Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
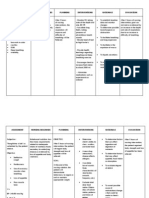
Definition of Terms
Hochgeladen von
Abegail AbaygarOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Definition of Terms
Hochgeladen von
Abegail AbaygarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Definition of Terms To convey clearly the meaning of the words used in this study, the researcher defined the
terms used operationally, as follows: Bioethics - is the study of typically controversial ethics brought about by advances in biology and medicine. It is also moral discernment as it relates to medical policy, practice, and research. Bioethicists are concerned with the ethical questions that arise in the relationships among sciences, biotechnology, medicine, politics, law, and philosophy. It also includes the study of the more commonplace questions of values ("the ethics of the ordinary") which arise in primary care and other branches of medicine. Ethics - also known as moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong conduct. Nursing Ethics - is a branch of applied ethics that concerns itself with activities in the field of nursing. Nursing ethics shares many principles with medical ethics, such
as beneficence, non-maleficence and respect for autonomy. It can be distinguished by its emphasis on relationships, human dignity and collaborative care. Nursing - is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Ethical Dilemmas - is a complex situation that often involves an apparent mental conflict between moral imperatives, in which to obey one would result in transgressing another. This is also called an ethical paradox since in moral philosophy, paradox often plays a central role in ethics debates. Ethical dilemmas are often cited in an attempt to refute an ethical system or moral code, as well as the worldview that encompasses or grows from it.
Duty of Care - is a legal obligation imposed on an individual requiring that they adhere to a standard of reasonable care while performing any acts that could foreseeably harms others. It is the first element that must be established to proceed with an action in negligence. Nurse-patient relationship - in Hildegard E. Peplau's Interpersonal Relations Model theory is essential to nursing practice. It is the nurseclient interaction that is toward enhancing the client's well-being, and the client may be an individual, a family, a group or a community. Healthcare System - is the organization of people, institutions, and resources to deliver health care services to meet the health needs of target populations. Profession - is a vocation founded upon specialized educational training, the purpose of which is to supply objective counsel and service to others, for a direct and definite compensation, wholly apart from expectation of other business gain. Collaborative Care - is a healthcare philosophy and movement that has many names, models, and definitions that often includes the provision of mental health, behavioral health and substance use services in primary care. Clinical Practice - is defined as a model of practice that involves those activities with and on behalf of clients, especially those activities completed in the clients presence and with the clients collaboration. These activities are informed by an ecologically based Bio Psychosocial Assessment. Societal Development - tempts to explain qualitative changes in the structure and framework of society that help the society to better realize its aims and objectives. Development can be broadly defined in a manner applicable to all societies at all historical periods as an upward ascending movement featuring greater levels of energy, efficiency, quality, productivity, complexity, comprehension, creativity, mastery, enjoyment and accomplishment.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ethics Handbook for Energy Healing Practitioners: : A Guide for the Professional Practice of Energy Medicine and Energy PsychologyVon EverandEthics Handbook for Energy Healing Practitioners: : A Guide for the Professional Practice of Energy Medicine and Energy PsychologyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Intoduction To Nursing EthicsDokument17 SeitenIntoduction To Nursing EthicsAnjo Pasiolco CanicosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics of care and conscientious objectionVon EverandEthics of care and conscientious objectionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics in Health Services Management, Sixth Edition (Excerpt)Dokument12 SeitenEthics in Health Services Management, Sixth Edition (Excerpt)Health Professions Press, an imprint of Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co., Inc.57% (7)
- Ethical Diversity in Healthcare Delivery: Ethics in Healthcare & BeyondVon EverandEthical Diversity in Healthcare Delivery: Ethics in Healthcare & BeyondNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioethicsDokument1 SeiteBioethicsNica Mariz Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Nursing EthicsDokument18 SeitenIntroduction To Nursing EthicsAbeer salehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal and Ethical Issues in NursingDokument14 SeitenLegal and Ethical Issues in NursingRohini Rai0% (1)
- HCE Module 1 - Introduction To Health Care EthicsDokument4 SeitenHCE Module 1 - Introduction To Health Care EthicsAlaiza AvergonzadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healthcare Ethics l1Dokument4 SeitenHealthcare Ethics l122-55921Noch keine Bewertungen
- NATUNO - LEIRA - Pre AssessmentDokument1 SeiteNATUNO - LEIRA - Pre AssessmentLei KeneptNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conceptual Framework SystemsDokument13 SeitenConceptual Framework SystemsClara Ines0% (1)
- Code of Ethics Types of LawDokument39 SeitenCode of Ethics Types of Lawsusan_grace123100% (1)
- Legeal & EthicalDokument6 SeitenLegeal & EthicalNaro LemtorNoch keine Bewertungen
- KD BN Prima Facie 2013Dokument60 SeitenKD BN Prima Facie 2013Aldo HamkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal & Ethical IssuesDokument13 SeitenLegal & Ethical IssuesAnusha Verghese50% (2)
- Code of EthicsDokument12 SeitenCode of EthicsFriends ForeverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing EthicsDokument6 SeitenNursing EthicsAliza Bea CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 CHN 1Dokument6 SeitenModule 2 CHN 1Danz KieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal N Ethical Issues in CCNDokument12 SeitenLegal N Ethical Issues in CCNPoova RagavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TFN SES 3 - Chap8 - 9Dokument54 SeitenTFN SES 3 - Chap8 - 9Prince Charles AbalosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1. EthicsDokument11 SeitenLecture 1. EthicsMuez AlkeblawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics PrinciplesDokument20 SeitenEthics PrinciplesZizi ZiziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Care Ethics 2024Dokument13 SeitenHealth Care Ethics 2024celestineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Room Presentation: Subject: Advanced Nursing PracticeDokument17 SeitenClass Room Presentation: Subject: Advanced Nursing PracticeJinto PhilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joyce FDokument7 SeitenJoyce FAnj Perez BondocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics and Derontology in MidwiveryDokument55 SeitenEthics and Derontology in Midwiverymbok diyirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1: THEORIES AND PRINCIPLES OF HEALTH CARE ETHICS (39 charactersDokument17 SeitenModule 1: THEORIES AND PRINCIPLES OF HEALTH CARE ETHICS (39 charactersblaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOPIC E Principles of BioethicsDokument12 SeitenTOPIC E Principles of BioethicsblaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics HWDokument8 SeitenEthics HWhelloaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nur 223 Health Care Ethics (Bioethics)Dokument42 SeitenNur 223 Health Care Ethics (Bioethics)Gemmalene PaclebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of Ethics of INC AND ICNDokument5 SeitenCode of Ethics of INC AND ICNanimesh pandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of EthicsDokument17 SeitenCode of EthicsSundaraBharathi100% (2)
- FUNDADokument6 SeitenFUNDARichard Castada Guanzon Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- ANA Code of EthicsDokument14 SeitenANA Code of EthicsyayayogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM108 Module1 Topic A 1stsem20-21Dokument4 SeitenNCM108 Module1 Topic A 1stsem20-21mirai desuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theoretical Basis of Community Health Nursing-1Dokument49 SeitenTheoretical Basis of Community Health Nursing-1Sri WahyuniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Therapuetic NurseDokument4 SeitenTherapuetic NurseAzimah Mohd MasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSG As A PRFSN Set 3Dokument25 SeitenNSG As A PRFSN Set 3saranya amuNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUGAS KEPERAWATAN TRANSKULTURAL - Ceri Lee - 9103022002Dokument3 SeitenTUGAS KEPERAWATAN TRANSKULTURAL - Ceri Lee - 9103022002CerileeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal and Ethical Issues FinalDokument8 SeitenLegal and Ethical Issues FinalmandykalerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 A. Fundamentals of Pharmacy Practice PDFDokument270 Seiten8 A. Fundamentals of Pharmacy Practice PDFaulia haninNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer Health EducDokument4 SeitenReviewer Health Educjulia.caballero0107Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phenomenon-A Term Given To Describe An Idea or Response About An Event, ADokument10 SeitenPhenomenon-A Term Given To Describe An Idea or Response About An Event, AYesha Therese Eduarte MagsombolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dimensions of Health and WellnessDokument4 SeitenDimensions of Health and WellnessJoylyn Mendez LlenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Practice in Physical TherapyDokument19 SeitenProfessional Practice in Physical TherapyRizwan BashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Nursing Ethics: Foundations of ResponsibilitiesDokument24 SeitenBasic Nursing Ethics: Foundations of ResponsibilitiesAndrea TylerNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Health EducationDokument19 SeitenHistory of Health EducationVictor Z. DyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HealthEthics ResDokument2 SeitenHealthEthics ResNicole QuinsayasNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEALTH ETHICS: UNDERSTANDING THE ETHICAL IMPLICATIONS OF MODERN HEALTHCAREDokument10 SeitenHEALTH ETHICS: UNDERSTANDING THE ETHICAL IMPLICATIONS OF MODERN HEALTHCAREMelchor Felipe Salvosa100% (1)
- Ethics in NursingDokument8 SeitenEthics in NursingPappsy De MungaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ppts EthicsDokument55 SeitenPpts EthicsSimran JosanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical PrinciplesDokument7 SeitenEthical PrinciplesimanumeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Legal Issues Related To Gerontological Care HCDokument41 SeitenEthical Legal Issues Related To Gerontological Care HCtamika sealyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concepts and Definitions MOL-AOLDokument4 SeitenBasic Concepts and Definitions MOL-AOLNicole Allyson DomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaidah Dasar Bioetika & Prima FacieDokument60 SeitenKaidah Dasar Bioetika & Prima FacieSamdiSutantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtue Ethics in Nursing - Focus on CharacterDokument4 SeitenVirtue Ethics in Nursing - Focus on CharacterChubs Riego100% (1)
- EthicsDokument107 SeitenEthicsaa zzNoch keine Bewertungen
- HemmorhoidectomyDokument3 SeitenHemmorhoidectomyAbegail AbaygarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan !Dokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan !Abegail AbaygarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map - Abby !Dokument2 SeitenConcept Map - Abby !Abegail AbaygarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study and NCP!Dokument8 SeitenDrug Study and NCP!Abegail Abaygar100% (1)
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPAbegail Abaygar100% (1)
- DfgdfgdfsdsadaDokument328 SeitenDfgdfgdfsdsadaabulhayat1969Noch keine Bewertungen
- History and Philosophy of Sports 2Dokument12 SeitenHistory and Philosophy of Sports 2Demic CascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To SemanticsDokument18 SeitenIntroduction To SemanticsM Naeem Raza100% (6)
- The Validity of Knowledge: Chapter XivDokument10 SeitenThe Validity of Knowledge: Chapter Xivbeni rimananNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Power of Communication Ek Ruka Hua FaislaDokument3 SeitenThe Power of Communication Ek Ruka Hua FaislaYogesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atlas ShruggedDokument6 SeitenAtlas ShruggedAustin Kohlman50% (2)
- Character Building: Pancasila: Comparison of Pancasila Ideology With Liberalism and CommunismDokument12 SeitenCharacter Building: Pancasila: Comparison of Pancasila Ideology With Liberalism and CommunismPura AmiliiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raffestin Space, Territory, TerritorialityDokument22 SeitenRaffestin Space, Territory, TerritorialitySamuel Daza CáceresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Estate Research MethodsDokument9 SeitenReal Estate Research Methodsbhau_bhauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus-Folk Literature in English TranslationDokument22 SeitenSyllabus-Folk Literature in English TranslationMariecris Barayuga Duldulao-AbelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETHICSDokument2 SeitenETHICSRosevick BadocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReedDokument3 SeitenReedPam-plang BorbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linguistic AnthropologyDokument2 SeitenLinguistic AnthropologyMuhammad RiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 Personalities TypesDokument16 Seiten16 Personalities Typestrapinkk10% (10)
- David Harvey - Explanation in Geography-Edward Arnold (1986) PDFDokument541 SeitenDavid Harvey - Explanation in Geography-Edward Arnold (1986) PDFAntonio Carelli100% (4)
- All Things Are Possible To Him Who BelieveDokument20 SeitenAll Things Are Possible To Him Who BelieveKrishnan Subrahmanyam100% (3)
- The PlagueDokument5 SeitenThe PlaguePrivate ChannelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entrepreneurship Theory of Cantillon and SchumpeterDokument6 SeitenEntrepreneurship Theory of Cantillon and SchumpeterYan ŸanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Humanistic Interpretive Approaches in AnthropologyDokument3 SeitenHumanistic Interpretive Approaches in AnthropologyNIlesh BhagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Common GoodDokument3 SeitenThe Common GoodGaby TaniosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bertrand Russell BooksDokument8 SeitenBertrand Russell BooksBo AndyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Queenborough - Occult Theocracy v2.01Dokument793 SeitenQueenborough - Occult Theocracy v2.01robo707100% (1)
- The University of Chicago PressDokument20 SeitenThe University of Chicago PressBob_McBobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory U Exec SummaryDokument21 SeitenTheory U Exec SummaryJohn Michael100% (8)
- Mufaro's Daughters Show True CharacterDokument6 SeitenMufaro's Daughters Show True CharacterAkari Chan0% (1)
- Christian Lotz - The Art of Gerhard Richter - Hermeneutics, Images, Meaning-Bloomsbury Academic (2015)Dokument273 SeitenChristian Lotz - The Art of Gerhard Richter - Hermeneutics, Images, Meaning-Bloomsbury Academic (2015)Hugo Houayek100% (2)
- Philip McMichael Incorporating ComparisonDokument14 SeitenPhilip McMichael Incorporating Comparisoncesarzaldivar1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics ALL LESSONS PRELIM FlashcardsDokument17 SeitenEthics ALL LESSONS PRELIM FlashcardsJoshua LagonoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Haskins) Practical Guide To Critical Thinking PDFDokument14 Seiten(Haskins) Practical Guide To Critical Thinking PDFZack100% (1)
- 2016 Book TheSocialDevelopmentalConstrucDokument256 Seiten2016 Book TheSocialDevelopmentalConstrucYazmin Medina Hernandez100% (1)
- Hell Put to Shame: The 1921 Murder Farm Massacre and the Horror of America's Second SlaveryVon EverandHell Put to Shame: The 1921 Murder Farm Massacre and the Horror of America's Second SlaveryBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Prisoners of Geography: Ten Maps That Explain Everything About the WorldVon EverandPrisoners of Geography: Ten Maps That Explain Everything About the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1143)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broken: The most shocking childhood story ever told. An inspirational author who survived it.Von EverandBroken: The most shocking childhood story ever told. An inspirational author who survived it.Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (42)
- 1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed: Revised and UpdatedVon Everand1177 B.C.: The Year Civilization Collapsed: Revised and UpdatedBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (109)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (31)
- If You Tell: A True Story of Murder, Family Secrets, and the Unbreakable Bond of SisterhoodVon EverandIf You Tell: A True Story of Murder, Family Secrets, and the Unbreakable Bond of SisterhoodBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1788)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (327)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- Selling the Dream: The Billion-Dollar Industry Bankrupting AmericansVon EverandSelling the Dream: The Billion-Dollar Industry Bankrupting AmericansBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (17)
- The Last Outlaws: The Desperate Final Days of the Dalton GangVon EverandThe Last Outlaws: The Desperate Final Days of the Dalton GangBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryVon EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (44)
- The Body Is Not an Apology, Second Edition: The Power of Radical Self-LoveVon EverandThe Body Is Not an Apology, Second Edition: The Power of Radical Self-LoveBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (364)
- Nicole Brown Simpson: The Private Diary of a Life InterruptedVon EverandNicole Brown Simpson: The Private Diary of a Life InterruptedBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (16)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassVon EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (21)
- Hearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBIVon EverandHearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBIBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (19)
- The Girls Are Gone: The True Story of Two Sisters Who Vanished, the Father Who Kept Searching, and the Adults Who Conspired to Keep the Truth HiddenVon EverandThe Girls Are Gone: The True Story of Two Sisters Who Vanished, the Father Who Kept Searching, and the Adults Who Conspired to Keep the Truth HiddenBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (36)
- Reasonable Doubts: The O.J. Simpson Case and the Criminal Justice SystemVon EverandReasonable Doubts: The O.J. Simpson Case and the Criminal Justice SystemBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (25)
- Swamp Kings: The Story of the Murdaugh Family of South Carolina & a Century of Backwoods PowerVon EverandSwamp Kings: The Story of the Murdaugh Family of South Carolina & a Century of Backwoods PowerNoch keine Bewertungen
- For the Love of Men: From Toxic to a More Mindful MasculinityVon EverandFor the Love of Men: From Toxic to a More Mindful MasculinityBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (56)
- Hey, Hun: Sales, Sisterhood, Supremacy, and the Other Lies Behind Multilevel MarketingVon EverandHey, Hun: Sales, Sisterhood, Supremacy, and the Other Lies Behind Multilevel MarketingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (102)
- The Exvangelicals: Loving, Living, and Leaving the White Evangelical ChurchVon EverandThe Exvangelicals: Loving, Living, and Leaving the White Evangelical ChurchBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (12)
- His Needs, Her Needs: Building a Marriage That LastsVon EverandHis Needs, Her Needs: Building a Marriage That LastsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (99)
- Briefly Perfectly Human: Making an Authentic Life by Getting Real About the EndVon EverandBriefly Perfectly Human: Making an Authentic Life by Getting Real About the EndNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyVon EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (31)