Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nursing Care Plans of A Patient With Stroke
Hochgeladen von
Joy JarinOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing Care Plans of A Patient With Stroke
Hochgeladen von
Joy JarinCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
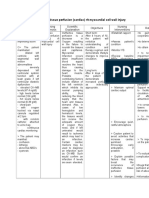
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Nursing Intervention
Assess functional ability/extent of impairment initially and on a regular basis. Classify according to 04 scale.
Rationale
Identifies strengths/deficiencies and may provide information regarding recovery. Assists in choice of interventions, because different techniques are used for flaccid and spastic paralysis. Reduces risk of tissue ischemia/injury. Affected side has poorer circulation and reduced sensation and is more predisposed to skin breakdown/decubitus. Helps maintain functional hip extension; however, may increase anxiety, especially about ability to breathe. Prevents contractures/foot drop and facilitates use when/if function returns. Flaccid paralysis may interfere with ability to support head, whereas spastic paralysis may lead to deviation of head to one side.
Evaluation
Objective:
- Inability to purposefully move within the physical environment - impaired coordination; limited range of motion -decreased muscle strength/cont rol
Impaired Physical Mobility related to paresis as evidenced by inability to purposefully move within the physical environment; impaired coordination; limited range of motion; decreased muscle strength / control
After 8 hours of nursing intervention the pt. will:
- Maintain/increase strength and function of affected or compensatory body part. - Maintain optimal position of function as evidenced by absence of contractures, foot drop. - Demonstrate techniques / behaviors that enable resumption of activities. - Maintain skin integrity.
After 8 hours of nursing intervention the pt. has: - Maintained/increased strength and function of affected or compensatory body part. - Maintained optimal position of function as evidenced by absence of contractures, foot drop. - Demonstrated techniques/behaviors that enable resumption of activities. -Maintained skin integrity. Goal met.
Change positions at least every 2 hrs. (Supine, side lying) and possibly more often if placed on affected side. Position in prone position once or twice a day if patient can tolerate.
Prop extremities in functional position; use footboard during the period of flaccid paralysis. Maintain neutral position of head.
1. Left side body paralysis
1. Left side body paralysis
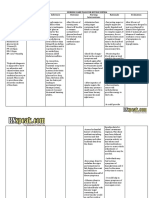
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Nursing Intervention
Rationale
Evaluation
Assist to develop sitting balance (e.g., raise head of bed; assist to sit on edge of bed, having patient use the strong arm to support body weight and strong leg to move affected leg; increase sitting time) and standing balance (e.g., put flat walking shoes on patient, support patients lower back with hands while positioning own knees outside patients knees, assist in using parallel bars/walkers). Encourage patient to assist with movement and exercises using unaffected extremity to support/move weaker side.
Aids in retraining neuronal pathways, enhancing proprioception and motor response.
May respond as if affected side is no longer part of body and needs encouragement and active training to reincorporate it as a part of own body.
4. Slurred speech
Assessment Objectives: Slurred speech
Diagnosis Impaired verbal communication related to impaired cerebral circulation; neuromuscular impairment, loss of facial/oral muscle tone/control; generalized weakness/fatig ue
Planning The patient will be able to: Establish method of communication in which needs can be expressed. Use resources appropriately. Practice and implement speech therapy activities while at the same time using alternative methods of communication.
Nursing Intervention Post notice at nurses station and patients room about speech impairment. Provide special call bell if necessary. Provide alternative methods of communication, e.g., writing or felt board, pictures. Provide visual clues gestures, pictures, needs list, demonstration). Talk directly to patient, speaking slowly and distinctly. Use yes/no questions to begin with, progressing in complexity as patient responds.
Rationale
Evaluation
Allays anxiety related to inability to The patient was able to: communicate and fear that needs will not be met promptly. Call bell Established method that is activated by minimal of communication pressure is useful when patient is in which needs can unable to use regular call system. be expressed. Used resources Provides for communication of appropriately. needs/desires based on individual Practiced and situation/underlying deficit. implement speech therapy activities while at the same time using alternative methods of communication. Reduces confusion/anxiety at having to process and respond to large amount of information at one time. As retraining progresses, advancing complexity of communication stimulates memory and further enhances word/idea association.
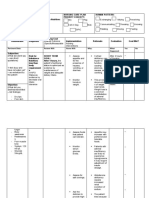
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Nursing Intervention Speak in normal tones and avoid talking too fast. Give patient ample time to respond. Talk without pressing for a response.
Rationale Patient is not necessarily hearing impaired, and raising voice may irritate or anger patient. Forcing responses can result in frustration and may cause patient to resort to automatic speech, e.g., garbled speech, obscenities. It is important for family members to continue talking to patient to reduce patients isolation, promote establishment of effective communication, and maintain sense of connectedness with family.
Evaluation
Encourage SO/visitors to persist in efforts to communicate with patient, e.g., reading mail, discussing family happenings even if patient is unable to respond appropriately. Respect patients preinjury capabilities; avoid speaking down to patient or making patronizing remarks.
Enables patient to feel esteemed, because intellectual abilities often remain intact.
4. Slurred speech
2. Difficulty of swallowing
Assessment Patient exhibits difficulty swallowing
Diagnosis Impaired swallowing secondary to stroke
Planning The patient will be able to: Demonstrate feeding methods appropriate to individual situation with aspiration prevented. Maintain desired body weight.
Nursing Intervention
Rationale
Evaluation The patient: Demonstrated feeding methods appropriate to individual situation with aspiration prevented. Maintained desired body weight.
Review individual pathology/ability to Nutritional interventions/choice of swallow, noting extent of paralysis; feeding route is determined by these clarity of speech; facial, tongue factors. involvement; ability to protect airway/ episodes of coughing or choking; presence of adventitious breath sounds; amount/character of oral secretions. Weigh periodically as indicated. Have suction equipment available at bedside, especially during early feeding efforts. Promote effective swallowing, e.g.: Schedule activities/medications to provide a minimum of 30 min rest before eating; Assist patient with head control/support, and position based on specific dysfunction; Timely intervention may limit amount/untoward effect of aspiration. Promotes optimal muscle function, helps to limit fatigue.
Counteracts hyperextension, aiding in prevention of aspiration and enhancing ability to swallow. Optimal positioning can facilitate intake/reduce risk of aspiration, e.g., head back for decreased posterior propulsion of tongue, head turned to weak side for unilateral pharyngeal paralysis, lying down on either side for reduced pharyngeal contraction.
2. Difficulty of swallowing
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Nursing Intervention
Place patient in upright position during/after feeding as appropriate;
Rationale
Uses gravity to facilitate swallowing and reduces risk of aspiration. Increases salivation, improving bolus formation and swallowing effort. Aids in sensory retraining and promotes muscular control.
Evaluation
Serve foods at customary temperature and water always chilled;
Stimulate lips to close or manually open mouth by light pressure on lips/under chin, if needed; Feed slowly, allowing 3045 min for meals;
Feeling rushed can increase stress/level of frustration, may increase risk of aspiration, and may result in patients terminating meal early. Although use may strengthen facial and swallowing muscles, if patient lacks tight lip closure to accommodate straw or if liquid is deposited too far back in mouth, risk of aspiration may be increased. If swallowing efforts are not sufficient to meet fluid/nutrition needs, alternative methods of feeding must be pursued.
Limit/avoid use of drinking straw for liquids;
Maintain accurate I&O; record calorie count.
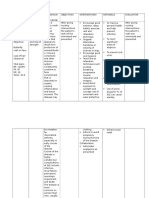
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Nursing Intervention Assess extent of altered perception and related degree of disability. Determine Functional Independence Measure score.
Rationale Determination of individual factors aids in developing plan of care/choice of interventions and discharge expectations.
Evaluation
Ineffective coping related to situational crises vulnerability, cognitive perceptual changes as evidenced by inappropriate use of defense mechanisms, inability to cope/difficulty asking for help, change in usual communication patterns, inability to meet basic needs/role expectations, difficulty problem solving
The patient will be able to: - Verbalize acceptance of self in situation. - Talk/ communicate with SO about situation and changes that have occurred. - Verbalize awareness of own coping abilities. - Meet psychological needs as evidenced by appropriate expression of feelings, identification of options, and use of resources.
The patient was be able to:
- Verbalize acceptance of self Identify meaning of the Independence/ability is highly valued in loss/dysfunction/change to American society but is not as significant in situation. - Talk/ patient. Note ability to in some other cultures. Some patients communicate understand events, provide accept and manage altered function with SO about realistic appraisal of situation. effectively with little adjustment, situation and whereas others have considerable difficulty recognizing and adjusting to changes that have deficits. In order to provide meaningful occurred. support and appropriate problem-solving, - Verbalize healthcare providers need to understand awareness of own the meaning of the stroke/limitations to coping abilities. patient. - Meet psychological Determine outside stressors, e.g., Helps identify specific needs, provides family, work, social, future opportunity to offer information/support needs as evidenced by nursing/healthcare needs. and begin problem-solving. appropriate Consideration of social factors, in addition to functional status, is important expression of in determining appropriate discharge feelings, destination. identification of options, and use Encourage patient to express Demonstrates acceptance of/assists of resources.
feelings, including hostility or anger, denial, depression, sense of disconnectedness. patient in recognizing and beginning to deal with these feelings.
3. Disturbed body image
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Nursing Intervention Note whether patient refers to affected side as it or denies affected side and says it is dead.
Rationale Suggests rejection of body part/negative feelings about body image and abilities, indicating need for intervention and emotional support. Helps patient see that the nurse accepts both sides as part of the whole individual. Allows patient to feel hopeful and begin to accept current situation.
Evaluation
Acknowledge statement of feelings about betrayal of body; remain matter-of-fact about reality that patient can still use unaffected side and learn to control affected side. Use words (e.g., weak, affected, right-left) that incorporate that side as part of the whole body. Identify previous methods of dealing with life problems. Determine presence/quality of support systems. Support behaviors/efforts such as increased interest/participation in rehabilitation activities. 3. Disturbed body image
Provides opportunity to use behaviors previously effective, build on past successes, and mobilize resources.
Suggest possible adaptation to changes and understanding about own role in future lifestyle.
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Nursing Intervention
Evaluation
Objective: >lethargic >BP: 180/100
Decreased Cardiac Output r/t malignant hypertension as manifested by decreased stroke volume.
Short term goal: After 8 hours of nursing interventions, the client will have no elevation in blood pressure above normal limits and will maintain blood pressure within acceptable limits.
Independent: Monitor BP every 1-2hours, or every 5 minutes during active titration of vasoactive drugs. Monitor ECG for dysrhythmias, conduction defects and for heart rate. Suggest frequent position changes. Encourage patient to decrease intake of caffeine, cola and chocolates
After 6 hours of nursing interventions, the client had no elevation in blood pressure above normal limits and will maintain blood pressure within acceptable limits. Goal was met.-
5. Blood pressure of 180/100
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Self Care DeficitDokument4 SeitenSelf Care DeficitEllaine RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncp-Impaired Verbal CommunicationDokument4 SeitenNcp-Impaired Verbal CommunicationEzra TuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Verbal and or Written CommunicationDokument2 SeitenImpaired Verbal and or Written CommunicationHanya Bint Potawan100% (1)
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortDokument2 SeitenImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortRis NapolisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan CVADokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plan CVAessevyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Role Perf Romance FinalDokument1 SeiteIneffective Role Perf Romance Finalasymptomaticcrisis0% (1)
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenAmlodipine Drug StudyKervin TalledoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDokument2 SeitenIneffective Tissue PerfusionDiane ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Acute Pain RT CancerDokument3 SeitenNCP Acute Pain RT CancerCharissa Magistrado De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan SeizureDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Seizuretimie_reyes100% (1)
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDokument3 SeitenImpaired Verbal CommunicationCalimlim KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Stroke PatientsDokument7 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Stroke Patients_cezca_85% (89)
- NCP IschemicDokument19 SeitenNCP IschemicChristina Espiña EjercitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Cerebrovascular AccidentDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Cerebrovascular AccidentJobelle AcenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVA Activity IntoleranceDokument1 SeiteCVA Activity IntoleranceNursesLabs.com75% (4)
- NCP Spiritual DistressDokument3 SeitenNCP Spiritual DistressAngelo ArabejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan CVADokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan CVAhermesdave175% (4)
- ASPIRIN Drug Study ERDokument1 SeiteASPIRIN Drug Study ERMargueretti Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 02Dokument6 SeitenAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 02AgronaSlaughterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired MobilityDokument3 SeitenImpaired MobilityYeana AlonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDokument3 SeitenImpaired Verbal CommunicationDesiree Deleon Guerrero0% (2)
- Calcitriol - Drug InformationDokument13 SeitenCalcitriol - Drug InformationNikesh DoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaPuteri AzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gcic NCP Seizure PICUOSMUNDokument2 SeitenGcic NCP Seizure PICUOSMUNhanyaklein100% (3)
- Lung Cancer (Nursing Care)Dokument5 SeitenLung Cancer (Nursing Care)heiyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stroke Nursing Care PlanDokument1 SeiteStroke Nursing Care PlanTracy PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pain Management Teaching PlanDokument9 SeitenPain Management Teaching PlanMarion Liana DayritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icu NCPDokument4 SeitenIcu NCPdrsabuegNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Dokument4 SeitenAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDokument6 SeitenImpaired Verbal CommunicationLaura Sansonetti100% (1)
- NCP 2 Addison's DiseaseDokument4 SeitenNCP 2 Addison's DiseaseRenee RoSeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP LocDokument2 SeitenNCP LocMel RodolfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument2 SeitenNCPJhel NabosNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sDokument4 Seiten"Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sAllisson BeckersNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP LymphedemaDokument1 SeiteNCP Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- NCP ImmobilityDokument2 SeitenNCP Immobilityxxxcamzxxx67% (6)
- Anatomy and Physiology of CVADokument4 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of CVAKimsha ConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Failure - Nursing ManagementDokument9 SeitenHeart Failure - Nursing ManagementAuni Akif Aleesa100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Fracture PN303Dokument10 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Fracture PN303Fryam Bells100% (3)
- Nursing Diagnosis of Prostate CancerDokument3 SeitenNursing Diagnosis of Prostate CancerSyafiqAzizi100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Planapi-38118511380% (10)
- Patriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. YingDokument1 SeitePatriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. Yingjanna mae patriarca100% (1)
- NCP-Impaired Physical MobilityDokument3 SeitenNCP-Impaired Physical MobilityRene John FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disturbed Body ImageDokument3 SeitenDisturbed Body Imagenura100% (1)
- NCP SLEDokument13 SeitenNCP SLEMary Mae Bercacio Buella100% (3)
- Nursing Care Process (NCP) Stress Overload PrepartumDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Process (NCP) Stress Overload PrepartumFrederene JavelonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVA Nursing Management BANGDokument4 SeitenCVA Nursing Management BANGAna Louise BatallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument10 SeitenNursing Care PlanMalou SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Set 1Dokument18 SeitenNCP Set 1Augene Toribio50% (2)
- AssessmentDokument2 SeitenAssessmentBriggette AnnangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEalth Education Plan CVADokument4 SeitenHEalth Education Plan CVAJoenaCoy ChristineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dysphagia Feeding Case Study Assignment IpeDokument5 SeitenDysphagia Feeding Case Study Assignment Ipeapi-644004752Noch keine Bewertungen
- Excess Fluid VolumeDokument27 SeitenExcess Fluid VolumeAdrian Ardamil100% (1)
- EIN BaruDokument8 SeitenEIN BaruNatalia LusianingsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icu ReqDokument9 SeitenIcu Reqzygote_23100% (1)
- Self Care DeficitDokument2 SeitenSelf Care DeficitCalimlim KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPAldrece CastroverdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ve Efn2 TB U07Dokument11 SeitenVe Efn2 TB U07Milka Rocha FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Problem: Symptoms and Nursing Care PlanDokument7 SeitenThyroid Problem: Symptoms and Nursing Care PlanAisa ShaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reframing The Competency of Nurses: The 4 C's of TransculturalityDokument1 SeiteReframing The Competency of Nurses: The 4 C's of TransculturalityJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growing Old in Prison? A Review of National and International Research On Ageing OffendersDokument44 SeitenGrowing Old in Prison? A Review of National and International Research On Ageing OffendersJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- LINKDokument2 SeitenLINKJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract of Feasibility StudyDokument1 SeiteAbstract of Feasibility StudyJoy Jarin100% (2)
- Abstract of WhirlDokument1 SeiteAbstract of WhirlJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract BarangayDokument2 SeitenAbstract BarangayJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract OnlineDokument1 SeiteAbstract OnlineJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MenstruationDokument37 SeitenMenstruationJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Feb 2012, Web.) : ProteinuriaDokument25 Seiten4 Feb 2012, Web.) : ProteinuriaJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research CongressDokument2 SeitenResearch CongressJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sleep If You Can: © 2009 Steven A. Hessler All Rights ReservedDokument1 SeiteSleep If You Can: © 2009 Steven A. Hessler All Rights ReservedJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budonoside (Drug Study)Dokument1 SeiteBudonoside (Drug Study)Joy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opportunistic Diseases For AIDSDokument9 SeitenOpportunistic Diseases For AIDSJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCMH Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenCCMH Drug StudyJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mary Joy M. Jarin NCM 101 Bsn-2A: Reflection Paper "The Womb"Dokument1 SeiteMary Joy M. Jarin NCM 101 Bsn-2A: Reflection Paper "The Womb"Joy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVP - Nursing Performance ChecklistDokument3 SeitenCVP - Nursing Performance ChecklistJoy Jarin75% (4)
- Ros Labs Functional (CASE STUDY)Dokument4 SeitenRos Labs Functional (CASE STUDY)Joy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute GastroenteritisDokument19 SeitenAcute GastroenteritisJoy Jarin100% (1)
- Nutrition For Low Infant BirthDokument70 SeitenNutrition For Low Infant BirthJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euthenics, Report, Maternal and ChildDokument88 SeitenEuthenics, Report, Maternal and ChildJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MenstruationDokument37 SeitenMenstruationJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biliary SystemDokument48 SeitenBiliary SystemJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health InformaticsDokument19 SeitenHealth InformaticsJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - The Period of Pregnancy & Prenatal DevelopmentDokument41 SeitenChapter 5 - The Period of Pregnancy & Prenatal DevelopmentJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary SystemDokument67 SeitenUrinary SystemJoy Jarin100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - The Period of Pregnancy & Prenatal DevelopmentDokument41 SeitenChapter 5 - The Period of Pregnancy & Prenatal DevelopmentJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newborn 1Dokument44 SeitenNewborn 1Joy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journals - IntrapostpartumDokument13 SeitenJournals - IntrapostpartumJoy JarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursingbulletin Laws Affecting The Practice of NursingDokument4 SeitenNursingbulletin Laws Affecting The Practice of Nursingseigelystic100% (43)
- MCAT 2011 Eng+keyDokument5 SeitenMCAT 2011 Eng+keyOmar GillNoch keine Bewertungen
- The PharmakeusDokument3 SeitenThe PharmakeusRimon AromatherapyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Performance Appraisal SystemDokument15 SeitenProject Report On Performance Appraisal Systemapa_kul89081573Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rehabilitating Juvenile DeliquentsDokument28 SeitenRehabilitating Juvenile DeliquentsMohammed Tahir kalefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Principles of High Quality AssessmentDokument3 Seiten12 Principles of High Quality Assessmentemilyaranas67% (3)
- Developing VirtueDokument26 SeitenDeveloping VirtueTulungan Para sa Modular at Online ClassesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project All NumeratesDokument1 SeiteProject All NumeratesGrace Joy S ManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Age 4 5 Chota Bheem Vol1 Print Learn CenterDokument101 SeitenAge 4 5 Chota Bheem Vol1 Print Learn CenterAbhishek SenGuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade9 Week2 Arts DLL FormatDokument1 SeiteGrade9 Week2 Arts DLL FormatRod ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Messages Self Help Through Popular CultureDokument149 SeitenMessages Self Help Through Popular CultureAnton TvrdikNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lecture-Discussion ModelDokument22 SeitenThe Lecture-Discussion Modelsarah abou najm100% (1)
- Marico Bangladesh LimitedDokument4 SeitenMarico Bangladesh LimitedMonjurull MannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- English - Follow 1 To 2 Step DirectionDokument27 SeitenEnglish - Follow 1 To 2 Step DirectionMICHELE PEREZ100% (1)
- Stage 1: Trust vs. MistrustDokument3 SeitenStage 1: Trust vs. MistrustCep Loreine GendranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diass Unit III Lesson 1 Discipline of CommunicationDokument18 SeitenDiass Unit III Lesson 1 Discipline of CommunicationLester King Vidal AgaloosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absolutely FeminineDokument11 SeitenAbsolutely FeminineJustina von DanzigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion 8 2 Frontiers of MicroeconomicsDokument1 SeiteDiscussion 8 2 Frontiers of MicroeconomicsTech TricksNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 Job Interview Tips - How To Make A Great ImpressionDokument7 Seiten21 Job Interview Tips - How To Make A Great ImpressionAJAI KUMAR NAVARETNAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPS PUBLIC SPEAKING 2018 - Amy TamanDokument5 SeitenRPS PUBLIC SPEAKING 2018 - Amy TamanDhanta RamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case #7 Balancing Values-An Indian Perspective On Corporate ValuesDokument4 SeitenCase #7 Balancing Values-An Indian Perspective On Corporate ValuesRyšard GvozdovičNoch keine Bewertungen
- FCE Reading and UseDokument11 SeitenFCE Reading and Usekevcully33% (3)
- Als Skills Quarter 3 Week 4 Las 1Dokument1 SeiteAls Skills Quarter 3 Week 4 Las 1doris rondeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aliens Among Us - A Ufo Conspiracy Hypothesis in A Religion - John WhiteDokument9 SeitenAliens Among Us - A Ufo Conspiracy Hypothesis in A Religion - John WhiteEnrico BiaginiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Motivation in Banks: Are There Differences Between Sexes?Dokument79 SeitenWork Motivation in Banks: Are There Differences Between Sexes?deepakNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Facets of UnderstandingDokument1 Seite6 Facets of UnderstandingEmmi M. RoldanNoch keine Bewertungen
- An in Depth of Johnny in Juno and The PaycockDokument1 SeiteAn in Depth of Johnny in Juno and The PaycockNikhil A Bheeroo0% (1)
- Article 13Dokument10 SeitenArticle 13MahaZakhourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficacy of Attachment-Based Family Therapy Compared To Treatment As Usual For Suicidal Ideation in Adolescents With MDDDokument11 SeitenEfficacy of Attachment-Based Family Therapy Compared To Treatment As Usual For Suicidal Ideation in Adolescents With MDDGabriela MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gu Lingfei 191 Chapter 191 After The MealDokument49 SeitenGu Lingfei 191 Chapter 191 After The Mealsekayi D GonyoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLM RESEARCH 7 Week 5 Classification of Observable Properties of MatterDokument5 SeitenSLM RESEARCH 7 Week 5 Classification of Observable Properties of MatterAnn NecdoteNoch keine Bewertungen