Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lab Practical I Review
Hochgeladen von
WutWut0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
115 Ansichten7 SeitenThis document provides a summary of the key concepts and experiments covered in the Lab Practical I Review for Biology 1406. The review covers the following topics: properties of water including structure, behavior, and role as a solvent; biological molecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids; use of the compound microscope; cell structure and the cell theory; movement of molecules including diffusion, osmosis, and tonicity; and enzymes as biological catalysts. The document lists the main points for each experiment or concept that will be important to know for the practical.
Originalbeschreibung:
Lab Practical review for first semester labs
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document provides a summary of the key concepts and experiments covered in the Lab Practical I Review for Biology 1406. The review covers the following topics: properties of water including structure, behavior, and role as a solvent; biological molecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids; use of the compound microscope; cell structure and the cell theory; movement of molecules including diffusion, osmosis, and tonicity; and enzymes as biological catalysts. The document lists the main points for each experiment or concept that will be important to know for the practical.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
115 Ansichten7 SeitenLab Practical I Review
Hochgeladen von
WutWutThis document provides a summary of the key concepts and experiments covered in the Lab Practical I Review for Biology 1406. The review covers the following topics: properties of water including structure, behavior, and role as a solvent; biological molecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids; use of the compound microscope; cell structure and the cell theory; movement of molecules including diffusion, osmosis, and tonicity; and enzymes as biological catalysts. The document lists the main points for each experiment or concept that will be important to know for the practical.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 7
Lab Practical I Review
Biology 1406
Exercise 1 Properties of Water
1. Structure of Water
a. Angular structure, b. polar covalent bonds, c. intermolecular hydrogen bonding
---
2. Behavior of water: Hydrogen bonding
a. b. c. d. Cohesion/Adhesion, surface tension, capillary action, imbibition high specific heat and heat of vaporization,
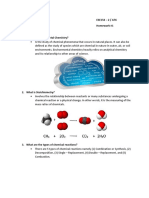
3. Nearly universal solvent:
a. Hydrophilic - Polar and ionic substances b. Hydrophobic nonpolar substances
4. Dissociation, electrolytes and acids/bases
a. the pH scale.
Exercise 3 Biological Molecules
1. Organic/Inorganic molecules
a. b. a. b. c. d. Functional groups Monomers, dimers, polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids. Benedicts Iodine Sudan III Biuret Tests
2. Four categories of Organics:
3. Biochemical Tests match reagents to organic molecules
a. b. c. d. a. b.
4. Experimental Controls, Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data
Know (and recognize) what positive results look like Know what each test indicates.
Exercise 4 The Microscope
1. Proper Handling and Use of the Compound Light Microscope a. name and function of each part b. sequence of procedures used to view specimen c. proper techniques in the use and handling of the scope d. Proper cleaning and storage of scopes
2. Lens Magnification a. magnification and names of each objective b. calculated total magnification with each 3. Properties of the Microscope, including: a. Inversion b. Resolution c. Working Distance d. Field of View.
Exercise 5 Cell Structure and Function
1. State the Cell Theory a. Historic Contributions of Hooke and Leeuwenhoek, b. Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow 2. Distinguish the two cell types: a. Prokaryotic - bacteria b. Eukaryotic cells with nucleus 3. Distinguish Plant and Animal cell structure a. Recognize each organelle and internal structure or contents. b. Know cellular (metabolic) function of organelle
Exercise 7 The Movement of Molecules
1. Selective permeability of biological membranes
a. b. a. b. What is exchange and why is it necessary? What properties of molecules allow transport? Random movement of particle Direction of movement in relation to concentration gradient
2. Role of Diffusion in transport
3. Factors affecting the rate of diffusion 4. Osmosis vs. Dialysis 5. Tonicity (what causes water to move inward or out of cells).
a. b. c. Effect of tonicity on animal cells vs. plant cells. Terms: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic, Crenation, Plasmolysis, Turgor pressure.
6. Silver Nitrate test for presence of NaCl.
Exercise 8 Enzymes: Biological Catalysts
1. Define Catalyst, enzyme, substrate, active site, enzyme-substrate complex. 2. Know factors that effect enzyme activity. 3. Denaturation: cause and effect. 4. Know the reactions used in lab:
a. b. c. d. Substrates (hydrogen peroxide, starch), catalysts used ( MnO2, catalase, salivary amylase), products of the reactions sources of the enzymes (biological catalysts).
5. Know the significance of 37oC.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Bio Principles Unit 1Dokument34 SeitenBio Principles Unit 1a_shapiro099Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology: M.B:shamsDokument9 SeitenBiology: M.B:shamsmohamed sabryNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCH 2333 - DGD 1Dokument19 SeitenBCH 2333 - DGD 1Simon HagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Introduction To BiochemistryDokument14 SeitenModule 1 - Introduction To BiochemistryMurfaiza OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Lesson Plans Biomed Academy-Mr. Rabold Unit 1-Biochemistry and Scientific Research ProtocolDokument8 SeitenDaily Lesson Plans Biomed Academy-Mr. Rabold Unit 1-Biochemistry and Scientific Research Protocolward dajacNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Coordinated Science Syllabus ChecklistDokument21 SeitenIGCSE Coordinated Science Syllabus ChecklistMelissa LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studyguide AnswerkeyDokument23 SeitenStudyguide Answerkeyapi-237676607Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem IntroductionDokument317 SeitenBiochem IntroductionTrisha DicangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Introduction A PDFDokument107 SeitenBiochem Introduction A PDFDaevy Toribio AmdosNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiochemistryDokument9 SeitenBiochemistryClarissa IsuriñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH Biologi TG4Dokument28 SeitenRPH Biologi TG4lilyraj100% (1)
- RPT Biology Form4Dokument50 SeitenRPT Biology Form4Nadiah BorhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide For Human Physiology Exam 1Dokument24 SeitenStudy Guide For Human Physiology Exam 1Rick GillNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO024 Session-1 IGDokument6 SeitenBIO024 Session-1 IGKenny McCormickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bisc 102 NotesDokument49 SeitenBisc 102 NotesEvonda HollisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Keystone Exam ReviewDokument58 SeitenBiology Keystone Exam ReviewLian LzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0653 Combined ScienceDokument131 Seiten0653 Combined ScienceGodfrey RugareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agri Science 302 Advanced Biochemistry: (9 Hours Lecture Per Week For 6 Weeks)Dokument8 SeitenAgri Science 302 Advanced Biochemistry: (9 Hours Lecture Per Week For 6 Weeks)j8m8l8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme of Work Biology Form 4 2013Dokument33 SeitenScheme of Work Biology Form 4 2013Sitinorsyahidah JantanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: Grade 2, Semester 1Dokument8 SeitenChemistry: Grade 2, Semester 1Ahmed AlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMJK Phor Tay Biology Form 4 (Yearly Plan 2015)Dokument8 SeitenSMJK Phor Tay Biology Form 4 (Yearly Plan 2015)pooyenpengNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Biology Eoc Study GuideDokument99 Seiten2015 Biology Eoc Study GuidedkissamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Outline: The Human Organism: I. DefinitionsDokument13 SeitenChapter 1 Outline: The Human Organism: I. DefinitionsSteffi MurielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dwnload Full Essentials of Biology 4th Edition Mader Solutions Manual PDFDokument35 SeitenDwnload Full Essentials of Biology 4th Edition Mader Solutions Manual PDFpursuitreexpel6735100% (11)
- Dwnload Full Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFDokument35 SeitenDwnload Full Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFdanagarzad90y100% (11)
- Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDokument35 SeitenLiving in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manualjerrybriggs7d5t0v100% (20)
- Bio 101 Study Guide Test 1Dokument8 SeitenBio 101 Study Guide Test 1mattyg35Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cricket Respiration: Teacher's Notes PurposeDokument3 SeitenCricket Respiration: Teacher's Notes PurposeSing JiinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Bio Prelims 2Dokument5 SeitenCell Bio Prelims 2raphaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 14th Edition Widmaier Solutions ManualDokument26 SeitenVanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 14th Edition Widmaier Solutions Manualconsignedurylic75hi100% (24)
- Wang 14te408 Fieldlesson2Dokument8 SeitenWang 14te408 Fieldlesson2api-251571132Noch keine Bewertungen
- GIANAN, Tyrone Joshua D. ESE150 - 2 / A76 2019151002 Homework #1Dokument5 SeitenGIANAN, Tyrone Joshua D. ESE150 - 2 / A76 2019151002 Homework #1Tyrone GiananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology The Essentials 2nd Edition by Marielle Hoefnagels ISBN Solution ManualDokument10 SeitenBiology The Essentials 2nd Edition by Marielle Hoefnagels ISBN Solution Manualmichael100% (25)
- Chem 113 Introduction To Biochemistry Pt. 1Dokument11 SeitenChem 113 Introduction To Biochemistry Pt. 1janson021cuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDokument25 SeitenLiving in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions ManualJonathanSwansonbwyi100% (63)
- Lecture 1Dokument50 SeitenLecture 1AMRAPALI SANTOSH PAWARNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 5 MembranesDokument7 SeitenCHAPTER 5 MembranesNadeem IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2013Dokument27 SeitenScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2013Haslinda SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Ecosystems in Extreme EnvironmentsVon EverandModel Ecosystems in Extreme EnvironmentsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Biology All Master NotesDokument105 SeitenBiology All Master Notesapi-260042275Noch keine Bewertungen
- L1 IntroDokument51 SeitenL1 IntroSwayam100% (1)
- Chemistry Worksheet Summer AssignmentDokument10 SeitenChemistry Worksheet Summer AssignmentJohn Joseph CambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Bio f4 2013xDokument46 SeitenRPT Bio f4 2013xriyashreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT BIO F4 2013Dokument46 SeitenRPT BIO F4 2013riyashreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC2Introduction To BiochemistryDokument38 SeitenMC2Introduction To BiochemistryKimberly SalarzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology I M6Dokument19 SeitenGeneral Biology I M6Anjhiene CambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vasquez, Angelica, Bio30lL, Activity 3,2020Dokument6 SeitenVasquez, Angelica, Bio30lL, Activity 3,2020Angelica VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fat StyupidDokument17 SeitenFat StyupidVincent LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of Biology 4th Edition Mader Solutions ManualDokument25 SeitenEssentials of Biology 4th Edition Mader Solutions ManualDavidLeekemt100% (49)
- Botany II PDFDokument7 SeitenBotany II PDFMuhammad AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACT Biology-Dr. Rehab Final Revision 1Dokument10 SeitenACT Biology-Dr. Rehab Final Revision 1m.mansoor3377Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Von EverandChemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dwnload Full Campbell Essential Biology 5th Edition Simon Solutions Manual PDFDokument32 SeitenDwnload Full Campbell Essential Biology 5th Edition Simon Solutions Manual PDFplenalabasia3h8brg100% (13)
- Kami Export - Semester I Final Exam Study Guide - Bio23Dokument4 SeitenKami Export - Semester I Final Exam Study Guide - Bio23Ryan FungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - Topic 2 - Mollecular Biology - (11 HL and SL)Dokument40 SeitenUnit 2 - Topic 2 - Mollecular Biology - (11 HL and SL)John DoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Human Physiology: An IntroductionVon EverandQuantitative Human Physiology: An IntroductionBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Syllabus Cambridge o Level BiologyDokument12 SeitenSyllabus Cambridge o Level BiologyNisha AliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For JavaScript The Web Warrior Series 6th Edition Vodnik Gosselin 1305078446 9781305078444Dokument35 SeitenSolution Manual For JavaScript The Web Warrior Series 6th Edition Vodnik Gosselin 1305078446 9781305078444thomasmartin26051993fpw100% (26)
- Biochemistry Ch. 1 IntroDokument3 SeitenBiochemistry Ch. 1 IntroBryantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Code: Bio 1 Course Name: General BiologyDokument50 SeitenCourse Code: Bio 1 Course Name: General BiologySamleigh TazraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4 ReportDokument2 SeitenLab 4 ReportWutWutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5 ReportDokument3 SeitenLab 5 ReportWutWutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6 ReportDokument2 SeitenLab 6 ReportWutWutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - The Cell - WorksheetDokument3 SeitenChapter 6 - The Cell - WorksheetWutWutNoch keine Bewertungen
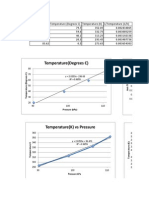
- Gas Laws DataDokument7 SeitenGas Laws DataWutWutNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Tip For Beating ProcrastinationDokument1 SeiteA Tip For Beating ProcrastinationWutWutNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Lab 2 Enzyme CatalysisDokument20 SeitenAP Lab 2 Enzyme CatalysisJason Woods0% (1)
- AP Biology Lab 9Dokument35 SeitenAP Biology Lab 9WutWut0% (1)
- Carbohydrates NotesDokument5 SeitenCarbohydrates NotesWutWut100% (1)
- Ap: Lab-Related Ap Exam Essays Lab 1. Osmosis and DiffusionDokument16 SeitenAp: Lab-Related Ap Exam Essays Lab 1. Osmosis and DiffusionWutWutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quest 8 KeyDokument7 SeitenQuest 8 KeyWutWut0% (1)
- Problem Set 4 ProteinsDokument1 SeiteProblem Set 4 ProteinsGloria HoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Asset Classes: Shalin Vyas March 2013Dokument38 SeitenIntroduction To Asset Classes: Shalin Vyas March 2013Jorden Rongkup SimickmuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energetics Q + MSDokument32 SeitenEnergetics Q + MSmamta2111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cellulose Cross and BevanDokument2 SeitenCellulose Cross and BevanHorácio Henrique CampeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5070 Chemistry ECR v1.1 080316Dokument153 Seiten5070 Chemistry ECR v1.1 080316warisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz: Lab. Modeling Finance Saturday, 22 June 2019: QuestionsDokument2 SeitenQuiz: Lab. Modeling Finance Saturday, 22 June 2019: QuestionsWilliam SuryadharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Initial A Level Assessment PDFDokument18 SeitenInitial A Level Assessment PDFsimonbamfordNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFA Level 1 FundamentalsDokument5 SeitenCFA Level 1 Fundamentalskazimeister1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Multiple ChoiceDokument13 SeitenUnit 1 Multiple ChoiceJinJinKiraieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Direct DyesDokument53 SeitenDirect DyesKashif Chaudhry100% (1)
- Audit of ContractsDokument26 SeitenAudit of ContractsSarvesh Khatnani100% (2)
- Ammonia and Its UsesDokument1 SeiteAmmonia and Its UsesFatema KhatunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet-Bond ValuationDokument4 SeitenWorksheet-Bond ValuationShelly SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yamamoto Et Al. - 2009 - Γ-Selective Cross-Coupling Reactions of PotassiumDokument9 SeitenYamamoto Et Al. - 2009 - Γ-Selective Cross-Coupling Reactions of PotassiumVictor CiocalteaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Nitroalkenes To Primary Amine PDFDokument45 SeitenCatalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Nitroalkenes To Primary Amine PDFjohannes karcherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complexometric Titration With EDTADokument8 SeitenComplexometric Titration With EDTAManP13100% (1)
- CSWDokument49 SeitenCSWnickbyfleetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Training Project Report SbimfDokument41 SeitenSummer Training Project Report SbimfPrateek PanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIDIC Guarantees Bonds and RetentionsDokument7 SeitenFIDIC Guarantees Bonds and RetentionspieremicheleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federico Paredes For Petitioners. Demetrio V. Pre For Private RespondentsDokument27 SeitenFederico Paredes For Petitioners. Demetrio V. Pre For Private RespondentsLove BarondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of National Saving OrganizationDokument41 SeitenFunctions of National Saving OrganizationAamir Khan83% (40)
- ChecklistDokument18 SeitenChecklistAdzcer HadullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peptide PPT 1Dokument26 SeitenPeptide PPT 1sheetal_5012Noch keine Bewertungen
- TBR OChem2 OptDokument305 SeitenTBR OChem2 OptRamski91% (11)
- Organic Chemistry Experiment 6Dokument7 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Experiment 6Rogeni Misaelle Petinglay100% (8)
- TSXe ReviewDokument290 SeitenTSXe ReviewexsarafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isomers HandoutDokument5 SeitenIsomers HandoutMohamed MeeranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 597 PDFsam 290120 CUDokument197 Seiten597 PDFsam 290120 CUSomenath PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignments QuestionDokument8 SeitenAssignments Questionmuhammad qasim0% (1)
- Aromaticity PDFDokument9 SeitenAromaticity PDFabyssabhi100% (2)