Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
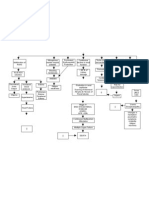
Chronic Renal Failure
Hochgeladen von
Ivana Yasmin BulandresOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chronic Renal Failure
Hochgeladen von
Ivana Yasmin BulandresCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
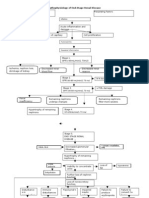
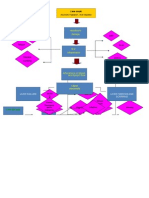
Hypertension Non-modifiable factors: Age greater than 60 years old Hereredofamilial disease (DM, HPN) Gender Race Increase
ease BP to kidneys
Obstruction
Modifiable factors: Hydronephrosis Increased protein and cholesterol intake Smoking Alcohol intake DM, HPN Recurrent infections Use of analgesics
Back-up of urine
Renal artery damaged/ weakened Injury to nephrons/ kidneys
Distend the ureters and might progress to the kidneys
Urine not able to drain out of kidneys
Too much pressure to the kidneys LEGEND: Pathophysiology Complications Nephrosclerosis Clinical Manifestations Lab results or diagnostic exam Nursing Diagnosis Destruction of glomerulus Fibrosis occurs Tissue Necrosis
Distention of the renal pelvis and its calyces
Atrophy of the Kidneys
Deterioration and destruction of kidney nephrons
CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE
Increase BUN Decrease Glomerular filtration rate Increase Serum Creatinine (6.65 g/dL) 37
Hypertrophy of remaining nephrons
Dehydration
Dilute Polyuria
Inability to concentrate urine
Loss of sodium in urine
Hyponatremia (123 mg/dL)
Hct= 30.4% WBC= 16.4 T/cumm Neutrophils= 90% Lymphocytes= 8%
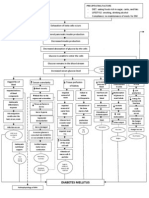
further loss of nephron function Gram Staining Gram positive cocci in pairs are rare Loss of non-excretory function Cellulitis Delayed wound healing Decrease H+ excretion Decrease Potassium excretion Hyperkalemia Decrease Sodium reabsorption in tubules Decreased urine output, oliguria, 10cc Decrease Excretion of Nitrogenous waste Loss of excretory function
Dopamine side drip x 10cc for 1 hour Dobutamine side drip x 20cc for 1 hour
Disturbances in reproductive system Immune disturbances due to uremic toxins Decrease Lipoprotein lipase activities Impaired insulin action
3 1
Decreased libido and infertility Immunosuppression /leukocytes suppresion Accumulation of lipids in peripheral tissues Increase glucose level
Infection
Metabolic Acidosis
Decrease Phosphate excretion Hyperphosphatemia
Increase triglycerides Atherosclerosis Decrease Calcium absorption Hypocalcemia Release PTH Hyperparathyroidism
Hypergylcemia
Water retention
Failure to produce erythropoietin
Anemia
Palor, fatigue, pale palpebral conjunctiva Hct= 30.4% Osteodystrophy, hypocalcemia
Hgb= 10.2 mg% RBC= 3.4 T/cumm
Hypertension Heart Failure Pulmonary Edema, Peripheral Edema 38
Decrease activation of Vitamin D
Decrease calcium absorption in GIT
Infection r/t presence of wound on left foot as evidenced by redness and swelling Independent: Monitor vital signs Do proper wound care Do proper hand washing before and after handling the area Stress proper Maintain proper and adequate hydration and catheterize Collaborative: Monitor laboratory findings Cloxacillin 500 mg IVTT q 6O ANST
2
Increase BUN Increase uric acid, (9.8 mg/dL) Sepsis Proteinuria Trace, 5 mg/dL Increase Creatinine (6.65 mg/dL)
Uremia
Peripheral Nerve Changes
Pericarditis Continuous Multisystem affection CNS Changes Pruritus Multiple organ failure Uremic Encephalopathy
Bleeding
Altered Taste (Metallic)
Fluid Volume excess r/t water retention Independent: Monitor blood pressure Monitor intake and output Record occurrence of dyspnea Note presence of edema Observe and assess skin and mucous membrane Collaborative: Administer Lasix 20mg IV Dopamine side drip x 10cc for 1 hour
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion r/t decreased hemoglobin concentration in blood Independent: Monitor vital signs Assess for signs of changes in mentation Assess capillary refill Monitor GCS Collaborative: Administer O2 therapy Administer: Salbutamol nebulization q 80 Trombocil 50 mg 1 tab BID
DEATH
39
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CKDDokument3 SeitenCKDMarc Lawrence Balderas CAra100% (1)
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDokument9 SeitenNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsKimberly Bomediano100% (1)
- End-Stage Renal DiseaseDokument3 SeitenEnd-Stage Renal DiseaseAkira Pongchad B100% (1)
- Chronic Renal FailureDokument1 SeiteChronic Renal Failurejj_cuttingedges100% (2)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDokument3 SeitenChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept maps100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure (Condensed) Part 2Dokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure (Condensed) Part 2deborah malnegro100% (5)
- CKD PathophysiologyDokument1 SeiteCKD Pathophysiologylloyd_santino67% (3)
- Pathophysiology CKDDokument1 SeitePathophysiology CKDReymon Mary JanineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRDDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRDRonald Lavada RN100% (1)
- Acute Renal Failure PathoDokument4 SeitenAcute Renal Failure PathoGlenn Asuncion Pagaduan100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Hypertension: RAAS Activation and Organ DamageDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Hypertension: RAAS Activation and Organ DamageAlvin RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology CVDDokument1 SeitePathophysiology CVDPamela Shiermaine FilomenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDokument3 SeitenChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramMeine MheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseKeij AranetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Dokument1 SeitePathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Pathophysiology ESRDDokument9 SeitenPathophysiology ESRDJaye DangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal FailureDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Chronic Renal FailureBettinaFernando80% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailurePerry Oliver AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDokument3 SeitenChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramJake CaballoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map On Renal FailureDokument1 SeiteConcept Map On Renal FailureJessilda Damian VeranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenHypertension PathophysiologyJems60% (5)
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDokument1 SeitePathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsReina SamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of DM IIDokument6 SeitenPathophysiology of DM IIJulie SimaurioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Dokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2faula rocamora100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failuresugarmontejo67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failurekristel_nicole18yaho100% (3)
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDokument2 SeitenPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Holy Angel University Case AnalysisDokument42 SeitenHoly Angel University Case AnalysisJeLyn Valencia DiwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology - ESRDDokument5 SeitenPathophysiology - ESRDheiyu100% (3)
- Pathophysiology Renal FailureDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology Renal FailureHampson Malekano100% (2)
- Pathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)Dokument3 SeitenPathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)marshmalou86% (7)
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDokument3 SeitenHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Colon Cancer and Associated ComplicationsDokument5 SeitenPathophysiology of Colon Cancer and Associated ComplicationsKristaMaeC.Lazo0% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating FactorsDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating Factorsguillermojerry100% (2)
- Laennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenLaennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyTrixie Al Marie100% (3)
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDokument3 SeitenAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Cirrhosis of The LiverDokument48 SeitenManagement of Cirrhosis of The LiverksofianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Kidney Disease Stages, Causes, SymptomsDokument5 SeitenChronic Kidney Disease Stages, Causes, Symptomsjazzy penzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Disorders, Renal Failure, & Renal Dialysis: Remerose C. Ragasa, R.NDokument41 SeitenRenal Disorders, Renal Failure, & Renal Dialysis: Remerose C. Ragasa, R.NremeroseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureDokument40 SeitenPresented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureRavanshi ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYPOCALCEMIADokument27 SeitenHYPOCALCEMIAJeffri SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Kidney Injury: DR Hodan Ahmed Dept of Pediatrics and Child Health Amoud Medical School, AUDokument32 SeitenAcute Kidney Injury: DR Hodan Ahmed Dept of Pediatrics and Child Health Amoud Medical School, AUMohamoud MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternative NamesDokument67 SeitenAlternative NamespashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medsurg ReviewDokument34 SeitenMedsurg ReviewestberryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of DMDokument5 SeitenPathophysiology of DMRgn Mckl100% (3)
- Chronic Renal FailureDokument54 SeitenChronic Renal Failuresanjivdas100% (3)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument39 SeitenChronic Kidney DiseaseAgatha RogerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute-Renal-Failure Lecture OnlyDokument17 SeitenAcute-Renal-Failure Lecture OnlyeyesontheskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Endocrine DisordersDokument55 Seiten1 - Endocrine Disorderscephas chinkoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Failure: Manelle R. Singzon BSN 4A1-1Dokument30 SeitenRenal Failure: Manelle R. Singzon BSN 4A1-1Manelle SingzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Failure Acute and Chronic: NPN 200 Medical Surgical Nursing IDokument31 SeitenRenal Failure Acute and Chronic: NPN 200 Medical Surgical Nursing IJuan ValadezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusDokument3 SeitenPa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusPong's Teodoro SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Renal Failure Pathophysiology, Stages, Complications & ManagementDokument18 SeitenAcute Renal Failure Pathophysiology, Stages, Complications & ManagementSteven Paul DaclesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mohit Rana Vhk-1233 VTH Bvsc. & AhDokument26 SeitenMohit Rana Vhk-1233 VTH Bvsc. & AhAdarshBijapurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Kidney Disease: DR - SarmisthaDokument19 SeitenChronic Kidney Disease: DR - SarmisthaGebby MamuayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Functions & Diseases ExplainedDokument19 SeitenLiver Functions & Diseases ExplainedRacha MougharbelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing: Lab Values: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideVon EverandNursing: Lab Values: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS-v1.1) Symptom Checklist InstructionsDokument3 SeitenAdult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS-v1.1) Symptom Checklist InstructionsCiara GordonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 - 213the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome-A Systematic ReviewDokument4 Seiten06 - 213the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome-A Systematic ReviewAnni SholihahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MD, DM MS & MCHDokument3 SeitenMD, DM MS & MCHAshik ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic SystemDokument4 SeitenLymphatic SystemleixxaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines and Levels of Care For Pediatric Intensive Care UnitsDokument16 SeitenGuidelines and Levels of Care For Pediatric Intensive Care Unitssridhar_physioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Illness: Al Duane B. Ungab, RN, MANDokument61 SeitenChronic Illness: Al Duane B. Ungab, RN, MANJainah Rose Ferrer GubacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Cerebral Palsy 2022Dokument53 SeitenIntroduction To Cerebral Palsy 2022Namakau MuliloNoch keine Bewertungen
- (1-3) Hypoglycemia Induced Hemichorea (HpogC) (IJGN) - Shashi PrakashDokument3 Seiten(1-3) Hypoglycemia Induced Hemichorea (HpogC) (IJGN) - Shashi Prakashneeraj2811Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biocompatibility Tests: by Sahana.R PG-1YrDokument12 SeitenBiocompatibility Tests: by Sahana.R PG-1YrSahana RangarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Neurodynamics and Sports Medicine: Origins and DevelopmentDokument8 SeitenClinical Neurodynamics and Sports Medicine: Origins and DevelopmentWahid NasrudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychosis Clinical Learning Module With VsimDokument3 SeitenPsychosis Clinical Learning Module With VsimNicole PutratzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient Satisfaction With Anesthesia Care Among Open Cholecystectomy Patients in A Tertiary Hospital in The PhilippinesDokument46 SeitenPatient Satisfaction With Anesthesia Care Among Open Cholecystectomy Patients in A Tertiary Hospital in The PhilippinesCharisse Alexia DinopolNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.malignant Tumours of Epithelial Cell Origin-2Dokument86 Seiten2.malignant Tumours of Epithelial Cell Origin-2Dinesh Kr. YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- HopeDokument24 SeitenHopeKeydie VillacrucisNoch keine Bewertungen
- KapnografijaDokument9 SeitenKapnografijaMarijana JakobovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Reality in TBIDokument9 SeitenVirtual Reality in TBIsampathNoch keine Bewertungen
- CODE STROKE Checklist:: NotesDokument1 SeiteCODE STROKE Checklist:: NotesAdam MochtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spinal Cord Injury and Compression PDFDokument6 SeitenSpinal Cord Injury and Compression PDFRem AlfelorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measure Free PSA Levels with iFlash AnalyzerDokument4 SeitenMeasure Free PSA Levels with iFlash AnalyzerNIGHT tubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post-Mortem Inspection of BovinesDokument2 SeitenPost-Mortem Inspection of BovinesMuhammad SiddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDokument2 SeitenHypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseYna AcerdenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arogya Sanjeevani Policy-Brief SynopsisDokument13 SeitenArogya Sanjeevani Policy-Brief SynopsisvikrantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final-Exam-Santosa HospitalDokument3 SeitenFinal-Exam-Santosa HospitalWitrian NuranggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induced Abortion: Dr. Ali Murad Dr. Wassan NoriDokument12 SeitenInduced Abortion: Dr. Ali Murad Dr. Wassan NoriAmmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost-Effectiveness of Periodontitis TreatmentsDokument7 SeitenCost-Effectiveness of Periodontitis TreatmentsSebastián BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preventing Drug Therapy ProblemsDokument28 SeitenPreventing Drug Therapy ProblemsKhalid Bin AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1: 4D's Concept Map About Medical Technology ProfessionDokument2 SeitenModule 1: 4D's Concept Map About Medical Technology ProfessionErshid BahangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation Intro TuberculosisDokument8 SeitenPresentation Intro TuberculosisEidi IdhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMR Guideline7001495889Dokument64 SeitenAMR Guideline7001495889Drkrantianand Anand100% (1)
- STEMI Inferior Wall Onset 3 Hours Killip I: Dr. Juzny Alkatiri, SP - PD, SP - JP, Fiha, FinasimDokument33 SeitenSTEMI Inferior Wall Onset 3 Hours Killip I: Dr. Juzny Alkatiri, SP - PD, SP - JP, Fiha, FinasimAnwar Mo SajaNoch keine Bewertungen