Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Anaesthesia
Hochgeladen von
Davis KallanCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anaesthesia
Hochgeladen von
Davis KallanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Available 0.5% 1% 2% 5% Dose 3mg/kg (7mg/kg with Adren Met in liver by N-dealkylation to monoethylglycine xylidide Terminal life 1.
5h Increase in Heart failure/Liver disease
Lignocaine
Lignocaine Mepivacaine BUpivacaine Metabolised by Liver
Amide Linkage
2,6 Diisopropylphenol Dose 2-2.5 mg/Kg IV Store in egg phos/glycerol/soybean oil Drugs Induction time = 1a/b circ Recovery - 5min foll bolus Action by IV across BBB
Available as 0.25%, 0.5% Dose 2mg/kg Terminal life 3h Metabolised by N-dealkylation to 2,6 pipecoloxylidide
Bupivicaine
Procaine Chlorprocaine Tetracaine
Ester linkages
Metabolised in plasma by psyudocholinesterase Induction Sedation TIVA (6mg/ml min) Obstructed Airway Haemodynamic comprimise Epilepsy Hypotension (elderly) Hypovolemia (Cardiac Hx Respiratory Depression (apnoea) Pain on Inj (Use Lignocaine) Epilepsy Glucuronidation in Liver 0.3% excreted unchanged Little protein binding Elimination T1/2 3-4.8h
Indications Propofol
Local
Reversible compression of nerve conduction Inhibition of Na channels Higher Myelination is Less Susc to Aneasth Mechanism
C/I
S/E
Lipophilic ring Hydrophyllic amino group Intermediate chain Amide/Ester
Drug Structure Metabolism
Treat Oxygenation Seizure - Diazepam.Thiopentone
Neuro: confusion, agitation disorientation, convuslions coma
IV Drugs Toxicity
Sodium 5-ethyl-5(methylbutyl)-2-thiopentone Induction bolus 5mg/kg Stored in N2 and NaCO3 6% Indications Induction Barb Coma (Neuroprotctive Head Inj) Airway comprimised Haemodynamic comprimis Porphyria (Prec acute attack Hypotension Respiratory Depression Delayed recovery if large doses Not used for Infusion (30% unch at 24h) Extensive skin necrosis if inj in tiss (pH 10.8) 80% Binding plasma proteins Metabolised in Liver T1/2 11h 10%-15% drug met/h
Thiopentol Cardiac: Bupivicaine>Lignocaine Hypotension, Heart block,Vntricular Arrythmia Treat with aggressive resuscitation
xenon
Inert gas B/G 0.2 MAC 70% No CV Res S/E Not in Clinical Use yet
C/I
S/E
Potentiation of Gly/GABAa Inhibition of nAch Site of Action Hippocampus
Mechanisms of Action
PD
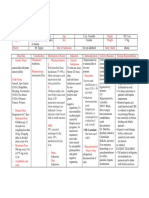
Aneasthesia Drugs
Inltration Regional Block Spinal Epidural Local
General Aneasthetics
Etomidate
D-ethyl-1-methylbutyl-imidazole-5-carboxylate Rapid Acting Duration 2-3 minutes CV Stability Dose 0.3mg/Kg PD S/E 76% Protein Bound T1/2 75min: MEt by ester hydrolysis in Liver/Plasma ACTH Suppression N&V 30% Pain on Inj Excititory Phenomena
Induction Maintenance
Intravenous General Inhalation
Anaesthesia
Ketamine
Phencyclidine derivative Induction agent - dissociative anaesthesia (thalamus-cortex) Dose 2.5 mg/kg Cause less CV and Respiratory depression Greater hallucination incidence C/I Head injuries (Riases ICP) 12% Protein bound Met in liver (glucuronidation T1.2 2.5h
1:65,000 AD Path: Disruption of Ryanodine in SR Ca Hypermetabolic reaction Mortality 80%
Malignant Hyperpyrexia
Nitric Oxide
Weak aneasthetic B/G 0.4 Good alangesic props Diffuses rapidly into air lled spaces C/I Pneumothorax
PD
Treatment is DANTROLENE Active cooling Req ICU Management
Used to maintain anaesthesia Admin with N2/O2 Not used for Induction
Mechanisms Volatile Anaesthetics
Activation GABAa Inhibition nAchR
Desurance 0.4 Sevourance 0.6 Isourane 1.2 Halothane 2.5 Blood Gas Solubility Partial pressure build up in blood Greater insolubility - quick high Pp MAC Conc at 1 atm at which 50% of pt do not move in response to surgical stimulus
Administer by vaporisers % of gas mixture (1-2% norm)
Can be affected by Age, Clinical Condition Conc Drug Admin, Use of NO
Halothane
Halogenated hydrocarbon Stored in .0001% thymol MAC 0.7% Induction anaesthesia Metabolism 20% by redox pathways
S/E
Respiratory Depression CV Depression and Hypotension Arrythmias - Bradycardia,Ventricular arrythmias Halothane hepatitis
Drugs 1-chloro-triuroethyl-diuromethyl ether Pungent odour - No inhalation induction MAC 1.2% Minimal metabolic transformation 0.2% Less CVD than Halothane No hepatitis High MAC 2.0% Inhalational induction 4% Biotransformation gen FClean prole, rapid uptake and recovery Renal toxicity due to F-
Isourane
Sevourane
Enurane
MAC 1.6% Pungent odour Risk epiletiform activity at high concentrations
Desurane
Rapid onset and recovery Very pungent Tachycardia at high concentrations
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Calculation of DosesDokument12 SeitenCalculation of DosesFranklin Jayoma ManaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 2Dokument2 SeitenCase 2Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 1Dokument2 SeitenCase 1Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney 1Dokument2 SeitenKidney 1Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Imaging 2Dokument1 SeiteClinical Imaging 2Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GoodDokument2 SeitenGoodDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Imaging: Small-Bowel Obstruction: State-of-the-Art Imaging and Its Role in Clinical ManagementDokument1 SeiteClinical Imaging: Small-Bowel Obstruction: State-of-the-Art Imaging and Its Role in Clinical ManagementDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney 3Dokument2 SeitenKidney 3Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 1Dokument2 SeitenCase 1Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney 4Dokument2 SeitenKidney 4Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney 2Dokument2 SeitenKidney 2Davis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AzygouDokument1 SeiteAzygouDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- KidneyDokument2 SeitenKidneyAnandraojs JsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CatholicDokument2 SeitenCatholicDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Imaging Techniques and Their Uses in DiagnosisDokument1 SeiteMedical Imaging Techniques and Their Uses in DiagnosisDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- About NSD: On 28 February 1928, DR C.V Raman Had Announced The Discovery of TheDokument1 SeiteAbout NSD: On 28 February 1928, DR C.V Raman Had Announced The Discovery of TheDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV RamanDokument1 SeiteCV RamanDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Indian CinemaDokument1 SeiteHistory of Indian CinemaDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AADokument1 SeiteAADavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bollywood: The Hindi Film IndustryDokument3 SeitenBollywood: The Hindi Film IndustryDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TamilDokument2 SeitenTamilDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Studies, Now Provides Its Mite in The Field of Higher Education Imparting The MostDokument1 SeiteManagement Studies, Now Provides Its Mite in The Field of Higher Education Imparting The MostDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marana Simhasanam Vanaprastham: Malayalam Cinema Is TheDokument1 SeiteMarana Simhasanam Vanaprastham: Malayalam Cinema Is TheDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 42 Diabetic Retinopathy Classification and Typical LesionsDokument1 Seite42 Diabetic Retinopathy Classification and Typical LesionsDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cinema of IndiaDokument4 SeitenCinema of IndiaDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConjunctivitisDokument1 SeiteConjunctivitisDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Concept MapDokument8 SeitenRenal Concept MapDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Indian edition of GQ magazineDokument2 SeitenThe Indian edition of GQ magazineDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retinal DetachDokument1 SeiteRetinal DetachDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonometry PDFDokument1 SeiteTonometry PDFDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihelminthes and AntimalarialDokument14 SeitenAntihelminthes and AntimalarialSaid OmaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antifungal ClassDokument25 SeitenAntifungal ClassRifa AudinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum VitaeDokument2 SeitenCurriculum VitaedeepajolyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash Hand OveringDokument96 SeitenCash Hand Overingpradeep kumar racharlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S22MARDokument4 SeitenS22MARWulan YuniarsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walmart 4 Dollar Drug ListDokument6 SeitenWalmart 4 Dollar Drug ListCucho0% (2)
- Interpretation, Taylor & Francis Publiser, London.: Daftar PustakaDokument3 SeitenInterpretation, Taylor & Francis Publiser, London.: Daftar PustakaAnonymous 5K38SwLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabel ObatDokument6 SeitenTabel Obatiik abdulkholikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rishum 1 262421216 2Dokument1 SeiteRishum 1 262421216 2HellcroZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceiling-Price-List-F 30 Sep 2020Dokument21 SeitenCeiling-Price-List-F 30 Sep 2020nagashayana gNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ketoconazole dosage and safetyDokument2 SeitenKetoconazole dosage and safetyPawitra JayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRCSUDokument536 SeitenBRCSUKristineNoch keine Bewertungen
- A REVIEW On Dissolution DIFFERENT MODELDokument17 SeitenA REVIEW On Dissolution DIFFERENT MODELKalyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Pharmacists AssociationDokument4 SeitenPhilippine Pharmacists AssociationAbby LumanglasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cannabinoids - Structures, Effects, and ClassificationDokument19 SeitenCannabinoids - Structures, Effects, and ClassificationDaphne HernaezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intranasal Midazolam Versus Intravenous Diazepam For The Treatment of Acute Seizures in Paediatric PatientsDokument5 SeitenIntranasal Midazolam Versus Intravenous Diazepam For The Treatment of Acute Seizures in Paediatric PatientsArif KusumawidjayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morphine and Alternative Opioids in Cancer Pain: The EAPC RecommendationsDokument7 SeitenMorphine and Alternative Opioids in Cancer Pain: The EAPC RecommendationsSri HariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Amoxicillin PDFDokument4 SeitenDrug Study Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nalmefene opioid antagonist alcohol dependenceDokument3 SeitenNalmefene opioid antagonist alcohol dependencePrashanth RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 2Dokument13 SeitenGroup 2arifpharmjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibuprofen Oral Use Immediate Release Formulations 200 800 MG Product Specific Bioequivalence Guidance Revision 1 - enDokument3 SeitenIbuprofen Oral Use Immediate Release Formulations 200 800 MG Product Specific Bioequivalence Guidance Revision 1 - enkamara.ammariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Pustaka FarmasiDokument3 SeitenDaftar Pustaka Farmasipermata putriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmaceutical AnalysisDokument73 SeitenPharmaceutical AnalysisChristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30-09 PsicoDokument5 Seiten30-09 PsicoASMFKASFKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internship - RX Drugs (Part 1)Dokument4 SeitenInternship - RX Drugs (Part 1)pjoanneloisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Chapter 5Dokument64 Seiten13 Chapter 5yoganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EtoposideDokument3 SeitenEtoposideNoamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 5Dokument430 SeitenClass 5Subash NeupaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Pharmacology: A Brief History and Key ConceptsDokument96 SeitenGeneral Pharmacology: A Brief History and Key Conceptsvetprabu34Noch keine Bewertungen