Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Drug Study
Hochgeladen von
Mark Anthony Taña GabiosaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Drug Study
Hochgeladen von
Mark Anthony Taña GabiosaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Clonidine hydrochloride (Catapres) Brand Name: Antihypertensives: Apo-Clonidine (CAN), Catapres, Catapres-TTS (transdermal preparation), Dixarit (CAN), NuClonidine
(CAN) Analgesic: Duraclon Pregnancy Category C Drug classes: Antihypertensive, Sympatholytic, centrally acting, Central analgesic Therapeutic actions Stimulates CNS alpha2-adrenergic receptors, inhibits sympatheticcardioaccelerator and vasoconstrictor centers, and decreases sympathetic outflow from the CNS. Indications Hypertension, used alone or as part of combination therapy
Treatment of severe pain in cancer patients in combination with opiates; epidural more effective with neuropathic pain (Duraclon) Unlabeled uses: Tourette's syndrome; migraine, decreases severity and frequency; menopausal flushing, decreases severity and frequency of episodes; chronic methadone detoxification; rapid opiate detoxification (in doses up to 17 mcg/kg/day); alcohol and benzodiazepine withdrawal treatment; management of hypertensive "urgencies"; (oral clonidine "loading" is used; initial dose of 0.2 mg then 0.1 mg every hour until a dose of 0.7 mg is reached or until BP is controlled) Contraindications Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to clonidine or any adhesive layer components of the transdermal system.
Adverse effects
Oral therapy Drowsiness, sedation, dizziness, headache, fatigue that tend to diminish within 4 6 wk, dreams, nightmares, insomnia,
hallucinations, delirium, nervousness, restlessness, anxiety, depression, retinal degeneration CHF, orthostatic hypotension, palpitations, tachycardia, bradycardia,Raynaud's phenomenon, ECG abnormalities manifested asWenckebach period or ventricular trigeminy Rash, angioneurotic edema, hives, urticaria, hair thinning and alopecia, pruritus, dryness, itching or burning of the eyes, pallor
Dry mouth, constipation, anorexia, malaise, nausea, vomiting, parotid pain, parotitis, mild transient abnormalities in liver
function tests Impotence, decreased sexual activity, diminished libido, nocturia, difficulty in micturition, urinary retention Weight gain, transient elevation of blood glucose or serum creatinephosphokinase, gynecomastia, weakness, muscle or joint pain, cramps of the lower limbs, dryness of the nasal mucosa, fever
Transdermal system Drowsiness, fatigue, headache, lethargy, sedation, insomnia, nervousness
Dry mouth, constipation, nausea, change in taste, dry throat
Impotence, sexual dysfunction
Transient localized skin reactions, pruritus, erythema, allergic contact sensitization and contact dermatitis,
localized vesiculation,hyperpigmentation, edema, excoriation, burning, papules, throbbing, blanching, generalized macular rash Drug Interactions: Decreased antihypertensive effects with TCAs (imipramine)
Paradoxical hypertension with propranolol; also greater withdrawal hypertension when abruptly discontinued and patient is taking beta-adrenergic blocking agents Nursing considerations CLINICAL ALERT! Name confusion has been reported between clonidine and Klonopin(clonazepam); use caution. Do not discontinue abruptly; discontinue therapy by reducing the dosage gradually over 2 4 days to avoid rebound hypertension, tachycardia, flushing, nausea, vomiting, cardiac arrhythmias (hypertensive encephalopathy and death have occurred after abrupt cessation of clonidine). Do not discontinue prior to surgery; monitor BP carefully during surgery; have other BP-controlling drugs on standby. Store epidural injection at room temperature; discard any unused portions.
Reevaluate therapy if clonidine tolerance occurs; giving concomitant diuretic increases the antihypertensive efficacy ofclonidine. Monitor BP carefully when discontinuing clonidine; hypertension usually returns within 48 hr. Assess compliance with drug regimen in a supportive manner with pill counts, or other methods.
Generic Name: Ferrous sulfate Trade Name: Classification: Iron Preparation Dose, Route,:PO MECHANISM OF ACTION :Elevates the serum iron concentration which then helps to form High or trapped in the reticuloendothelial cells for storage and eventual conversion to a usable form of iron. INDICATIONS: Prevention and treatment of iron deficiency anemias, Dietary supplement for iron. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Hypersensitivity, Severe hypotension. ADVERSE EFFECT: Dizzines, N & V, Nasal Congestion, Dyspnea, Hypotension, CHF, MI, Muscle cramps, Flushing NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Advise patient to take medicine as prescribed. Caution patient to make position changes slowly to minimize orhtostatic hypotension.
Instruct patient to avoid concurrent use of alcohol or OTC medicine without consulting the physician. Advise patient to consult physician if irregular heartbeat, dyspnea, swelling of hands and feet and hypotension occurs. Inform patient that angina attacks may occur 30 min. after administration due reflex tachycardia. Encourage patient to comply with additional intervention for hypertensio n like proper diet, regular exercise, lifestyle changes and stress management. Generic Name:Sodium Bicarbonate Brand Name:Sodium Bicarbonate Classifications:gastrointestinal agent; antacid; fluid and electrolyte balance agent Pregnancy Category:C Availability: 325 mg, 520 mg, 650 mg tablets; 4.2%, 5%, 7.5%, 8.4% injection Actions: Short-acting, potent systemic antacid. Rapidly neutralizes gastric acid to form sodium chloride, carbon dioxide, and water. After absorption of sodium bicarbonate, plasma alkali reserve is increased and excess sodium and bicarbonate ions are excreted in urine, thus rendering urine less acid. Not suitable for treatment of peptic ulcer because it is shortacting, high in sodium, and may cause, gastric, distention, systemic, alkalosis, and possibly acid-rebound. Therapeutic effects: Shortacting, potent systemic antacid; rapidly neutralizes gastric acid or systemic acidosis. Contraindications: Prolonged therapy with sodium bicarbonate; patients losing chloride (as from vomiting, GI suction, diuresis); heart disease, hypertension; renal insufficiency; peptic ulcer; pregnancy (category C). Cautious use: Edema, sodium-retaining disorders; lactation; older adults patients. Route & dosage : Adult:PO 0.32 g 14 times/d or 1/2 tsp of powder in glass of water Administration:Oral Adverse effects GI:Belching, gastric distention, flatulence. Metabolic:Metabolic alkalosis; electrolyte imbalance: sodium overload (pulmonary edema), hypocalcemia (tetany), hypokalemia, milk-alkali syndrome, dehydration. other:Rapid IV in neonates (Hypernatremia, reduction in CSF pressure, intracranial hemorrhage). Skin:Severe tissue damage following extravasation of IV solution. Urogenital:Renal calculi or crystals, impaired kidney function. Nursing implications : Assessment & Drug Effects: Be aware that long-term use of oral preparation with milk or calcium can cause milk-alkali syndrome: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, headache, mental confusion, hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia, soft tissue calcification, renal and ureteral calculi, renal insufficiency, metabolic alkalosis. Lab tests: Urinary alkalinization: Monitor urinary pH as a guide to dosage (pH testing with nitrazine paper may be done at intervals throughout the day and dosage adjustments made accordingly). Lab tests: Metabolic acidosis: Monitor patient closely by observations of clinical condition; measurements of acid-base status (blood pH, Po2, Pco2, Hco3-, and other electrolytes, are usually made several times daily during acute period). Observe for signs of alkalosis (over treatment)
Observe for and report S&S of improvement or reversal of metabolic acidosis. Generic Name: calcium carbonate (KAL see um KAR boe nate) Brand Name: Alka-Mints, Cal-Gest, Calcarb, Calci Mix, Calci-Chew, Calci-Mix, Calcium Concentrate, Calcium Liquid Softgel, Calcium Oyster Shell, Caltrate, Mechanism of Action: Calcium carbonate can neutralise gastric acid rapidly and effectively. However, it may adversely activate Ca dependent processes, leading to secretion of gastric and hydrochloric acid. It can induce rebound acid secretion and, prolonged high doses may cause hypercalcemia, alkalosis and milk-alkali syndrome. Absorption: Converted to calcium chloride by gastric acid. Some of the calcium is absorbed in the intestines. Calcium is absorbed in soluble, ionized form; solubility of calcium is increased in an acidic environment. Classification: Calcium/with Vitamins / Antacids, Antireflux Agents & Antiulcerants / Electrolytes Indications: Chronic Renal Failure Dosage Adult: PO Hyperacidity Per tab contains 500 mg calcium carbonate: Take 1-2 tab as needed, up to a max of 16 tab/day. May suck or chew tablets. Hyperphosphataemia in chronic renal failure Initial: 2.5 g/day, up to 17 g/day in divided doses. Administration: May be taken with or without food. Take w/ meals for better absorption. Avoid taking w/ large amt of fibre-rich food. Contraindications: Patients with Ca renal calculi or history of renal calculi; hypercalcaemia; hypophosphataemia. Patients with suspected digoxin toxicity. Special Precautions: Renal impairment, hypoparathyroid disease, hypercalcaemia-associated diseases. Calcium absorption is impaired in achlorhydria; use an alternate salt and take with food. Caution when used in patients with a history of kidney stones. Adverse Drug Reactions: Constipation, flatulence; hypercalcaemia; metabolic alkalosis; milk-alkali syndrome, tissuecalcification. Gastric hypersecretion and acid rebound (with prolonged use). Drug Interactions: Co-administration with thiazide diuretics or vit D may lead to milk-alkali syndrome and hypercalcaemia. Decreased absorption with corticosteroids. Decreases absorption of tetracyclines, atenolol, iron, quinolones, alendronate, Na fluoride, Zn and calcium-channel blockers. Enhances cardiac effects of digitalis glycosides and may precipitate digitalis intoxication. Potentially Fatal: Co-administration with thiazide diuretics or vit D may lead to milk-alkali syndrome and hypercalcaemia. Decreased absorption with corticosteroids. Decreases absorption of tetracyclines, atenolol, iron, quinolones, alendronate, Na fluoride, Zn and calcium-channel blockers. Enhances cardiac effects of digitalis glycosides and may precipitate digitalis intoxication.
Generic Name: Amlodopine Brand Name: Norvasc Classifications: cardiovascular agent; calcium channel blocker Pregnancy Category:C Availability 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg tablets Actions Amlodipine is a calcium channel blocking agent that selectively blocks calcium ion reflux across cell membranes of cardiac and vascular smooth muscle without changing serum calcium concentrations. It predominantly acts on the peripheral circulation, decreasing peripheral vascular resistance, and increases cardiac output.
Therapeutic effects Amlodipine reduces systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial blood pressure. Uses : Treatment of mild to moderate hypertension and angina. Contraindicatons: Hypersensitivity to amlodipine. Route & Dosage: Hypertension adult:PO 510 mg once daily geriatric:start with 2.5 mg, adjust dose at intervals of not less than 2 wk Renal Impairment Start with 2.5 mg, adjust dose at intervals of not less than 2 wk Administration: Oral Adverse effects: CV:Palpitations, flushing tachycardia, peripheral or facial edema, bradycardia, chest pain, syncope, postural hypotension. CNS:Light-headedness, fatigue, headache. GI:Abdominal pain, nausea, anorexia, constipation, dyspepsia, dysphagia, diarrhea, flatulence, vomiting. Urogenital:Sexual dysfunction, frequency, nocturia. Respiratory:Dyspnea. Skin:Flushing, rash. other:Arthralgia, cramps, myalgia. Nursing Implications : Assessment & Drug Effects: Monitor BP for therapeutic effectiveness. BP reduction is greatest after peak levels of amlodipine are achieved 6 9 h following oral doses.Monitor for S&S of dose-related peripheral or facial edema that may not be accompanied by weight gain; rarely, severe edema may cause discontinuation of drug. Monitor BP with postural changes. Report postural hypotension. Monitor more frequently when additional antihypertensives or diuretics are added. Monitor heart rate; dose-related palpitations (more common in women) may occur. Patient & Family Education
Report significant swelling of face or extremities. Take care to have support when standing & walking due to possible dose-related light-headedness/dizziness. Report shortness of breath, palpitations, irregular heartbeat, nausea, or constipation to physician. Do not breast feed while taking this drug without consulting physician.
Generic Name: Insulin Brand Names: Humulin R - Injection 100 units/mL human insulin (rDNA) - Injection 500 units/mL human insulin (rDNA) Novolin R - Injection 100 units/mL human insulin (rDNA) Novolin ge Toronto (Canada) NPH, Isophane Insulin Suspension Humulin N - Injection 100 units/mL human insulin (rDNA) Novolin N - Injection 100 units/mL human insulin (rDNA) Class: Antidiabetic agent Regular, Insulin Injection Pharmacology: Insulin and its analogs lower blood glucose levels by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake, especially by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production. Insulin inhibits lipolysis, proteolysis, and enhances protein synthesis. Indications and Usage Management of type 1 diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (noninsulin-dependent) not properly controlled by diet, exercise, and weight reduction. In hyperkalemia, infusions of glucose and insulin lower serum potassium levels. IV or IM regular insulin may be given for rapid effect in severe ketoacidosis or diabetic coma. Highly purified (single component) and human insulins are used for treatment of local insulin allergy, immunologic insulin resistance, lipodystrophy at injection site, temporary insulin administration, and in newly diagnosed diabetic patients. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to any ingredient of the product; during episodes of hypoglycemia. Dosage and Administration Parenteral Insulins : Insulin preparations are classified into 3groups based on promptness, duration, and intensity of action following subcutaneous administration. These classifications are rapid- (regular), intermediate- ( NPH ), or longacting. Maintenance doses are given subcutaneous and must be individualized by monitoring patients closely. Consider following dosage guidelines.
Nursing Intervention: Parenteral insulins Regular insulin is for subcutaneous, IM, or IV administration only. Not for intradermal, intra-arterial, or oral administration. Long-acting insulins are for subcutaneous administration only. Not for intradermal, IM, IV, intra-arterial, or oral administration.
Administer direct subcutaneous injections into abdominal wall, thigh, or deltoid. Rotate injection sites within same region. Do not use regular insulin if cloudy, thickened, discolored, or contains particulate matter. Do not use long-acting insulin if white material (insulin) remains at bottom of bottle after mixing or if there are clumps. If mixing regular insulin with long-acting insulin, draw regular insulin into syringe first. If using insulin pen, mix contents by rolling between the palms 10 times then inverting 180 10 times, then prime the pen before each dose. Do not administer if white material (insulin) remains visibly separated from the liquid after mixing, if clumps are noted, or if solid white particles stick to walls of cartridge.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Differents Kind of Mountain and HillDokument8 SeitenDifferents Kind of Mountain and HillMark Anthony Taña GabiosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross StitchDokument1 SeiteCross StitchMark Anthony Taña GabiosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Longitude Is A Geographic Coordinate That Specifies The EastDokument1 SeiteLongitude Is A Geographic Coordinate That Specifies The EastMark Anthony Taña GabiosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agn PediaDokument5 SeitenAgn PediaMark Anthony Taña GabiosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- If Things DonDokument1 SeiteIf Things DonMark Anthony Taña GabiosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- If Things DonDokument1 SeiteIf Things DonMark Anthony Taña GabiosaNoch keine Bewertungen
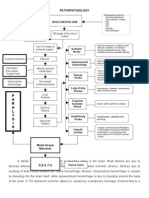
- Stoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Dokument7 SeitenStoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Mark Anthony Taña GabiosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MefenamicDokument2 SeitenMefenamicMark Anthony Taña GabiosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan of Client With Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDokument28 SeitenNursing Care Plan of Client With Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceCj Aguilar50% (2)
- Marijuana: A Medicine For CancerDokument11 SeitenMarijuana: A Medicine For CancerXylvia Hannah Joy CariagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Diabetes: Diagnosing Maturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY)Dokument32 SeitenDiagnostic Diabetes: Diagnosing Maturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY)Christian SalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy: Case ReportDokument2 SeitenPhotodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy: Case ReportMedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effectiveness and Efficiency in Ultrasonic ScalingDokument17 SeitenEffectiveness and Efficiency in Ultrasonic ScalingsabihuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otalgia & TinnitusDokument19 SeitenOtalgia & Tinnitushonda matizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intracavernosal Injection InformationDokument4 SeitenIntracavernosal Injection InformationJason ArbogastNoch keine Bewertungen
- TraumaAirway Management - ValDokument36 SeitenTraumaAirway Management - ValValerie Suge-MichiekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Perspective For Probiotics: A Review: ArticleDokument12 SeitenIndian Perspective For Probiotics: A Review: ArticleMurali DathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holistic Dental Approach For Visually Impaired Children: A Narrative ReviewDokument8 SeitenHolistic Dental Approach For Visually Impaired Children: A Narrative ReviewIJAR JOURNAL100% (1)
- Pathology MnemonicsDokument27 SeitenPathology MnemonicsdyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elevated BilirubinDokument5 SeitenElevated BilirubinNovita ApramadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Chlorhexidine Varnishes in Preventing and Treating Periodontal DiseaseDokument4 SeitenUse of Chlorhexidine Varnishes in Preventing and Treating Periodontal Diseasetaher adelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review 1Dokument5 SeitenLiterature Review 1api-550490262Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geriatric Physical TherapyDokument6 SeitenGeriatric Physical Therapyirdasriwahyuni0% (1)
- Airborne PrecautionDokument2 SeitenAirborne PrecautionEckry SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsurgical Training With FreshDokument5 SeitenMicrosurgical Training With FreshBob sponjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dip HIV Man (SA) Regulations 24-1-2017Dokument9 SeitenDip HIV Man (SA) Regulations 24-1-2017matentenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Hemangioendothelioma An Unusual Presentation of A Rare Vascular TumorDokument5 SeitenComposite Hemangioendothelioma An Unusual Presentation of A Rare Vascular TumorTian Nopita SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Carcinoid Tumor of The Urinary BladderDokument5 SeitenPrimary Carcinoid Tumor of The Urinary BladdermikalraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric EndrocinologyDokument453 SeitenPediatric Endrocinologyrayx323100% (1)
- Human Body WorkbookDokument25 SeitenHuman Body Workbookjk centralNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOP For Staphylococcus AureusDokument4 SeitenSOP For Staphylococcus AureusDr. StormNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 5776299055374141065Dokument505 Seiten4 5776299055374141065Bairon German Patiño VanegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi-Specialty Hospital: Ram Sharada Healthcare Pvt. LTDDokument48 SeitenMulti-Specialty Hospital: Ram Sharada Healthcare Pvt. LTDsubhash goelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Price List of Hasc Hearing Aids (Rexton) W.E.F. 1/6/2012: Arena Digital FamilyDokument6 SeitenPrice List of Hasc Hearing Aids (Rexton) W.E.F. 1/6/2012: Arena Digital FamilyPaulo DantasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental Health: The ComponentDokument1 SeiteDental Health: The Componentmaddie g.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology تفريغ د شافعي 2013Dokument45 SeitenHematology تفريغ د شافعي 2013Arwa Qishta100% (1)
- Maxillary Sinus Approaches-1Dokument23 SeitenMaxillary Sinus Approaches-1Ahmed KhattabNoch keine Bewertungen