Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Air University: Electrical Engineering Department
Hochgeladen von
Ali AhmadOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Air University: Electrical Engineering Department
Hochgeladen von
Ali AhmadCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Air University
Electrical Engineering Department
Digital Data Networks (BETE- VIII)
Experiment # 1 Basic Functions of the Telephone Set
Objectives: To present the fundamental principles governing the theory and operation of the telephone set. Equipments required: 1. 2. 3. 4. Telephone set available at the lab office. Standard length twisted pair wire. Non standard length twisted pair wire. Oscilloscope.
Introduction: Before discussing the operation of the telephone set, let us consider some of the basic functions that it serves: 1- It must notify the user of an incoming call through an audible tone such as ring or bell. 2- It should be able to transduce a callers speech to electrical signals and conversely, electrical signals must be transduced to audible speech signals. 3- It should provide a method of dialing subscriber numbers. 4- The ability to regulate the speech amplitude of the calling party. 5- It must gain the attention of the central office when a user requests service by lifting the handset.
6- There must be a nominal amount of feedback from its microphone to its speaker. 7- When the telephone set is not in use, an open circuit DC path must be provided to the central office. 8- In addition to receiving voice, it must be able to receive other call progress tones such as busy, ringing and so on from the central office. The Conventional Telephone Set:
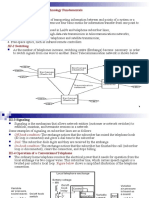
Figure (1) Block diagram of the telephone set.
According to the block diagram shown above: 1- The dialing circuit could be rotary dial switch or the modern DualTone Multifrequency (DTMF) keypad. 2- When the telephone is at rest in its cradle, this is called on-hook condition, and when the handset is lifted off its cradle, then it is on off-hook condition. 3- The power for the telephone set is derived from a -48V DC supply located at the central office. 4- The hybrid circuit is used to transform the two wire subscriber loop into four wires, hence separating the transmitted and received signals (full-duplex). 5- Equalizer circuit is used to regulate voice amplitude.
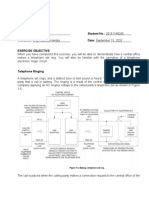
Bell 500 Telephone Set: It was introduced in 1951, and been used as industrial standard for more than four decades. Figure (2) illustrates the schematic diagram of Bell 500 telephone set.
Figure (2) Schematic diagram Bell 500 telephone set. S1 and S2 are on-hook and off-hook switches, both are either open (on-hook) or closed (off-hook). D1 is Rotary Dialing Switch, and D2 shorts receiver when you are dialing. S3 shorts receiver output when in the on-hook position. The capacitor in the ringing circuit is used to block the DC current and pass the AC ringing current, its value combined with the coil inductance, is selected to provide a high impedance to voice frequencies.
The balancing network allows the manufacturer to adjust a small amount of feedback from the telephone sets transmitter to its receiver.
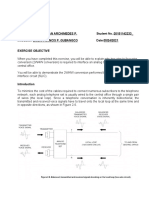
When handset is lifted off its cradle, the normal -48V DC on-hook voltage supplied by the telephone company drops to (-5 to -8) V DC due to the impedance that the telephone set presents to the line, figure (3) illustrates the on-hook and ringing voltages for the telephone set.
Figure (3) On-hook and ringing voltages for the telephone set. When the telephone set is at off-hook, the DC current starts to flow in the subscriber loop and hence to the central office, as a result the central office will send a dial tone to the caller indicating that service is available and number may be dialed. Experimental work:
1. Connect the telephone set to socket provided by the central office using the standard twisted pair wire. 2. Using the oscilloscope, measure and draw the on-hook voltage. 3. Using telephone set available at the DSP lab to ring the set available at your experimental lab, measure and draw the ringing voltage provided by the central office using oscilloscope. 4. Connect the telephone set to socket provided by the central office using the non standard twisted pair wire. 5. Repeat steps 2 and 3. Questions: 1. Explain the Balancing Network in figure (2). 2. Draw the voltage versus current diagram of VR given in figure (2). 3. According to the circuit given in figure (2), explain the operation of L1, L2, L3, and L4. 4. What is the effect of the length of the subscriber loop on the transmitted and received signal?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Module 2 - Telephone Instrument and Signals PDFDokument62 SeitenModule 2 - Telephone Instrument and Signals PDFKobe MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTION The Telephone SetDokument6 SeitenINTRODUCTION The Telephone SetAly RoseteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephone: University of The East College of Engineering ECE DepartmentDokument5 SeitenTelephone: University of The East College of Engineering ECE DepartmentShiela Monique FajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telecommunications Technology Fundamentals: III-1 TransmissionDokument24 SeitenTelecommunications Technology Fundamentals: III-1 Transmissionkheyrto foodareNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1-1 Introduction To Basic TelephoneDokument37 SeitenCH 1-1 Introduction To Basic TelephoneJohn Farhan88% (8)
- Telephone Instruments and SignalsDokument17 SeitenTelephone Instruments and SignalsSai KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TelephonyDokument53 SeitenTelephonyAngeline MontalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephone Network System Part 1Dokument109 SeitenTelephone Network System Part 1MelvirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.telephone System and NetworkDokument78 Seiten1.telephone System and NetworkCarla BelenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECX4233 - Session 04 - Integrated Telephone Circuits © OUSLDokument6 SeitenECX4233 - Session 04 - Integrated Telephone Circuits © OUSLzkasunNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 113 The Public Telephone Network 4Dokument25 SeitenECE 113 The Public Telephone Network 4Erven Micabalo UmbaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephony LectureDokument23 SeitenTelephony LectureGlenda GragedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BF Power SupplyDokument5 SeitenBF Power SupplyGiovanni LorchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCS Unit-5Dokument25 SeitenDCS Unit-5Anonymous BbZceWkVnNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSNL ReportDokument34 SeitenBSNL ReportPrahlad KaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review in TelephonyDokument44 SeitenReview in TelephonyLone XRangerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Communication Telecommunication TelecommunicationDokument6 SeitenCommunication Communication Telecommunication TelecommunicationRey BernardinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air University: Electrical Engineering DepartmentDokument4 SeitenAir University: Electrical Engineering DepartmentAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-I-VDC - Voice and Data Communication BookDokument14 SeitenUnit-I-VDC - Voice and Data Communication BookAnonymous 4wy3T5DnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 310MV InstructionsDokument29 Seiten310MV InstructionsMIGUELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephone Instruments, Signals and CircuitsDokument25 SeitenTelephone Instruments, Signals and CircuitsMukesh100% (20)
- EEE1001 Basic Electronics and Electrical Engineering Digital Assignment-02Dokument18 SeitenEEE1001 Basic Electronics and Electrical Engineering Digital Assignment-02SonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 6 Hybrid FunctionDokument26 SeitenExperiment 6 Hybrid FunctionHey BrinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On One Months Industrial Training at BHEL, Hardwar.: "Electronics & Communication Engineering"Dokument24 SeitenReport On One Months Industrial Training at BHEL, Hardwar.: "Electronics & Communication Engineering"Akash SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elective ReviewerDokument9 SeitenElective Reviewerbevzromero22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Controlled Electrical ApplianceDokument17 SeitenMobile Controlled Electrical ApplianceSmile AravindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telecommunication NetworksDokument15 SeitenTelecommunication NetworksendalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Signal Corporation Installation and Service InstructionDokument29 SeitenFederal Signal Corporation Installation and Service InstructionTiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Code ModulationDokument78 SeitenPulse Code ModulationHamid HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refurbish Antique Telephones for Fun and Hobby: Step by Step Instructions to Take an Old Telephone and Return It to Its Original Working Order. No Electronics or Telephone Knowledge Needed.Von EverandRefurbish Antique Telephones for Fun and Hobby: Step by Step Instructions to Take an Old Telephone and Return It to Its Original Working Order. No Electronics or Telephone Knowledge Needed.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Telephone Set: Old Telephone Services (POTS), Which Involves Subscribers Accessing The PublicDokument2 SeitenStandard Telephone Set: Old Telephone Services (POTS), Which Involves Subscribers Accessing The PublicjeevanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephony: Martyn Miguel Q. Tadena, ECE, ECTDokument72 SeitenTelephony: Martyn Miguel Q. Tadena, ECE, ECTJohn Paul FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) Unnao:, Uttar PradeshDokument38 SeitenBharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) Unnao:, Uttar PradeshGAURAV SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Telephone Signaling: Prepared By: ABUAN, RAMIL LDokument20 SeitenBasic Telephone Signaling: Prepared By: ABUAN, RAMIL LRamil L. AbuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TellabDokument13 SeitenTellabAly RoseteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Telephone Instrument and SignalsDokument55 SeitenLecture 1 Telephone Instrument and SignalsMikaela VillalunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephone in TDokument36 SeitenTelephone in TNedim ZaklanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Telecom Networks: Chapter-2Dokument17 SeitenBasics of Telecom Networks: Chapter-2tazebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nec512 Experiment 1 CoDokument11 SeitenNec512 Experiment 1 CoJohn Daniel CoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSNL Telephone KnowledgeDokument27 SeitenBSNL Telephone KnowledgeiamsudhirkrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture #3Dokument37 SeitenLecture #3ShebNoch keine Bewertungen
- SubscriberLoop BDokument19 SeitenSubscriberLoop Bmgoldiieeee0% (1)
- My Homemade PBXDokument11 SeitenMy Homemade PBXaarshpatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide To Cable TV Premise Wire TestingDokument34 SeitenGuide To Cable TV Premise Wire TestingMostafa MohmmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wire Communications HandoutsDokument1 SeiteWire Communications HandoutsmgoldiieeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephone HandsetDokument3 SeitenTelephone HandsetYogesh PalkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telecom Equipment Technology: A Summer Training Report OnDokument32 SeitenTelecom Equipment Technology: A Summer Training Report OnAditya ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephone Exchange SystemDokument7 SeitenTelephone Exchange SystemkellechaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephone Ring CircuitDokument9 SeitenTelephone Ring CircuitS M DineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSNL Report - 1 - NBADokument10 SeitenBSNL Report - 1 - NBAkhadarbasha.n nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephone NetworkDokument18 SeitenTelephone NetworkasuraboiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telecom Networks Lecture1Dokument31 SeitenTelecom Networks Lecture1Basir Usman100% (2)
- Analog Switching TelephoneDokument10 SeitenAnalog Switching Telephoneboutheina ghedeirNoch keine Bewertungen
- VT Report ElectroinicsDokument48 SeitenVT Report ElectroinicshguptabhelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted By: Pravin Kumar 07EC75Dokument28 SeitenSubmitted By: Pravin Kumar 07EC75Pravin SahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorVon Everand110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Electronics Explained: Fundamentals for Engineers, Technicians, and MakersVon EverandElectronics Explained: Fundamentals for Engineers, Technicians, and MakersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Build Your Own Low-Power Transmitters: Projects for the Electronics ExperimenterVon EverandBuild Your Own Low-Power Transmitters: Projects for the Electronics ExperimenterBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- Matlab Training Session Vii Basic Signal Processing: Frequency Domain AnalysisDokument8 SeitenMatlab Training Session Vii Basic Signal Processing: Frequency Domain AnalysisAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Training Session Iii Numerical Methods: Solutions To Systems of Linear EquationsDokument14 SeitenMatlab Training Session Iii Numerical Methods: Solutions To Systems of Linear EquationsAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lectrue # 12 and 13 - 30-04-08Dokument26 SeitenLectrue # 12 and 13 - 30-04-08Ali AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - 30-01-08Dokument17 SeitenLecture 2 - 30-01-08Ali AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Purpose of Business Activity: LECTURE # 01 & 02Dokument9 SeitenThe Purpose of Business Activity: LECTURE # 01 & 02Ali AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Training - SIMULINKDokument8 SeitenMatlab Training - SIMULINKAtta RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Training Session Iv Simulating Dynamic Systems: Sampling The Solution EquationDokument9 SeitenMatlab Training Session Iv Simulating Dynamic Systems: Sampling The Solution EquationAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Training Session Ii Data Presentation: 2-D PlotsDokument8 SeitenMatlab Training Session Ii Data Presentation: 2-D PlotsAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To: Artificial IntelligenceDokument31 SeitenIntroduction To: Artificial IntelligenceAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Printing The Model:: SimulinkDokument8 SeitenPrinting The Model:: SimulinkAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operators: Introduction To ASIC DesignDokument6 SeitenOperators: Introduction To ASIC DesignAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Symbian Os: AIR University AU, PAF Complex, E-9, IslamabadDokument64 SeitenIntroduction To Symbian Os: AIR University AU, PAF Complex, E-9, IslamabadAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Level Logic ( 0', 1') .: Introduction To ASIC DesignDokument8 Seiten2-Level Logic ( 0', 1') .: Introduction To ASIC DesignAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 5.1: Multiplexer #1 Using OperatorsDokument10 SeitenExample 5.1: Multiplexer #1 Using OperatorsAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sequential Code in VHDLDokument42 SeitenSequential Code in VHDLAli Ahmad0% (1)
- Introduction To VHDL: AIR University AU, E-9, IslamabadDokument29 SeitenIntroduction To VHDL: AIR University AU, E-9, IslamabadAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acknowledgement - 2Dokument11 SeitenAcknowledgement - 2Ali AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ASIC Design: Lab Report InstructionsDokument1 SeiteIntroduction To ASIC Design: Lab Report InstructionsAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- System On Chips Soc'S & Multiprocessor System On Chips MpsocsDokument42 SeitenSystem On Chips Soc'S & Multiprocessor System On Chips MpsocsAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- State Machine Block DiagarmDokument6 SeitenState Machine Block DiagarmAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Chips Are DesignedDokument46 SeitenHow Chips Are DesignedAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ASIC Design: Lab Report StandardsDokument1 SeiteIntroduction To ASIC Design: Lab Report StandardsAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air University Fall 2005 Faculty of Engineering Department of Electronics Engineering Course InformationDokument2 SeitenAir University Fall 2005 Faculty of Engineering Department of Electronics Engineering Course InformationAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Filters in VHDL LabDokument5 SeitenDigital Filters in VHDL LabAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second SessionalCourseOutlineDokument1 SeiteSecond SessionalCourseOutlineAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Introduction To AsicsDokument15 SeitenChapter 1: Introduction To AsicsAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment # 3: The EndDokument1 SeiteAssignment # 3: The EndAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment#5Dokument1 SeiteAssignment#5Ali AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment#4Dokument1 SeiteAssignment#4Ali AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument1 SeiteAssignment 1Ali AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- T-Spice User's Guide: Release 16.3 June 2015Dokument579 SeitenT-Spice User's Guide: Release 16.3 June 2015Laxmi GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Loss and Gain CalculationDokument84 SeitenHeat Loss and Gain Calculationafraz_xecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kobelco 30SR Service ManualDokument6 SeitenKobelco 30SR Service ManualG NEELAKANDANNoch keine Bewertungen
- JKM410 430N 54HL4 (V) F3 enDokument2 SeitenJKM410 430N 54HL4 (V) F3 enAmer CajdricNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cobit 2019 Design Toolkit With Description - Group x.20201130165617871Dokument46 SeitenCobit 2019 Design Toolkit With Description - Group x.20201130165617871Izha Mahendra75% (4)
- ZzzsaDokument4 SeitenZzzsanikzperaltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internship Report Sui Asset Department (FROM 29 JUNE 2016 TO 24 JULY 2016)Dokument13 SeitenInternship Report Sui Asset Department (FROM 29 JUNE 2016 TO 24 JULY 2016)Jawaid HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scooptram ST14 Battery: Fully Battery Electric Loader With 14-Tonne CapacityDokument8 SeitenScooptram ST14 Battery: Fully Battery Electric Loader With 14-Tonne CapacityAnonymous Mdw6y7Q1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solucionario Statistics For Business and Economics - David R. Anderson, Dennis J. Sweeney - 8edDokument8 SeitenSolucionario Statistics For Business and Economics - David R. Anderson, Dennis J. Sweeney - 8edTukumaneriko Filiponditoniko0% (1)
- A Study On Welding Defects of Pressure VesselDokument24 SeitenA Study On Welding Defects of Pressure Vesseladamahmad1992100% (1)
- Fallout New OrleansDokument44 SeitenFallout New Orleansender000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research Proposal RubricsDokument1 SeiteResearch Proposal RubricsRonnie Dalgo0% (1)
- Stock Market Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenStock Market Lesson PlanWilliam BaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPT Health and Safety GuidelinesDokument9 SeitenMPT Health and Safety GuidelinesJohn PajeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crimp HandbookDokument24 SeitenCrimp Handbookrony_lesbtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bhopal Gas TragedyDokument25 SeitenBhopal Gas TragedyHarry AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Proposal CarolingDokument7 SeitenProject Proposal CarolingAmparo Daniel Einstein D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- ITS Quick Ref GuideDokument6 SeitenITS Quick Ref GuidedhanahbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Convection (Formulae & Problems)Dokument15 SeitenFree Convection (Formulae & Problems)ananth2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Java Lang OutOfMemoryError Handbook - PlumbrDokument28 SeitenJava Lang OutOfMemoryError Handbook - PlumbrcuonglunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reynolds EqnDokument27 SeitenReynolds EqnSuman KhanalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 10211 Heat2 Heat3Dokument16 SeitenIso 10211 Heat2 Heat3nsk377416100% (1)
- BOOKSDokument8 SeitenBOOKSAhmer SohailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Secure BackupDokument294 SeitenOracle Secure BackupCarlos ValderramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AAE 11.3.1 User Guide ClientDokument475 SeitenAAE 11.3.1 User Guide Clientme4ias100% (2)
- Nessus 6.3 Installation GuideDokument109 SeitenNessus 6.3 Installation GuideminardmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sem 638 Manual de MantenimientoDokument12 SeitenSem 638 Manual de MantenimientoJhon Simanca100% (1)
- Android VersionsDokument7 SeitenAndroid VersionsEdna Mae Salas GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (EngineeringEBookspdf) Failure Investigation of Bolier PDFDokument448 Seiten(EngineeringEBookspdf) Failure Investigation of Bolier PDFcarlos83% (6)
- 2501 Solid Drawn Copper Tubes For General Engineering PurposesDokument8 Seiten2501 Solid Drawn Copper Tubes For General Engineering PurposesKaushik SenguptaNoch keine Bewertungen