Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hepatitis Comparison Table
Hochgeladen von
Angelique Ramos PascuaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hepatitis Comparison Table
Hochgeladen von
Angelique Ramos PascuaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
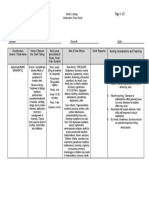
Hepatitis A (HAV) What is it? HAV is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver.
It does not lead to chronic disease.
Hepatitis B (HBV) HBV is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver. The virus can cause liver cell damage, leading to cirrhosis (scarring of the liver) and cancer.
Hepatitis C (HCV) HCV is a virus that causes inflammation of the liver. This infection can lead to cirrhosis and cancer.
Hepatitis D (HDV)
Hepatitis E (HEV)
HDV is a virus that HEV is a virus that causes causes inflammation of the liver. inflammation of It is rare in the United the liver. It only States. There is no infects people with chronic state. HBV. 2 to 8 weeks. 2 to 9 weeks. Average 40 days.
Incubation period 15 to 50 days. 45 to 160 days. Average Average 30 days. 120 days.
2 to 25 weeks. Average 7 to 9 weeks.
How is it spread? Transmitted by Contact with infected blood, Contact with infected fecal/oral route, seminal fluid, vaginal blood, contaminated through close secretions, contaminated IV needles, razors person-to-person needles, including and tattoo/body contact or ingestion tattoo/body piercing tools. piercing tools. of contaminated food Infected mother to Infected mother to and water. newborn. Human bite. newborn. NOT easily Sexual contact. spread through sex. Symptoms May have none. May have none. Some Even fewer acute Adults may have people have mild flu-like cases seen than any light stools, dark symptoms, dark urine, light other hepatitis. urine, fatigue, fever stools, jaundice, fatigue and Otherwise same as and jaundice fever. HBV. (yellowing of the skin). Treatment of chronic disease No specific Interferon and anti-virals. Interferon treatment. (peginteferon) along with the antiviral ribavirin.
Contact with infected blood, contaminated needles. Sexual contact with HDVinfected person.
Transmitted through fecal/oral route. Outbreaks associated with contaminated water supply in other countries.
Same as HBV.
Same as HBV.
Interferon.
Supportive.
Vaccine Two doses of At birth, a second dose vaccine, first dose at between 1 and 2 months, 12 months, second third dose between 6 and dose 6 months later. 18 months. Who is at risk? Household or sexual Infant born to infected contact with an mother, having sex with infected person or infected person or multiple living in an area with partners, IV drug users, HAV outbreak. emergency responders, Travelers to health care workers, men developing countries, who have sex with men, men who have sex household contacts of with men and IV and chronically infected persons non-IV drug users. and dialysis patients. Prevention Get a hepatitis A vaccine. Take immune globulin within two weeks of exposure.
None.
HBV vaccine prevents HDV infection.
None.
Anyone who had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992, health care workers, IV drug users, dialysis patients, infants born to infected mother and having multiple sex partners.
IV drug users, Travelers to developing men who have sex countries, especially with men, dialysis pregnant women. patients, healthcare workers, infants born to infected mothers and those having sex with a HDV infected person. Get a hepatitis B Avoid drinking or using vaccine to prevent potentially contaminated HBV infection. water. Practice safe sex. Wash your hands with soap and water after going to the toilet.
Get a hepatitis B vaccine. Take immune globulin within two weeks of exposure.
Practice safe sex. Clean up spilled blood with bleach. Wear gloves when touching blood.
Practice safe sex. Wash hands with Don't share razors or soap and water after Clean up infected blood with toothbrushes. going to the toilet. bleach and wear protective gloves. Don't inject street Use household drugs. bleach to clean Don't share razors, surfaces toothbrushes or needles. Don't get a tattoo or contaminated with body piercing. feces, such as Don't inject street drugs. changing tables. Don't get a tattoo or body Practice safe sex. piercing.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- InmjDokument8 SeitenInmjParth100% (2)
- Edema Assessment - PhysiopediaDokument3 SeitenEdema Assessment - PhysiopediaJovie Anne Cabangal100% (1)
- FMcase 2Dokument27 SeitenFMcase 2Ryan Townsend100% (3)
- The Pharmacists Guide To Antimicrobial Therapy and StewardshipDokument244 SeitenThe Pharmacists Guide To Antimicrobial Therapy and StewardshipAyman Khalil100% (1)
- Revised NBI Clearance Application Form V1.7 (Fill-In PDFDokument1 SeiteRevised NBI Clearance Application Form V1.7 (Fill-In PDFDavid RobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory QuizDokument32 SeitenRespiratory Quiztajamulhussainshah0% (1)
- Spinal TumorsDokument59 SeitenSpinal TumorsAl-Banji MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nclex Questions - Pediatric NursingDokument8 SeitenNclex Questions - Pediatric NursingAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care For Elderly - TAGALOGDokument29 SeitenCare For Elderly - TAGALOGKarl Kevin MarbellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors influencing compliance to exercise therapy among diabeticsDokument4 SeitenFactors influencing compliance to exercise therapy among diabeticsAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurse of FutureDokument51 SeitenNurse of FutureAngelica YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hindi Pa Man Nauso Ang Salitang SelfieDokument1 SeiteHindi Pa Man Nauso Ang Salitang SelfieAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metropolitan Medical Center Antibiotic Storage ChartDokument1 SeiteMetropolitan Medical Center Antibiotic Storage ChartAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potential Side EffectsDokument5 SeitenPotential Side EffectsAngelique Ramos Pascua100% (1)
- Days and Dates: Learn With Television Learn OnlineDokument1 SeiteDays and Dates: Learn With Television Learn OnlineAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globe BillDokument3 SeitenGlobe BillAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Key Areas of ResponsibilityDokument11 Seiten11 Key Areas of ResponsibilityAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Key Areas of ResponsibilityDokument11 Seiten11 Key Areas of ResponsibilityAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philhealth ManilaDokument1 SeitePhilhealth ManilaAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CoeDokument3 SeitenCoeAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual AcuityDokument4 SeitenVisual AcuityAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Criteria For Proposal Evaluation PointsDokument3 SeitenCriteria For Proposal Evaluation PointsAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architectural Design and Key AnswerDokument13 SeitenArchitectural Design and Key AnswerAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aventus AdvisoryDokument1 SeiteAventus AdvisoryAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kabayan Beach Resort Beach Front: Life GuardDokument1 SeiteKabayan Beach Resort Beach Front: Life GuardAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes and Effects of Poverty ExplainedDokument2 SeitenCauses and Effects of Poverty ExplainedAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obtain Nursing Documents for Quebec Skilled Worker Program ApplicationDokument1 SeiteObtain Nursing Documents for Quebec Skilled Worker Program ApplicationAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bipolar DisorderDokument44 SeitenBipolar DisorderAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refractive Errors - Myopia, Hyperopia, AstigmatismDokument2 SeitenRefractive Errors - Myopia, Hyperopia, AstigmatismAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes and Effects of Poverty ExplainedDokument2 SeitenCauses and Effects of Poverty ExplainedAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IELTS General Training Reading Practice Test 2014 PDFDokument16 SeitenIELTS General Training Reading Practice Test 2014 PDFmunish0875Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plague Words or Phrases-IELTSDokument2 SeitenPlague Words or Phrases-IELTSSujib BarmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CD EbnDokument7 SeitenCD EbnAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pascua, Angelique Ramos 003 Bunnay, Angadanan, IsabelaDokument1 SeitePascua, Angelique Ramos 003 Bunnay, Angadanan, IsabelaAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Let's Be More Than, More Than This, OhDokument1 SeiteLet's Be More Than, More Than This, OhAngelique Ramos PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 - LEC DOH Programs For Communicable - Non-Communicable DiseasesDokument21 Seiten02 - LEC DOH Programs For Communicable - Non-Communicable DiseasesJAN CAMILLE LENONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stroke NoteDokument2 SeitenStroke NoteHanry WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Uas B.ingDokument6 SeitenSoal Uas B.ingNopriani InuarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bells Palsy FPUK Web PDFDokument11 SeitenBells Palsy FPUK Web PDFRadhaKrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health 8 Q3 TGDokument67 SeitenHealth 8 Q3 TGAngelica TumamakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung Cancer Research Paper ThesisDokument7 SeitenLung Cancer Research Paper Thesispukjkzplg100% (1)
- Emergency Drugs Used in DentistryDokument53 SeitenEmergency Drugs Used in Dentistryasmita1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- CPD Jaundice PDFDokument53 SeitenCPD Jaundice PDFAnto PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breath Stacking A Guide For PatientsDokument2 SeitenBreath Stacking A Guide For PatientsaagarwalmdNoch keine Bewertungen
- NizoralDokument4 SeitenNizoralianecunar100% (2)
- diphenhydrAMINE BENADRYLDokument1 SeitediphenhydrAMINE BENADRYLHope SerquiñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Safety ProfileDokument6 SeitenCore Safety ProfileGilang Bhaskara (Whiteheart Angel)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ref 4Dokument13 SeitenRef 4indah setiyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- XII. Health Teaching PlanDokument11 SeitenXII. Health Teaching PlanCharlester Paver0% (3)
- Chapter 4 Social Pharmacy Introduction To Microbiology and Common NoteskartsDokument6 SeitenChapter 4 Social Pharmacy Introduction To Microbiology and Common NoteskartsSushovan AshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdminal Compartment SyndromeDokument9 SeitenAbdminal Compartment SyndromeRafael BagusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laparoscopic Surgery During PregnancyDokument10 SeitenLaparoscopic Surgery During PregnancySyahpikal SahanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advice Following Nasal Surgery Fes Sep20Dokument8 SeitenAdvice Following Nasal Surgery Fes Sep20Adela MarcovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dementia AssignmentDokument19 SeitenDementia AssignmentVandna Vikram Novlani50% (2)
- 2017 AAS ProgramDokument20 Seiten2017 AAS ProgramSiddharth NandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- q4 Health 8 Week 5 1 1newDokument4 Seitenq4 Health 8 Week 5 1 1newdream kingNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABISola Real CorrectedDokument48 SeitenABISola Real CorrectedMarie Prisc ShellNoch keine Bewertungen