Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CE 15 Problem Set Take Home Exercises
Hochgeladen von
gemnikkicOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CE 15 Problem Set Take Home Exercises
Hochgeladen von
gemnikkicCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CE
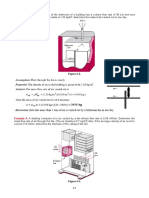
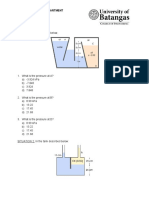
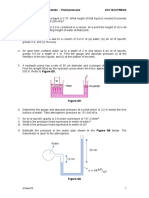
15 Problem Set Take Home Exercise To be submitted on December 6 Problem 1 In the figure below, determine the gage pressure at point A in pa. Is it higher or lower than atmospheric? Take = 9790 N/m3 and 133100 N/m3 for mercury. Problem 2 All fluids are at 20C. Determine the pressure difference (Pa) between points A and B. Take the specific weights to be Benzene: 8640 N/m3 Kerosene: 7885 N/m3 Mercury: 133100N/m3 Water: 9790 N/m3
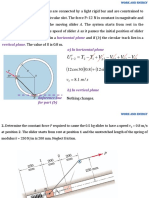
Problem 3 Gate AB is a homogenous mass of 180 kg, 1.2 m wide into the paper, hinged at A, and resting on a smooth bottom at B. All fluids are at 20C. For what water depth h will the force at point B be zero? Let =12360 N/m3 for glycerin and 9790 N/m3 for water. Problem 4 The circular gate ABC has a 1-m radius and is hinged at B. Compute the force P just sufficient to keep the gate from opening when h = 8 m. Neglect atmospheric pressure.
Problem 5 Pressurized water fills the tank in the figure below. Compute the net hydrostatic force on the conical surface ABC. Problem 6 Gate ABC is a circular arc, sometimes called a Tainter gate, which can be raised and lowered by pivoting about point O. For the position shown, determine: a) The hydrostatic force of the water on the gate. b) The line of action of the force. Does the force pass through point O? Use unit weight of water = 9810 N/m3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CelerityDokument23 SeitenCelerityswabrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- BernoulliDokument25 SeitenBernoulliAlberto Preciados AlumbroNoch keine Bewertungen
- TG-Op1 Enunciados v01Dokument53 SeitenTG-Op1 Enunciados v01VlmScarletQcaritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle On Buoyancy Stability of Floating BodiesDokument12 SeitenPrinciple On Buoyancy Stability of Floating Bodiesprincess dee tolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- P5 3B Gutierrez JohnPaulDokument5 SeitenP5 3B Gutierrez JohnPauljp gutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics IIIDokument93 SeitenFluid Mechanics IIIRanjeet Singh0% (1)
- Evaluation Set 1: Civil Engineering Department Review in Hydraulics 1st Semester AY 2020-21Dokument4 SeitenEvaluation Set 1: Civil Engineering Department Review in Hydraulics 1st Semester AY 2020-21Yedda M IlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prismoidal Formula 2Dokument11 SeitenPrismoidal Formula 2anggaxkusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Ch1 ProblemDokument5 SeitenTutorial Ch1 ProblemKiat HauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water QuestionsDokument1 SeiteWater QuestionshhhhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tolentino Sample Refresher Notes in MathDokument6 SeitenTolentino Sample Refresher Notes in MathDindo Mojica100% (2)
- First Law of ThermodynamicsDokument5 SeitenFirst Law of ThermodynamicsNikko ManaleseNoch keine Bewertungen
- HWK 5 Solution PDFDokument3 SeitenHWK 5 Solution PDFJohn Miko JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM Dec - 2009Dokument20 SeitenFM Dec - 2009Divyesh Morabiya80% (5)
- Isra University Faculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering H.W (#4)Dokument10 SeitenIsra University Faculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering H.W (#4)tariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Properties ProblemsDokument1 SeiteFluid Properties ProblemsTOOBA KHALILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument31 SeitenChapter 6Camille LardizabalNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUEZ CANAL University Fluid Mechanics AssignmentDokument3 SeitenSUEZ CANAL University Fluid Mechanics Assignmentmahmoud EissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 1 - Introduction To Fluid MechanicsDokument9 SeitenSheet 1 - Introduction To Fluid MechanicsMugiwara SparrowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Forces and TorquesDokument10 SeitenMagnetic Forces and TorquesMahmoud EldabahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bernoulli's Equation ProblemsDokument9 SeitenBernoulli's Equation ProblemsAboo Sdam AL MkahalNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRELIM EXAM: Directions, Problems 1-4Dokument1 SeitePRELIM EXAM: Directions, Problems 1-4Lian HebronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Statics PDFDokument3 SeitenFluid Statics PDFAnisa RachmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 01 20-21 Properties of Fluid RevDokument2 SeitenSheet 01 20-21 Properties of Fluid RevBibaswan MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLUID MECHANICS BuoyancyDokument19 SeitenFLUID MECHANICS BuoyancyAngelo ColendresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Questions Fluid MechanicsDokument10 SeitenSample Questions Fluid MechanicsjrmmansayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW#2 Solutions ME363 Fall 2007 PDFDokument8 SeitenHW#2 Solutions ME363 Fall 2007 PDFjessicaHannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- K Subra 1000 Solved ProblemsDokument2 SeitenK Subra 1000 Solved ProblemsMat0% (1)
- Math word problemsDokument6 SeitenMath word problemsjadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics New ProblemsDokument5 SeitenHydraulics New ProblemsEugine BalomagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Pressure Fundamentals ExplainedDokument23 SeitenFluid Pressure Fundamentals ExplainedSamuel GaétanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Bouyancy 01Dokument18 Seiten4 Bouyancy 01Soledad AceitunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- How far can a painter climb a ladder without slipping? (S = 2.55 mDokument1 SeiteHow far can a painter climb a ladder without slipping? (S = 2.55 mnsbaruaole0% (1)
- PPSDokument94 SeitenPPSaamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Laplace TransformDokument77 SeitenChapter 3 Laplace TransformafiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic - 7 - Permeability & SeepageDokument32 SeitenTopic - 7 - Permeability & Seepagejimmys45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of MaterialsDokument101 SeitenStrength of MaterialsLucksy Marcus PalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial #3 #ProblemsDokument5 SeitenTutorial #3 #ProblemsAisha AbuzgaiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring system analysisDokument18 SeitenSpring system analysisRhys Lim YH100% (1)
- BSABE2 - Blasquez - Lab Report 2Dokument7 SeitenBSABE2 - Blasquez - Lab Report 2Lorenzo Niño BlasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-3 - Engg Mech PDFDokument6 SeitenAssignment-3 - Engg Mech PDFNiteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- (REVIEW IN HYDRAULICS) EvaluationDokument5 Seiten(REVIEW IN HYDRAULICS) EvaluationYedda M IlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRB Homework #2Dokument1 SeiteDRB Homework #2Vianca CamilLe Incognito-Castillo PanganibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Tutorial Pressure Sept19Dokument7 Seiten2 Tutorial Pressure Sept19hairinnisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Working Fluid in ThermodynamicsDokument13 SeitenThe Working Fluid in ThermodynamicsFarouk BassaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Chep Thermodynamics and Thermochemisty Ques. Final EDokument27 Seiten02 Chep Thermodynamics and Thermochemisty Ques. Final Esumitmanit08100% (2)
- Depth of Water in Conical Tank in Upright and Inverted Positions - Solid Geometry ReviewDokument2 SeitenDepth of Water in Conical Tank in Upright and Inverted Positions - Solid Geometry ReviewimrancenakkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics 6713 Tutorials and SolutionsDokument42 SeitenHydraulics 6713 Tutorials and SolutionsAsun RajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCESQ 2018 QuestionsDokument3 SeitenNCESQ 2018 QuestionsKhent Alfred B. DerechoNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIBRATION TITLEDokument49 SeitenVIBRATION TITLEMark Oliver BernardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ems TutorialDokument43 SeitenEms TutorialJohn Eric Balarao Ferranco33% (3)
- 3 ChannelDokument45 Seiten3 ChannelPatrick YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument20 SeitenChapter 3Heart VenturanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheet 4Dokument3 SeitenActivity Sheet 4Shiebastian ArietaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics Example Problems ExplainedDokument109 SeitenFluid Mechanics Example Problems ExplainedStevenMvuyana0% (2)
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Lectures on Theoretical PhysicsVon EverandMechanics of Deformable Bodies: Lectures on Theoretical PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Lectures on Theoretical Physics, Vol. 2Von EverandMechanics of Deformable Bodies: Lectures on Theoretical Physics, Vol. 2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Mecánica de Fluidos: Problema 1Dokument4 SeitenMecánica de Fluidos: Problema 1JUAN DAVID MAYA ZAMORANoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 1Dokument2 SeitenProblem Set 1Johanna Gwenn Taganahan LomaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYDRAULICS TOPIC 1 FLUID PROPERTIES UNIT PRESSURE 23 May 2022Dokument41 SeitenHYDRAULICS TOPIC 1 FLUID PROPERTIES UNIT PRESSURE 23 May 2022samera salihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gear PatternDokument1 SeiteGear PatterngemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide WPC STPDokument21 SeitenGuide WPC STPNamasivayam KaliappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joining Processes: Permanent JointsDokument31 SeitenJoining Processes: Permanent JointsgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Comprehension - Context CluesDokument1 SeiteReading Comprehension - Context CluesgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Code Gauss JordanDokument1 SeitePython Code Gauss JordangemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Directory: 2 Edition Q2 2015Dokument21 SeitenMarketing Directory: 2 Edition Q2 2015gemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sustainability - Debate NotesDokument2 SeitenSustainability - Debate NotesgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Examination - Fluid MechanicsDokument1 SeiteSample Examination - Fluid MechanicsgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 1 Quiz ADokument1 SeiteScience 1 Quiz AgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Press Fit PDFDokument9 SeitenPress Fit PDFMohd Hilmi IzaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Curved Beams PDFDokument8 SeitenAnalysis of Curved Beams PDFdarkkimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 130 Pose BibleDokument15 Seiten130 Pose BibleGabi Oliveira100% (7)
- CH 3 Load and Stress AnalysisDokument143 SeitenCH 3 Load and Stress AnalysisgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Dynamic Force AnalysisDokument22 SeitenChapter 2 Dynamic Force AnalysissreeshpsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cornell LetterDokument1 SeiteCornell LettergemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - DepreciationDokument3 SeitenChapter 5 - DepreciationgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- English - Exercises - Verb TensesDokument3 SeitenEnglish - Exercises - Verb TensesgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConjunctionsDokument2 SeitenConjunctionsgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration FormulasDokument9 SeitenVibration FormulasgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises - English 1 - PronounsDokument1 SeiteExercises - English 1 - PronounsgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises - Math 1 - Absolute Value InequalityDokument2 SeitenExercises - Math 1 - Absolute Value InequalitygemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabrication of Plastics and Elastomers QuizDokument5 SeitenFabrication of Plastics and Elastomers QuizgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Economy - Selection of AlternativesDokument1 SeiteEngineering Economy - Selection of AlternativesgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiments For Light MeterDokument5 SeitenExperiments For Light MetergemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet Forming ProcessesDokument93 SeitenSheet Forming ProcessesgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 1 SET THEORY AND OPERATIONS Exercises and SolutionsDokument5 SeitenMATH 1 SET THEORY AND OPERATIONS Exercises and Solutionsgemnikkic50% (4)
- Debate PaperDokument2 SeitenDebate PapergemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises - Volume - Cylinder - Answer KeyDokument2 SeitenExercises - Volume - Cylinder - Answer KeygemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises - English 1 - Pronouns - HandoutDokument1 SeiteExercises - English 1 - Pronouns - HandoutgemnikkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heater Catalog 0618Dokument576 SeitenHeater Catalog 0618abasakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slip Form HandbookDokument301 SeitenSlip Form HandbookAhmed Mostafa AL-Aboudy67% (3)
- Copper (II) Sulfate - Reagent - Anhydrous 98 - Acros OrganicsDokument5 SeitenCopper (II) Sulfate - Reagent - Anhydrous 98 - Acros OrganicsGaryoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No. 2 The Microscope: Term FunctionDokument5 SeitenActivity No. 2 The Microscope: Term FunctionUNSA MANENoch keine Bewertungen
- Specialized lubricants maximize steel industry productivityDokument16 SeitenSpecialized lubricants maximize steel industry productivitySioney MonteiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling TechniquesDokument17 SeitenSampling TechniquesDebjyoti SanyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitocote ET402 : Constructive SolutionsDokument4 SeitenNitocote ET402 : Constructive Solutionsnoto.sugiartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- C55Dokument4 SeitenC55Rufo CascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASAL Biology Sample PDFDokument32 SeitenASAL Biology Sample PDFandry hidayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry P Block ElementsDokument14 SeitenChemistry P Block ElementsSurendra Tyagi0% (1)
- SITI SOLEHAH BINTI OMAR (2015834112) /EH224 7A1 Heuristics of ReactorDokument2 SeitenSITI SOLEHAH BINTI OMAR (2015834112) /EH224 7A1 Heuristics of ReactorSolehah OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NBS18 Heat TreatmentDokument46 SeitenNBS18 Heat Treatmentshailesh_tiwari_mechNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAO 2016-08 Features and CAPDokument64 SeitenDAO 2016-08 Features and CAPDianne Kristine Avila100% (4)
- Chapter 8 EXERGYDokument37 SeitenChapter 8 EXERGYzabidullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPE 37084 Horizontal Well Length: Drill Short or Long Wells?Dokument9 SeitenSPE 37084 Horizontal Well Length: Drill Short or Long Wells?Waleed Barakat MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Media File Sheehan Perf of HDG in Coastal Envs PDFDokument18 SeitenMedia File Sheehan Perf of HDG in Coastal Envs PDFFrankie ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Longair - Light and ColorDokument38 SeitenLongair - Light and Colormordsith90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding The Results of An Intelligent Pig InspectionDokument18 SeitenUnderstanding The Results of An Intelligent Pig InspectionLeonardo VazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit Tests: by Mohneet Chitkara B Pharma Semester 1 2150991058Dokument13 SeitenLimit Tests: by Mohneet Chitkara B Pharma Semester 1 2150991058Mohneet ChitkaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brewery Product Guide - FINAL 0619 PDFDokument3 SeitenBrewery Product Guide - FINAL 0619 PDFVictor LeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry 1 Activity Sheet Quarter 2-MELC 12 Week 6Dokument9 SeitenGeneral Chemistry 1 Activity Sheet Quarter 2-MELC 12 Week 6Joshua De La VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
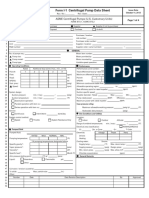
- Form I-1 Centrifugal Pump Data SheetDokument4 SeitenForm I-1 Centrifugal Pump Data SheetJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Kimia Pertengahan Tahun Form 4Dokument11 SeitenSoalan Kimia Pertengahan Tahun Form 4Ridzuan Mohd AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everything StarsDokument166 SeitenEverything StarsBilly The KidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Check Maf Kia Carnival DieselDokument7 SeitenCheck Maf Kia Carnival Dieseljulio797Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion and Osmosis LabDokument2 SeitenDiffusion and Osmosis LabJustin NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9Dokument10 Seiten9Laurentiu Chilibaru-Cristina OpritescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSc Surveying and Water Resources TopicsDokument3 SeitenMSc Surveying and Water Resources TopicsNirjhor KabirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Mass TransferDokument22 SeitenHeat and Mass TransferAtthuru ManikantaNoch keine Bewertungen