biology Practicals 2020-21 Without ReadingStylish HeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bar Exam Questions Week 1Dokument30 SeitenBar Exam Questions Week 1Mark Bantigue100% (1)
- Importance of The On Board Crew Trainings and Drills For The Improvement of The Vessels' SafetyDokument8 SeitenImportance of The On Board Crew Trainings and Drills For The Improvement of The Vessels' SafetyilgarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TMP DEDADokument8 SeitenTMP DEDAFrontiersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Di SilvioDokument47 SeitenDi SilviomaryroseengNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Research Presented ToDokument28 SeitenA Research Presented ToAngeliePanerioGonzagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cable Selection Table For CapacitorDokument1 SeiteCable Selection Table For CapacitorShashiSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safey Data Sheet: 1 Identification of SubstanceDokument6 SeitenMaterial Safey Data Sheet: 1 Identification of SubstanceRaihan MajumderNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Study Resource Was: Current Asset - Cash & Cash Equivalents CompositionsDokument2 SeitenThis Study Resource Was: Current Asset - Cash & Cash Equivalents CompositionsKim TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Vital Statistics Reports: Births: Final Data For 2019Dokument51 SeitenNational Vital Statistics Reports: Births: Final Data For 2019Simon ReichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decide If Surrogacy Is The Right ChoiceDokument13 SeitenDecide If Surrogacy Is The Right ChoiceSheen CatayongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication Edition 2020Dokument230 SeitenPublication Edition 2020Mech Dept GMITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switchyard Equipments, Switching Schmes & LayoutsDokument66 SeitenSwitchyard Equipments, Switching Schmes & LayoutsPraveen Kumar88% (17)
- Cruz v. CA - G.R. No. 122445 - November 18, 1997 - DIGESTDokument2 SeitenCruz v. CA - G.R. No. 122445 - November 18, 1997 - DIGESTAaron Ariston80% (5)
- Vertico SynchroDokument16 SeitenVertico SynchrozpramasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wrestling Strength and ConditioningDokument12 SeitenWrestling Strength and ConditioningTintin BilatbatNoch keine Bewertungen
- API 572 Practise QuestionDokument58 SeitenAPI 572 Practise Questionbelonk_182100% (6)
- Mammalian Temperature Regulation - 12Dokument13 SeitenMammalian Temperature Regulation - 12wadson chirwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOCDokument14 SeitenTOCAthirah HattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Prerequisite Program v2Dokument78 SeitenComplete Prerequisite Program v2Ramasubramanian Sankaranarayanan100% (1)
- Science Grade 7: Active Reading Note-Taking GuideDokument140 SeitenScience Grade 7: Active Reading Note-Taking Guideurker100% (1)
- RSA 12 - Laser Attacks Safety GuidelinesDokument19 SeitenRSA 12 - Laser Attacks Safety Guidelinesrona putriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Savings at DCL PDFDokument83 SeitenEnergy Savings at DCL PDFnsprasad88100% (1)
- Data Sheet HFE-7000 Prod SpecDokument6 SeitenData Sheet HFE-7000 Prod Specsshaffer_9Noch keine Bewertungen