Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
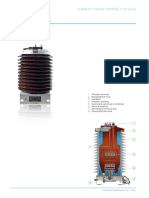
Live Tank CT
Hochgeladen von
bisas_rishiOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Live Tank CT
Hochgeladen von
bisas_rishiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Circuit breakers: Circuit breakers are available as live tank, dead tank, or grounded tank designs.
Dead tank means interruption takes place in a grounded enclosure and current transformers are located on both sides of the break (interrupter contacts). Interrupter maintenance is at ground level and seismic withstand is improved versus live tank designs. Bushings (more accurately described as gas-filled weathersheds, because, unlike the condenser bushings found on bulk oil circuit breakers, gas breakers do not have true bushings) are used for line and load connections that permit installation of bushing current transformers for relaying and metering at a nominal cost. The dead tank breaker does require additional insulating oil or gas (i.e., more insulating oil or gas than just the amount required to perform successful interruption and to maintain adequate dielectric strength) to provide the insulation between the interrupter and the grounded tank enclosure. Live tank means interruption takes place in an enclosure that is at line potential. Live tank circuit breakers consist of an interrupter chamber that is mounted on insulators and is at line potential. This approach allows a modular design as interrupters can be connected in series to operate at higher voltage levels. Operation of the contacts is usually through an insulated operating rod or rotation of a porcelain insulator assembly via an operating mechanism at ground level. This design minimizes the quantity of oil or gas required as no additional quantity is required for insulation of a grounded tank enclosure. The live tank design also readily adapts to the addition of pre-insertion resistors or grading capacitors when they are required. Seismic capability requires special consideration due to the high center of gravity of the live tank breaker design, and live tank circuit breakers require separate, structure mounted, free standing current transformers. Grounded tank means interruption takes place in an enclosure that is partially at line potential and partially at ground potential. Although the grounded tank breakers current transformers are on the same side of the break (interrupter contacts) the grounded tank breaker relays just like a dead tank breaker. The grounded tank breaker design came about as a result of the installation of a live tank breaker interrupter into a dead tank breaker configuration. Current transformer: The Outdoor Current Transformers may be Live Tank Design or Dead Tank Design. In the Live tank design, Active part (ie Core with secondary and Primary duly insulated) is in the top tank. Top Tank is live and secondary is insulated and taken to the bottom tank. In Dead Tank design, Active part is in bottom tank. The bottom tank is dead ( in ground Potential) and the primary is insulated and taken to the top tank for primary termination.
Dead Tank is more applicable because its cheaper. The manufacturing of bushing for power transformer can be used is this case and automatic wrapping of paper made it easy to manufacture (time and cost reduces) and available in plenty from many manufacturers. Installation is easier since the tank is far from live line. Advantages of Live tank --> a) Shorter primary conductor gives better rigidity and high short circuit current withstanding capability. b) With uniformly distributed primary winding these CTs are with lower reactance -->provides inherent better transient performance. c) Main source of heat - high current part is only in primary tank -- ensures less heating of bushing/core compared to dead tank type design. This ensures better thermal stability and less problem created through dissolved gas in insulating oil. In case something goes wrong - a well designed live tank CT wont explode only from top unlike the blast of insulator core of dead tank CTs' which can damage human life a well as the other substation equipments nearby.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Iec 62052-31-2015Dokument192 SeitenIec 62052-31-2015shepherd100% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Standard Operating Procedure - Format (Recovered)Dokument16 SeitenStandard Operating Procedure - Format (Recovered)Mahadev Kovalli75% (8)
- BS en 12101-3-2015Dokument104 SeitenBS en 12101-3-2015Đăng Luật LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMC 256plus User Manual PDFDokument154 SeitenCMC 256plus User Manual PDFbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barbell 55 Workout Plan by Guru Mann PDFDokument4 SeitenBarbell 55 Workout Plan by Guru Mann PDFbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Relay Testing Flowchart Valence Electrical Training Services PDFDokument2 SeitenDigital Relay Testing Flowchart Valence Electrical Training Services PDFbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barbell 55 Nutrition Plan by Guru Mann PDFDokument8 SeitenBarbell 55 Nutrition Plan by Guru Mann PDFbisas_rishi100% (1)
- Understanding of Electrical HarmonicsDokument2 SeitenUnderstanding of Electrical Harmonicsbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line Petroling ReportDokument2 SeitenLine Petroling Reportbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 132Kv System Battery Report I.R.O. Dharampur 132/33Kv Station For The Month of January 2013Dokument4 Seiten132Kv System Battery Report I.R.O. Dharampur 132/33Kv Station For The Month of January 2013bisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance Procedure For Switchyard Equipment Volume-II (EHDokument39 SeitenMaintenance Procedure For Switchyard Equipment Volume-II (EHbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load DetailsDokument2 SeitenLoad Detailsbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BO Lighting Arrester 2Dokument16 SeitenBO Lighting Arrester 2bisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Data and Standards SF: - Gas Insulated Switchgear GISDokument3 SeitenTechnical Data and Standards SF: - Gas Insulated Switchgear GISbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WES B Ngal State Electricity Transmission Company TE: T E Limi DDokument1 SeiteWES B Ngal State Electricity Transmission Company TE: T E Limi Dbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wbsedcl Tariff 2013-14Dokument33 SeitenWbsedcl Tariff 2013-14Abhishek VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- United Bank of India Annex-Iii AS ON 01.06.2014 Deposit AccountsDokument5 SeitenUnited Bank of India Annex-Iii AS ON 01.06.2014 Deposit Accountsbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- My ElectricalDokument3 SeitenMy Electricalbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Calculate The Power of Capacitors: Calculation ExampleDokument2 SeitenHow To Calculate The Power of Capacitors: Calculation Examplebisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MainDokument1 SeiteMainbisas_rishiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Worksheet PDFDokument1 Seite05 Worksheet PDFZelalemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access Online Vol IsDokument20 SeitenAccess Online Vol IsMohan RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- E11 WI VFD ManualDokument146 SeitenE11 WI VFD Manualkamal_khan85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pfisterer HV Cable SystemsDokument11 SeitenPfisterer HV Cable Systemsgabriel_petre2001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Condenser BushingsDokument8 SeitenFundamentals of Condenser Bushingswaqas_a_shaikh4348Noch keine Bewertungen
- CNC Machine ReportDokument21 SeitenCNC Machine Reportring-a-lingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 KV Insulation Diagnostic System Megger Delta Adiradh Energy 1Dokument4 Seiten12 KV Insulation Diagnostic System Megger Delta Adiradh Energy 1raju singh shekhawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nema GD 3-2019 WatermarkedDokument11 SeitenNema GD 3-2019 WatermarkedNoli CorralNoch keine Bewertungen
- BB2 PDFDokument28 SeitenBB2 PDFMedoBoudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue SediverDokument28 SeitenCatalogue SedivermarcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saudi Aramco Test Report: DC Cable Holiday Testing 3-Jul-18 CP-SATR-X-3201Dokument3 SeitenSaudi Aramco Test Report: DC Cable Holiday Testing 3-Jul-18 CP-SATR-X-3201karthi51289Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Slides On Electrostatic ConductorsDokument61 SeitenLecture Slides On Electrostatic ConductorsRitick srivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- InstruDokument37 SeitenInstrucxrxixsxNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB 02201001 eDokument98 SeitenTB 02201001 eKush SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CX Series: Dry Insulation: Model CX Up To 72.5 KVDokument4 SeitenCX Series: Dry Insulation: Model CX Up To 72.5 KVEric DondebzangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 220/132 Grid Substation PresentationDokument19 Seiten220/132 Grid Substation PresentationRéyâńśh Sìņğhánìa100% (1)
- Aeropan 2017 GBDokument20 SeitenAeropan 2017 GBPaulo DiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding SystemDokument13 SeitenBonding SystemHilman NurzenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity Unit Test Review AnswersDokument12 SeitenElectricity Unit Test Review AnswersRon ChongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Denon AVR-4810 - CIDokument245 SeitenDenon AVR-4810 - CIrd6i100% (1)
- 83837d 1 PDFDokument183 Seiten83837d 1 PDFKhedr HamoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Insulation Health Monitoring White Paper EnglishDokument13 SeitenMotor Insulation Health Monitoring White Paper EnglishFauzan Fakhrul ArifinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aging Characteristics of Polymeric Materials by Repeated Surface Flashovers in Vacuum Under Microsecond PulseDokument8 SeitenAging Characteristics of Polymeric Materials by Repeated Surface Flashovers in Vacuum Under Microsecond PulseGilang Satria PasekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power CablesDokument167 SeitenPower CablessubramanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elastimold CableDokument40 SeitenElastimold CableArmin Fernández GerardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrostaticsDokument87 SeitenElectrostaticsart angelNoch keine Bewertungen
- RA 40 - Working With ElectricityDokument1 SeiteRA 40 - Working With ElectricitykazishahNoch keine Bewertungen