Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hazid Against Hazop
Hochgeladen von
Dan CostinOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hazid Against Hazop
Hochgeladen von
Dan CostinCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
J RAMESH BABU :
Predominantly HAZOP deals with process related hazards, HAZID deals with non or other than process related hazards like facility hazards etc. HAZOP focuses on the equipment or pipeline or piece of equipment as node, whereas HAZID takes the facility as a node. HAZOP deals with the internal hazards of the equipment and HAZID deals with the external hazards. While HAZID provides inputs for the COMAH or QRA, HAZOP provides input for the design, operation and maintenance etc. Both techniques use the guidewords to initiate the thoughts making the group hazard identification systematic. Both are complimentary to each other. To supplement what has been discussed earlier HAZID is used in all stages. Though HAZID is very handy as PHA tool during early stages for plant life cycle in making crucial decisions like site selection, layout, and identification of Major Accident Scenarios etc it is done at various stages of plant life cycle including operational and decommissioning phase. Many corporate standards including ADNOC, UAE insist on this requirement. Utility of HAZID varies depending on the stage we use it. For example during Construction stage, construction stage related issues are discussed and in operational stage issues like Management of Change are also dealt with. Boundaries of HAZID can be defined depending on the corporate philosophy and other supplementary tools used by the corporate to avoid overlapping of boundaries/ duplication of issues. David Graham : HAZID is done at a very early stage in the project, at the scope and flowsheet stage. HAZOP is done after the PIDs have been issued for approval, for example when the Client and Contractor have agreed that the process has been sufficiently developed. The HAZID and HAZOP systems I work with are not free of charge. They belong to the particular Client or Contractor I'm working for. I have my own systems for HAZID and HAZOP for other companies who don't have systems e.g Middle East companies who prefer to issue guidelines rather than procedures. These are not free either. Use Google to get free information or attend an IChemE or AIChemE course on hazard study. Kadayam. R. Ramasubramanian HAZID ( Hazard Identification): (Shell) HAZID (Hazard Identification) is a technique for early identification of potential hazards and threats. The technique has two styles, Conceptual and Detailed and should be applied at the very outset of a new venture or during the early stages of a development. It is therefore likely to be the first formal HSE-related study for any new project. The major benefit of HAZID is that early identification and assessment of the critical HSE hazards provides essential input to project development decisions. This will lead to safer and more costeffective design options being adopted with a minimum cost of change penalty. HAZOP ( Hazard & Operability Study): (ICI) # Hazard and Operability study is a formal, systematic, critical examination of the process and engineering intentions of the facilities to assess the hazard potential due to mal-operation or mal-function of individual items of equipment and the consequential effects on operation of the facility as a whole. # The method identifies the possible hazards and postulates possible accident scenarios. The safety features provided in the design are then reviewed to determine whether the safeguards are adequate or not. Actions are recommended if deficiency is found in the safeguards provided. The process demonstrates to the owner / management that prudent steps have been taken to make the installation as safe as practicable. # Hazop is done after the design reviews are completed and the P&IDs are issued. After the Hazop, when all the recommendations are implemented, the P&IDs are approved for construction.
John Boyd (facilitator for too many years in the Oil & Gas and Mining industries) Hazid (with or without formalized RA / Matrix etc.) can be used at any time in the life cycle of a plant from early project life to decommissioning. It is a very flexible tool and can be used to identify activity /HSE / project risks via brainstorming in a workshop environment. Production of a report post workshop draws a line in the sand at how the project or work schedule risks are being addressed at that period in time. If there are any incidents during the project ... any regulator or incident investigator can review the reports to ensure due diligence by the design / project team. From a Hazid, a risk register can be developed which can be re-visited as the work progresses. Hazop on the other hand is a structured, formal method of assessing robustivity of a process design or critical procedure and should follow the international standard IEC 61882. For a process design it should assess P&IDs at the 'frozen design' position (as per IEC 61882) and should not be used as a 'design forming' tool - Hazid and other tools are good for that . Hazop is, by its generic nature a design testing tool where designers and operators in a workshop environment, led by a suitably qualified facilitator, challenge the 'ready' design by theoretically stretching it outside of its normal parameters and proving that the system has adequate protection and is suitable to go to the next phase in the design process ( if its a large installation) or to be constructed . A good Hazop study should result in very few actions ... proving that the design is indeed ready for Hazop. I have been asked in the past to review Hazops by others which resulted in over 200 actions ?? The IChemE have intimated that Hazop is being abused and that some engineers / project managers use it to design systems they use PFDs instead of P&IDs etc, etc and have no real respect for how important (with legal connotations) Hazop is... in my extended journey through industry I have seen various Hazop titles such as Conceptual Hazop, Detailed Design Hazop, Course Hazop, 'Easter' Hazop ... no good .... there's just Hazop and if the design goes wrong and you have to bear witness in court ... just remember a 'Course' Hazop by definition is not at the 'frozen' design position, therefore not ready for Hazop .. so try to defend that fact and that you, as the Facilitator, allowed it to happen. Hazop under IEC 61882 is one of the few standards that have been accepted verbatim worldwide. In a world of major process incidents that shows how important the tool is for the Process Industry.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- BQ - Electrical Calibration Relay Bld803, NPBDokument2 SeitenBQ - Electrical Calibration Relay Bld803, NPBKazuya KasumiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of Violent Video Games Research Paper English Comp2Dokument11 SeitenThe Effects of Violent Video Games Research Paper English Comp2api-451442670Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crime Data Analysis 1Dokument2 SeitenCrime Data Analysis 1kenny laroseNoch keine Bewertungen
- انظمة انذار الحريقDokument78 Seitenانظمة انذار الحريقAhmed AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXP 2 - Plug Flow Tubular ReactorDokument18 SeitenEXP 2 - Plug Flow Tubular ReactorOng Jia YeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Riber 6-s1 SP s17-097 336-344Dokument9 SeitenRiber 6-s1 SP s17-097 336-344ᎷᏒ'ᏴᎬᎪᏚᎢ ᎷᏒ'ᏴᎬᎪᏚᎢNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reaction Engineering-II - R2015 - 10-04-2018Dokument2 SeitenChemical Reaction Engineering-II - R2015 - 10-04-201818135A0806 MAKKUVA BHAVYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Lichens - Naturally Scottish (Gilbert 2004) PDFDokument46 SeitenLichens - Naturally Scottish (Gilbert 2004) PDF18Delta100% (1)
- RRC Group D Notification 70812Dokument11 SeitenRRC Group D Notification 70812admin2772Noch keine Bewertungen
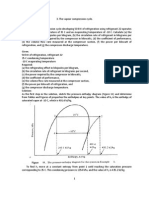
- The Vapour Compression Cycle (Sample Problems)Dokument3 SeitenThe Vapour Compression Cycle (Sample Problems)allovid33% (3)
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) : SRS PrecautionsDokument1 SeiteHVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) : SRS PrecautionssoftallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alugbati Plant Pigment Extraction As Natural Watercolor SourceDokument6 SeitenAlugbati Plant Pigment Extraction As Natural Watercolor SourceMike Arvin Serrano100% (1)
- ReliabilityDokument5 SeitenReliabilityArmajaya Fajar SuhardimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blueprint Huynh My Ky Duyen 2022 McDonald'sDokument2 SeitenBlueprint Huynh My Ky Duyen 2022 McDonald'sHuỳnh Mỹ Kỳ DuyênNoch keine Bewertungen
- API 510 Practise Question Nov 07 Rev1Dokument200 SeitenAPI 510 Practise Question Nov 07 Rev1TRAN THONG SINH100% (3)
- Advances of Family Apocynaceae A Review - 2017Dokument30 SeitenAdvances of Family Apocynaceae A Review - 2017Владимир ДружининNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 45001:2018 & OHSAS 18001:2007 Clause-Wise Comparison MatrixDokument3 SeitenISO 45001:2018 & OHSAS 18001:2007 Clause-Wise Comparison MatrixvenkatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yogananda Scientific HealingDokument47 SeitenYogananda Scientific HealingSagar Pandya100% (4)
- Pantera 900Dokument3 SeitenPantera 900Tuan Pham AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Staff Food Consumption Reports Sep-2019Dokument4 SeitenDaily Staff Food Consumption Reports Sep-2019Manjit RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cadorna, Chesca L. - NCPDokument2 SeitenCadorna, Chesca L. - NCPCadorna Chesca LoboNoch keine Bewertungen
- NRF Nano EthicsDokument18 SeitenNRF Nano Ethicsfelipe de jesus juarez torresNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA-QC TPL of Ecube LabDokument1 SeiteQA-QC TPL of Ecube LabManash Protim GogoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feeder BrochureDokument12 SeitenFeeder BrochureThupten Gedun Kelvin OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food and Beverage Control Systems Can Help You Introduce The Same Financial Rigour To Your Dining Establishment or Catering Company That YouDokument11 SeitenFood and Beverage Control Systems Can Help You Introduce The Same Financial Rigour To Your Dining Establishment or Catering Company That Younarinder singh saini100% (4)
- FEM 3004 - Lab 10 Part 2editedDokument26 SeitenFEM 3004 - Lab 10 Part 2editedAINA NADHIRAH BINTI A ROZEY / UPMNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPSS1213 Mar98Dokument3 SeitenOPSS1213 Mar98Tony ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mainstreaming Gad Budget in The SDPDokument14 SeitenMainstreaming Gad Budget in The SDPprecillaugartehalagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refinería Kirkuk PDFDokument11 SeitenRefinería Kirkuk PDFcesarinarragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Composting SystemsDokument8 SeitenHome Composting Systemssumanenthiran123Noch keine Bewertungen