Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Manual Instrucciones Power-One Forza 48-25600 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Paul RasmussenOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Manual Instrucciones Power-One Forza 48-25600 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Paul RasmussenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
POWER SUPPLY SYSTEM Forza 48-25600 PPC Instruction Manual
Revision: / Document number: 037879
Copyright Power One AS. All Rights Reserved. Power-One, AS Kobbervikdalen 75 P.O.Box 1543 N-3007 Drammen Unless specifically noted, all addresses, data, characters and persons referenced herein, and all examples involving names of companies and products, are fictitious examples and are designed solely to illustrate the use of Power One products. If you find errors or problems with this documentation, please notify Power One. Power One does not guarantee that this document is error-free. The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Power One logo is a registered trademark of Power One Corporation. All other trademarks or product names mentioned herein are trademarks of their respective owners.
Title page - Instruction Manual
Document Number: Revision: Date: System: Ouput Voltage: Publisher: 037879 / 08.07.2004 Forza 48-25600 PPC 48V Power-One as Postboks 1543 N-3007 Drammen NORWAY Amendment record:
Revision (Issue)
/
Description
First issue
Author
Hans Andre Dokka
Date
23.07.04
Originated Hans Andre Dokka Date 23.07.04 Signed
Approved Roar Fagerhus Signed
Date 23.07.04
Introduction to the manual
Introduction to the manual
Objectives and audience
This manual provides the user with the necessary information to understand how the Power Supply System is made and functions, together with sufficient information to enable the user to safely install, commission, maintain and operate the equipment in a safe and efficient manner. This manual has been prepared to be used by professional and properly trained personnel selected by our customers. This manual assumes that the technician has an understanding of power systems in general and understands safety procedures for working around AC and DC voltage. The user of this document should be familiar with electronic circuitry and wiring practices and have some expertise as an electronic or electromechanical technician. The information contained herein was applicable at the time the manual was ready for printing. Power One reserves the right to change specifications and designs without notice and without incurring obligation or liability. This manual is the work product of Power One and embodies confidential proprietary data in which Power One retains all rights, including exclusive right of use, reproduction, distribution and sale. It is submitted under a confidential relationship for a specific purpose, and the recipient agrees by accepting this work product, not to supply or disclose any information regarding it to any unauthorized person.
Symbols and conventions
The following words and symbols found throughout this manual are meant to highlight particularly important matters regarding specific information concerning the personnel, equipment or the process. Note! The text set off in this manner present an important piece of information that is essential to highlight.
CAUTION The text set off in this manner provides warning notice that failure to follow these directions can result in damage to equipment.
WARNING THE TEXT SET OFF IN THIS MANNER PROVIDES WARNING NOTICE THAT FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE DIRECTIONS CAN RESULT IN BODILY HARM OR LOSS OF LIFE AND/OR EXTENSIVE DAMAGE TO EQUIPMENT
Introduction to the manual
Document number: 028410.fm Revision: B
Introduction to the manual Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manual: Abbreviation:
PPS PMP CMP FMP PCS PCU GMC PPR PBDU PBC PDU PPRD PPC PBF PCB LVD PLD MCB MCCB
Description:
P1 Power Supply System P1 Modular Power Convection-cooled Modular Power Fan-cooled Modular Power P1 Control and Supervision P1 Control Unit Galero Modular Controller P1 Power Rack P1 Battery Distribution Unit P1 Battery Cabinet P1 Distribution Unit P1 Power Rack with DC Distribution P1 Power Supply Cabinet P1 Battery Fuse Unit Printed Circuit Board Low voltage disconnection Partial load disconnection Miniature circuit breaker Moulded case circuit breaker
Disclaimer
Power One is not responsible for system problems that are the result of installation or modification of the instructions provided in this manual.
Questionnaire for feed-back
We urge you to complete and return the questionnaire on our web page at the following address: http://www.power-one.com/feedback.html. Let us know your remarks on and suggested improvements to this manual. We appreciate your comments in our achievement to improve our documentation. If you have any problems with your system, e.g. you wonder how to install a new PMP rectifier or you have some questions regarding messages or alarms on the control module, please see the Troubleshooting section. If this does not solve your problem, please seek assistance at your local Power One office, or our head office in Norway. These also concern any indistinctness in the manual.
vi
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 028410.fm Revision: B
Table of contents
Contents:
1 System description Forza PPC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1 1.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2 1.2 Technical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3 1.3 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3 1.4 System description - Forza . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4 1.4.1 FMP 32 - Rectifier module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4 1.4.2 PCS - Controller system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4 1.4.3 PPR 32/4 19"- Subrack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4 1.4.4 PBDU, PBF and PDU - Distribution modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5 1.4.4.1 Low voltage disconnection (LVD) (Option) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5 1.4.4.2 Partial load disconnection (PLD) (Option). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5 2 Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1 2.1 Safety - Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2 2.2 Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2 2.2.1 Lethal voltages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2 2.2.2 Grounding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3 2.2.3 Precautions for lead acid batteries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3 2.2.4 Weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3 2.2.5 High temperatures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3 2.3 Cautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4 2.3.1 Storage and transportation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4 2.3.2 Handling electrostatic sensitive devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4 2.3.3 Traceability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4 2.3.4 Breakers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4 3 Installation guide Forza PPC guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1 3.1 Site requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2 3.2 AC Power source requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2 3.3 Technical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2 3.4 Installation procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2 3.4.1 Unpacking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2 3.4.2 Tools required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2 3.4.3 Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4 3.4.3.1 Connection of mains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4 3.4.3.2 DC connections from top. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5 3.4.3.3 Connection of Common positive (+) DC cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7 3.4.3.4 DC connection from bottom (Only for special made cabinets) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7 3.4.3.5 Connection of live DC cables (- 48V) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8 3.4.3.6 Connection of communication and current share signals. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8 3.4.3.7 Connection of expansion cabinet(s) with copper bars. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8 3.4.3.8 Connection of expansion cabinet(s) cable to copper rail under floor level . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-10 3.4.3.9 Connections of fuse alarms between cabinets.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-11 3.4.4 Connection of alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-12 3.4.5 Connection of symmetry measurement and temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3-13 4 Commissioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1 4.1 Commissioning overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Table of contents
vii
Table of contents
4.2 Tools and test equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2 4.2.1 Tools list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2 4.2.2 Test equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2 4.3 Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2 4.4 Commissioning procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3 4.5 Test of output voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4 4.5.1 Float charge (U1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4 4.5.2 Adjustment of float charge, U1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4 4.5.3 Boost charging (U2) (if applicable) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4 4.6 Battery supervision . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5 4.7 Battery test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5 4.8 Commissioning record . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6 5 Product description PCS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1 5.1 General - Product description PCS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2 5.2 Technical specification: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3 5.3 Operation - Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3 5.3.1 Starting the PCS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3 5.3.2 Adding modules to the system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3 5.3.3 Removing / replacing modules in the system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4 5.4 Operation - Control unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4 5.5 Connecting to PC. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5 5.6 Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5 5.6.1 Show voltage and currents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5 5.6.2 Show alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5 5.6.3 Show messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5 5.6.4 Show data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5 5.6.5 Select/adjust U1-U4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6 5.6.6 Adjust limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6 5.6.7 Miscellaneous . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7 5.7 Boost charging. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8 5.8 Battery test. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9 5.9 Other functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9 5.9.1 Temperature compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9 5.9.2 Battery current limit (option) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9 5.9.3 High load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9 6 Product description FMP 32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1 6.1 General - Product description FMP 32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2 6.2 Technical specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2 6.2.1 Mains input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2 6.2.2 DC output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2 6.2.2.1 Mains input 190-240VAC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2 6.2.2.2 Mains input 85-185VAC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2 6.2.3 Module dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2 6.2.4 Weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2 6.2.5 Other technical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3 6.3 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
viii
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Table of contents
6.4 Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4 6.4.1 Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4 6.4.2 Transport . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4 6.4.3 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4 6.5 Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4 6.6 EMC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4 7 Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1 7.1 General - Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2 7.2 Construction and function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3 7.2.1 External connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3 7.2.2 Internal functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3 7.3 Connections between subrack / rectifier shelfs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4 7.4 Connections main / extension cab. Subracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5 7.5 Addressing module positions in subrack1, subrack2 etc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6 8 Product description PBDU 25-50/3xNH1-3/2xNH1-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1 8.1 General - Product description PBDU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2 8.2 Technical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2 8.3 Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2 8.4 Cable area output connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2 8.5 Commissioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3 8.6 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3 9 Product description PDU 25-50/24xMCB (300A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1 9.1 General Product description PDU 25 24xMCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2 9.2 Technical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2 9.3 Construction and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2 9.4 Cable area output connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3 9.5 Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3 9.6 High ohmic distribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3 9.7 Commissioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3 9.8 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3 10 Product description PDU 25-50 16xMCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-1 10.1 General Product description PDU 25-50 16xMCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-2 10.2 Technical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-2 10.3 Construction and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-2 10.4 Cable area remote distribution connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-2 10.5 Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-3 10.6 Commissioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-3 10.7 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10-3 11 Product description PCS Alarm interface unit BM0546 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-1 11.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-2 11.2 Technical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-2 11.3 Remote alarms, symmetry measurement and temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-3
Table of contents
ix
Table of contents
11.4 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-3 12 Maintenance and Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-1 12.1 Installing new modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-2 12.2 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-2 12.3 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-4 12.4 Torque table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-4 Appendix A: Drawings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .A-1 A.1 Menu tree PCS - 017438 - Rev: C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2 A.2 Cabinet layout Forza 48 - 037810 - Rev: / . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3 A.3 General connection drawing Forza - 037396 - Rev: / . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-4 A.4 General block diagram Forza main cabinet - 037397 - Rev: B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-5 A.5 General block diagram Forza extension cabinet - 037398 - Rev: A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-6 A.6 Schematic diagram PCS + Power Forza - 037400 - Rev: / . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-7 A.7 Schematic diagram PCS Alarm interface unit PBDU NH1-3 - 037811 Rev: / . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-8 A.8 Schematic diagram PBDU 25 - 032566 - Rev: / . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-9 A.9 Schematic diagram PDU 25 w/LED - 037822- Rev: / . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-10 A.10 Schematic diagram PDU 25-max16xMCB - 024499 - Rev: / . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-11 A.11 Schematic diagram PPR 32/4pos Forza (Part 1 of 2) - 037407 - Rev: / . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-12 A.12 Schematic diagram PPR 32/4pos Forza (Part 2 of 2) - 037407 - Rev: / . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-13 Appendix B: Configuration Forza (c-000262.pcg) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .B-1 Appendix C: Distribution PBDU 5xNH1-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .C-1 C.1 Main cabinet PBDU 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .C-1 Appendix D: Distribution PDU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-1 D.1 Main cabinet PDU 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-1 D.2 Main cabinet PDU 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-2 D.3 Main cabinet PDU 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-3 D.4 Extension Cabinet PDU 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-4 D.5 Extension Cabinet PDU 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-5 D.6 Extension Cabinet PDU 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-6 D.7 Extension Cabinet PDU 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-7
Forza 48-25600 PPC
System description Forza PPC
1 System description Forza PPC
System description Forza PPC
Document number: 037136.fm Revision: /
1-1
System description Forza PPC
1.1 General
Forza modular DC power cabinet systems are designed to meet rigid telecom applications with very high reliability and flexibility for future expansion. This cabinet power solutions provide rectification, system management and power distribution while maintaining high reliability and offering flexibility for future expansion. The Forza Power Systems are based on hot-swappable rectifier modules (FMP 32.48) output power available at 3200W per module. System management is accomplished through messages and alarms displayed on the system controllers (PCS) LCD screen and can also be displayed remotely via the PC-based PowCom1 software package. Highly scalable PPC range with vertical raiser bars for hot live expansion or rectifier shelfs and DC distribution. Note! Normally rectifier modules are installed in the cabinet at shipment, but in some particular cases rectifier modules are shipped separately. Figure 1-1 Typical system drawing
POWER ON MESSAGE ALARM
POWER ON MESSAGE ALARM CANCEL
CANCEL
RS232
PBDU 1
PDU 1
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
1.
Communication program for remote control of the power suplly system
1-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037136.fm Revision: /
System description Forza PPC
1.2 Technical data
Figure 1-2 Principle drawing
PCS DC distribution AC
FMP 32
F F
FMP 32
LVD
FB
BATT
Input: Output: -voltage: -current: -voltage: -current: -power: Rectifier: Height: Width: Depth: 230/400 V 3-phase (site configurable) <2x10A per module 48V DC nominal / 64000W pr cabinet Max 64A per. module, 48V Max 3200W pr. module. 4,2 kg 2150 mm 600 mm 600 mm
Weight: Cabinet dim.:
1.3 Operation
z
The Forza 48-64000 is a floor cabinet solution with a built in DC-bus that enables the plug-in connection of rectifier subracks and battery / load breaker shelves. This system can accommodate up to 20 rectifier modules, a supervision module (PCS) and DC distribution with a wide range of plug-in DC load distributions (low and high ohmic). Up to 64000W/48V steady state power per cabinet. The system is based up on hot swappable 48V/3200W rectifier modules, which are working in parallel with automatic load sharing. The cabinet system is normally configured with N+1 redundancy, with N as the number of rectifier modules necessary for feeding the load and charging the battery and 1 as the redundant rectifier module. In normal operation the rectifier modules, FMP 32, are feeding the load and simultaneously maintain the batteries in a fully charged state. During a mains input power failure, the rectifiers are shut down and the batteries deliver the power required by the load, for a certain backup time. If the battery voltage drops below the pre-set level, the low voltage disconnection circuit, LVD disconnects the batteries automatically to prevent battery
System description Forza PPC
Document number: 037136.fm Revision: /
1-3
System description Forza PPC
deep discharge and thus prolong the battery life. When the mains input power is restored, the rectifiers start up automatically feeding the load, closes LVD circuit and are starting recharge the batteries.
z
The system performance is supervised and controlled from the supervisory unit, PCS. From this unit output DC voltage is set, alarm thresholds, LVD circuit operation, temperature compensated battery charging, etc. Any malfunction will be indicated by LED, text in the display and operation of dry contacts. How ever, PCS is not a single point of failure. In the event of malfunction in the PCS, basic tasks like feeding the load and charging batteries, will be maintained by the rectifier modules directly at preset default values. The alarm and threshold setting of the Forza can be set locally by use of the PCS push buttons and menu guided operation or remotely, by use of the PowComTM program.
1.4 System description - Forza
This system consists of the following modules;
1.4.1 FMP 32 - Rectifier module
The Power-One FMP 32 rectifier provides extremely reliable DC power in the highest possible density. The module incorporates the latest in power monitoring solutions through an internal microprocessor, giving up to the second updates to the system controller and adjacent rectifiers, guaranteeing tightly controlled load sharing among rectifiers, and providing status and identification information to the controller. Other features include 3xLED for rectifier status indication, thermal protection with de-rating and input over voltage disconnection with automatic reset. The rectifier units are hot swappable and can be quickly removed and replaced without disrupting the system or load. See: Product description FMP 32
1.4.2 PCS - Controller system
PCS - is a supervisory system with onboard software for monitoring and operation of power supply systems based up on Power One rectifier modules. The design is based up on the philosophy of having one main controller supervision for the entire power supply system, and use of distributed intelligence by local micro controllers. A RS485 data bus takes care of internal communication between the various units. RS232 for remote operation from PC. PowComTM software PowComTM is a communications software package that allows the remote control of the Forza system. The software uses a Windows based interface to allow access to the PCS. PowComTM is installed on a remote PC and can access the system by either direct connection, a LAN, or through a dial-up modem. Network interface The Power-One Network Interface (PNI) is an optional component, that allows the PCS unit to be remotely accessed via Ethernet and SNMP. The SNMP protocol allows enhanced managing capabilities and enables the system to be accessed from any location. The protocol uses simple commands to configure and control the system and relay the system status to the operator. Using this monitoring ability allows the alarm messages to be transmitted to any location. The PNI also can be used in conjunction with PowComTM software either through a modem or Ethernet connection. See: Product description PCS 2
1.4.3 PPR 32/4 19"- Subrack
PPR 32/4 19 is a subrack for interconnecting of modules in the FMP 32 series, and requires no operation. The subrack has up to four module positions (4xFMP 32 rectifiers.) Each subrack may be euipped according to present power requirements, and later be completed with additional FMP 32 modules. The subrack has a connection for AC in, DC out and RS485 for communication. Modules are hot swappable under full load conditions.
1-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037136.fm Revision: /
System description Forza PPC
1.4.4 PBDU, PBF and PDU - Distribution modules
DC distribution modules with battery breakers, load breakers, shunt for measurement of current, alarm for battery and load. Load outputs: Several available load breaker modules based on: MCCBs: 1x1500A, 2x600A, 2x384A and 4x384A MCBs: 24x2-63A, 16x80-100A, 24x216A High ohmic. Knife fuses: 5xNH1-3 and 9xNH00 Battery outputs: Several available battery breaker modules based on: MCCBs: 1x1500A, 2x600A and 4x384A MCBs: 12x100A. Knife fuses: 5xNH1-3 See product description PBDU, PBF and PDU for detailed information about the actual module. The distribution has no special operation other than switching the battery and load breakers on and off. All DC distribution breakers are supervised by measuring voltage drop across each breaker. Breakers which are not connected to any load, will not cause breaker alarm even if they are left open. Due to a small leakage current (2,5-3 mA) through the alarm circuit the voltage measured with a DVM (Digital Volt Meter) on an open breaker output, will be nearly equal to output rectifier voltage. If a battery breaker fault occurs or is simulated it might take from 2-10 minutes before the fault is indicated, depending on the battery condition. The distribution module has common "+" and breakers in "-" leg. For more information see schematic drawing in Appendix A. 1.4.4.1 Low voltage disconnection (LVD) (Option)
The system can be equipped with low voltage battery disconnection, which prevents the batteries from deep discharging, thus prolonging the battery life. A disconnection requires a detected mains failure at the supervision unit. Threshold for disconnection is available. If disconnection occurs, the batteries will not supply power to the load until they have been recharged to set voltage level, which can be adjusted by the user. If disconnection occurs, the batteries will be reconnected when mains supply return. 1.4.4.2 Partial load disconnection (PLD) (Option)
Partial load disconnection is voltage or time dependent (has to be specified when ordering). At a mains outage, PCS will open the PLD contactor when batteries has discharged down to a certain voltage, or the battery voltage has been under a certain voltage for a predetermined time. The disconnecting has to be set according to the present load and battery manufacturers discharge tables or requirements. The distribution module has common "+" and breakers in "-" leg. For more information see schematic drawing in Appendix A.
System description Forza PPC
Document number: 037136.fm Revision: /
1-5
System description Forza PPC
1-6
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037136.fm Revision: /
Safety
2 Safety
Safety
Document number: 028580.fm Revision: A
2-1
Safety
2.1 Safety - Introduction
This document contains recommended safety guidelines for working with the equipment mentioned in this documentation. The instructions in the Customer Documentation must be followed by properly trained and authorized personnel when installing, operating, commissioning or maintaining this equipment. Neglecting the instructions may be dangerous to personnel and equipment. Although the purpose of safety devices, routines and regulations are meant to take care of the safety of the user, nobody is excused from using common sense at all times when operating or otherwise handling the equipment. These above mentioned safety guidelines include Warnings, Cautions and Notes.
2.2 Warnings
2.2.1 Lethal voltages
WARNING! OBSERVE HIGH VOLTAGE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS BEFORE ATTEMPTING TO WORK ON THE SYSTEM WITH THE POWER CONNECTED. POTENTIALLY LETHAL VOLTAGES ARE PRESENT WITHIN THIS SYSTEM.
WARNING! CARE MUST BE TAKEN WHEN HANDLING ALL POWER CABLES. THERE MUST BE NO DAMAGE OF ANY KIND TO THE INSULATION OF THE CABLES AND POINTS CARRYING LETHAL VOLTAGES SHOULD NOT BE EXPOSED. FOR SAFETY REASONS, MAKE SURE THE CABLES ARE NOT CONNECTED TO THE POWER SUPPLY WHEN ROUTING THEM. All persons who perform any operations on this equipment should be advised of the potential dangers. Ensure that the following guidelines and cautions are observed, when dealing with high voltage systems and equipment:
z
Potentially lethal voltages are present within the system. Ensure that all power supplies are completely isolated by setting all power switches to OFF, disconnecting all relevant connectors and removing all relevant breakers before attempting any maintenance work. Do not rely on switches alone to isolate a power supply. Potentially lethal voltages are present within this system. Ensure that high voltage safety requirements are implemented before attempting to work on the system with power connected. Potentially lethal voltages can be induced if the equipment is not grounded (earthed) correctly. Ensure that all ground connections are secure.
2-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 028580.fm Revision: A
Safety
2.2.2 Grounding
WARNING! THE SYSTEM SHOULD BE HARD-WIRED TO THE INCOMING SAFETY EARTH. A SOLID HIGH CURRENT GROUND CONNECTION, CAPABLE OF SINKING THE MAXIMUM SYSTEM CURRENT, IS REQUIRED.
WARNING! DUE TO HIGH LEAKAGE CURRENT IN THIS SYSTEM, A CONDUCTOR SHOULD BE CONNECTED BETWEEN THE GROUNDING POINT IN THE POSITIVE DC BUSBAR TO THE CABINET. THIS CONDUCTOR IS CONNECTED ON ITS OWN TO THE EARTH BAR AND NOT SHARED WITH OTHER SAFETY CONDUCTORS.
2.2.3 Precautions for lead acid batteries
WARNING! THIS EQUIPMENT USES LEAD ACID BATTERIES. WHEN HANDLING THE BATTERIES FOLLOW THE INSTRUCTIONS DELIVERED WITH THE BATTERY SET, AS THE FLUIDS CONTAINED WITHIN THESE BATTERIES ARE KNOWN TO BE A HEALTH HAZARD. THE DISPOSAL OF LEAD ACID BATTERIES IS SUBJECT TO LEGAL REQUIREMENTS FOR HAZARDOUS WASTE, THEREFORE DISPOSAL LOCALLY MUST BE UNDERTAKEN SAFELY AND WITH DUE CARE.
Ensure the following guidelines are observed when dealing with equipment that may contain lead acid batteries:
z z
Any attempt to burn these batteries may result in an explosion and the generation of toxic fumes. Should a lead acid battery suffer damage, it must be moved into a well-ventilated area. Contact with the corrosive fluid must be avoided. Neutralize any acid corrosion with copious amounts of a solution of baking soda and water. Wipe of all traces of soda. If the lead acid battery is removed from the equipment to which it is fitted, any exposed contact must be insulated prior to disposal. Ensure that protective full-face shields, rubber gloves and aprons are worn and insulated tools are used when working with the batteries.
2.2.4 Weight
WARNING! MUCH OF THE HARDWARE THAT COMPRISES THIS EQUIPMENT IS SUFFICIENTLY HEAVY TO REQUIRE HANDLING BY TWO OR MORE PEOPLE, OR BY SPECIALISED LIFTING EQUIPMENT.
2.2.5 High temperatures
WARNING! CARE MUST BE TAKEN WHEN HANDLING THE EQUIPMENT AS SOME OF IT MAY REACH HIGH TEMPERATURES.
Safety
Document number: 028580.fm Revision: A
2-3
Safety
2.3 Cautions
2.3.1 Storage and transportation
CAUTION! During storage and transportation, the units must remain in their original packages in order to avoid mechanical damage, maintain tracability, and protect the units against electrostatic discharge.
2.3.2 Handling electrostatic sensitive devices
CAUTION! An electrostatic sensitive device is an electronic component that may be permanently damaged by the discharge of electrostatic charges encountered in routine handling, testing and transportation.
2.3.3 Traceability
CAUTION! Units are labelled with permanently attached product identification labels. The labels are designed to be indelible throughout the life span of the equipment, unless mistreated. Make sure that the product identification labels are present on the equipment and are not subjected to unusual wear or mistreatment.
2.3.4 Breakers
CAUTION! When replacing breakers, it must be to the same types.
2-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 028580.fm Revision: A
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
3 Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
3-1
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
3.1 Site requirements
The site should be suitable and ready for the Power supply. If it is not or you are unsure about this, contact your supervisor before continuing. Check, using a spirit level, that the site is level.
3.2 AC Power source requirements
WARNING! HIGH LEAKAGE CURRENT. ENSURE EARTH IS CONNECTED BEFORE CONNECTING MAINS SUPPLY.
WARNING! PRIOR TO INSTALLING MAINS CABLING, ENSURE THAT THE SYSTEM IS ISOLATED FROM ALL AC MAINS SUPPLIES.
WARNING! ONLY QUALIFIED ELECTRICIAN MAY CARRY OUT THE MAINS INSTALLATION
3.3 Technical data
Input voltage: 230V AC 3-phase (3 wire system) or 230V/400V AC 3-phase (5 wire system) Current: Max 20A/ 230V single phase per module.
3.4 Installation procedure
The power supply systems are delivered completely assembled in crates and are ready to be installed without any pre-assembly. Note! Normally rectifier modules are installed in the cabinet at shipment, but in some particular cases rectifier modules are shipped separately.
3.4.1 Unpacking
Check that the received equipment is in accordance with the packing list. Ensure that the cabinet and the equipment have not been damaged during transportation. You must report any parts that are damaged, missing or incorrect. If possible, correct the problem before continuing.
3.4.2 Tools required
The following tools are required for a safe installation of the Forza system:
z z z
Anti-static hand strap Socket wrench, insulated Screwdriver set, flat, insulated
3-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
z z z
Screwdriver set, torx, insulated Screwdrivers, pozidrive (cross head), sizes 1, 2, and 3, insulated Torque spanner (for battery connection), insulated
WARNING! USE ONLY SINGLE-ENDED, FULLY INSULATED TOOLS: SHAFTS OF SCREWDRIVERS ETC.; SHOULD BE INSULATED.
CAUTION! Care must be taken when installing this system. The units can be damaged and can cause damage if not handled with care. Pay particular attention to the order in which units are installed.
CAUTION! NEC/CEC. 1. 2. 3. 4.
Installation in USA / Canada must conform with the requirements in
Pull out all rectifier modules in order to lower the overall weight. Move cabinet to the right place and rise into on upright position. Use a water leveller making sure that cabinet is levelled. Adjust cabinet legs if necessary. If necessary the cabinet can be fixed to the floor through the plinth or towards the wall. Plinth
Figure 3-1
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
3-3
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Figure 3-2
Wall bracket
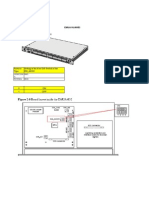
Tapties M6 Torx 30
Loose the wall bracket located on the upper part on left and right side by unscrewing the two tapties. Drag the wall bracket up and fasten it to the cabinet again (see Figure 3-2). The cabinet is now ready to be fixed to the wall.
3.4.3 Connections
See also: Product description PBF Product description PDU Product description PBDU Make input and output connections as described below. 3.4.3.1 Connection of mains
The power supply system has connections for up to four input mains at the terminal blocks located in the upper/lower left side of the cabinet. Number of input mains depends on number of subracks in the cabinet. Input mains cables to be tread through the plastic tube from top (only mains located in the top of the cab.). Connection of three-phase input mains according to the label located beside the terminal blocks Mains cable area:Max. 16 mm2 pr input. When connecting mains to terminal blocks use, depending on type of cable, either:
z
use a cable tie around conductors as close to the terminal block as possible, to prevent a stranded conductor to come loose and touch any secondary conductive parts on the backplane or, remove as little insulation on cable as possible before entering into terminal block, so that the jacket prevent a stranded conductor to come loose and touch any secondary conductive parts on the backplane (Note! The insulation on the cable must have a clearing of minimum 1mm in the terminal blocks). Connection of mains
Plastic tubes
Figure 3-3
Terminal blocks
Mains label
Mains 1
Mains 2
3-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Mains 1: is supplying subrack 1, position 1, 2, 3 and 4, and subrack 2, position 5 and 6 Mains 2 is supplying subrack 2, position 7 and 8, and subrack 3 position 9, 10, 11 and 12 Mains 3: is supplying subrack 4, position 13, 14, 15 and 16, and subrack 5, position 17 and 18 Mains 4 is supplying subrack 5, position 19 and 20, and subrack 6 position 21, 22, 23 and 24 Figure 3-4
Recommended mains fuse: 3 x 230V AC feed 3 x 400V AC feed 3.4.3.2 3 pole 63A C char, per mains. 3 pole 40A D char, per mains.
DC connections from top
The cabinet has got a special designed cable gland at the top for entrance of larger cables, 50mm2 up to 240mm2 . For cables 50mm2 the left hand vertical cable duct can be used The following description describes how to install 50 to 240mm2 cables. 1. 2. Remove cabinet top cover. Remove the horizontal sheet metal, which is mounted in front of the cable glands. (Fixed from top with 2xM4 screws)
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
3-5
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Figure 3-5
Front view
M4 screws
Horizontal sheet metal
3.
Horizontal sheet metal removee.8596.242 611.2400.0017 Tc
Remove all the cable bushings located over the positive copper bus bar except from the one half of the inner row.
Note! It is important to select the input cable positions systematically, using the inner row first, in order to take care of future expansion of cables Figure 3-6 Front view
4.
Remove the "knock out" of the bushing by a hammer and screwdriver or similar tool. Fit the two bushing parts around the cable and if necessary clamp it with the attached screws.
Figure 3-7
5.
If the opening is too big compared to size of cable, wind some scotch tape around the cable.
3-6
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
6.
When all cable bushings are fitted and mounted, replace all the unused bushings. Secure the bushings by fitting the sheet horizontal metal and fix it by enclosed M8 washers and nuts.
Connection of Common positive (+) DC cables
3.4.3.3
Where the entrance should be will vary due to cable properties (size and flexibility). The cable duct (located on the left side of the cabinet) is only accessible for up to 50mm2 cables. Bigger cables are to be tread trough the cable gland on top of the cabinet. Note that some systems will only have the possibility to connect 1-6 cables Connect cables according to Figure 3-8, request torque 30 Nm Figure 3-8 Connection of common positive DC cables
Connection points when you need 11-12 cables Connection points when you need 9-10 cables Connection points when you need 7-8 cables
Connection points when you need 5 or 6 cables Connection points when you need 3 or 4 cables Connection points when you need 1 or 2 cables
3.4.3.4
DC connection from bottom (Only for special made cabinets)
Cable entry from the bottom, use cable duct located on the left hand side for cables 50 mm2. For larger cables use bottom entrance of cabinet. Connect common positive (+) DC cables according to Figure 3-9, request torque 30 Nm.
Note! Some cabinets will only have the possibility to connect 1-6 cables.
Figure 3-9
Connection points when you need 7 or 8 cables Connection points when you need 9 or 10 cables Connection points when you need 11 or 12 cables
Bottom entrance of cabinet
Connection points when you need 1 or 2 cables Connection points when you need 3 or 4 cables Connection points when you need 5 or 6 cables
7.
Grounding of power cabinets.
The system is made common positive, 0V positive and 48V negative. A grounding terminal, meant for central earth, is located on the top of the cabinet. Internal grounding of the system may easily be removed in case a floating output voltage is requested. Unscrew the two torx screws shown in and remove the
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
3-7
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
copper plate. When the output is floating, the positive block in the system may be used for grounding. This way, a grounding cable of max. 240mm2 may be connected to the positive block. Figure 3-10
2 x Torx
Copper plate
Common positive (+) connected to the chassis of the cabinet
3.4.3.5
Connection of live DC cables (- 48V)
See product description of individual unit.
3.4.3.6 Connection of communication and current share signals.
Note! Only applicable if system consist of more than one cabinet See: Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack/rectifier shelf. 3.4.3.7 Connection of expansion cabinet(s) with copper bars.
Only if the system consists of more than one cabinet.
Technical data
Double U-shaped copper bars, 1000 sqmm. Removable top side panels with punch outs for paralleling. Expansion cabinet to be placed towards right or left. Live expansion by isolated copper bars.
3-8
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Figure 3-11
Screw Washers Copper bar
Connection point Nut Washers
Taptites M6 Torx 30 Copper bars
Mounting of parallel copper bars
1. 2. 3.
Remove top, top side panels and front panels in that order. Knock out the punch outs for paralleling. (Located on the top side panels). Use attached screws, nuts and washers for mounting of the copper bars. Required torque: 30 Nm.
Note! Do not use spring washer against copper.
The copper bars is to be mounted on top of the connection points (see Figure 3-11 and Figure 3-12) With two (double) copper bars (see Figure 3-13)
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
3-9
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Figure 3-12
Figure 3-13
3.4.3.8
Connection of expansion cabinet(s) cable to copper rail under floor level
Only for special made cabinets and if the system consist of more than one cabinet.
Technical data
Double U-shaped copper bars, 1000 sqmm. Cable from U-shaped copper bars to copper rail section under floor level. Expansion cabinet to be placed towards right or left. Live expansion by cables from power cab. to copper rail section.
Mounting of cable between cabinet and copper rail
Mount cables from rail section in power cabinets on to rail section under floor level.
3-10
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Figure 3-14
Floor level
+ Copper rail - Copper rail
3.4.3.9 Connections of fuse alarms between cabinets.
For alarm monitoring of the fuses there is one common (serial) distribution fuse alarm signal from each distribution unit, in each cabinet. This serial signal is terminated at the top/bottom of each cabinet. Figure 3-15
Termination point for serial fuse alarm signal Previous cabinet Next cabinet / Main cabinet Fuse alarm signal
If the system consists of more than one cabinet, the cabinets fuse alarm must be connected together using the fuse alarm contact. For this purpose use max a 1.5mm2 cable. When all cabinets fuse alarm is connected together, connect one cable from cabinet 1 to main cabinet. Figure 3-16
Main cabinet
Ext. cab. 1
Ext. cab. n
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
3-11
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
3.4.4 Connection of alarms
For remote supervision of the alarms, there are 6 potential free alarm contacts. Each alarm contact represents different alarm conditions. See Appendix B - Configuration for an alarm overview. Potential free alarm contacts for remote signalling at PBDU interface are located on the back of the distribution.
Note! Alarm contacts are shown in alarm position.
Figure 3-17
Connection of alarms
18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
ALARM 6
ALARM 5
ALARM 4
J13
ALARM 3
ALARM 2
ALARM 1
Alarm cabling install:
The green connectors can be easily removed, if desired, for ease in installing the wires to the connector. Power-One recommends using 22 AWG wires to connect alarms to the alarm output terminals. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Remove the green plug from each connector. Determine whether to reference normally closed or normally open with reference to common for each alarm contact. Strip the wires back approximately 10mm. Stranded wire may be soldered or covered with copper ferrule if desired. Insert wire into the correct positions in the green connector and tighten screw to clamp wire into connector. Route the wires through the cable area at the top left of the cabinet.
3-12
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
3.4.5 Connection of symmetry measurement and temperature sensor
The PCS can supervise the symmetry of up to 4 battery branches. The drawing shows how to connect the symmetry cables for 1 battery branch.
Note! The number of battery branches to be supervised has to be set in the PCS in order to activate the symmetry measurement.
It is also possible to add a temperature probe to the system for temperature compensated charging of the battery bank. Fasten the temperature probe in the middle of the topmost battery bank. The temperature probe will measure the ambient temperature of a battery bank and the PCS will adjust the float charge according to the temperature compensation factor set in the PCS. This factor must be set in the PCS according to the battery manufacturer recommendation. Figure 3-18 Connection of symmetry measurement and temp. sensor
- Blue T Green + Red
1 2 3
J11
Temp. probe
-36V Blue -24V Green -12V Red -36V Blue -24V Green -12V Red -36V Blue -24V Green -12V Red -36V Blue -24V Green -12V Red
1 1 J4 3 4 5 J4 6 7 8 J4 9 10 11 J4 12
Batt. sym. 1
Batt. sym. 2
Batt. sym. 3
-48V -36V -24V -12V 0V
Batt. sym. 4
Installing the Symmetry cabling and the battery temperature sensor:
1. 2. 3.
Remove the green plug from each connector. Strip the wires back approximately 10mm. Stranded wire may be soldered or covered with copper ferrule if desired. Insert wire into the correct positions in the green connector and tighten screw to clamp wire into connector.
The wires are pre-routed with fastener strips on the cabinet sidewall and down to the battery bank.
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
3-13
Installation guide Forza PPC guide
3-14
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037134.fm Revision: /
Commissioning
4 Commissioning
Commissioning
Document number: 037145.fm Revision: /
4-1
Commissioning
4.1 Commissioning overview
Before the system was delivered, it has been thoroughly inspected and tested. The following chapter is a guide to the set-up and operation of the control functions of the system.
Note! Before starting commissioning read the product description for the individual modules.
WARNING ONLY TECHNICAL STAFF WITH THE NECESSARY EXPERIENCE AND KNOWLEDGE, WITH REGARD TO THE POWER SUPPLY SUPPORT SYSTEM AND ITS BATTERIES, MAY PERFORM THE COMMISSIONING. IT IS IMPORTANT TO FOLLOW ALL SAFETY REGULATIONS.
If there are any difficulties in increasing the voltage to alarm level, the alarm level can be adjusted to a lower level.
4.2 Tools and test equipment
4.2.1 Tools list
The essential commissioning tools are listed below:
z z z z z z
Anti-static hand strap Socket wrench, insulated Screwdriver set, flat, insulated Screwdriver set, torx, insulated Screwdrivers, pozidrive (cross head), sizes 1, 2, and 3, insulated Torque spanner (for battery connection), insulated
4.2.2 Test equipment
z z
Multimeter (3 Digit, 0 1% DC) Load resistance, to connect 0-100% of total capacity to the system.
4.3 Preparation
Check the installation to ensure the following:
z z
Site is clean and safe Grounding: The equipment is correctly grounded. The grounding cable size, color and routing conform to the requirements. Power: The incoming mains AC power is available for this site. The site power switch and circuit breakers are clearly labelled. The power cables are correctly terminated.
4-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037145.fm Revision: /
Commissioning
4.4 Commissioning procedure
1. 2. Verify cabinet levelled vertically. Remove covers and check that all connections are made according to the installation drawing. Verify that all connections are properly tightened with a sufficient torque. (See Torque table in the Maintenance and troubleshooting chapter) Make sure that all rectifier modules are unplugged. Verify correct mains voltage on input mains terminals in cabinet by measuring each individual phase voltage towards neutral. Turn off mains voltage after verifying. Set battery breaker(s) in "off" position. Install all FMP 32 modules. Set load breakers into "on" position. Switch on mains voltage. The yellow LED on the rectifiers should blink
3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
10. Green LED on PCS (control unit) should blink for approximately 20 sec. 11. Yellow LED on rectifiers should turn off. 12. Output voltage will increase slowly to U1. 13. Verify right polarity on battery connection by measuring the voltage drop across battery breaker(s) (Normally not more than 5V DC) 14. Turn battery breaker to "on" position. 15. If any alarms are present they should be reset in accordance with Show alarms in product description PCS. No alarms should be present. 16. If the system shows any communication failure from a rectifier position without any rectifier installed. Select "Accept removed parts" from the Miscellaneous menu on PCS. (For more information see product description PCS.) 17. Attach all the system covers in their correct places. 18. Clean the site. 19. Fill in the commissioning record (see end of chapter).
Commissioning
Document number: 037145.fm Revision: /
4-3
Commissioning
4.5 Test of output voltage
4.5.1 Float charge (U1)
Be sure that the PCS is operating. Connect load, approx. 50% of total capacity, to the system. Check the voltage according to the battery manufactures requirements. If the batteries require other float charging voltage, adjust the output voltage from the PCS. (See product description PCS) If nothing else is required, use the following values:
Battery type
Open lead-acid batteries Sealed lead-acid batteries Table 4-1
Float charge
2,23V/Cell 2,27V/Cell
Boost charge
2,33V/Cell -
4.5.2 Adjustment of float charge, U1
Output voltage is factory pre-set to: See Appendix B. The total voltage has to be in accordance to the number of battery cells. Please verify number of cells and the battery manufacturers requirements. Adjust output voltage from the PCS (control unit).
Note! A sealing protects the potentiometer in the subrack. Do not break the seal.
4.5.3 Boost charging (U2) (if applicable)
Open lead-acid batteries.
Automatic boost charging - calculation of the time the battery voltage has been below certain levels. Automatic activating of boost charging for this calculated time multiplied by a (boost) factor. Activate boost charging from the "Set/select U1-U4" menu in the PCS. Return to float charge manually by selecting "U1", or automatically after a pre-set time.
Sealed lead-acid batteries.
Most of the manufactures of sealed lead acid batteries do not recommend boost charging. If this type of battery is used, the boost function should be disabled.
Boost charging figures
Observe and write down all of the boost charging figures. Parameters to be read/set/adjusted from PCS or PC with PowCom1 installed.
1.
Communication program for remote control of the power supply system.
4-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037145.fm Revision: /
Commissioning
4.6 Battery supervision
For systems with symmetry cables supplied:
Set number of battery strings according to number of battery strings in the system. The settings are to be done in the control unit via a PC with PowCom installed or directly in the PCS. (if symmetry failure is indicated) The symmetry fault alarm is to be simulated by pulling out one symmetry cable from battery string. Measure that setting is in accordance with battery manufacturer recommendations.
For systems with temp. probe cable supplied:
The temperature compensation is factory pre-set. Check that the temp. probe is activated and verify that the compensation level is according to the battery manufacturers requirements. (If no compensation level is available from the battery manufacture, Power One recommends it to be set to 0,5V).
4.7 Battery test
The settings should be done according to the battery manufacturer requirements, but as a rule of thumb the following settings can be used for standard VR lead batteries: No. of test pr. year U3 Test End voltage b.test Batt. test time Ah limit for test = = = = = 2 1,9 V/cell 1,94V/cell 40% of expected backup time 40% of nominal battery capacity
Parameters to be set/adjusted from the PCS (Battery test menu) or "Supervision - Set parameters menu in PowCom.
Commissioning
Document number: 037145.fm Revision: /
4-5
Commissioning
4.8 Commissioning record
This is a step-by-step commissioning record for easy commissioning of Power-One Supply Systems. Do not continue if any faults occur during this commissioning. The checkpoints are to be considered as a minimum for commissioning of the system.
Checked (D) Result
1. 2. 3.
4. 5.
6. 7.
8.
9.
Check that rack is levelled Check that all breakers are turned to off position and that no rectifiers are mounted in the subrack(s). Connect AC, and measure voltage on the mains input connections in the cabinet, Is to be 230V AC (Measure 230V from phase to N when 400V mains input is used) Mount rest of the rectifiers After connection of battery, verify right polarity by measuring the voltage drop across the battery breakers (normally not more than 5V DC). Check float charge, U1, and boost charge, U2. Is to be adjusted according to the battery manufacture requirements. Check temperature compensation. Is to be adjusted according to the battery manufacture requirements. Check temperature read off compare to the room temperature. Check symmetry measurement and set number of battery strings according to actually supervised battery strings in the system. Check alarm transmission by running an alarm test.
Commissioning record
L1-N:..V AC L2-N:...............V AC L3-N:...............V AC
U1:..V DC U2:.........V DC Comp. :.V/10oC Read off:oC
Number: . Alarm limit:
Table 4-2
4-6
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037145.fm Revision: /
Product description PCS
5 Product description PCS
Product description PCS
Document number: 017433.fm Revision: F
5-1
Product description PCS
5.1 General - Product description PCS
PCS - Power One Control System is a supervisory system particularly designed for supervision of Power One power supply systems based up on PMP 25 and FMP 32 rectifier modules. The design is based up on the philosophy of having one main controller supervision for the entire power supply system, and use of distributed intelligence by local micro controllers. A RS485 data bus takes care of internal communication between the various units. Visual notification of alarm and warning conditions are indicated by front panel LEDs while descriptions of the alarms are provided through RS232 D-sub connector using PC-based PowComTM1 software package.
WARNING! WHEN EXTERNAL EARTHED EQUIPMENT IS CONNECTED TO THE PCS CONTROL UNIT, THE EXTERNAL UNIT MUST BE CONNECTED TO SAME EARTH AS THE PCS CONTROL UNIT.
A complete supervisory system do always consist of the following units:
Main Controller
Master unit in the system communicating with all distributed micro controllers. Has LCD display, menu driven operation, visual alarm indication, RS232 contact for remote operation and RS 485 for internal communication with 128 addresses. (64 rectifiers and 64 other remote micro controllers).
Internal Power
DC/DC converter providing galvanic isolated DC power to the control system
Alarm Interface
Input for current reading, battery and load breaker monitoring, battery temperature, battery symmetry measurement. Output for operating two individual contactors (LVD and PLD), 6 potential free alarm contacts. Five analogue or digital inputs for supervision of miscellaneous signals (ventilation, door open, etc) Figure 5-1 Basic block diagram
PCS- -Main MainController Controller PCS PCS- -Internal InternalPower Power PCS (BM0500) (BM0500) PCS- -Alarm AlarmInterface Interface PCS (BM0494) (BM0494) PMPController Controller PMP (PMP 25/50) (PMP 25 / FMP 32) RS 232 Optional RS 485 or RS 232 (via converter )
RS 485
In addition PMP 25 and FMP 32 has an internal micro controller communicating with the other units.
1. PowCom - Communication program for remote control (by modem or zero-modem cable) of the power supply system.
5-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 017433.fm Revision: F
Product description PCS
5.2 Technical specification:
z z z z
Input voltage: Power consumption: Output: Instrumentation:
18-72V DC Approx. 30W 12V/500mA for modem Three LED's, green - OK, yellow - Message, red - Alarm 2 x 20 character alphanumeric LCD display with backlight. 5mm character height (Optional) RS 232 for remote operation via PowCom. RS 485 for internal communication with 128 addresses (64 rectifiers and 64 subcontrollers). Optional RS 485 for communication with additional 128 addresses. Overall max. capability is 128 rectifiers and 128 sub-controllers. Menu driven operation Up to 24 pre-defined alarms 16 programmable alarms Internal clock with battery backup Multiple language choice Temperature compensated charging Boost charging, manually and automatic LVD control of two contactors, voltage or time controlled Battery test, manual or automatic with symmetry measurement. Alarm relay test Adjustable battery current Software controlled start up after mains outage and battery test Enhanced battery monitoring
Interface:
Basic functions:
CAUTION Risk of explosion if lithium battery is replaced by an incorrect type. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturers instructions.
5.3 Operation - Introduction
The PCS communicates on a RS485 serial network with the rectifiers modules (called Modules) and one or many I/O units (called Units). There may be up to 64 Modules and 63 Units on one serial channel. There are two RS485 serial channels available and if more than 64 modules or more than 63 units are needed in a system both channels will be used.
5.3.1 Starting the PCS
When the PCS is started it will spend approx. 20 seconds analysing the system and testing all addresses for connected modules and units. During this period the green LED on the PCS will blink. No alarms will be given during this period. When the PCS finds a module or a unit it will add it to the inventory. It will remember this until a master reset, or a reconfiguring is done, even if it is turned off.
5.3.2 Adding modules to the system
When a rectifier is added to the system it will remain off until the PCS detects it. The PCS constantly scans for new modules and units, but it may take up to 5 minutes from the time a module is inserted until it is registered. During this time the yellow warning LED of the module will blink. When the PCS locates the module, the LED will stop blinking. The new module will give a current sharing fault until its output voltage has been adjusted. This may take additional time. If the PCS is turned off and on again it will reanalyse the system and find the new module faster. This is only recommended as a solution if it is important to cut short the time used to find new modules.
Product description PCS
Document number: 017433.fm Revision: F
5-3
Product description PCS
5.3.3 Removing / replacing modules in the system
Since the PCS communicates with the modules and units by a serial link, removing a module or unit will appear to the PCS as a communication failure. This will cause an error message. To remove the error message use the Accept removed parts item on the Miscellaneous menu, or press the reconfigure button in the Inventory window in PowCom. Make sure that there are no valid communication faults caused by any failure before doing this, as it will cause all not communicating modules and units to be removed from the inventory. This will make all communication faults disappear, but it will not fix any problems so it must only be used if the communication fault is caused by the module or unit being intentionally removed.
5.4 Operation - Control unit
Figure 5-2 Front view of control unit
System LEDs
RS232 Interface
The control unit is equipped with four push buttons: CANCEL, , , and (ENTER). The arrow keys are used to go up and down in the menu hierarchy, to adjust limits and to select options. key is used to go one level deeper to the menu system and to confirm adjustments. The CANCEL The key takes you one level up in the menu hierarchy in addition to cancel the adjustments. To adjust the alarm limits, use the arrow keys to select "adjust limits". Press to enter the sub menu, and once more to select "alarm limit". By using the and keys the various alarm limits can be checked. To adjust a limit: select the correct limit and press . The correct password must be entered before a new value can be set. keys to set and to confirm each The password is set to 1234 by default, but can be changed. Use the digit. CANCEL can be used to correct a digit. When the correct password is entered it stays active for approximately 2 minutes. The adjust mode is indicated by a : (colon) in front of the value and a steady cursor behind. Use the keys to adjust the alarm limit and press to confirm the value or CANCEL to revert to the previous value. To return to main menu, press the CANCEL button. If the PCS is left unattended the display will return to main menu automatically after 2 minutes. The backlight will be turned off after 2 minutes without any key pressed. Pressing any key will turn it back on.
5-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 017433.fm Revision: F
Product description PCS
5.5 Connecting to PC
Connect to a PC with PowComTM installed. The BAUD rate in the PowComTM COM port settings must be set to the same as the PCS is set to (9600 is the default baud rate of the PCS). If modem is to be used, connect modem before initiation. Push INIT MODEM in the miscellaneous menu.
Pin out of the RS 232 connector: Pin
2 3 5
Function
Receive Transmit 0V (ground)
5.6 Menus
5.6.1 Show voltage and currents
The control module normally shows system voltage and battery current. Pressing the arrow will show system voltage and distribution current, pressing once more will show system voltage and rectifier current.
5.6.2 Show alarms
This item displays the current alarm status. If there are several alarms use the keys to scroll through the various alarms. New alarms or disappearing alarms will be updated immediately on the menu. Some alarms have to be reset manually, by pressing at the show alarms display. The alarms to be reset are: Battery failure and symmetry failure.
5.6.3 Show messages
This item displays any messages. If there are several messages use the keys to view the various messages. New or disappearing messages will be updated immediately on the menu.
5.6.4 Show data
This menu is used to display various measurements.
Module data This menu shows information from the individual rectifier modules. Use the keys to select the module number. Press enter to view another page of information. Four pages of information are available for each module. The information available is communication status, module current, mean current, module temperature, module measured voltage, Module OVP limit, alarm information, Serial number and module software version number. Module alarms are indicated by 3 letter flags. The meanings of these are as follows. MNS - No input mains. LOW - Output voltage low OFF - No operation, caused by no mains or other failure OVS - Overvoltage shutdown. FAN - Fan failure, will cause the module to go off and OFF to be set. CUR - Current sharing fault. Current deviates too much from average. TMP - Temperature is high, will eventually cause the module to go off and off to be set. Unit data This menu shows information from the individual units. Units are I/O parts of the system like alarm interface cards, distribution cards etc. The information available is communication status, serial number and unit software version number. The menu is operated as the module data menu. Temperature The battery temperature is shown.
Product description PCS
Document number: 017433.fm Revision: F
5-5
Product description PCS
Ext. measurements Up to 8 "external measurements" can be shown. These measurements are not standard measurements. Both text and inputs are system specific and are defined in the configuration. If there are not configured any measurements NA will be shown when enter is pressed. Dist. current Show the distribution current from individual distributions. Up to 64 distributions can be shown. Require distributions with Distribution interface (PDU-IF). If no such distributions are available NA will be shown when enter is pressed. Symmetry voltage The symmetry voltage for each battery branch is shown.
5.6.5 Select/adjust U1-U4
This menu is used to select one of the references for the 4 charge modes, U1 - float voltage, U2 - boost voltage, U3 - battery test voltage, U4 - spare. Also use to adjust these references. The voltage references can be adjusted in steps of 0,1V.
z z z z
U1 Normal. The U1 reference is shown, press to change U1 (The float charge voltage) U2 Boost. The U2 reference is shown, press to change U2 (The boost charge voltage) U3 Test. The U3 reference is shown, press to change U3 (The Battery test voltage) U4 Spare. The U4 reference is shown, press to change U4 (The spare voltage) (Not normally used)
5.6.6 Adjust limits
The menu has the following items: alarm limits, boost parameters, battery test and temperature compensation. Parameters can be set/adjusted by entering the different sub-menus.
Alarm limits. This menu contains High voltage, low voltage, Over voltage shutdown limit, low voltage disconnect, partial low voltage disconnect limits, load reconnect limit, high load limit, high temperature limit. Boost parameters. This menu contains the limits for boost charging control. See section 5.7 Boost charging Battery test. This menu contains the limits for battery test. See section 5.8 Battery test Temperature comp. This menu turns the temperature compensation on and off, and set the compensation factor. Batt. Cur. Limit This menu turn the battery current limiting on and off, and set the limit. Note! Current limiting is not available on all systems. Sys. specific limits This menu show up to 8 system specific limits. These are limits that are non-standard limits that are defined in the configuration. The description and function of these limits are defined in the system configuration. If there are not configured any limits NA will be shown when enter is pressed. Dist. current lim. This menu allows the setting of current limits for individual distributions. Limits for up to 64 distributions can be set. If the load current of a distribution gets higher than the limit a high distribution current alarm will be given. Require distributions with Distribution interface (PDU-IF). If no such distributions are available NA will be shown when enter is pressed.
5-6
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 017433.fm Revision: F
Product description PCS
5.6.7 Miscellaneous
The miscellaneous menu makes it possible to set the date and time, change password, view version information, initialise modem, and show symmetry voltages and temperature.
Set time The clock is shown. Press the PCS is turned off.
to adjust the clock. The clock is battery backed and will keep the time even if
Relay test Press to check the alarm relays. The relays will be activated one and one. Use the witch relay should be activated.
keys to select
Alarm blocking Allows the alarm relays to be disabled during maintenance. One alarm relay will normally be active as long as the alarms are blocked. Version Show the PCS software version, configuration number and serial number. Set new password Choose "set new password" from the "miscellaneous" menu. Press , enter the old password and press Enter the new password and confirm by pressing . To avoid mistyping the new password has to be entered once more. Confirm by pressing . Shunt A The nominal current of the battery shunts. Shunt mV The nominal voltage of the battery shunts. Network address Several PCS's may be connected together in a multidrop RS232 network. Each module then needs to have a unique address between 2 and 255. The address may be set here. Baud rate Select the baud rate for the RS232 serial port of the PCS. Either 2400 or 9600. Init modem Press enter to send a string to init a modem. Additional initiation may be required in beforehand depending on the modem. Accept removed parts Since the PCS communicates with the modules and units by a serial link, removing a module or unit will appear to the PCS as a communication failure. This will cause an error message. If the module or unit is intentionally removed the PCS must be told that it is OK that the module or unit is gone. Selecting this menu and reply YES to the question will cause the PCS to assume that all not communicating modules and units are removed purposely. Note! Do not do this if there is an actual communication alarm caused by a fault in a module or unit. Reset to defaults Will reset alarm limits etc. to the default value without deleting logged data or system information. It is recommended to try this instead of Master Reset if a reset is needed. In some cases it might still be necessary to do a master reset. After a reset always check all limits and adjust them to the desired level. Master reset Will completely reset the PCS deleting all stored data. If possible download the data to a PC before doing this. Use this only if absolutely necessary. After a reset always check all limits and adjust them to the desired level.
Product description PCS
Document number: 017433.fm Revision: F
5-7
Product description PCS
5.7 Boost charging
Boost charging can be activated by three methods in the PCS: Manually boost charging - Choose U2 boost in the referance menu for activating boost charging. (Return to float charge manually by choosing "U1", or automatically after a pre-set time.) Periodic boost charging - after a pre-set period boost charge will be automatically activated for a pre-set time. Interval and boost time to be programmed (for example 4 hours every 3rd week). Automatic boost charging - when during a mains failure the battery voltage falls below t1 limit value, a timer is started. When the mains return, the system will start an automatic boost. This will last a certain time after the battery voltage reach the t2 limit. This time will be multiplied with a boost factor; K. t1 limit, t2 limit and the factor can all be set. Figure 5-3 Boost charging
Adjustable values:
Boost (voltage) Boost time Boost interval Boost factor Boost t1 limit Boost t2 limit Automatic boost
40 - 60 Volts 0 - 200 hours 3 - 16 weeks 1.0 - 16 40 - 60 Volts 40 - 60 Volts Passive - Active , and then select disable.
Disabling of automatic boost charge: Choose "Boost parameters" in the "Adjust limits" menu. Push
Note! Most of the manufactures of sealed lead acid batteries do not recommend boost charging. If this type of battery is used, the boost function should be totally disabled by settings as follows: Boost time = 0 U2 boost = U1 normal
5-8
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 017433.fm Revision: F
Product description PCS
5.8 Battery test
Battery test may be activated manually by selecting U3 (in the "Choose reference" menu or by PC with PowCom installed. Rectifier voltage will decrease to pre-set value (U3, adjustable), and logging of battery voltage, battery current and Ah starts. The battery test will automatically be interrupted and output rectifier voltage will rise to U1 level, if programmed time, Ah or end voltage is reached during the test. The test is considered as accepted if time or Ah causes the interruption. If the battery voltage reaches programmed end voltage, the battery is considered as faulty, an alarm will be indicated and further automatic testing is interrupted. Battery test can also be activated automatically 0-4 times a year. Select no. of tests. The measurement will automatically be started at mains interruption but will not be saved if duration of mains outage is less than 30 min.
Parameter settings. The idea of this feature is to make partial discharges of the battery, approx. 30-40% of the capacity, in order to discover faults before it actually becomes a problem. The settings should be done according to the battery manufacturer requirements, but as a rule of thumb the following settings can be used for standard VR lead batteries: U3 Test = 1,9 V/cell End voltage b.test = 1,94V/cell Batt. test time = 40% of expected backup time Ah limit for test = 40% of nominal battery capacity
Parameters to be set/adjusted from the "battery test" menu or PC with PowCom installed.
Adjustable values: Battery test voltage, (U3) Symmetry limit End voltage battery test Test duration Ah limit for test Time for test No of test/year No of batteries branches Battery type
0 - 100 Volts 0,0 - 4,0 Volts 0 - 100 Volts 0 - 20 hours 0 - 50000 Ah 0 - 23 0-4 0 - 12 4 blocks, 23 cell-, 23 cell+, 3 blocks or 2 blocks
Number of batteries must be equal to number of symmetry measurements. If symmetry cables are not in use, number of batteries must be set to 0 (zero).
5.9 Other functions
5.9.1 Temperature compensation
The supervisory module can adjust the charging voltage to compensate for temperatures above or below 20oC. T > 20oC lower charging voltage. T < 20oC higher charging voltage. The temperature compensation function can be enabled and disabled and the level of compensation is adjustable.
5.9.2 Battery current limit (option)
Battery current can be controlled by the PCS. The PCS will adjust the rectifier current limit so that the total rectifier current may not exceed "load current + desired battery current". Rapid changes in load current will lead to changes in battery current, due to this variation the current can be above the limit for a limited time.
5.9.3 High load
The "High load" alarm is activated when the load current exceeds the capacity of the installed modules multiplied by the high load limit. This is an indication that you should install more rectifier capacity.
Product description PCS
Document number: 017433.fm Revision: F
5-9
Product description PCS
5-10
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 017433.fm Revision: F
Product description FMP 32
6 Product description FMP 32
Product description FMP 32
Document number: 036259.fm Revision: /
6-1
Product description FMP 32
6.1 General - Product description FMP 32
6-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 036259.fm Revision: /
Product description FMP 32
6.2.5 Other technical data
Protection: Short circuit proof. Automatic current limiting. Selective shut down of modules at excess output voltage. Thermal protection reduces the output power at environmental temp. above maximum level. Shut down at >app 75oC with an automatic restart. Input over-voltage disconnection at >275VAC with automatic reset at <260VAC. High output voltage / shut down. Low voltage / module failure. Each alarm has a common LED indicator on the front panel and a common potential free contact for external signalling. IP 20 -60 to +85C Fan cooled, speed controlled and alarmed.
Alarms:
Enclosure: Storage: Cooling:
6.3 Operation
FMP 32 has status indicators that is located on the front panel of the module. The output voltage is adjusted from the Controller. There are three LEDs situated on the rectifier's front panel, which indicate the operating condition of the rectifier. Figure 6-1 Front view of FMP 32
FMP 32 has LED indicators as follows:
GREEN Power ON YELLOW Current Limit / Thermal protection. Communication failure (flashing). RED Module failure / high output voltage / shutdown.
Product description FMP 32
Document number: 036259.fm Revision: /
6-3
Product description FMP 32
6.4 Environment
The FMP 32 rectifiers meet the Environmental Standard requirements of: ETS 300 019-1-3 class 3.1 / 3M1 for Operating (Stationary In-Use) Temperature Range: -40C to +65C (up to 2000m) and -40C to +55C (above 2000m)
6.4.1 Storage
ETS 300 019-2-1 Class 1.2.
6.4.2 Transport
ETS 300 019-2-2 Class 2.3.
6.4.3 Operation
ETS 300 019-2-3 Class 3.2.
6.5 Safety
The FMP 32rectifiers fulfil those international and national safety standards for these systems according to grounding, fire protection and other safety matters as specified in the following standards: EN60950 / IEC 60950 UL1950 CSA C22-2 No. 950
6.6 EMC
The rectifiers' EMC meets the requirements of: EN61000-6-1, EN 61000-6-2, EN 61000-6-3 and FCC Part 15 Class B
6-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 036259.fm Revision: /
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
7 Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
Document number: 037142.fm Revision: /
7-1
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
7.1 General - Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
Note! All examples, pictures and drawings in this documentation are based on cabinets with 4 x PPR.
PPR 32/4 is a subrack/rectifier shelf for interconnecting of FMP 32 modules. Each subrack/rectifier shelf has 4 module positions. Each subrack/rectifier shelf may be equipped according to present power requirements, and later be completed with additional FMP 32 modules. For high power requirements several subracks may be paralleled. Figure 7-1 Front view of subrack / rectifier shelf
7-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037142.fm Revision: /
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
7.2 Construction and function
7.2.1 External connections
Description PL4, PL6 PL3, PL5 PL2, PL1, PL12, PL11, PL22, PL21, PL32, PL31 Bus bar connections Function RS 485 interface. Current share with other PPR 32/4
Input mains DC output.
7.2.2 Internal functions
Description Dip swich 1-6 Function Dip switch setting for programming the address of each module position, has to be set if PCS is used for supervision. See Table 7-1 Addressing module positions Each module position has two dip switches 1-6 that are parallel connected.
Figure 7-2
Front and back view of the subrack
PL4 (COM) PL6 (COM) PL3 (CUR) PL5 (CUR) PL2 PL1 Dip switches PL12 PL11 PL22 PL21 PL32 PL31
Negative (DC output) Positive (DC output)
PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5
PE N L
Input mains
Note! You can only address 64 modules in one com. channel. If more than 64 modules are used, module position 65 will have address 0 (Dip switch off). This will also be com. channel 2, new com. cable from main cabinet.
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
Document number: 037142.fm Revision: /
7-3
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
7.3 Connections between subrack / rectifier shelfs
Figure 7-3 Example shows a cabinet with 3 x PPR
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5 PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5
FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48
Use cable marked with Brown 1 between PL6 in subrack/rectifier shelf 1 to PL4 in subrack/rectifier shelf 2. Use cable marked with Orange 3 between PL5 in subrack/rectifier shelf 1 to PL3 in subrack/rectifier shelf 2. Use cable marked with Brown 1 between PL6 in subrack/rectifier shelf 2 to PL4 in subrack/rectifier shelf 3. Use cable marked with Orange 3 between PL5 in subrack/rectifier shelf 2 to PL3 in subrack/rectifier shelf 3.
Note! If the system consist of more subracks connect after the same method between subracks as described above.
7-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037142.fm Revision: /
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
7.4 Connections main / extension cab. Subracks
Figure 7-4
Mains cabinet
Extension cabinet 1
Extension cabinet 2
PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5 PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5 PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5
FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48
PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5 PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5 PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5
FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48
PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5 PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5 PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5
FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48
z z z z
Use cable marked with Brown 1 between PL6 in main cabinet to PL4 in extension cabinet1. Use cable marked with Orange 3 between PL5 in main cabinet to PL3 in extension cabinet1. Use cable marked with Brown 1 between PL6 in extension cabinet1 to PL4 in extension cabinet2. Use cable marked with Orange 3 between PL5 in extension cabinet1 to PL3 in extension cabinet2.
Note! If the system consist of more extension cabinets connect after the same method between cabinets as described above.
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
Document number: 037142.fm Revision: /
7-5
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
7.5 Addressing module positions in subrack1, subrack2 etc
Subrack no.
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 7 7 7 7 7 7 7
Com. channel
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Module position
1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 10 10 11 11 12 12 13 13 14 14 15 15 16 16 17 17 18 18 19 19 20 20 21 21 22 22 23 23 24 24 25 25 26 26 27 27 28
Connection
1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6
Dip switch on/off
Off Off 1 1 2 2 1+2 1+2 3 3 1+3 1+3 2+3 2+3 1+2+3 1+2+3 4 4 1+4 1+4 2+4 2+4 1+2+4 1+2+4 3+4 3+4 1+3+4 1+3+4 2+3+4 2+3+4 1+2+3+4 1+2+3+4 5 5 1+5 1+5 2+5 2+5 1+2+5 1+2+5 3+5 3+5 1+3+5 1+3+5 2+3+5 2+3+5 1+2+3+5 1+2+3+5 4+5 4+5 1+4+5 1+4+5 2+4+5 2+4+5 1+2+4+5
Table 7-1 Addressing module positions
7-6
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037142.fm Revision: /
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
7 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 13 13 13 13 13 13 13 13 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 15 15
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
28 29 29 30 30 31 31 32 32 33 33 34 34 35 35 36 36 37 37 38 38 39 39 40 40 41 41 42 42 43 43 44 44 45 45 46 46 47 47 48 48 49 49 50 50 51 51 52 52 53 53 54 54 55 55 56 56 57 57
1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6
1+2+4+5 3+4+5 3+4+5 1+3+4+5 1+3+4+5 2+3+4+5 2+3+4+5 1+2+3+4+5 1+2+3+4+5 6 6 1+6 1+6 2+6 2+6 1+2+6 1+2+6 3+6 3+6 1+3+6 1+3+6 2+3+6 2+3+6 1+2+3+6 1+2+3+6 4+6 4+6 1+4+6 1+4+6 2+4+6 2+4+6 1+2+4+6 1+2+4+6 3+4+6 3+4+6 1+3+4+6 1+3+4+6 2+3+4+6 2+3+4+6 1+2+3+4+6 1+2+3+4+6 5+6 5+6 1+5+6 1+5+6 2+5+6 2+5+6 1+2+5+6 1+2+5+6 3+5+6 3+5+6 1+3+5+6 1+3+5+6 2+3+5+6 2+3+5+6 1+2+3+5+6 1+2+3+5+6 4+5+6 4+5+6
Table 7-1 Addressing module positions
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
Document number: 037142.fm Revision: /
7-7
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
15 15 15 15 15 15 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 17 17 17 17 17 17 17 17 18 18 18 18 18 18 18 18 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 19 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 21 21 21 21 21 21 21 21 22 22 22 22 22
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
58 58 59 59 60 60 61 61 62 62 63 63 64 64 65 65 66 66 67 67 68 68 69 69 70 70 71 71 72 72 73 73 74 74 75 75 76 76 77 77 78 78 79 79 80 80 81 81 82 82 83 83 84 84 85 85 86 86 87
1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6
1+4+5+6 1+4+5+6 2+4+5+6 2+4+5+6 1+2+4+5+6 1+2+4+5+6 3+4+5+6 3+4+5+6 1+3+4+5+6 1+3+4+5+6 2+3+4+5+6 2+3+4+5+6 1+2+3+4+5+6 1+2+3+4+5+6 Off Off 1 1 2 2 1+2 1+2 3 3 1+3 1+3 2+3 2+3 1+2+3 1+2+3 4 4 1+4 1+4 2+4 2+4 1+2+4 1+2+4 3+4 3+4 1+3+4 1+3+4 2+3+4 2+3+4 1+2+3+4 1+2+3+4 5 5 1+5 1+5 2+5 2+5 1+2+5 1+2+5 3+5 3+5 1+3+5 1+3+5 2+3+5
Table 7-1 Addressing module positions
7-8
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037142.fm Revision: /
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
22 22 22 23 23 23 23 23 23 23 23 24 24 24 24 24 24 24 24 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 26 27 27 27 27 27 27 27 27 28 28 28 28 28 28 28 28 29 29 29 29 29 29 29 29
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
87 88 88 89 89 90 90 91 91 92 92 93 93 94 94 95 95 96 96 97 97 98 98 99 99 100 100 101 101 102 102 103 103 104 104 105 105 106 106 107 107 108 108 109 109 110 110 111 111 112 112 113 113 114 114 115 115 116 116
1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6
2+3+5 1+2+3+5 1+2+3+5 4+5 4+5 1+4+5 1+4+5 2+4+5 2+4+5 1+2+4+5 1+2+4+5 3+4+5 3+4+5 1+3+4+5 1+3+4+5 2+3+4+5 2+3+4+5 1+2+3+4+5 1+2+3+4+5 6 6 1+6 1+6 2+6 2+6 1+2+6 1+2+6 3+6 3+6 1+3+6 1+3+6 2+3+6 2+3+6 1+2+3+6 1+2+3+6 4+6 4+6 1+4+6 1+4+6 2+4+6 2+4+6 1+2+4+6 1+2+4+6 3+4+6 3+4+6 1+3+4+6 1+3+4+6 2+3+4+6 2+3+4+6 1+2+3+4+6 1+2+3+4+6 5+6 5+6 1+5+6 1+5+6 2+5+6 2+5+6 1+2+5+6 1+2+5+6
Table 7-1 Addressing module positions
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
Document number: 037142.fm Revision: /
7-9
Product description PPR 32/4 19 Subrack
30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 32 32 32 32 32 32 32 32
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
117 117 118 118 119 119 120 120 121 121 122 122 123 123 124 124 125 125 126 126 127 127 128 128
1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6 1-6
3+5+6 3+5+6 1+3+5+6 1+3+5+6 2+3+5+6 2+3+5+6 1+2+3+5+6 1+2+3+5+6 4+5+6 4+5+6 1+4+5+6 1+4+5+6 2+4+5+6 2+4+5+6 1+2+4+5+6 1+2+4+5+6 3+4+5+6 3+4+5+6 1+3+4+5+6 1+3+4+5+6 2+3+4+5+6 2+3+4+5+6 1+2+3+4+5+6 1+2+3+4+5+6
Table 7-1 Addressing module positions
7-10
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037142.fm Revision: /
Product description PBDU 25-50/3xNH1-3/2xNH1-3
8 Product description PBDU 25-50/3xNH1-3/2xNH1-3
Product description PBDU 25-50/3xNH1-3/2xNH1-3
Document number: 037876.fm Revision: /
8-1
Product description PBDU 25-50/3xNH1-3/2xNH1-3
8.1 General - Product description PBDU
The battery and distribution unit is designed for breaking three battery branches and distribution of 48V DC to telecommunication equipment.
8.2 Technical specifications
Voltage: Number of breakers: Size of breakers: Dimensions: 48V nominal. Max 5 x NH1-3 (3 for Battery and 2 for Load) Has to be specified when ordering (50A-630A, NH1-3) 19"/7U (H=311mm)
8.3 Installation
Cable entry from top of cabinet:
The battery and distribution module is a "plugable" module that connects directly to the systems rail section. Decide where on the top of cabinet you want the entrance of the negative (-) cables for battery breaker and distribution breakers (knives 5xNH1-3). Entrance will vary due to cable properties (size and flexibility). The cable duct (located on the left side of the cabinet) is only accessible for up to 50mm2 cables. The negative (-) connection is to be done directly on the breakers. (see Figure below)
Cable entry from bottom of cabinet (only for special made cabinets):
The battery and distribution module is a "plugable" module that connects directly to the systems rail section. Decide where from the bottom of the cabinet you want the entrance of the negative (-) cables for battery and distribution breakers (knives 5xNH1-3). Entrance will vary due to cable properties (size and flexibility). The cable duct (located on the left side of the cabinet) is only accessible for up to 50mm2 cables. The negative (-) connection is to be done directly on the breakers. (see Figure below) Figure 8-1
Connection of negative - cables for load
Connection of negative - cables for battery
8.4 Cable area output connections
Load connections: Cable area max. 240mm2
8-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037876.fm Revision: /
Product description PBDU 25-50/3xNH1-3/2xNH1-3
8.5 Commissioning
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Measure voltage drop across battery breaker to make sure battery is correctly polarised. (Normally not more than 5V DC) Insert breakers to the battery and distribution unit. Pull out one of the battery breakers and verify battery breaker alarm in the controller Verify disappearing of alarm when the breaker is inserted again. Pull out one of the load breakers and verify breaker alarm in the controller Verify disappearing of alarm when the breaker is inserted again. Repeat the above mentioned steps for each battery and distribution module.
8.6 Maintenance
The module does not need any special maintenance except for ordinary cleaning.
Product description PBDU 25-50/3xNH1-3/2xNH1-3
Document number: 037876.fm Revision: /
8-3
Product description PBDU 25-50/3xNH1-3/2xNH1-3
8-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037876.fm Revision: /
Product description PDU 25-50/24xMCB (300A)
9 Product description PDU 25-50/24xMCB (300A)
Product description PDU 25-50/24xMCB (300A)
Document number: 025153B.fm Revision: B
9-1
Product description PDU 25-50/24xMCB (300A)
9.1 General Product description PDU 25 24xMCB
The distribution is designed for distribution of 48V DC to telecommunication equipment.
9.2 Technical specifications
WARNING! MAX CURRENT 300A
Voltage: Number of breakers: Size of breakers: Dimensions:
48V DC nominal. Max. 24 x MCB's Has to be specified when ordering (1-63A). 19/5U (H=222mm)
9.3 Construction and functions
The distribution module has common "+" and all the MCBs connected in the "-" branch. Figure 9-1 Common + connection. Output connection positive cables
MCBs connected to the - branch Output connection. Negative cables
On the top of the distribution there is a horizontal cable duct for fixing output cabling. Figure 9-2 Cable duct seen from top of distribution
9-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 025153B.fm Revision: B
Product description PDU 25-50/24xMCB (300A)
9.4 Cable area output connections
Load connections: Cable area max. 16 mm2
9.5 Installation
The distribution module is a plug able module that connects directly to the systems rail section. Use cable duct located on the left side of the cabinet for guiding of cables to the distribution. Positive cables are to be connected in terminal blocks at the common "+" bar, and negative cables are to be connected directly to the MCB's. Use torque 2,5 3,5 Nm on these connections.
9.6 High ohmic distribution
WARNING! INFLAMMABLE. CARE MUST BE TAKEN WHEN HANDLING THE EQUIPMENT AS SOME OF IT MAY REACH VERY HIGH TEMPERATURES.
The distribution unit may be delivered with high ohmic resistance wires mounted on the MCB breakers. A maximum of 6W loss in each wire gives the following:
Resistance (m)
120 60 30 15 Table 9-1
Max continuous current (A)
7 10 14 20
Longer output cables can be used, if more resistance is needed. 2,5mm2 6mm2 10mm2 16mm2 7,2 m/m 3 m/m 1,8 m/m 1,1 m/m
9.7 Commissioning
1. 2. 3. 4. Switch on all MCB's in the distribution units. Turn off one of the fuses and verify fuse alarm at PCS Verify disappearing of alarm when turning the fuse on again. Repeat the two above-mentioned steps for one MCB in each distribution module.
9.8 Maintenance
The distribution does not need any special maintenance except for ordinary cleaning.
Product description PDU 25-50/24xMCB (300A)
Document number: 025153B.fm Revision: B
9-3
Product description PDU 25-50/24xMCB (300A)
9-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 025153B.fm Revision: B
Product description PDU 25-50 16xMCB
10 Product description PDU 25-50 16xMCB
Product description PDU 25-50 16xMCB
Document number: 023981.fm Revision: A
10-1
Product description PDU 25-50 16xMCB
10.1 General Product description PDU 25-50 16xMCB
The distribution is designed for distribution of 48V DC to remote distribution cabinet(s).
10.2 Technical specifications
Voltage: Number of breakers: Size of breakers: Dimensions: 48V DC nominal. Max. 16 x MCB 384A (3 x 160A in parallel) 19/5U (H=222mm)
10.3 Construction and functions
The distribution module has common "+" and all the MCBs connected in the "-" branch. Figure 10-1 Common + connection. Output connection positive cables
MCBs connected to the - branch Figure 10-2
Output connection. Negative cables
Common + connection. Output connection positive cables. Seen from top of cabinet
10.4 Cable area remote distribution connections
Remote distribution cables: Cable area max. 35 mm2
10-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 023981.fm Revision: A
Product description PDU 25-50 16xMCB
10.5 Installation
The distribution module is a "plugable" module that connects directly to the systems rail section. Use cable duct located on the left side of the cabinet for guiding of cables to the distribution. Positive cables to be connected to the terminals at the common + bar and negative cables to be connected directly to the MCBs.
10.6 Commissioning
1. 2. 3. 4. Switch on all MCB's in the distribution unit. Turn off one of the breakers and verify breaker alarm at PCS Verify disappearing of alarm when turning the breaker on again. Repeat the above mentioned steps for one MCB in each distribution module.
10.7 Maintenance
The distribution does not need any special maintenance except for ordinary cleaning.
Product description PDU 25-50 16xMCB
Document number: 023981.fm Revision: A
10-3
Product description PDU 25-50 16xMCB
10-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 023981.fm Revision: A
Product description PCS Alarm interface unit BM0546
11 Product description PCS Alarm interface unit BM0546
Product description PCS Alarm interface unit BM0546
Document number: 036136.fm Revision: A
11-1
Product description PCS Alarm interface unit BM0546
11.1 General
PCS alarm interface unit consist of PCB0546, which is an alarm board for Power One systems. The unit is located on the left or backside of the distribution. Access from top of the cabinet.
11.2 Technical data
Connection:
z z z z z z z z z z z
Plugable terminal blocks max. 1,5mm2
2x input for current reading (common + or -). (J2 and J12) Breaker monitoring, battery and load. (J5 and J6) Control signal for individual operating LVD and PLD. (J1) 6 x potential free change over contacts. (J13) 4 x input for symmetry measurement. (J4) Battery temp sensor. (J11) 3 x analogue inputs. (J4 pin 10-12) (Pin 12 = Analog 1, Pin 11 = Analog 2 and Pin 10 = Analog 3) 2 x digital inputs (fire, door open, etc). (J3) 2 x digital output (J10) RS485 interface for communication with plant controller PCS. (J7 and J16) Up to four units per system.
11-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 036136.fm Revision: A
Product description PCS Alarm interface unit BM0546
11.3 Remote alarms, symmetry measurement and temperature sensor
Alarms: Six dry alarm contacts for remote signalling (J13). Symmetry: Four separate inputs, each supervising battery branch symmetry voltage (J4). Temperature: One connection point for connection of Power- One temperature sensor (J11). Figure 11-1 BM0546 alarm board
1
Alarm contacts are shown in alarm position
Alarm 1
2 3 4
Disconnect 1
Alarm 2
5 6 7
NO NC C NO NC C NO NC C
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 2 1 4 3 2 1 3 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 8 1
Alarm 3
J1
J13
Disconnect 2
8 9 10
Reconnect System voltage 0V Battfuse alarm 4 Battfuse alarm 3 Battfuse alarm 2 Battfuse alarm 1 +12V Ext. transfoshunt -12V Distrfuse alarm Battfuse manual Digital input -Shunt 2 +Shunt 2 -Shunt 1 +Shunt 1 Comm. RJ45
Alarm 4
11 12 13
J14 J6 J9
Digital output
Alarm 5
14 15 16
Alarm 6
12V
17 18
3 2 1 1 2 3
J10
- Blue T Green + Red
J5
J11 Temp. probe
-36V Blue -24V Green -12V Red -36V Blue -24V Green -12V Red -36V Blue -24V Green -12V Red -36V Blue -24V Green -12V Red
J3
Batt. sym. 1
1 2 J4 3 4 5 J4 6 7 8 J4 9 10 11 J4 12
J12 J2 J16
Batt. sym. 2
Batt. sym. 3
-48V -36V -24V -12V 0V
J7
Batt. sym. 4
Comm. RJ45
8 1
11.4 Maintenance
The PCS alarm interface unit does not need any special maintenance.
Product description PCS Alarm interface unit BM0546
Document number: 036136.fm Revision: A
11-3
Product description PCS Alarm interface unit BM0546
11-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 036136.fm Revision: A
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
12 Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Document number: 037043.fm Revision: /
12-1
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
12.1 Installing new modules
Install new modules according to following statements. 1. Plug in module. 2. Ignore the module alarm caused current sharing. 3. Wait. After 1 minute the yellow LED will start blinking. Wait for max. 4 min. 4. Verify that yellow LED stops blinking. 5. The alarm should now disappear.
12.2 Troubleshooting
This guide is a step-by-step recommendation of what to do if problems occur. If first step of recommendation do not solve the problem continue to the next one. If the problem cannot be solved please call your local Power - One office for assistance.
Low system voltage:
z z z z
Check the batteries with a voltmeter. Check "low volt alarm" limit in controller / PowCom. Check that the system is not in battery "test mode". Check modules, mains and load situation compared to rectifier capacity.
High system voltage:
z z z
Check the batteries with a voltmeter. Check "High volt alarm" limit in controller / PowCom. Check that the system is not in "boost/Charge mode".
Load/battery disconnected:
z z z z
Verify that input mains is present Check system DC voltage with voltmeter Compare system DC voltage with disconnected thresholds in controller / Powcom. If breaker blows once more, there is either a too high load or short circuit at the system
Mains error:
z z
Check mains fuses. Check mains voltage.
Distribution fuse failure:
z z
Localise the blown fuse. Check the equipment that is connected to the blown fuse (there may be a reason for this fuse to blow) and reconnect it.
12-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037043.fm Revision: /
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Battery failure:
z z
Check the batteries. Check the "battery test" parameters in controller / Powcom.
Module failure:
z z z
Localise the module. Pull it out. Wait for 30 sec. and reinstall it according to 12.1 Installing new modules.
Battery temp alarm:
z z z
Check the batteries. Check ventilation. Check reading in controller / Powcom.
Symmetry fault:
z z z
Reset the alarm. Check connections according to number of batteries in controller / Powcom. Check batteries.
Battery fuse failure:
z z z
Localise the breaker. Check the batteries. Reconnect the breaker.
High load:
z z
Check load situation according to capacity of the system. Increase number of modules.
Urgent module failure:
z
See "Module failure".
Communication failure:
z z
Check if there is a module in current position. See "module failure".
Temp probe failure:
z z
Check connection on temp probe. Replace temp probe.
Alarms are blocked (only with LCD display):
z
Check " miscellaneous" menu in controller.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Document number: 037043.fm Revision: /
12-3
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
12.3 Maintenance
The connections on the terminal blocks and circuit breakers must be checked according to the 12.4 Torque table minimum once a year. Minimum once a year output voltage should be verified to be within limits. Result of the test should be filed to see any deviations. In addition the system needs normal cleaning and verifying of right operation. It is very important to keep air inlets and outlets free from dust or other materials, which may prevent free air circulation through the cubical.
12.4 Torque table
TYPE:
Terminal block for rail Terminal block for rail Terminal block Weidemullers Terminal block Weidemullers Terminal block Weidemullers Miniature circuit breaker Miniature circuit breaker Miniature circuit breaker Miniature circuit breaker Moulded case circuit breaker Moulded case circuit breaker Moulded case circuit breaker Moulded case circuit breaker Table 12-1 Torque
MODEL / DESCRIPTION:
AKG 16mm2 AKG 35mm WDU 4mm WDU 10mm WDU 16mm Siemens Merlin G ABB CBI HY-MAG ABB 160A - S2 ABB 160A/250A - S3/S4 ABB 630A - S6 Terasaki - XS125CJ
2
TORQUE:
2,5 Nm 3,5 Nm 0,6 Nm 2,0 Nm 3,0 Nm 2,5 Nm 3,5 Nm 2,0 Nm 3,0 Nm 5,0 Nm 9,0 Nm 9,0 Nm 9,0 Nm
12-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037043.fm Revision: /
Appendix A: Drawings
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A-1
A.1 Menu tree PCS - 017438 - Rev: C
Show voltage/ Batt. current
Show voltage/ Distr. current
Show voltage/ Rect. current
Show alarms
Show alarms
Show messages
Show messages
Show data
Module data
Unit data
Symmetry voltage 5 Symmetry voltage 6 Symmetry voltage 7 Symmetry voltage 8 Symmetry voltage 9 Symmetry voltage 10 Symmetry voltage 11 Symmetry voltage 12
Temperature
Ext. measurements U1 normal voltage Distr. current Select/adjust U1-U4 U2 boost voltage Symmetry voltage 1 U3 test voltage Symmetry voltage 2 U4 spare voltage Symmetry voltage 3 Reference Symmetry voltage 4
Adjust limits
Alarm limits
Low voltage
Boost parameters
Boost time
High voltage
set time
Battery test
Symmetry limit
Boost interval
Overvolt. Shutdown Load/battery disconnect Partial disconnect Load/battery reconnect
Miscellaneous
Relay test
Temperature comp.
Enable temp. comp.
Test end voltage
Boost factor
Alarm blocking Menu language Version Syst. specific limits Set new password Distr. current lim. Batt. current limit
Enable current limit Batt. current limit
Comp. factor
Test duration
Boost t1
Ah- limit
Boost t2
Time of test
Autoboost enable
High load
Shunt current
No of tests/year
Temperature alarm
Shunt voltage
No of batteries
Network address
Battery type
Baud rate
Init modem
Accept removed parts
Date:
Designer:
Control:
Approved:
Scale:
05.09.2002
Reset to defaults
SK
Replacement for: Replaced by:
Master reset C:\Documents and Settings\orjans\Skrivebord\017438.vsd
Menu tree PCS
Page 1 of 1
ref: Rev:
017438
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A-2
A.2 Cabinet layout Forza 48 - 037810 - Rev: /
45
40
POWER ON MESSAGE ALARM
POWER ON MESSAGE ALARM CANCEL
CANCEL
RS232
35
PBDU 1 PDU 1
30
25
PDU 1
PDU 2
20
PDU 2
15
PDU 3
PDU 3
10
PDU 4
5
FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48 FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
FMP 32.48
WxHxD=600x2150x600mm
Date: Designer:
WxHxD=600x2150x600mm
Scale:
12.07.04
SK
1:10
Cabinet layout Forza 48-25600
Page 01 of 01
ref:
037810
Rev:
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A-3
Input mains terminal located in top of the cabinet
Mains 4 (behind mains 3)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Mains 1 (near front of cab.)
Mains 2 (behind mains 1)
Mains 3 (behind mains 2)
3 4
6 7
3 4
6 7
3 4
6 7
Connection point for distribution fuse alarm signal Optional 6 extra positive output 6 positive output connections connections
400Vac 3 phase
PE N N N L1 L2 L3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
PE N N N L1 L2 L3
PE N N N L1 L2 L3
PE N N N L1 L2 L3
Document number: Appendix A.fm
POWER ON MESSAGE RS232 ALARM
3 4
6 7
3 4
6 7
3 4
6 7
230Vac 3 phase
PE L1 L1 L2 L2 L3 L3
PE L1 L1 L2 L2 L3 L3
PE L1 L1 L2 L2 L3 L3 PE L1 L1 L2 L2 L3 L3 For systems with more than 3 rectifier shelves
PCS control unit
CANCEL
Distribution units with negative terminals only. Positive connections in top of the cabinet
Distribution units with negative and positive terminals.
PCS alarm interface unit BM0546 Connection of alarms and signals from cable duct.
PCS alarm interface unit BM0546 Connection of alarms and signals from cable duct.
J4
Batt. Sym. 3
-12V Red -24V Green -36V Blue
0V
-12V Red 9 -24V Green 8 -36V Blue 7 -12V Red 6 -24V Green 5 -36V Blue 4 8 6 l 1 8 i 3 . 5 8 2 l 3 0 5 . 8 5 2 3 8 . 1 8 6 l 3 9 5 1 2 . 0 0 c
J4
Batt. Sym.2
-12V Red -24V Green -36V Blue 0 l 3 9 5 1 3 r e c - 0 l c 1 9 8 . 2 7 4 2 0 c - 0 l 3 9 . 5 8 2 2 3
0V
-12V
-12V
. 1 8
-24V
J4
Batt. sym. 1
-24V
A.3 General connection drawing Forza - 037396 - Rev: /
-36V
-12V Red 3 -24V Green 2 -36V Blue 1
-36V
-12V Red . -24V Green -36V Blue
-48V
-48V
+ Red T Green - Blue
3 2 1
J11
Temp. probe
Alarm 6
18 17 16
J13
Alarm 5
15 14 13
J13
Alarm 4
12 11 10
J13
Alarm 3
9 8 7
J13
Alarm 2
6 5 4
J13
10.05.04
SK
1:10
Page 01 of 01
Alarm 1
3 2 1
J13
Alarm contacts are shown in alarm position
Alarm contacts are shown in alarm position
General connection drawing Forza 48 Top entry caninet
037396
A-4
A.4 General block diagram Forza main cabinet - 037397 - Rev: B
1 1
+ Output - Output
Quantity of subracks will vary due to the actual order
8 8
+ PL4 COM PL6 COM
BM0635
8 PL3 Current share 8 PL5 Current share
Subrack for 4xFMP 32
Sub Rack n
L N PE L N PE L N PE L N PE
OPTION: Current share exten.cab. subrack 1 BM0635 PL5 OPTION: Communication exten. cab. subrack 1 BM00635 PL6
PCS - Control unit with power
J6 Com Modem
8
BM0479
J7 Com PCS
J3 Com system 1
8
RS 232
J4 Com system 2
8
J8 Power PCS
8 8 8 8 8
J8 Power J5 Com 2 J4 Com 2 J2 Com 1 J3 Com1
BM0500
Main cabinet PBF/PBDU PL1, Pin1 and 2
1 2
1 2
J1
PCS alarm interface unit
8 8
J7 Com J16 Com
BM0546
For more details, see connection drawing
PDU 25
0V - Load 1 - Load n
Quantity and type of distributions will vary due to the actual order
PDU 25 w/PLD
0V - Load 1 - Load n
PDU 25
- Load 1 - Load n
PBDU 25
- Load 1 - Load n - Batt. 1 - Batt. n
PBF 25
- Batt. 1 - Batt. n
Date:
Designer:
Scale:
12.07.04
SK
General block diagram Forza Main cabinet
Page 1 of 1
ref: Rev:
037397
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A-5
A.5 General block diagram Forza extension cabinet - 037398 - Rev: A
1 1
+ Output - Output
Communication from prev. cab. Last subrack BM00635 PL4
8 8
+ PL4 COM PL6 COM
BM0635
Current share from prev. cab. Last subrack BM0635 PL3
PL3 Current share 8 8 PL5 Current share
Subrack for 4xFMP 32
Sub Rack 1
L N PE L N PE L N PE L N PE
Quantity of subracks will vary due to the actual order
8 8
+ PL4 COM PL6 COM
BM0635
8 PL3 Current share 8 PL5 Current share
Subrack for 4xFMP 32
Sub Rack 2
L N PE L N PE L N PE L N PE
8 8
+ PL4 COM PL6 COM
BM0635
8 PL3 Current share 8 PL5 Current share
Subrack for 4xFMP 32
Sub Rack n
L N PE L N PE L N PE L N PE 8
OPTION: Current share exten.cab. subrack 1 BM0635 PL5 OPTION: Communication exten. cab. subrack 1 BM00635 PL6
PCS alarm interface unit
J7 Com J16 Com
BM0546
For more details, see connection drawing
PDU 25
0V - Load 1 - Load n
Quantity and type of distributions will vary due to the actual order
PDU 25 w/PLD
0V - Load 1 - Load n
PDU 25
- Load 1 - Load n
PBDU 25
- Load 1 - Load n - Batt. 1 - Batt. n
PBF 25
- Batt. 1 - Batt. n
Date:
Designer:
Scale:
08.07.04
SK
General block diagram Forza Extension cabinet
Page 1 of 1
ref: Rev:
037398
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A-6
A.6 Schematic diagram PCS + Power Forza - 037400 - Rev: /
J6 Com Modem
8
BM0479
J7 Com PCS
J3 Com system 1
8
J4 Com system 2
8
J8 Power PCS
8
8 8 8 8
J8 Power J5 Com 2 J4 Com 2 J2 Com 1 J3 Com 1
BM0500
1 2
J1
Connect according to Block diagram
Date:
Designer:
Scale:
10.05.04
SK
Schematic diagram PCS + Power Forza
Page 1 of 1
Powec ref: ref:
Rev:
037400
/
A-7
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A.7 Schematic diagram PCS Alarm interface unit PBDU NH1-3 - 037811 Rev: /
8 8
1 + 2 1 + 2 1 2
*
Distr. breaker alarm signal Located in top of the cabinet
12
J7 Com. J16 Com. J2 Shunt 1 J12 Shunt 2
BM0546
For more details, see connection drawing
Distribution fuse Batt. fuse manual
J5
1 2 3 4 1 2
J6 Batt. fuse 0V Sys. voltage J14
Signal PDU PL 1
1 2 3
J1 Disconnect 1
4 5 6
J1 Disconnect 2
Quantity and type of distributions will vary due to the actual order
Signal PDU w/PLD PL 1
Reconnect Disconnect
7 8 9
J1 Reconnect
1
1 2
Digital input 0 J3 Digital input 1
Signal PDU PL 1
12
Signal and power PBF PL 1
1
Batt. fuse alarm Batt. fuse alarm Batt. fuse alarm Distr. fuse alarm Shunt 1 + Shunt 1 Sys voltage 0V
Date:
Designer:
Scale:
Connect according to Block diagram
12.07.04
SK Page 1 of 1
Powec ref: ref:
Schematic diagram PCS alarm interface unit Forza PBDU NH1-3 - 3xbatt/2xload fuses
Rev:
037811
/
A-8
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A.8 Schematic diagram PBDU 25 - 032566 - Rev: /
0V
- batt 1 - batt 2 - batt 3
- Load 1 - Load n
12 batt. fuse al. batt. fuse al. batt. fuse al. distr. fuse al. shunt 1 + shunt 1 sys voltage 0V
PBDU PL 1
1
Date:
Designer:
Control:
Approved:
Scale:
27.03.2003
RFA
Replacement for: Replaced by:
http://esmtier.power.one:7777/files/ content/MyWorkspaces/ES Documents/ cc/tg/vsd/25/032566.vsd
Schematic diagram PBDU 25
Page 1 of 1
Powec ref: ref:
Rev:
032566
/
A-9
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A.9 Schematic diagram PDU 25 w/LED - 037822- Rev: /
0V
- Load 1
- Load n
PDU 24xMCB PL1
X1 X2 X3 X4 X5
LED board
BM0660
BM0554
Date:
Designer:
Scale:
13.07.04
SK Page 1 of 1
Powec ref: ref:
Schematic diagram PDU 25 w/LED
Rev:
037822
Document number: Appendix A.fm
/
A-10
A.10 Schematic diagram PDU 25-max16xMCB - 024499 - Rev: /
0V
- Load 1
- Load n
PDU 25-max16xMCB PL1
1
Date:
14.01.200 0
Designer:
Approved:
Scale:
RFA
Replacement for: Replaced by:
Schematic diagram PDU 25max16xMCB
G:\cc\tg\vsd\25\ 024499.vsd
Page 1 of 1
Powec ref: powec
ref: 024499
Rev:
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A-11
A.11 Schematic diagram PPR 32/4pos Forza (Part 1 of 2) - 037407 - Rev: /
8 8 8 8
PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5
BM0635 Subrack 1
L L N N PE PE
+
1
L L N N PE PE
L L N N PE PE
7 6 5
L L N N PE PE
Mains 1
4 8 3 8 2 1 1 8 8
PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5
BM0635 Subrack 2
L L N N PE PE
+
5
L L N N PE PE
L L N N PE PE
7 6 5
L L N N PE PE
Mains 2
4 8 3 2 1 1 8 8 8
PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5
BM0635 Subrack 3
L L N N PE PE
+
9
L L N N PE PE
10
L L N N PE PE
11
L L N N PE PE
12
Date:
Designer:
Scale:
10.05.04
SK Page 1 of 2
ref: Rev:
Schematic diagram PPR 32/4pos. Forza
037407
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A-12
A.12 Schematic diagram PPR 32/4pos Forza (Part 2 of 2) - 037407 - Rev: /
8 8 8 8
PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5
BM0635 Subrack 4
L L N N PE PE
+
13
L L N N PE PE
14
L L N N PE PE
15
7 6 5
L L N N PE PE
16
Mains 3
4 8 3 8 2 1 1 8 8
PL4 PL6 PL3 PL5
BM0635 Subrack 5
L L N N PE PE
+
17
L L N N PE PE
18
L L N N PE PE
19
7 6 5
L L N N PE PE
20
Mains 4
4 3 2 1 1
Date:
Designer:
Scale:
10.05.04
SK Page 2 of 2
ref: Rev:
Schematic diagram PPR 32/4pos. Forza
037407
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A-13
Document number: Appendix A.fm
A-14
Configuration Forza (c-000262.pcg)
Appendix B: Configuration Forza (c-000262.pcg)
Configuration Forza (c-000262.pcg)
Document number: 037895.fm Revision: /
B-1
Configuration Forza (c-000262.pcg)
B-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037895.fm Revision: /
Configuration Forza (c-000262.pcg)
Configuration Forza (c-000262.pcg)
Document number: 037895.fm Revision: /
B-3
Configuration Forza (c-000262.pcg)
B-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037895.fm Revision: /
Distribution PBDU 5xNH1-3
Appendix C: Distribution PBDU 5xNH1-3
C.1 Main cabinet PBDU 1
Breaker 160A
F1 F2 FB1 FB2 FB3 X X X X X
200A 250A
300A
630A
Char.
NH1-3 NH1-3 NH1-3 NH1-3 NH1-3
Type of equipment
Battery 1 Battery 2 Battery 3
-Battery 1
-Battery 2
- Load
F1
F2
FB1
FB2
FB3
Distribution PBDU 5xNH1-3
Document number: 037812.fm Revision: /
-Battery 3
C-1
Distribution PBDU 5xNH1-3
C-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037812.fm Revision: /
Distribution PDU
Appendix D: Distribution PDU
D.1 Main cabinet PDU 1
Fuse
F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 F13 F14 F15 F16 F17 F18 F19 F20 F21 F22 F23 F24
6A
10A 16A 20A 25A 32A 40A 50A 200A Char.
X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C
PLD
Type of equipment
+0V Load
-Load
Distribution PDU
Document number: 037813.fm Revision: /
D-1
0V
Distribution PDU
D.2 Main cabinet PDU 2
Fuse
F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 F13 F14 F15 F16 F17 F18 F19 F20 F21 F22 F23 F24
6A
10A 16A 20A 25A 32A 40A 50A 200A Char.
X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C
PLD
Type of equipment
+0V Load
-Load
D-2
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037813.fm Revision: /
0 V
Distribution PDU
D.3 Main cabinet PDU 3
Fuse
F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 F13 F14 F15 F16 F17 F18 F19 F20 F21 F22 F23 F24
6A
10A 16A 20A 25A 32A 40A 50A 200A Char.
X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C
PLD
Type of equipment
+0V Load
-Load
Distribution PDU
Document number: 037813.fm Revision: /
D-3
0V
Distribution PDU
D.4 Extension Cabinet PDU 1
Fuse
F1 F2
6A
10A 16A 20A 25A 32A 40A 50A 160A Char.
X X C C
PLD
Type of equipment
+ LOAD
F1
F2
D-4
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037813.fm Revision: /
Distribution PDU
D.5 Extension Cabinet PDU 2
Fuse
F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 F13 F14 F15 F16 F17 F18 F19 F20 F21 F22 F23 F24
6A
10A 16A 20A 25A 32A 40A 50A 200A Char.
X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C
PLD
Type of equipment
+0V Load
0V 0V
-Load
Distribution PDU
Document number: 037813.fm Revision: /
D-5
Distribution PDU
D.6 Extension Cabinet PDU 3
Fuse
F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 F13 F14 F15 F16 F17 F18 F19 F20 F21 F22 F23 F24
6A
10A 16A 20A 25A 32A 40A 50A 200A Char.
X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C
PLD
Type of equipment
+0V Load
-Load
D-6
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037813.fm Revision: /
0V
Distribution PDU
D.7 Extension Cabinet PDU 4
Fuse
F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 F13 F14 F15 F16 F17 F18 F19 F20 F21 F22 F23 F24
6A
10A 16A 20A 25A 32A 40A 50A 200A Char.
X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C
PLD
Type of equipment
+0V Load
-Load
Distribution PDU
Document number: 037813.fm Revision: /
0V 0V
D-7
Distribution PDU
D-8
Forza 48-25600 PPC
Document number: 037813.fm Revision: /
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Manual Instrucciones Power One Forza 48 25600pdfDokument112 SeitenManual Instrucciones Power One Forza 48 25600pdfMohammad KilaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspiro Instruction Manual 2RU BCG.00075 - ABDokument103 SeitenAspiro Instruction Manual 2RU BCG.00075 - ABJack SmitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Power OneDokument106 SeitenManual Power OneJoseMiguelBlancoAlvarez100% (1)
- Triple Play: Building the converged network for IP, VoIP and IPTVVon EverandTriple Play: Building the converged network for IP, VoIP and IPTVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mejor Manual de Radio 3000SDokument128 SeitenMejor Manual de Radio 3000SJuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- APM30 Installationv1Dokument18 SeitenAPM30 Installationv1Eder Luis Stupka100% (2)
- 001-ZXDT CSU501B (V2.06.00.07) Centralized System Management Unit Operation GuideDokument160 Seiten001-ZXDT CSU501B (V2.06.00.07) Centralized System Management Unit Operation GuideYonas TadesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNMT (WindowXP) Installation ManualDokument21 SeitenPNMT (WindowXP) Installation ManualAsanka SanjeewaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSU602A Centralized System Management Unit Product Description V1.0 - 20210202 - ENDokument11 SeitenCSU602A Centralized System Management Unit Product Description V1.0 - 20210202 - ENVictor ArticaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Luminato Quickstartmanual 002Dokument23 SeitenLuminato Quickstartmanual 002Diego LombardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPCLK3000 User Guide PDFDokument118 SeitenIPCLK3000 User Guide PDFAbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZXDU68 B451 (V6.0R20M02) DC Power System Product DescriptionDokument32 SeitenZXDU68 B451 (V6.0R20M02) DC Power System Product DescriptionVictor ArticaNoch keine Bewertungen
- mdb400 Installation PDFDokument186 Seitenmdb400 Installation PDFlegereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Data Configuration Guide For Ipasolink 200 PDFDokument20 SeitenFast Data Configuration Guide For Ipasolink 200 PDFAmlan Chowdhury100% (1)
- SMU05A Control Unit User Manual PDFDokument138 SeitenSMU05A Control Unit User Manual PDFAndres Guamanga100% (1)
- NR8961 2+0 Configuration StepsDokument11 SeitenNR8961 2+0 Configuration Stepshan handokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liberty Port-ZTE-ZXDU58-B121 Product Description PDFDokument29 SeitenLiberty Port-ZTE-ZXDU58-B121 Product Description PDFJCARLOS COLQUENoch keine Bewertungen
- Configure IPasolink400Dokument31 SeitenConfigure IPasolink400ajus adyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 315ips-Odu Ds210rb2 User Manual - (Zte) Sep 7th, 2012Dokument28 Seiten315ips-Odu Ds210rb2 User Manual - (Zte) Sep 7th, 2012Syed Rizwan Hussain100% (1)
- Evolution Series EDGE Technical Description Rev C - LetterDokument43 SeitenEvolution Series EDGE Technical Description Rev C - LetterErivelton SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emerson Candeo RectifierDokument166 SeitenEmerson Candeo RectifierPablo SanabriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mabo Te PoliceDokument107 SeitenMabo Te PoliceMokete0% (1)
- BTS3900 GSM Site Maintenance Terminal User Guide - (V300R008 - 0Dokument147 SeitenBTS3900 GSM Site Maintenance Terminal User Guide - (V300R008 - 0Syed Bilal Ahmad100% (3)
- IMaster MAE V100R023C10SPC150 Upgrade Expert Operation Guide (Virtual Cluster Remote Cold Backup System, TaiShan)Dokument101 SeitenIMaster MAE V100R023C10SPC150 Upgrade Expert Operation Guide (Virtual Cluster Remote Cold Backup System, TaiShan)muthurfeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cordex CXC HP Controller Software Manual PDFDokument236 SeitenCordex CXC HP Controller Software Manual PDFJose Pino100% (1)
- ZXMW NR8250 8120 V2 03 02 Commissioning Guide 1 PDFDokument54 SeitenZXMW NR8250 8120 V2 03 02 Commissioning Guide 1 PDFpandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 401387076R2.4.1 - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 9364 Metro Cell Indoor and Outdoor - TroubleshootingDokument52 Seiten401387076R2.4.1 - V1 - Alcatel-Lucent 9364 Metro Cell Indoor and Outdoor - TroubleshootingiveliveloilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generation Principles and Handling Measures of Configuration Conflicts On The 3900 Series Multi-Mode Base StationDokument48 SeitenGeneration Principles and Handling Measures of Configuration Conflicts On The 3900 Series Multi-Mode Base StationSimos SemovNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZXDU28&ZXDU58+B900 CSU+ (V1.20C) +Monitoring+Unit+Alarm+List 340937Dokument2 SeitenZXDU28&ZXDU58+B900 CSU+ (V1.20C) +Monitoring+Unit+Alarm+List 340937Daisy TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual - SMU01 (Modbus Protocol) V2.0Dokument62 SeitenManual - SMU01 (Modbus Protocol) V2.0Angga SyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipu1000 1kva STSWDokument17 SeitenIpu1000 1kva STSWrichmapacheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectifier PS4890 DescriptionDokument57 SeitenRectifier PS4890 DescriptionMuhammad Rauf AkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- H3I ENVA ZTE Rectifier Integration Guide For Huawei CabinetDokument7 SeitenH3I ENVA ZTE Rectifier Integration Guide For Huawei CabinetArmen AyvazyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delta Power PDFDokument62 SeitenDelta Power PDFvanhuong87Noch keine Bewertungen
- BSC6900 GSM Commissioning Guide (V900R011C00 - 01)Dokument70 SeitenBSC6900 GSM Commissioning Guide (V900R011C00 - 01)Ammar JalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dkg-307 Automatic Mains Failure Unit: Canbus and Mpu VersionsDokument54 SeitenDkg-307 Automatic Mains Failure Unit: Canbus and Mpu VersionsMohammed Bouziane100% (1)
- EMUA ConnectionDokument12 SeitenEMUA ConnectionIndRa IdNoch keine Bewertungen
- TP and External Alarm Connection and Test Guide - Ver.3.1 - DraftDokument33 SeitenTP and External Alarm Connection and Test Guide - Ver.3.1 - DraftPetyo GeorgievNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pace Pmu User's GuideDokument49 SeitenPace Pmu User's GuideTummanerale Srikantaswamy Mahesh88% (8)
- Magma AGW Release V1.8-5G-SA. .Validation - ReportDokument41 SeitenMagma AGW Release V1.8-5G-SA. .Validation - ReportAgustin Vizcarra LizarbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Firmware Update ODU With IDU AGS-20 - r1 PDFDokument17 SeitenFirmware Update ODU With IDU AGS-20 - r1 PDFmohammd khairyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lithium Battery Solution For Telkomsel - V0.0.0 PDFDokument9 SeitenLithium Battery Solution For Telkomsel - V0.0.0 PDFDaman HuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMUB User GuideDokument58 SeitenEMUB User GuideИван МальковNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMU User Guide (V100R001 - 13)Dokument70 SeitenEMU User Guide (V100R001 - 13)Lubo PicturesMaker50% (2)
- ZTE Access Systems Series ZXA10 C300 C300M C350M v1.0 PDFDokument26 SeitenZTE Access Systems Series ZXA10 C300 C300M C350M v1.0 PDFинж. Михаил МихайловNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3he09758aaabtqzza Vol1 7210 Sas-K Installation GuideDokument120 Seiten3he09758aaabtqzza Vol1 7210 Sas-K Installation GuideLuis Angel ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3900 Series & 5900 Series Base Station Installation Guides-Wireless Network Info Community-Huawei ConnectDokument7 Seiten3900 Series & 5900 Series Base Station Installation Guides-Wireless Network Info Community-Huawei ConnectDavid TombeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC848894724 - Product Manual I2 PMSDokument93 SeitenCC848894724 - Product Manual I2 PMSNarendra Kumar Soni100% (2)
- UM1M830BNA Rev M NCU Controller (6150) PDFDokument268 SeitenUM1M830BNA Rev M NCU Controller (6150) PDFanon_760637530Noch keine Bewertungen
- ZTE - CBTS I2 Installation ManualDokument194 SeitenZTE - CBTS I2 Installation ManualConstatineDoe100% (1)
- Eguard Commissioning Guideline PDFDokument37 SeitenEguard Commissioning Guideline PDFDry On100% (1)
- Signaling in Telecommunication NetworksVon EverandSignaling in Telecommunication NetworksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- SHB 9300 Servo Position Controller v2-0 EN PDFDokument462 SeitenSHB 9300 Servo Position Controller v2-0 EN PDFGuillermo Osvaldo Rivera MelladoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALR Compact Repeater - Installation and Service Manual - 044 - 05252 Rev A February 2007Dokument54 SeitenALR Compact Repeater - Installation and Service Manual - 044 - 05252 Rev A February 2007Virgil PeiulescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wiring and Grounding Guidelines For Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) AC DrivesDokument102 SeitenWiring and Grounding Guidelines For Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) AC DrivesLinda Sanchez100% (1)
- Direct Smart Reefer Microprocessor Control System Revision 121 XX, 273 XX SoftwareDokument55 SeitenDirect Smart Reefer Microprocessor Control System Revision 121 XX, 273 XX Softwarepistol pete100% (2)
- Direct Smart R v. 6 10 08Dokument222 SeitenDirect Smart R v. 6 10 08Cristobal Campos100% (3)
- Mil STD 750eDokument685 SeitenMil STD 750ePaul Rasmussen100% (1)
- Charging Vrla BatteriesDokument20 SeitenCharging Vrla BatteriesPaul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressor ReliabilityDokument2 SeitenCompressor ReliabilityPaul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Freeport-Mcmoran Copper & Gold Inc.: Form 10-KDokument191 SeitenFreeport-Mcmoran Copper & Gold Inc.: Form 10-KPaul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla de Contenido de Electrolito Dynasty - HazmatDokument9 SeitenTabla de Contenido de Electrolito Dynasty - HazmatPaul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConstructionDokument388 SeitenConstructionPaul Rasmussen100% (1)
- RGM 300 User Manual ING REV. 8.1 15.09.2011Dokument44 SeitenRGM 300 User Manual ING REV. 8.1 15.09.2011Paul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.electric LP11Dokument38 SeitenG.electric LP11Paul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Información Tecnica Batería UPS12-540MRDokument6 SeitenInformación Tecnica Batería UPS12-540MRPaul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gases y Ventilación 6739Dokument3 SeitenGases y Ventilación 6739Paul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valve Regulated Lead Acid Battery For Ups Standby Power Applications 12V 35 AH at 20 HR RATE, 12V 148 WATTS/CELL at 15 Min RateDokument2 SeitenValve Regulated Lead Acid Battery For Ups Standby Power Applications 12V 35 AH at 20 HR RATE, 12V 148 WATTS/CELL at 15 Min RatePaul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expectativa de Vida 7329Dokument4 SeitenExpectativa de Vida 7329Paul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extender Tiempo de VidaDokument0 SeitenExtender Tiempo de VidaPaul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avtron Load BanksDokument53 SeitenAvtron Load BanksPaul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introducing Alber - PpsDokument102 SeitenIntroducing Alber - PpsPaul RasmussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Voltage SlidesDokument37 SeitenHigh Voltage SlidesusamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ni-Cad General Options (Pocket, Fibre & VRPP) PDFDokument3 SeitenNi-Cad General Options (Pocket, Fibre & VRPP) PDFogautierNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPV10-10B 4kwDokument4 SeitenDPV10-10B 4kwNovak OtaševićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Gas Generator Set QSK60 Series Engine - Cummins West AfricaDokument4 SeitenNatural Gas Generator Set QSK60 Series Engine - Cummins West AfricaVILAS VIJAYANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual Transmission FWD Mitsubishi ManualDokument276 SeitenService Manual Transmission FWD Mitsubishi ManualJose Chong Loo Gonzalez100% (2)
- RSSO65N03Dokument4 SeitenRSSO65N03multimetroNoch keine Bewertungen
- LV100 3000Dokument3 SeitenLV100 3000Tibi IonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mas 6110Dokument468 SeitenMas 6110Yurii ChinovNoch keine Bewertungen
- 98Dokument2 Seiten98StuartBohmNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS Vendor Lit 2012-08-06 To Present PDFDokument69 SeitenSS Vendor Lit 2012-08-06 To Present PDFDaniel Castillo Peña100% (2)
- CSG 600 User's ManualDokument9 SeitenCSG 600 User's ManualSlobodan MaksimovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- AH5As - Speaker PAGA SystemDokument2 SeitenAH5As - Speaker PAGA SystemRidho Saputro HutomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Touch Advanced Display (TAD) Installation Guide: ApplicationsDokument8 SeitenTouch Advanced Display (TAD) Installation Guide: ApplicationsRonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micropump Specs 030817Dokument9 SeitenMicropump Specs 030817Deepak PrmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 87ae786948d705a6047e1ca5caf6541b.xlsxDokument255 Seiten87ae786948d705a6047e1ca5caf6541b.xlsxshubhamjain1993Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Medical Catalog-Nanjing Ocean Medical Products Co.,LtdDokument28 Seiten2021 Medical Catalog-Nanjing Ocean Medical Products Co.,LtdWang BandasackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Fuel Gauge With Intelligent Headlamp Beam Control Using Raspberry PiDokument5 SeitenSmart Fuel Gauge With Intelligent Headlamp Beam Control Using Raspberry Pikssrao13Noch keine Bewertungen
- BMS Model List With Communication FunctionDokument3 SeitenBMS Model List With Communication FunctionÁlvaro Satué Crespo0% (1)
- ServiceInvoice FOCGA83488Dokument1 SeiteServiceInvoice FOCGA83488Anonymous FKn0IvPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Assesment LT & EI JobsDokument2 SeitenRisk Assesment LT & EI JobsMudassar MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turner - 2nd - Year - (Volume II of II) TPDokument135 SeitenTurner - 2nd - Year - (Volume II of II) TPravi9811075184Noch keine Bewertungen
- Make ElectricalDokument5 SeitenMake ElectricalShivalik c.h.s.Noch keine Bewertungen
- BakerDokument13 SeitenBakerGonçalo Filipe SousaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honeywell 50250 HEPA Air PurifierDokument9 SeitenHoneywell 50250 HEPA Air PurifierTravisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saipa X100 Stage3 Diag Training Dez 2010Dokument1 SeiteSaipa X100 Stage3 Diag Training Dez 2010JonSalchichonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elevator Line EnglischDokument12 SeitenElevator Line EnglischAlex StanciuNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlptecDokument15 SeitenAlpteczakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mill Stage IIDokument68 SeitenMill Stage IIShift InchargeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metron Fire Pump Controls: Standard CatalogDokument102 SeitenMetron Fire Pump Controls: Standard Catalogmohammad AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- ULV Cold Fogging Aerosol Applicators: Fontan Starlet Fontan StarletDokument2 SeitenULV Cold Fogging Aerosol Applicators: Fontan Starlet Fontan StarletFilip PungulNoch keine Bewertungen