Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sas
Hochgeladen von
Janine Erika Julom BrillantesOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sas
Hochgeladen von
Janine Erika Julom BrillantesCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
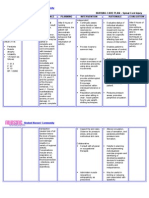
Results and Observations: Glucose Molisch test Moores test Violet ring Dark yellow with a caramel odor
Immediate rxn: -lime Green After 1 hour: -dark brown Sucrose Blue(violet) ring Light yellow Immediate rxn: -emerald green After 1 hour: -dark brown Starch Red(violet) ring Light yellow Immediate rxn: -emerald green After 1 hour: Green-black
Anthrone test
A positive reaction is indicated by appearance of a purple ring at the interface between the acid and test layers in the Molisch test. In our experiment, a purple, blue and a red ring were the colors formed at the junction of the two layers of Glucose, Sucrose, and Starch respectively. Glucose had a violet color on the lower part of the solution, while sucrose had a dark blue color on the lower part. Moore's test indicates the presence of carbohydrates in a specific compound. In the experiment, all solutions started clear but after boiling, glucose yielded a dark yellow solution having a caramel odor, while sucrose and starch yielded a light yellow color. The Anthrone test causes blue-green to appear when sugar is present in a sample. The test determines how much sugar is in a sample of any substance, including carbohydrates. In this experiment, when the anthrone reagent was poured onto glucose, sucrose, and starch, the immediate reactions formed a lime green and an emerald green color. After an hour, the glucose and sucrose solutions turned dark brown, while starch yielded a greenish black solution. Analysis & Conclusion: Molisch test is a sensitive chemical test for all carbohydrates based on the dehydration of the carbohydrate by sulfuric acid to produce an aldehyde ether which then condenses with the phenolic structure to form a purple colored compound. All carbohydrates monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides should give a positive reaction. The solutions tested - Glucose, sucrose, and starch yielded a positive reaction in the Molisch test since they are all carbohydrates. In the moores test, when the solution of reducing sugar is heated with a alkali, the solution will turn darker and therefore liberating a caramel odor. This is due to the liberation of an aldehyde which subsequent polymerizes to form a resinous substance, caramel. Glucose is a reducing sugar, while sucrose and starch are not, signifying that our results were correct and that only glucose will liberate a caramel odor.
In the Anthrone test, carbohydrates are dehydrated to form furfural to form a bluish green complex. Sugars react with the anthrone reagent to give a bluish green color. In our experiment, only starch gave a positive result that supposedly glucose and sucrose must also give. Some factors and inconsistencies may have been encountered for the other sugars not to give a positive result. By using the Molisch, Moores and Anthrone test, we became more familiar with the common principles, significant similiarities and differences in the reactions of carbohydrates in different quantitative tests, and that external factors in the testing process could affect the results. Molisch test is a test for carbohydrates and carbohydrate containing compounds. The Anthrone test is also a test from carbohydrates while the moores test is a test for reducing sugars.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Lab 7 Please ContinueDokument5 SeitenLab 7 Please ContinueMariano MarbellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VI. Analysis: CHEM 153 Lab Report (Experiment 5)Dokument3 SeitenVI. Analysis: CHEM 153 Lab Report (Experiment 5)Maria Angela OlinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp. 6ADokument1 SeiteExp. 6ARobin Carla Feliciano RmtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Anal5Dokument6 SeitenChem Anal5Christian Rey Hallera BalmoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Demo 3Dokument15 SeitenTeaching Demo 3Kent MaravillosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates PDFDokument56 SeitenCarbohydrates PDFJustine Salvo EvaristoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion Part 3Dokument6 SeitenDiscussion Part 3limNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characterization of CarbohydratesDokument3 SeitenCharacterization of CarbohydratesHyvieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.) The Molisch TestDokument12 Seiten1.) The Molisch Testnoelah salcedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1: CarbohydratesDokument6 SeitenExperiment 1: CarbohydratesEM Alberts100% (2)
- Genbio (Tests)Dokument5 SeitenGenbio (Tests)Alecz zzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion of ResultsDokument3 SeitenDiscussion of ResultsMonica ClauorNoch keine Bewertungen
- An ThroneDokument2 SeitenAn ThroneJames EullaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2 Group 1Dokument4 SeitenExperiment 2 Group 1jamielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 5 CarbohydratesDokument49 SeitenExpt 5 CarbohydratesColene MoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory 3Dokument4 SeitenLaboratory 3lili ry100% (1)
- General and Specific Tests For CarbohydratesDokument11 SeitenGeneral and Specific Tests For CarbohydratesBrian Rubiano0% (1)
- Experiment 3 General Reactions of Carbohydrates: NH OHDokument16 SeitenExperiment 3 General Reactions of Carbohydrates: NH OHAl Cris BarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Lab 2Dokument2 SeitenBiochem Lab 2Binoy SerinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis For Carbohydrates Using Glucose, Sucrose, Liver, Paper Pulp and Starch SamplesDokument9 SeitenQualitative Analysis For Carbohydrates Using Glucose, Sucrose, Liver, Paper Pulp and Starch SamplesKorrine Gumabon BalaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test For CarbohydratesDokument15 SeitenTest For CarbohydratesRandy AminolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Color Tests For Carbohydrates-2 PDFDokument48 SeitenGeneral Color Tests For Carbohydrates-2 PDFTimothy John BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomolecule Test JurnalDokument5 SeitenBiomolecule Test JurnalPurwanttyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Activity 1a & 1bDokument28 SeitenBiochemistry Activity 1a & 1bSushmita Mia Gapuz100% (1)
- Carbohydrates Cell MolecDokument7 SeitenCarbohydrates Cell Molecoink100% (1)
- Biochemistry Reactions of CarbohydratesDokument13 SeitenBiochemistry Reactions of CarbohydratesBridgette JuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates LabDokument21 SeitenCarbohydrates LabBernardMarkMateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Carbohydrate DetectionDokument16 SeitenQualitative Carbohydrate DetectionTristan Karl AbrugarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test For CarbohydratesDokument2 SeitenTest For CarbohydratesCamille EscobarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Written Report Act 3Dokument6 SeitenWritten Report Act 3Sherma Sheikh karimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt. 5 BIOCHEMLABDokument9 SeitenExpt. 5 BIOCHEMLABEloisah Vin Santiago Ragodon100% (1)
- Results and Discussion For CarbohydratesDokument4 SeitenResults and Discussion For CarbohydratesDusky25% (4)
- Worksheet Module 2Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet Module 2YuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOL 1362 Lab 1Dokument18 SeitenBIOL 1362 Lab 1Oluchi BairdNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Carbohydrate Is An Organic Compound With The General Formula CMDokument6 SeitenA Carbohydrate Is An Organic Compound With The General Formula CMHans Louie TabasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Experiment1 CarbohydratesDokument10 SeitenBiochemistry Experiment1 CarbohydratesChery-an PletNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem LabDokument8 SeitenBiochem LabMa Anna Cris LumongsudNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Test For CarbohydratesDokument8 Seiten3 Test For CarbohydratesAllyssa Lorraine PrudencioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1a & 1bDokument2 SeitenActivity 1a & 1bSushmita Mia GapuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates ExperimentDokument2 SeitenCarbohydrates ExperimentflorisamahinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post LabDokument2 SeitenPost LabJorianne Ledesma0% (1)
- Formal Report (Tests For Carbohydrates)Dokument15 SeitenFormal Report (Tests For Carbohydrates)Angelo TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification of Sugars From Natural SourcesDokument6 SeitenIdentification of Sugars From Natural SourcesShoomyla RashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Molisch TestDokument12 SeitenThe Molisch Testkamaksi100% (1)
- Tests For Carbohydrates Lecture1Dokument62 SeitenTests For Carbohydrates Lecture1Alessandra Franchesca CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 5Dokument9 SeitenLab Report 5Krizia Corrine St. PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 3 CARBOHYDRATESDokument4 SeitenExperiment No. 3 CARBOHYDRATESMissy Arabella PameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates Lab SlidesDokument42 SeitenCarbohydrates Lab SlidesZeian Jacob BaylaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 6 BioDokument2 SeitenExp 6 BioIrdina SufiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates ExperimentDokument12 SeitenQualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates Experimentasdf653652547Noch keine Bewertungen
- QUALITATIVE Laboratory ANALYSIS OF Activity 13 SugarsDokument19 SeitenQUALITATIVE Laboratory ANALYSIS OF Activity 13 SugarsCelestine MarivelezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 5Dokument12 SeitenLab Report 5aryavijay78% (9)
- General and Specific Tests For CarbohydratesDokument14 SeitenGeneral and Specific Tests For CarbohydratesarellanokristelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment-6A-6B-Answer-Guide (1) CARBOHYDRATESDokument4 SeitenExperiment-6A-6B-Answer-Guide (1) CARBOHYDRATESLleana TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CARBOHYDRATES LabDokument42 SeitenCARBOHYDRATES LabZiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates TestsDokument4 SeitenCarbohydrates TestsTk MakotoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 CARBOHYDRATE RECOGNIZITION 1.pptxDokument15 Seiten6 CARBOHYDRATE RECOGNIZITION 1.pptxfareaahtaieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Laboratory Expt. #1Dokument6 SeitenBiochemistry Laboratory Expt. #1Keth Samuel AdesasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingVon EverandBiochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- CS Form No. 32 Oath of OfficeDokument1 SeiteCS Form No. 32 Oath of OfficeJanine Erika Julom Brillantes100% (1)
- Daily Plan of ActivitiesDokument1 SeiteDaily Plan of ActivitiesJanine Erika Julom BrillantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Client With Mucoskeletal and Autoimmune Disorder and Gerontology NursingDokument27 SeitenNursing Client With Mucoskeletal and Autoimmune Disorder and Gerontology NursingJanine Erika Julom BrillantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anterior Cord SyndromeDokument8 SeitenAnterior Cord SyndromeJanine Erika Julom BrillantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursingcribcom Nursing Care Plan Spinal Cord InjuryDokument2 SeitenNursingcribcom Nursing Care Plan Spinal Cord InjuryJanine Erika Julom Brillantes100% (1)
- CeftriaxoneDokument1 SeiteCeftriaxoneJanine Erika Julom BrillantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health TeachingDokument3 SeitenHealth TeachingJanine Erika Julom BrillantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyJanine Erika Julom BrillantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHORTCUT DISTILLATION: Fenske Underwood Gilliland (FUG) : Chemical Engineer's GuideDokument87 SeitenSHORTCUT DISTILLATION: Fenske Underwood Gilliland (FUG) : Chemical Engineer's GuideAmey BodkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemistry of Organophosphorus Compounds. Phosphonium Salts, Ylides and Phosphoranes. - Hartley, F. (1994)Dokument455 SeitenThe Chemistry of Organophosphorus Compounds. Phosphonium Salts, Ylides and Phosphoranes. - Hartley, F. (1994)JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Edition Nelson Test BankDokument14 SeitenLehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Edition Nelson Test BankDonnaHalloend100% (35)
- Tutorial 3: CHM258 - SEP18-JAN19Dokument4 SeitenTutorial 3: CHM258 - SEP18-JAN19OberonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Organic Questions Q1Dokument5 SeitenUnit 1 Organic Questions Q1JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antoine CoefficientsDokument26 SeitenAntoine CoefficientsAndikaSeptianSitanggangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 5 Organic Components: Proteins and LipidsDokument2 SeitenExercise 5 Organic Components: Proteins and LipidsHanna Joy BringuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Kimberly CarterDokument175 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Kimberly CarterPinaki MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS Coll. Vol. 9 P632-Oxidation of Sec. Amines To Nitrones With H2O2 and Sodium TungstateDokument5 SeitenOS Coll. Vol. 9 P632-Oxidation of Sec. Amines To Nitrones With H2O2 and Sodium Tungstatesunil_vaman_joshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hazardous Chemical ListDokument9 SeitenHazardous Chemical ListWONG TSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry-Theory (Cyi 101) Organic ChemistryDokument15 SeitenChemistry-Theory (Cyi 101) Organic ChemistryPrasann KatiyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Withdrawing and Electron Donating GroupsDokument2 SeitenElectron Withdrawing and Electron Donating GroupsOmar Abd ElsalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 McmurryDokument23 SeitenChapter 5 McmurryCarolina XavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 18 TestDokument10 SeitenTopic 18 TestumerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biosintesis LipidDokument27 SeitenBiosintesis LipidNovia EkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyrrolo (1,2 A) Quinoxalines BasedDokument24 SeitenPyrrolo (1,2 A) Quinoxalines BasededwquimNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET 2019, Previous Year NEET Question Paper With The Answer Key For The Year 2019Dokument20 SeitenNEET 2019, Previous Year NEET Question Paper With The Answer Key For The Year 2019Zephyr EntranceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midak 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1840 012013Dokument9 SeitenMidak 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1840 012013TartuEd TechNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhenolDokument7 SeitenPhenolissraaflower0% (1)
- Specific Gravity ChartDokument2 SeitenSpecific Gravity ChartApril Trish Albaña0% (1)
- Carbohydrates WorksheetDokument2 SeitenCarbohydrates WorksheetLorlie AbrogarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioransformation2 180518095843 PDFDokument79 SeitenBioransformation2 180518095843 PDFSujyoti ShakyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14.5 Alkenes: Question PaperDokument12 Seiten14.5 Alkenes: Question PaperAbdullah AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume April 2016-2Dokument3 SeitenResume April 2016-2api-316780587Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDokument15 SeitenOxidation of Fatty AcidsMomena SafdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem 137 Carbohydrate WorksheetDokument3 SeitenBiochem 137 Carbohydrate WorksheetJoseph DagoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- McMurry 7e Ch19-23 Notes 5-29-07Dokument55 SeitenMcMurry 7e Ch19-23 Notes 5-29-07Kay BradyNoch keine Bewertungen
- C. Oliver Kappe - Microwaves in Organic Chemistry: From Laboratory Curiosity To Standard Practice in 25 YearsDokument2 SeitenC. Oliver Kappe - Microwaves in Organic Chemistry: From Laboratory Curiosity To Standard Practice in 25 YearsNstm3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organic ChemistryDokument8 SeitenOrganic ChemistryVinay ChilukuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6) Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes IIDokument44 Seiten6) Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes IIfarah_affandyNoch keine Bewertungen