Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
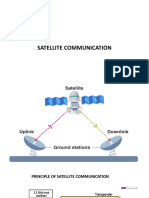
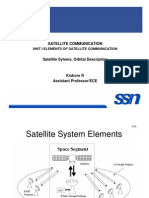
FDMA
Hochgeladen von
Shiju RaghavanOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
FDMA
Hochgeladen von
Shiju RaghavanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1/18
Unit II Transmission, Multiplexing, Modulation, Multiple Access & Coding
FDMA
Kishore R Assistant Professor/ECE
2/18
Objective
At the end of the session students will be able to understand Frequency Division Multiple Access Types of FDMA SPADE system
3/18
FDMA
4/18
FDMA
SHARE THE FREQUENCY
TIME IS COMMON TO ALL SIGNALS
DEVELOP A FREQUENCY PLAN FROM USER CAPACITY REQUESTS TRANSPONDER LOADING PLAN USED TO MINIMIZE IM PRODUCTS
TRANSPONDER LOADING PLAN
5/18
FDMA TRANSPONDER LOADING PLAN
Four medium-sized FM signals One large and four small digital signals
Available transponder bandwidth typically 27 to 72 MHz IMPORTANT TO CALCULATE INTERMODULATION PRODUCTS
6/18
INTERMODULATION
INTERMODULATION
WHEN TWO, OR MORE, SIGNALS ARE PRESENT IN A CHANNEL, THE SIGNALS CAN MIX TOGETHER TO FORM SOME UNWANTED PRODUCTS WITH THREE SIGNALS, 1, 2 AND 3, PRESENT IN A CHANNEL, IM PRODUCTS CAN BE SECOND-ORDER, THIRD-ORDER, FOURTH-ORDER, ETC.
ORDER OF IM PRODUCTS
7/18
IM PRODUCT ORDER
Second-order is 1 + 2, 2 + 3, 1 + 3 Third-order is 1 + 2 + 3, 21 - 2, 22 1.. Usually, only the odd-order IM products fall within the passband of the channel Amplitude reduces as order rises Only third-order IM products are usually important
3-IM products very sensitive to small signal changes. Hence, IM noise can change sharply with output amplifier back-off
8/18
IM EXAMPLE
There are two 10 MHz signals at 6.01 GHz and 6.02 GHz centered in a 72 MHz transponder 2-IM product is at 12.03 GHz 3-IM products are at [2(6.01) - 6.02] = 6.00 and [2(6.02) - 6.01] = 6.03 GHz
3-IM products
9/18
FDMA LIMITATIONS
Intermods cause C/N to fall Back-Off is needed to reduce IM Parts of band cannot be used because of IM Transponder power is shared amongst carriers Power balancing must be done carefully Frequencies get tied to routes
Patterned after terrestrial analog telecoms and so does not confer the full benefit of satellite broadcast capabilities
Single Access-Preassigned FDMA
10/18
11/18
Preassignment also may be made on the basis of a single channel per carrier (SCPC) single voice (or data) channel per carrier, not a transponder channel, which may in fact carry some hundreds of voice channels by this method. The carriers may be frequency modulated or phase-shift modulated earth station may be capable of transmitting one or more SCPC signals simultaneously
Example: Fixed Assignment
12/18
13/18
Demand Assignment
Demand assignment may be carried out in a number of ways In the polling method, a master earth station continuously polls all the earth stations in sequence if a call request is encountered Frequency slots are assigned from the pool of available frequencies The polling delay with such a system tends to become excessive as the number of participating earth stations increases
Instead of using a polling sequence, earth stations may request calls through the master earth station as the need arises centrally controlled random access The requests go over a digital orderwire, which is a narrowband digital radio link or a circuit through a satellite transponder reserved for this purpose. Frequencies are assigned, if available, by the master station, and when the call is completed, the frequencies are returned to the pool If no frequencies are available, the blocked call requests may be placed in a queue or a second call attempt may be initiated by the requesting station.
14/18
15/18
Instead of centrally controlled random access, control may be exercised at each earth station this being known as distributed control random access A good illustration of such a system is provided by the Spade system operated by INTELSAT on some of its satellites.
16/18
Channeling Scheme for SPADE
SPADE System
17/18
18/18
Summary
Preassigned FDMA Demand Assignment FDMA SCPC - SPADE
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GVon EverandIndoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 20-Module 4 Multiple Access Techniques - Reference Materials-09-11-2021 (09-Nov-2021) Material - I - 09-11-2021 - Multiple - Acess - TDokument49 Seiten20-Module 4 Multiple Access Techniques - Reference Materials-09-11-2021 (09-Nov-2021) Material - I - 09-11-2021 - Multiple - Acess - TGUNNSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Access TechniquesDokument114 SeitenMultiple Access TechniquesParthipan ParthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 Multiple Access TechniqueDokument57 SeitenUnit 5 Multiple Access TechniqueVinamra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EA-452 Chap9Dokument135 SeitenEA-452 Chap9ganeshuitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Acess TechniquesDokument49 SeitenMultiple Acess TechniquesGahan A V GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SatCom 5.1Dokument11 SeitenSatCom 5.1ThiruGovindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hybrid Multiple AccessDokument7 SeitenHybrid Multiple AccessParthipan Parthi100% (1)
- Study of Conventional and Wavelet Based Ofdm SystemsDokument36 SeitenStudy of Conventional and Wavelet Based Ofdm SystemsSai Revathi ChanduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering: Satish Kanapala, Assistant ProfessorDokument43 SeitenDepartment of Electronics & Communication Engineering: Satish Kanapala, Assistant ProfessorKvnsumeshChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Access TechniquesDokument50 SeitenMultiple Access TechniquesHarsha BomannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Access and Satellite CommunicationDokument72 SeitenMultiple Access and Satellite CommunicationAnees KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Access-FDMA, CDMA, TDMA, SDMA, DSSS, FHSS, ALOHA, PACKET RADIO...Dokument82 SeitenMultiple Access-FDMA, CDMA, TDMA, SDMA, DSSS, FHSS, ALOHA, PACKET RADIO...gk_gbu100% (4)
- Multiple Access TechniquesDokument22 SeitenMultiple Access TechniquesArun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IvDokument92 SeitenUnit IvPrabha GaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6042 Module 2-Satellite CommunicationDokument12 Seiten6042 Module 2-Satellite CommunicationAlenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1V. Satellite Access - 2Dokument49 Seiten1V. Satellite Access - 2Sai TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.multiple Access TechniquesDokument54 Seiten5.multiple Access Techniquesrama krishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tdma FdmaDokument15 SeitenTdma FdmaabenrajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMC Unit 4Dokument20 SeitenIMC Unit 4PJ DudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Communications A: Access Schemes in Satellite Networks - Professor Barry G EvansDokument46 SeitenSatellite Communications A: Access Schemes in Satellite Networks - Professor Barry G EvansMadhu Krishna KarthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Network ConfigurationsDokument19 SeitenSatellite Network ConfigurationsDeepak KariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple AccessDokument12 SeitenMultiple AccessPatricia KCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Computing: 1 Introdcution To WirelessDokument21 SeitenMobile Computing: 1 Introdcution To WirelesssathyapulseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part7 - Duplexing and Multiple Access TechniquesDokument25 SeitenPart7 - Duplexing and Multiple Access TechniquesSeegah JoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2A: - Bernhard (Chapter 2)Dokument28 SeitenLecture 2A: - Bernhard (Chapter 2)meoconhs2612Noch keine Bewertungen
- FDD TDDDokument93 SeitenFDD TDDNikhil ShardaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Access Techniques 1 PDFDokument34 SeitenMultiple Access Techniques 1 PDFAMEY PILANKARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module IDokument24 SeitenModule IVani DeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telecom ScenarioDokument112 SeitenTelecom Scenariotareq_blayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile: Technologies India Pvt. LTDDokument59 SeitenMobile: Technologies India Pvt. LTDRakesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tdma and FdmaDokument40 SeitenTdma and FdmarachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Spread Spectrum and Ultiple Ccess TechniqueDokument26 SeitenUnit 4 Spread Spectrum and Ultiple Ccess TechniqueThasleema BanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Hspa BasicDokument59 Seiten03 Hspa BasicRaufrmzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code Division Multiple Access: Data Transmission EE 723 Dr. Ibrahim MansourDokument13 SeitenCode Division Multiple Access: Data Transmission EE 723 Dr. Ibrahim Mansourks.sandheepNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4G and Beyond: LTE and LTE-AdvancedDokument125 Seiten4G and Beyond: LTE and LTE-AdvancedhgmyungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite and Radio CommunicationDokument33 SeitenSatellite and Radio CommunicationVigneshwar SureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite CommunicationDokument170 SeitenSatellite CommunicationSumithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Thirteen: Multiplexing and Multiple-Access TechniquesDokument20 SeitenChapter Thirteen: Multiplexing and Multiple-Access TechniquesDr-Harish Chandra MohantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular TelephonyDokument30 SeitenCellular TelephonyPusidu SepathNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Complete KnowledgeDokument86 Seiten3G Complete KnowledgeArvind GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OFDM HistoryDokument17 SeitenOFDM HistoryDekris DarutamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S2Dokument47 SeitenS2Praneeth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna Configurations: Channel User Data StreamDokument17 SeitenAntenna Configurations: Channel User Data StreamNavin KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Telecom ConceptsDokument111 SeitenBasic Telecom ConceptsMalik MazharNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Fundamentals & RF: GTL Welcomes You To The Basic Course OnDokument112 SeitenGSM Fundamentals & RF: GTL Welcomes You To The Basic Course OnShejin RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument24 SeitenChapter 5pkrsuresh2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Networks: Wcdma (Part Iii)Dokument23 SeitenWireless Networks: Wcdma (Part Iii)Shakeel AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Cellular CommunicationDokument110 SeitenModule 1 - Cellular CommunicationSwapnil NageNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Trends in Wireless Communication Technology: (With Suitable Multiple Access)Dokument87 SeitenNew Trends in Wireless Communication Technology: (With Suitable Multiple Access)Manoj ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adapted From T.S. Rappaport's Wireless Communications Multiple Access Techniques For Wireless CommunicationsDokument70 SeitenAdapted From T.S. Rappaport's Wireless Communications Multiple Access Techniques For Wireless CommunicationsMeera NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Complete KnowledgeDokument86 Seiten3G Complete KnowledgeAnonymous rlO8eENoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM System EssentialsDokument45 SeitenGSM System EssentialsDavidDavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Communication Network: Tahniyat AslamDokument46 SeitenComputer Communication Network: Tahniyat AslamMuhammad Wasim ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Cellular NetworkDokument45 SeitenIntroduction To Cellular NetworkHarsh JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digicom 101Dokument100 SeitenDigicom 101admerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Networks: Evolution (1) : First GenerationDokument112 SeitenCellular Networks: Evolution (1) : First Generationranbeer1991Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multiplexing and Multiple AccessDokument25 SeitenMultiplexing and Multiple AccessAbdou GayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fast Track to Your Extra Class Ham Radio License: Covers All FCC Amateur Extra Class Exam Questions July 1, 2020 Through June 30, 2024Von EverandThe Fast Track to Your Extra Class Ham Radio License: Covers All FCC Amateur Extra Class Exam Questions July 1, 2020 Through June 30, 2024Noch keine Bewertungen
- BillDokument1 SeiteBillShiju RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BillDokument1 SeiteBillShiju RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Gate EC Solved PaperDokument42 Seiten2010 Gate EC Solved PaperShiju RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NPS Database User's Guilde PDFDokument342 SeitenNPS Database User's Guilde PDFNguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE EC Question Paper 2011 With SolutionsDokument38 SeitenGATE EC Question Paper 2011 With SolutionsshailzworldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tubal PregnancyDokument3 SeitenTubal PregnancyShiju RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC 2012 With SolutionsDokument50 SeitenEC 2012 With Solutionsprabhjot singh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I Elements of Satellite CommunicationDokument24 SeitenUnit I Elements of Satellite CommunicationShiju RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Live On 24 Hours A DaDokument43 SeitenHow To Live On 24 Hours A DaShiju RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 101 Solar Panel Buyers GuideDokument6 Seiten101 Solar Panel Buyers Guideiitbhu_rajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Diodes - ... Torials - ExamCrazyDokument3 SeitenApplications of Diodes - ... Torials - ExamCrazyShiju RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Memtech ND11Dokument22 SeitenMemtech ND11Ebenezer AbishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab TutorDokument86 SeitenMatlab TutorManish GaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10Dokument17 SeitenChapter 10Shiju RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Op SeminarDokument6 SeitenOp SeminarShiju RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Paper 2Dokument9 SeitenBiology Paper 2Shiju RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installation Manual EnUS 2691840011Dokument4 SeitenInstallation Manual EnUS 2691840011Patts MarcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saic-M-2012 Rev 7 StructureDokument6 SeitenSaic-M-2012 Rev 7 StructuremohamedqcNoch keine Bewertungen
- X HM11 S Manual AUpdfDokument228 SeitenX HM11 S Manual AUpdfAntonio José Domínguez CornejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 10719 (Iso 1302) - 1Dokument1 SeiteIs 10719 (Iso 1302) - 1Svapnesh ParikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community-Based Monitoring System (CBMS) : An Overview: Celia M. ReyesDokument28 SeitenCommunity-Based Monitoring System (CBMS) : An Overview: Celia M. ReyesDiane Rose LacenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S SSB29 - Alternator Cables PM: WARNING: This Equipment Contains Hazardous VoltagesDokument3 SeitenS SSB29 - Alternator Cables PM: WARNING: This Equipment Contains Hazardous VoltagesMohan PreethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sika Saudi Arabia: Safety Data SheetDokument4 SeitenSika Saudi Arabia: Safety Data Sheetusman khalid100% (1)
- Ss1169 - Telecom Frameworx l1TMFDokument65 SeitenSs1169 - Telecom Frameworx l1TMFPrince SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Province of Camarines Sur vs. CADokument8 SeitenProvince of Camarines Sur vs. CACrisDBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved - in Capital Budgeting, Should The Following Be Ignored, ...Dokument3 SeitenSolved - in Capital Budgeting, Should The Following Be Ignored, ...rifa hanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management ModelsDokument4 SeitenStrategic Management ModelsBarno NicholusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam StatconDokument4 SeitenMidterm Exam Statconlhemnaval100% (4)
- G JaxDokument4 SeitenG Jaxlevin696Noch keine Bewertungen
- Government of India Act 1858Dokument3 SeitenGovernment of India Act 1858AlexitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dreamfoil Creations & Nemeth DesignsDokument22 SeitenDreamfoil Creations & Nemeth DesignsManoel ValentimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyro ShieldDokument6 SeitenPyro Shieldmunim87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fcode 54 en El SytucDokument2 SeitenFcode 54 en El SytucAga MenonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Communication LeaderDokument4 SeitenEffective Communication LeaderAnggun PraditaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CORDLESS PLUNGE SAW PTS 20-Li A1 PDFDokument68 SeitenCORDLESS PLUNGE SAW PTS 20-Li A1 PDFΑλεξης ΝεοφυτουNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme Bidirectional DC-DC ConverterDokument16 SeitenScheme Bidirectional DC-DC ConverterNguyễn Quang KhoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salva v. MakalintalDokument2 SeitenSalva v. MakalintalGain DeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk and Uncertainty in Estimating and TenderingDokument16 SeitenRisk and Uncertainty in Estimating and TenderingHaneefa ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Internet Use To Academic PerformaceDokument4 SeitenEffect of Internet Use To Academic PerformaceLeonard R. RodrigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- M70-700 4th or 5th Axis Install ProcedureDokument5 SeitenM70-700 4th or 5th Axis Install ProcedureNickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Devices RegulationsDokument59 SeitenMedical Devices RegulationsPablo CzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gathering Package 2023Dokument2 SeitenGathering Package 2023Sudiantara abasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bode PlotsDokument6 SeitenBode PlotshasanozdNoch keine Bewertungen
- La Bugal-b'Laan Tribal Association Et - Al Vs Ramos Et - AlDokument6 SeitenLa Bugal-b'Laan Tribal Association Et - Al Vs Ramos Et - AlMarlouis U. PlanasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of MathematicsDokument35 SeitenApplications of MathematicsRamdas Sonawane100% (1)
- Oasis 360 Overview 0710Dokument21 SeitenOasis 360 Overview 0710mychar600% (1)