Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Final Exam f4 Paper2 Skema
Hochgeladen von
Jacklynlim LkcOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Final Exam f4 Paper2 Skema
Hochgeladen von
Jacklynlim LkcCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
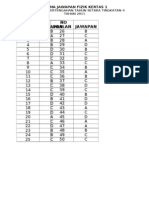
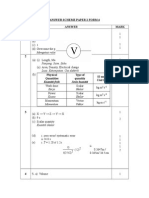
1
a b(i) (ii)
Micrometer screw gauge Reading = 1.5 mm + 0.18 mm = 1.68 mm Thickness of a piece of cardboard = = 0.336 mm
1.68 5
1 mark 1 mark 1 mark
c 2 a b c d 3 a b c
The reading using micrometer screw gauge is more accurate Vernier calipers Zero error +0.02 5.64 (+0.02) = 5.62 Diagram 3(a) The impulsive force in diagram 3(a) is much bigger that diagram 3(b)
v 2 = u 2 + 2as
2
1 mark 1 mark 1 mark 1 mark 2 marks 1 mark 1 mark 2 marks
v = 0 + 2(10 )5 v = 10ms 1
d(i)
F=
50( 0 10 ) 0.5 50( 0 10 ) 1.5
1 mark
= 1000 N
(ii)
F=
1 mark
= - 333.3 N 4 a b Pascals principle
P= F 200 = A ( 0.6 ) 2 F ma = A A PA 176.9 ( 3) = a 10
2
1 mark 1 mark
= 176.9 Pa c
P= m=
2 marks
= 499.9 kg d i upward force ii forward thrust iii drag iv weight 4 marks
(a)(i)
Magnitudes: F1 = F2 & F3 = F4
2 marks
Directions: F1 = F4 & F2 = F3 (ii) (iii) (b)(i) (ii) 6 (a) (i) (ii) (iii) Net Force is zero ( F= 0 ) Balanced force / NewtonThird Law of Motion / Force in equilibrium The air craft will experience acceleration or increase in vevlocity. A net Force exists ( F 0 ) The distance moved by the students hand in Diagram 6.2 is more then the distance moved by the students hand in Diagram 6.1 The work done in Diagram 6.2 is more as compared to the work done in Diagram 6.1 Work Done = Force x distance = 20 x 0.5 = 10 J The distance of projection increases as the energy gained increases. The principle of conservation of energy Same Iron ball is thrown from the same height.. Time taken is independent of the mass. s = ut + gt or t = v-u/g 7 (a) (i) (ii) (b) (i) Pascals principle Pressure at P is same as the pressure at Q. P= F /A = 50 N / 0.04 m = 1250 Pa P = F /A 1250 = F / 0.8 F = 1250 / 0.8 F = 1000 N When the handle is pressed down several times, a force is apllied to the small piston. The resultant pressure is transmitted uniformly to the larger piston. The force is greater due the large surface area and able to lift the load. Increase the cross-setional area of the large piston. Open the release valve. 1 mark 1 mark 2 marks 1 mark 1 mark 1 mark 2 marks 1 mark 1 mark 2 marks
(b) (i) (ii) (c) (i) (ii)
1 mark 1 mark 1 mark 1 mark
(ii)
1 mark
(c) (i)
2 marks
(ii) (iii)
2 marks 1 mark
(a)
Electric energy
Heat energy
1 mark
(b)
E = mc = (0.5)(4200)(100C - 30C = 147000 J = 147 kJ l = Pt / m = (500) (60) / 0.0125 = 2400000 JKg- = 2.4 x 10-6 JKg-
2 marks
(c)
2 marks
(d) (i)
Pt = mc 600 t = (3.0) (390) (170) = 198 900 t = 331.5 s
(ii)
l = Pt / m 600 t = (2.5)(900)(170) = 382500 t = 318.75 s 5 marks
(iii)
Pt = mc (900) t = (4.0) (400) (170) = 272 000 t = 302.22 s
(e) (i) (ii)
Plat S. H heats up faster.
1 mark 1 mark
Answer
Mark
9a(i) (ii)
Ability to return to original shape & size when applied force is removed Elastic cord M is thicker than elastic cord N. Maximum height reached by arrow in Diagram 9.2(b) is higher than in Diagram 9.2(a). The thicker the elastic cord, the higher the maximum height reached. Thicker elastic cord has bigger force constant. Thicker elastic cord has bigger elastic potential energy. F2 F1 Thicker elastic cord has bigger force constant, so need bigger force to stretch. Elastic potential energy to kinetic energy to gravitational potential energy Aspect Tight attire or light attire Sprint or acceleration Hard stepping plank Thicker mattress Landing with the body flat Mark Explanation 1 1 1 1 1 To reduce air resistance or to reduce weight Increase momentum or force To reduce time of impact, so impulsive force increases To lengthen time of impact, so impulsive force is reduced To lengthen time of impact, so impulsive force is reduced Mark 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2
b(i) (ii) c(i)
10a b(i) (ii) c(i) (ii) d(i) (ii) (iii) e
Ratio of 24.4o
sin i sin r
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Mark 1
Refractive index of diamond refractive index of glass Higher refractive index produces bigger angle of refraction Refractive index increases, density increases Density increases, angle of refraction increases Change in velocity Total internal reflection Light travels from denser medium to less dense medium. Incident angle critical angle Aspect Bundle of fine parallel optical fibres ni no Mark Explanation 1 Can carry thousands of phone calls simultaneously Produces total internal reflection when light travels from inner core to outer
cladding High flexibility High purity Small size of critical angle 1 1 1 Can be bend according to curved path Signal can travel over a long distance without losing information Total internal reflection can occur at relatively small incident angle 1 1 1
11a b
Rate of change of distance Speed limit : high speed produces big momentum . Big momentum is difficult to stop immediatly Passenger limit : big mass produces big inertia. Big inertia is difficult to stop immediatly Specification Type of brake : ABS Size of safety belt : Broad Type of windscreen : Safety glass Hardness of front portion : Moderately hard Mark Explanation 1 1 1 Provide stronger & smoother grip Larger area produces smaller pressure on the driver Upon collision, it breaks into rounded pieces that doesnt cut the driver Moderately hard front portion will crumple upon collision. Impact time increases, so impulsive force decreases Mark 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
The safest car is S, because it has ABS brake, broad safety belt, safety glass & moderately hard front portion d(i) PE=mgh =(60)(10)(0.8) = 480 J F=ma 50-40=(0.1)a a=100 m s-2 Thermal equilibrium For 2 objects in thermal contact : Net flow of heat is zero Both objects have same temperature The heat supply is used to overcome the forces of attraction between water molecules, so that it can change from liquid to gas
1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1
(ii)
12a b(i) (ii)
c Specification Rate of expansion of liquid : Uniform Thickness of glass bob : Thin Size of capillary tube : Thin Shape of capillary tube: Capillary tube with a bend portion Mark Explanation 1 1 1 Calibration of the thermometer scale is more accurate Heat can be transferred to the liquid quickly Mark 1 1
The scale of the thermometer can be 1 calibrated in smaller division, so it is more sensitive The liquid column doesnt drop too quickly after being removed from the patient so that its reading can be read accurately 1
The most suitable thermometer is Q, because the expansion rate of the liquid is uniform, thin glass at the bob, thin d(i) capillary tube with a bend portion. m= V =(13600)(1.2x10-6) = 1.632 x 10-2 kg (ii) Q=mc = (1.632x10-2)(139)(42-37) = 11.34 J
1 1
1 1 2 1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Useful Formulas For Astronomy & Astrophysics OlympiadDokument1 SeiteUseful Formulas For Astronomy & Astrophysics Olympiadvosmera83% (6)
- Answer Chemistry Trial Mara 2014Dokument15 SeitenAnswer Chemistry Trial Mara 2014RayChin0% (3)
- Kertas 2 Pep Pertengahan Tahun SBP 2011Dokument8 SeitenKertas 2 Pep Pertengahan Tahun SBP 2011KK-Yunn RuhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Kelantan 2010 Peraturan Pemarkahan Physics Paper 1Dokument14 SeitenPeperiksaan Percubaan SPM Kelantan 2010 Peraturan Pemarkahan Physics Paper 1nik mohamad solehinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement 10Dokument22 SeitenMeasurement 10Gaurav ShekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Units and MeasurementDokument16 SeitenNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 2 Units and MeasurementAman ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Tips Physics SPM Success Tips Answer Paper 2Dokument7 Seiten6th Tips Physics SPM Success Tips Answer Paper 2Cikgu FaizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Trial Phy Scheme P1P2Dokument9 Seiten2012 Trial Phy Scheme P1P2mizwhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Physic SolutionDokument330 Seiten11 Physic Solutioncrazy about readingNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics 12 May Chapter 2 Units and MeasurementsDokument18 SeitenNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics 12 May Chapter 2 Units and Measurementsnithya M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ariosn A'level PhysicsDokument60 SeitenAriosn A'level PhysicsFELECIAN AMOSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physic 11 SolutionDokument330 SeitenPhysic 11 Solutioncrazy about readingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Paper 1 Quarter Year Examination 2013 Marking SchemeDokument23 SeitenPhysics Paper 1 Quarter Year Examination 2013 Marking SchemeAnonymous IyNfIgG4ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 SBP Fizik SkemaDokument14 Seiten2011 SBP Fizik SkemaAimi LiyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2Dokument9 SeitenAnswer Trial SBP Physics SPM 2013 Paper 2Cikgu FaizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCESQ 2015 Answer KeyDokument10 SeitenNCESQ 2015 Answer KeyKenneth Joy SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Fizik Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011 Tingkatan 4Dokument11 SeitenSkema Fizik Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011 Tingkatan 4jeglila50% (4)
- CH 2 Units and Measurements Physics: ExercisesDokument21 SeitenCH 2 Units and Measurements Physics: ExercisesDrRajesh ShrotriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIIMS - Mbbs Entrance Sample Question PaperDokument24 SeitenAIIMS - Mbbs Entrance Sample Question PaperrichuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: (Chapter - 2) (Units and Measurement)Dokument32 SeitenPhysics: (Chapter - 2) (Units and Measurement)Deepak RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1 Unit MeasurementDokument8 SeitenCH 1 Unit MeasurementAnonymous XIwe3KKNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Spmsoalan) Skema Trial SPM 2014 MRSM PhysicsDokument14 Seiten(Spmsoalan) Skema Trial SPM 2014 MRSM PhysicsrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema 123 Fizik f4 Final 2009 MLKDokument15 SeitenSkema 123 Fizik f4 Final 2009 MLKShazreena ShazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Scheme Paper 2 Form 4 NUM Answer Mark 1: AverageDokument8 SeitenAnswer Scheme Paper 2 Form 4 NUM Answer Mark 1: AverageazrulakmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Engineering Diagnostic TestDokument2 SeitenCivil Engineering Diagnostic TestJan Alexis Monsalud100% (2)
- Class XII Physics DPP Set (29) - Prev Chaps + ACDokument15 SeitenClass XII Physics DPP Set (29) - Prev Chaps + ACShubham KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mesl Preboard 1Dokument13 SeitenMesl Preboard 1Chyno KangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme Trial PHYSICS 2013 Sem 3Dokument6 SeitenMark Scheme Trial PHYSICS 2013 Sem 3Zuraini ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jutpani SS20Dokument23 SeitenJutpani SS20Suman NakarmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 086 - 2004 Nov O Level Physics (5052) P1 P2 - Suggested Answers (PDF Library)Dokument4 Seiten086 - 2004 Nov O Level Physics (5052) P1 P2 - Suggested Answers (PDF Library)McDonald Whites JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReviewerDokument8 SeitenReviewerBebit FerolinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Schemep2Dokument8 SeitenAnswer Schemep2Joanne Sone100% (1)
- Math 2020Dokument48 SeitenMath 2020Arthas LaveentineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strap FootingDokument6 SeitenStrap Footingrukesh104Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics Skema K1 K2 K3Dokument14 SeitenTrial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics Skema K1 K2 K3NgauHWNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Weekend Knockout Quiz With Answer Key PDFDokument19 SeitenCE Weekend Knockout Quiz With Answer Key PDFppppp100% (1)
- Mesl 2019 PDFDokument10 SeitenMesl 2019 PDFSolayao, Jan Marvin J.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Modelling 2010 PaperDokument13 SeitenMathematical Modelling 2010 PaperAl Fukos KayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate Test - 11 (Civil) : R Ey FDokument6 SeitenGate Test - 11 (Civil) : R Ey FnikhilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preboard Day 3 February 2018Dokument5 SeitenPreboard Day 3 February 2018Justine Marowe AustriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vidyalangar Sample TestDokument4 SeitenVidyalangar Sample Testpaptc642002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 10solutionDokument3 SeitenAssignment 10solutionxopoc27809Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Section B and C and Paper 3Dokument21 SeitenAnswer Section B and C and Paper 3Adnan ShamsudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Fizik Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2011Dokument8 SeitenSkema Fizik Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2011Chin Shee YanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combined FootingDokument15 SeitenCombined FootingAnish NeupaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marking Scheme Premock 2022 Physics Class 10Dokument11 SeitenMarking Scheme Premock 2022 Physics Class 10UDHAY KIRANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design AssignmentDokument8 SeitenMachine Design AssignmentSharthak GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Structure AssignmentDokument11 SeitenSteel Structure AssignmentGetaneh HailuNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE MAINS Solved Paper 2013Dokument24 SeitenJEE MAINS Solved Paper 2013chithrasajeev67% (3)
- 5054 MJ 2023 P22Dokument16 Seiten5054 MJ 2023 P22Raahin RahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportVon EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationVon EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.forward Head PostureDokument2 Seiten1.forward Head PostureJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Posture... Just How Important Is It?: Source: Kansas Chiropractic Foundation WebsiteDokument4 SeitenGood Posture... Just How Important Is It?: Source: Kansas Chiropractic Foundation WebsiteJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spinal Nerve PicDokument6 SeitenSpinal Nerve PicJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Juliehodges - PHD .2007ThePracticeOfIyengarYogaDokument5 SeitenJuliehodges - PHD .2007ThePracticeOfIyengarYogaJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview With Gert Van LeeuwenDokument11 SeitenInterview With Gert Van LeeuwenJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Back The Neck The Lower Back The Sacrum The TailboneDokument1 SeiteUpper Back The Neck The Lower Back The Sacrum The TailboneJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Juliehodges - PHD .2007ThePracticeOfIyengarYoga PDFDokument275 SeitenJuliehodges - PHD .2007ThePracticeOfIyengarYoga PDFJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Demand ReflectionDokument2 SeitenTheory of Demand ReflectionJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Do in WayDokument28 SeitenThe Do in WayJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reusi Dat Ton The Origin of Nuat Boran by Danko Lara RadicDokument8 SeitenReusi Dat Ton The Origin of Nuat Boran by Danko Lara RadicJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- KHYF Yoga Therapy India 2017 2020 V2Dokument14 SeitenKHYF Yoga Therapy India 2017 2020 V2Jacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- What's So Amazing About Kitchari?Dokument5 SeitenWhat's So Amazing About Kitchari?Jacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity AnswersDokument5 SeitenActivity AnswersJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity AnswersDokument1 SeiteActivity AnswersJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS Level Physics: Terms & Definitions:-: MeasurementDokument13 SeitenAS Level Physics: Terms & Definitions:-: MeasurementJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel GCSE Additional Science Topic P2.2 Controlling and Using Electricity Test 15 - 16 With Mark SchemeDokument22 SeitenEdexcel GCSE Additional Science Topic P2.2 Controlling and Using Electricity Test 15 - 16 With Mark SchemePaul Burgess100% (1)
- Equations of HydrodynamicsDokument18 SeitenEquations of HydrodynamicsAryce_Noch keine Bewertungen
- BSC Hons PhysicsDokument65 SeitenBSC Hons PhysicsGarima Malhan0% (1)
- Chapter 17 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Energy and Momentum MethodsDokument11 SeitenChapter 17 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Energy and Momentum MethodsAnonymous ANoch keine Bewertungen
- MSPYDokument78 SeitenMSPYHenchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntiGravity v2Dokument7 SeitenAntiGravity v2Spin Fotonio100% (2)
- Csec Physics 2010 18 p2 Solutions PDFDokument105 SeitenCsec Physics 2010 18 p2 Solutions PDFAshley FerminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument53 SeitenChapter 4DkkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics, Turbulent Flow and Turbulence ModelingDokument247 SeitenFluid Mechanics, Turbulent Flow and Turbulence ModelingAhmad GhafouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Flow Characteristics at Rectangular and Trapezoidal Channel JunctionsDokument12 SeitenComparison of Flow Characteristics at Rectangular and Trapezoidal Channel Junctionsdinu69inNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz3 2015 SolutionsDokument8 SeitenQuiz3 2015 SolutionsGerald RattichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ubit 4Dokument72 SeitenUbit 4Divya SoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 6100259431964999893Dokument34 Seiten5 6100259431964999893Hardik ChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces, Movement, Shape and Momentum 1 QPDokument14 SeitenForces, Movement, Shape and Momentum 1 QPJeffrey PiggottNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16B-Zero-Point Energy and Its EffectsDokument1 Seite16B-Zero-Point Energy and Its EffectsPramendra YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- As 1 Physical Quantity & VectorsDokument4 SeitenAs 1 Physical Quantity & VectorsMelly FransiscaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion Mountain - Vol. 1 - Fall, Flow and Heat - The Adventure of PhysicsDokument603 SeitenMotion Mountain - Vol. 1 - Fall, Flow and Heat - The Adventure of Physicsmotionmountain100% (116)
- Egg Drop Background InformationDokument3 SeitenEgg Drop Background Informationapi-332369217Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pelton TurbineDokument8 SeitenPelton TurbineHammas Ahmed MirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book 1 Introductory Atomic Physics and Quantum MechanicsDokument94 SeitenBook 1 Introductory Atomic Physics and Quantum Mechanicsalek dimitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuclear ModelsDokument12 SeitenNuclear ModelsPoundra SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Particle and Field Dynamics: Comte Joseph Louis Lagrange (1736 - 1813) November 9, 2001Dokument27 SeitenParticle and Field Dynamics: Comte Joseph Louis Lagrange (1736 - 1813) November 9, 2001Mateo TopalovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.1 PacketDokument7 SeitenCh.1 PacketClaire ShinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8: "Motion": 1 Motion 2 Graphical Representation of Motion & GraphsDokument83 SeitenChapter 8: "Motion": 1 Motion 2 Graphical Representation of Motion & GraphsTejous TejousNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-6 Linear Momentum and Impulse-11 PDFDokument13 SeitenCH-6 Linear Momentum and Impulse-11 PDFvic100% (3)
- Electromagnetism ReferencesDokument7 SeitenElectromagnetism ReferencesNivethithaa DhanrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ib-Physics Sand IaDokument15 SeitenIb-Physics Sand IaEmanuella ChiemekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computational Investigation of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer of An Economizer by Porous Medium ApproachDokument11 SeitenComputational Investigation of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer of An Economizer by Porous Medium ApproachNico GallosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aimstutorial Aimstutorial: Physics-1 Physics-1Dokument38 SeitenAimstutorial Aimstutorial: Physics-1 Physics-1hariNoch keine Bewertungen