Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
AS Level Physics
Hochgeladen von
Arthur WongOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
AS Level Physics
Hochgeladen von
Arthur WongCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
AS Edexcel Physics unit 2
UNIT 2 - Waves
Shehan Rashmika Livera
Waves Mechanical waves Requires a medium. Generated by vibrated sources. The energy is transferred to the medium and transmitted by the particles. There are two types of mechanical waves: Longitudinal and Transverse Waves.
Longitudinal The direction of the wave is parallel to the vibration of the source. They have compressions and rare fractions. Experiment to observe the longitudinal wave Slinky. Examples of longitudinal waves Sound, Earthquakes
Transverse Waves The direction of the wave is perpendicular to the vibration. Can be polarized Examples Light, water wave, guitar strings.
Amplitude - Is the maximum displacement from the mean position of a particle. Period is the time taken for one complete oscillation. Frequency is the number of complete oscillations per second. Phase - is the position within a cycle that a particle occupies related to the onset of the cycle.
Electromagnetic waves Electromagnetic waves are created when charged particles are accelerated. Examples Radio waves Electromagnetic waves can also be created as a result of quantum jumps of electrons in atoms or from excited nuclei. The waves produced in this manner are emitted as photons. Photon is a discrete packet of energy.
Shehan Rashmika Livera
Waves
Wave equations
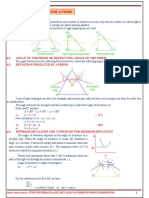
Reflections The law of reflection states that the angle between the incident ray and a normal drawn at the point of reflection is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal in the plane of the reflection. Refraction A ray of light at an angle to the normal changes direction when it passes from one medium to another. This effect is due to the change in wave speed and is known as refraction.
The ratio of the speeds in called the refractive index between the media: Refractive index from medium 1 to 2 =
Snells law
The incident angle and the refracted angle.
Shehan Rashmika Livera
Waves Critical angle and total internal reflection The angle at which total internal reflection occurs is termed as the critical angle.
Polarisation Transverse waves with particles oscillating in one plane only are said to be plane polarised. Longitudinal waves do not polarise. Because it does not have perpendicular motion in its wave.
Applications Anti glare sunglasses. Doppler Effect- The change in frequency due to the relative motion of the source to the observer is known as Doppler Effect.
This is dependent on the ratio of the speed of the moving source. Is the change in frequency f is the frequency, v is the velocity and c is the speed of light in vacuum. Applications - Mostly used in medicine; a blood blockage due to a clot can be detected sending ultrasound wave, and a pulse in heart. Super-positions When the waves add together to give maximum amplitude, constructive superposition occurs; when zero amplitude, destructive superposition.
Coherent sources Have same frequency and maintain a constant phase relationship. Maximum wavelength path difference Whole number or zero: in phase and constructive super position. /2 number will occur to destructive superposition.
To have stable interference: the wave are the same type the source are coherent the waves have similar amplitude at the point of super position.
Shehan Rashmika Livera
Waves
Diffraction When a wave passes through a gap or partially obstructed by a barrier, the wavefront spreads out into the shadow region. Its called Diffraction. Has the maximum diffraction when the wavelength of wave is equal to the length of the slit(gap) Wavelength of light is 400-700nm. 400nm Red and 700nm Blue wavelength
Shehan Rashmika Livera
Waves
Shehan Rashmika Livera
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1091)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Ewald's SphereDokument3 SeitenEwald's SphereVinodh SrinivasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seeleys Anatomy and Physiology 11th Edition Vanputte Test BankDokument24 SeitenSeeleys Anatomy and Physiology 11th Edition Vanputte Test BankHeatherWeaverioztf100% (40)
- Physics Wave Optics MCQDokument3 SeitenPhysics Wave Optics MCQManjunath Sripathy100% (4)
- Geofile: SuperpowersDokument4 SeitenGeofile: SuperpowersArthur WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRX CircuitsDokument9 SeitenTRX Circuitsarizona212100% (1)
- Guided Wave Photonics Fundamentals and Applications With MATLABDokument786 SeitenGuided Wave Photonics Fundamentals and Applications With MATLABdagouyi100% (4)
- Solu of Agarwal 4th EdtDokument38 SeitenSolu of Agarwal 4th EdtTamil Beats50% (4)
- A Practical Guide To Binocular CollimationDokument23 SeitenA Practical Guide To Binocular CollimationAlemx Ter67% (3)
- Chaika Lenses - Part 1 PDFDokument10 SeitenChaika Lenses - Part 1 PDFJoe GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deindividuation TheoryDokument4 SeitenDeindividuation TheoryArthur WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circle Voice 43-2 PDFDokument11 SeitenCircle Voice 43-2 PDFArthur WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV SampleDokument14 SeitenCV SampleArthur WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE (UNIT 5) (MCQS)Dokument21 SeitenCHE (UNIT 5) (MCQS)Aniket RupnawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- XRF Report PDFDokument11 SeitenXRF Report PDFIshtiaq AnjumNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEM and TEM BasicsDokument7 SeitenSEM and TEM BasicsJesús Rodríguez Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- AstigmatismDokument45 SeitenAstigmatismEevaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.TECH All 1st SEMDokument3 SeitenB.TECH All 1st SEMumesh.developer498Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 2Dokument7 SeitenExperiment No. 2shivansh4shekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEE Metamaterials Presentation-2Dokument23 SeitenIEEE Metamaterials Presentation-2Yaadeshkumaar100% (1)
- 3R-MSUSB Catalog CS5 En-1Dokument1 Seite3R-MSUSB Catalog CS5 En-1h_878236333Noch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Instruments: SubtitleDokument23 SeitenOptical Instruments: Subtitlestrxwberry creamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Thermo Scientific iCAP 7000 Plus Series ICP-OES Unique Charge Injection Device (CID) DetectorDokument4 SeitenThe Thermo Scientific iCAP 7000 Plus Series ICP-OES Unique Charge Injection Device (CID) DetectorTak Man TungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dielectric Waveguides and Optical FibersDokument191 SeitenDielectric Waveguides and Optical FibersVijay JanyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar (PLASMONICS)Dokument10 SeitenSeminar (PLASMONICS)Ankit JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)Dokument19 SeitenWavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)Mehroz FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-09: Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDokument5 SeitenCBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-09: Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsMayank MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jonathan Tennyson Et Al - Continuum States of The Hydrogen Molecule With The R-Matrix MethodDokument10 SeitenJonathan Tennyson Et Al - Continuum States of The Hydrogen Molecule With The R-Matrix MethodMaxnamewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectroscopy - Rotational Spectroscopy - WikiversityDokument36 SeitenSpectroscopy - Rotational Spectroscopy - WikiversityKishore KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIGMA Lens EnglishDokument15 SeitenSIGMA Lens Englishaleksandar71Noch keine Bewertungen
- HJHJBBBBDokument6 SeitenHJHJBBBBSupri GunNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Quantum Theory of Atoms - Spectroscopy in BoxesDokument20 SeitenThe Quantum Theory of Atoms - Spectroscopy in Boxesfun toNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refraction Through A Prism: Equilateral Prism Right Angled Prism Right Angled Isosceles PrismDokument7 SeitenRefraction Through A Prism: Equilateral Prism Right Angled Prism Right Angled Isosceles Prismashok pradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Data Reduction Using Matlab For Different Speckle Images Form Small Surfaces RoughnessDokument10 SeitenThe Data Reduction Using Matlab For Different Speckle Images Form Small Surfaces RoughnessIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edunova: Standard: 12 Subject: Physics Date: 03/07/2021 Marks: 200 Geometrical Optics - Refraction Time: 02H:00MDokument5 SeitenEdunova: Standard: 12 Subject: Physics Date: 03/07/2021 Marks: 200 Geometrical Optics - Refraction Time: 02H:00MVIKRAM CHOUDHARYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atkins, Solution, 7th EdDokument11 SeitenAtkins, Solution, 7th Edapi-3723327Noch keine Bewertungen