Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Uti
Hochgeladen von
Jugal AgarwalOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Uti
Hochgeladen von
Jugal AgarwalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UTI UNION TRUST OF INDIA
YEAR OF ESTABLISHMENT: ABOUT
1964
Unit Trust of India [UTI] is a financial organization in India, which was created by the UTI Act passed by the Parliament in 1964. For more than two decades it remained the sole vehicle for investment in the capital market by the Indian citizens. Its establishment has been a landmark in the history of investment trusts in India. In mid- 1980s public sector banks were allowed to open mutual funds. The real vibrancy and competition in the MF industry came with the setting up of the Regulator SEBI and its laying down the MF Regulations in 1993.UTI maintained its pre-eminent place till 2001, when a massive decline in the market indices and negative investor sentiments after Ketan Parekh scam created doubts about the capacity of UTI to meet its obligations to the investors. Fearing a run on the institution and possible impact on the whole market Government came out with a rescue package and change of management in 2001. Subsequently, the UTI Act was repealed and the institution was bifurcated into two parts. UTI Mutual Fund was created as a SEBI registered fund like any other mutual fund. The assets and liabilities of schemes where Government had to come out with a bail-out package were taken over directly by the Government in a new entity called Specified Undertaking of UTI, SUUTI. SUUTI holds over 27% stake Axis Bank. In order to distance Government from running a mutual fund the ownership was transferred to four institutions; namely SBI, LIC, BOB and PNB, each owning 25%. In February 2003, the UTI Act was repealed and UTI was stripped of its Special legal status as a trust formed by an Act of Parliament. The primary objective behind this was to bring all mutual fund players on the same level. UTI was re-organised into two parts: 1. The UTI Mutual Fund [UTIMF] 2. The Specified Undertaking [SUUTI] Presently, UTI operates under the name of UTI Mutual Fund. UTIMF is still the largest player in the industry.
SUBSIDIARIES OF UTI 1. The UTI Bank Ltd. 2. UTI Investor Services Ltd. 3. UTI Investment Advisory Services 4. UTI Securities Exchange Ltd. 5. UTI Institute of Capital Markets
ROLE OF UTI IN INDUSTRIAL FINANCE 1. Assistance to Corporate Sector 2. Form of Assistance 3. Purpose-wise Assistance 4. Industry-wise Assistance 5. Sectoral Distribution of Assistance 6. State-wise Distribution of Assistance
OBJECTIVES Basic objective: offer small and large investors the means of acquiring shares in the widening prosperity resulting from the steady, industrial growth of the country. Primary Objectives: 1. To promote and pool the small savings from the lower and middle income people who cannot have direct access to the stock exchange, 2. To give an opportunity to share the benefits and fruits of prosperity resulting from rapid industrialisation in India.
FUNCTIONS The main functions of UTI are as follows: 1. To encourage savings of lower and middle-class people. 2. To sell units to investors in different parts of the country. 3. To convert the small savings into industrial finance. 4. To give them an opportunity to share the benfits and fruits of industrialisation in the country. 5. To provide liquidity to units.
ADVANTAGES OF UTI 1. Good opportunity for small investors: Many investors cannot directly invest in financial instruments because minimum required investment in them is quite high. UTI is the best choice for them. 2. Cost of investment is low: This is low is UTI in comparison to direct investment because of many cost involved in it like brokerage cost, purchase cost, etc. 3. Wide choice of schemes: UTI provides investors a wide choice of schemes and they can invest according to their choice and capacity 4. Safe investments: UTI invests its funds in wide range of securities. Any risk in one security is offset by good return in other 5. Steady incomes: The unit holders are ensured of regular return on their investment as UTI distributes nine-tenth of its income in unit holders 6. Expert handlings: UTI has the advantage of having expert advice while making investment in the security of various companies. The expert can
analyse the financial strength of invest.
the company where UTI is going to
7. Tax concession: The investment in UTI carries some tax concessions. There is a wealth tax concession if the amount is invested in units. 8. Liquidity UTI announces repurchase price of units under various schemes. The investor needing his money back can sell the units to the trust and get the money back.
TYPES OF SCHEMES A. Based on maturity period 1. Open-Ended Schemes 2. Closed-Ended Schemes 3. Fund of Funds 4. Exchanged Traded Funds
B. Based on Investment Objective 1. Growth / Equity Oriented Schemes 2. Income / Debt Oriented Schemes 3. Balanced Fund 4. Liquid Fund 5. Gilt Fund 6. Index Fund
STATISTICS AND ACHIEVEMENTS It has over 70 schemes in domestic MF space and has the largest investor base of over 9 million in the whole industry. It is present in over 450 districts of the country and has 100 branches called UTI Financial Centres
or UFCs. About 50% of the total IFAs in the industry work for UTI in distributing its products. India Posts, PSU Banks and all the large Private and Foreign Banks have started distributing UTI products. The total average Assets Under Management (AUM) for the month of June 2008 was Rs. 530 billion and it ranked fourth. In terms of equity AUM it ranked second and in terms of Equity and Balanced Schemes AUM put together it ranked FIRST in the industry. This measure indicates its revenue- earning capacity and its financial strength.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Questionnaire On Job SatisfactionDokument3 SeitenQuestionnaire On Job SatisfactionD Attitude Kid89% (54)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Cyp Accounting, Taxation, Management and Audit ServicesDokument1 SeiteCyp Accounting, Taxation, Management and Audit ServicesCarol Ledesma Yap-PelaezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 101 Cheat Sheet (FInal)Dokument1 SeiteEcon 101 Cheat Sheet (FInal)Alex MadarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Drivers - Tgbta SteelDokument1 SeiteBusiness Drivers - Tgbta SteelJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBA Leaves and ReimbursementDokument2 SeitenIBA Leaves and ReimbursementJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBA Leaves and ReimbursementDokument2 SeitenIBA Leaves and ReimbursementJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBA Leaves and ReimbursementDokument2 SeitenIBA Leaves and ReimbursementJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activities of Exim Bank Its Support FunctionsDokument29 SeitenActivities of Exim Bank Its Support FunctionsJugal Agarwal0% (1)
- IBA Leaves and ReimbursementDokument2 SeitenIBA Leaves and ReimbursementJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Live Project in BankingDokument1 SeiteLive Project in BankingJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contents RevisedDokument92 SeitenContents RevisedAnoopKumarMangarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maruti Workers Are The Villains': Truth or Prejudice?: CommentaryDokument4 SeitenMaruti Workers Are The Villains': Truth or Prejudice?: Commentarydarrell1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Scenario PDFDokument6 SeitenBanking Scenario PDFHitendra SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ing Vy Sy A Bank Limited Annual ReportDokument156 SeitenIng Vy Sy A Bank Limited Annual ReportJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines On Banks' Asset Liability Management Framework - Interest Rate RiskDokument35 SeitenGuidelines On Banks' Asset Liability Management Framework - Interest Rate RiskMouBunchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume Template (With Instructions)Dokument2 SeitenResume Template (With Instructions)Jugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
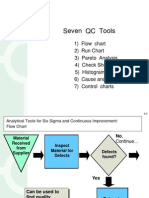
- Seven QC ToolsDokument13 SeitenSeven QC ToolsJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- TATA Steel Annual Report 2012 13Dokument228 SeitenTATA Steel Annual Report 2012 13leopold_forte6314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument7 SeitenPresentation 1Jugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exim Bank NFTP PresentationDokument30 SeitenExim Bank NFTP PresentationSagar GadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role Functions of Exim Bank1Dokument19 SeitenRole Functions of Exim Bank1Aneesha KasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Function Deployment (QFD) : The Voice of The CustomerDokument12 SeitenQuality Function Deployment (QFD) : The Voice of The CustomerJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award: SCM 462 Dr. Ron Tibben-LembkeDokument42 SeitenMalcolm Baldrige National Quality Award: SCM 462 Dr. Ron Tibben-Lembkemayank_kamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Control: Chapter 2-Total Quality Management and PrinciplesDokument62 SeitenQuality Control: Chapter 2-Total Quality Management and PrinciplessinghjagwantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Quality Control: by 4Th Edition © Wiley 2010 Powerpoint Presentation by R.B. Clough - Unh M. E. Henrie - UaaDokument40 SeitenStatistical Quality Control: by 4Th Edition © Wiley 2010 Powerpoint Presentation by R.B. Clough - Unh M. E. Henrie - UaaInderpreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument7 SeitenPresentation 1Jugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Financing in HUDCODokument20 SeitenProject Financing in HUDCOJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citation APA 6th NewbrandDokument4 SeitenCitation APA 6th NewbrandAarushi Gupta100% (1)
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument8 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ing Vy Sy A Bank Limited Annual ReportDokument156 SeitenIng Vy Sy A Bank Limited Annual ReportJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seven QC ToolsDokument13 SeitenSeven QC ToolsJugal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2 Mathematics of RetailingDokument10 Seiten3.2 Mathematics of RetailingharizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forex - DerivativesDokument5 SeitenForex - DerivativesAllyse CarandangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varengold Bank FX Trading-Challenge - Prize 1,000,000 USDDokument1 SeiteVarengold Bank FX Trading-Challenge - Prize 1,000,000 USDKostas KazakosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules Governing Acceptance of Fixed Deposit: Kerala Transport Development Finance Corporation LimitedDokument2 SeitenRules Governing Acceptance of Fixed Deposit: Kerala Transport Development Finance Corporation LimitedemilsonusamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sawsan Hassan Al SaffarDokument3 SeitenSawsan Hassan Al SaffarwaminoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Money LaunderingDokument24 SeitenMoney Launderingateen rizalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Axis Smallcap FundDokument1 SeiteAxis Smallcap FundManoj JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Indicators: - Stochastic Oscillator - Relative Strength Index - Moving Average Convergence-DivergenceDokument32 SeitenTechnical Indicators: - Stochastic Oscillator - Relative Strength Index - Moving Average Convergence-DivergenceChartSniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site Rental 24 Dec 2021Dokument16 SeitenSite Rental 24 Dec 2021Wega BluemartNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 CA Inter Audit Question Bank Part 1 Chapter 0 To Chapter 3Dokument146 Seiten01 CA Inter Audit Question Bank Part 1 Chapter 0 To Chapter 3Yash SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DeAngelo - 1990 - Equity Valuation and Corporate ControlDokument21 SeitenDeAngelo - 1990 - Equity Valuation and Corporate ControlAna Luisa EisenlohrNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTRP - Track Transaction HistoryDokument2 SeitenNTRP - Track Transaction HistorySathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AASB 112 Fact SheetDokument4 SeitenAASB 112 Fact SheetCeleste LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Directional Options TradingDokument24 SeitenDirectional Options Tradingmaoychris0% (1)
- Ocbc Ar2016 Full Report English PDFDokument236 SeitenOcbc Ar2016 Full Report English PDFMr TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clause 49 of Listing AgreementDokument18 SeitenClause 49 of Listing AgreementJatin AhujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Review Ceu PDFDokument28 SeitenIntegrated Review Ceu PDFHello Kitty100% (1)
- PA Sample MCQs 2Dokument15 SeitenPA Sample MCQs 2ANH PHẠM QUỲNHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Borrowing Costs - Assignment - For PostingDokument1 SeiteBorrowing Costs - Assignment - For Postingemman neriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viacom18 Gears Up For IPL Ex-Star Head Uday Shankar To Likely Drive Digital Initiatives?Dokument3 SeitenViacom18 Gears Up For IPL Ex-Star Head Uday Shankar To Likely Drive Digital Initiatives?bdacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilovepdf MergedDokument9 SeitenIlovepdf MergedGARTMiawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Value of MoneyDokument22 SeitenTime Value of Moneyshubham abrolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-5 Receivables ManagementDokument26 SeitenUnit-5 Receivables ManagementSarthak MattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skanray Technologies Pvt. LTD: Company ProfileDokument33 SeitenSkanray Technologies Pvt. LTD: Company ProfileMars NaspekovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Star Founder Raveendran Broke Down in Tears As Crises Engulfed Byju'sDokument14 SeitenStar Founder Raveendran Broke Down in Tears As Crises Engulfed Byju'sGAPL International SalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cover LetterDokument2 SeitenCover LetterBilal AslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 - Part 1 - Accounting FranchisesDokument13 SeitenChapter 11 - Part 1 - Accounting FranchisesJane Dizon100% (1)
- Standar Gaji Indonesia 2008 - 2009 UpdatedDokument8 SeitenStandar Gaji Indonesia 2008 - 2009 Updatedwitoyo100% (40)