Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
NCP 2
Hochgeladen von
hsiria100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
5K Ansichten2 SeitenMost activity intolerance is related to generalized weakness and debilitation. Aging process itself causes reduction in muscle strength and function. Assessment guides treatment. This aids in defining what patient is capable of. Encourage adequate rest periods, especially before meals, other ADLs, and ambulation.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
ncp 2
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMost activity intolerance is related to generalized weakness and debilitation. Aging process itself causes reduction in muscle strength and function. Assessment guides treatment. This aids in defining what patient is capable of. Encourage adequate rest periods, especially before meals, other ADLs, and ambulation.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
5K Ansichten2 SeitenNCP 2
Hochgeladen von
hsiriaMost activity intolerance is related to generalized weakness and debilitation. Aging process itself causes reduction in muscle strength and function. Assessment guides treatment. This aids in defining what patient is capable of. Encourage adequate rest periods, especially before meals, other ADLs, and ambulation.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
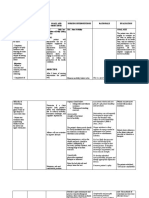
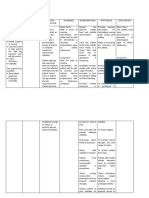
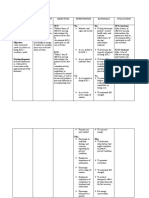
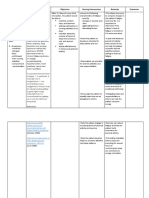
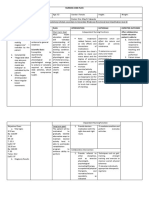
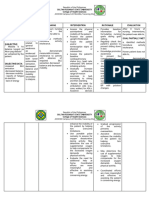
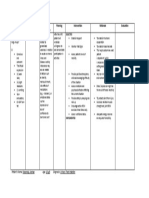
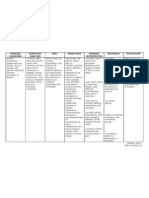
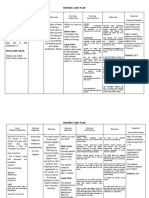
NURSING CARE PLAN
Assessment Nursing Scientific Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis Explanation
S: “lagi na lang Activity Most activity Patient will establish rapport to facilitate NPI. Patient
akong nakahiga” Intolerance; intolerance is improve mobility place the client in to prevent demonstrated
as verbalized by Level I r/t related to aeb participation a comfortable backaches or muscle improved
position aches.
the patient. difficulty walking generalized in the activities take and record to note any
mobility aeb
secondary to weakness and of daily living. vital signs significant changes participation in
O: body weakness debilitation ADL in which he
that may be brought
Conscious and secondary to about by the disease is capable of.
coherent acute or chronic Determine These may be
c body patient's perception temporary or
illness and
of causes of fatigue permanent, physical
weakness disease. This is or activity or psychological.
restless especially intolerance. Assessment guides
c poor apparent in treatment.
appetite; elderly patients This aids in
consumed ¼ of with a history of Assess patient's defining what patient
level of mobility. is capable of, which
the food served orthopedic, is necessary before
c limited ROM cardiopulmonary setting realistic
ambulatory c , diabetic, or goals.
assistance pulmonary- Assess nutritional Adequate energy
related status. reserves are required
for activity.
problems. The
Monitor patient's Difficulties
aging process sleep pattern and sleeping need to be
itself causes amount of sleep addressed before
reduction in achieved over past activity progression
muscle strength few days. can be achieved.
and function, Assess emotional Depression over
response to change inability to perform
which can impair in physical status. required activities
the ability to can further
maintain activity. aggravate the
Activity activity intolerance.
Encourage
intolerance may
adequate rest Rest between
also be related periods, especially activities provides
to factors such before meals, other time for energy
as obesity, ADLs, and conservation and
malnourishment, ambulation. recovery.
side effects of Refrain from Patients with
performing limited activity
medications nonessential tolerance need to
(e.g., - procedures. prioritize tasks.
blockers), or Assist with ADLs Assisting the
emotional states as indicated; patient with ADLs
such as however, avoid allows for
doing for patient conservation of
depression or what he or she can energy. Caregivers
lack of do for self. need to balance
confidence to providing assistance
exert one's self. with facilitating
progressive
endurance that will
ultimately enhance
the patient's activity
tolerance and self-
Encourage active esteem.
ROM exercises three Exercises maintain
times daily. muscle strength and
Teach energy joint ROM.
conservation These reduce
techniques. oxygen consumption,
allowing more
prolonged activity.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NCP DMDokument6 SeitenNCP DMstara123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Objective S Interventions Rationale Evaluatio NDokument2 SeitenCues Objective S Interventions Rationale Evaluatio NJoehoney BarreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument6 SeitenNCPNik Rose ElNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objective Nursing Interventions & Rationale EvaluationDokument4 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objective Nursing Interventions & Rationale Evaluationtherese BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationSienaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDokument3 SeitenNCP Activity IntoleranceWyen CabatbatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument6 SeitenNursing Care PlanperezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSESSMENT SUBJECTIVE: "Parang Hinang Hina Siya" As Verbalized by TheDokument4 SeitenASSESSMENT SUBJECTIVE: "Parang Hinang Hina Siya" As Verbalized by Thestiffmyster1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluationmyer pasandalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Intervention Plan for Fracture PatientDokument2 SeitenNursing Intervention Plan for Fracture PatientAce Dioso TubascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN FOR GBS MOBILITYDokument5 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN FOR GBS MOBILITYAvery SandsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 8 NCP (Multiple Sclerosis)Dokument2 SeitenCase 8 NCP (Multiple Sclerosis)je-ann catedralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity IntoleranceDokument3 SeitenActivity IntoleranceRaidis PangilinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: O Short Term: Short TermDokument3 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: O Short Term: Short TermRaidis PangilinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study NCPDokument6 SeitenCase Study NCPEarl Joseph DezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plans for Sleep Disturbance and Activity IntoleranceDokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plans for Sleep Disturbance and Activity IntoleranceJhessa Curie PitaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subjective: Sto: DX: DX: STO: Goal MetDokument3 SeitenSubjective: Sto: DX: DX: STO: Goal MetFaith BugtongNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Requirement - Caadlawon, Ariane KateDokument5 SeitenNCP Requirement - Caadlawon, Ariane KateAngel KateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Darwin Jay Sang An BSN 1aDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan Darwin Jay Sang An BSN 1aHaroldJohnCabalgadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cva NCP 1Dokument3 SeitenCva NCP 1MarcieNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Post OpDokument2 SeitenNCP Post OpEyanah Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Pregnant Client (Fatigue)Dokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pregnant Client (Fatigue)Reno Jun Nagasan50% (2)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument4 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjomsportg0% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN (For Case Study)Dokument2 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN (For Case Study)Kathleen Martinez100% (1)
- Dialysis-NCPDokument2 SeitenDialysis-NCPJennifer AlamonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP FormDokument3 SeitenNCP FormJasmine diokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Volume Excess Related To Decrease Glomerular Filtration Rate and Sodium RetentionDokument6 SeitenFluid Volume Excess Related To Decrease Glomerular Filtration Rate and Sodium RetentionKristel Abe100% (1)
- Disturbed SleepDokument3 SeitenDisturbed SleepNicole MapiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spina Bifida NCPDokument3 SeitenSpina Bifida NCPShahzad GulfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SORIANO, Angelica Joan M. - NURSING CARE PLAN Activity 3. NCM 114Dokument9 SeitenSORIANO, Angelica Joan M. - NURSING CARE PLAN Activity 3. NCM 114Angelica Joan SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018AITDokument2 Seiten2018AITColleen De la RosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abad, Izhiel C.: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenAbad, Izhiel C.: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationIzhiel AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP-post-op 2Dokument2 SeitenNCP-post-op 2Eyanah Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Goals and Interventions for Impaired MobilityDokument2 SeitenNursing Goals and Interventions for Impaired MobilityReyes MikkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subjective Data: Baseline Data of Client.: Reference: Nurse's Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Interventions, and RationalesDokument4 SeitenSubjective Data: Baseline Data of Client.: Reference: Nurse's Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Interventions, and RationalesJor GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentAdhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Act. IntoleranceDokument1 SeiteNCP Act. IntoleranceJanine Karla OrcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Activity IntoleranceDokument2 SeitenRisk For Activity IntoleranceBlessie FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired MobilityDokument3 SeitenImpaired MobilityYeana AlonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weak in Cannot: Formatted TableDokument4 SeitenWeak in Cannot: Formatted TableRijelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Objective Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument9 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Objective Interventions Rationale EvaluationkrampoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity IntoleranceDokument1 SeiteActivity IntoleranceasymptomaticcrisisNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN FOR POSTPARTUM FATIGUE AND BREASTFEEDING CHALLENGESDokument3 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN FOR POSTPARTUM FATIGUE AND BREASTFEEDING CHALLENGESJanelle Gift SenarloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument18 SeitenNursing Care PlanElla Grace PradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icu NCPDokument8 SeitenIcu NCPClaire Nicole ApostolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Intolerance R/T Generalized WeaknessDokument3 SeitenActivity Intolerance R/T Generalized Weaknesschanmin limNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: DX: Short TermDokument3 SeitenAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: DX: Short TermSalwa ZeinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue FinalDokument1 SeiteFatigue FinalasymptomaticcrisisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan FibromyalgiaDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Fibromyalgiaderic90% (10)
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - Heart Failure NCP - NCM 112 LecDokument4 SeitenEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - Heart Failure NCP - NCM 112 LecGen Paulo EstoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Family Nursing Problem Objective Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDokument3 SeitenProblem Family Nursing Problem Objective Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataAngela Jolhnem LanghuNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Risk For Activity IntoleranceDokument4 SeitenNCP Risk For Activity IntoleranceBAGUIO CATSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relapse Prevention Counseling Workbook: A Step-by-Step Guide to Sustainable Recovery: Holistic approaches to recovery and relapse preventionVon EverandRelapse Prevention Counseling Workbook: A Step-by-Step Guide to Sustainable Recovery: Holistic approaches to recovery and relapse preventionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exposure Therapy for Eating Disorders: A Comprehensive Guide to Exposure Therapy and Resilience-Building for Eating DisordersVon EverandExposure Therapy for Eating Disorders: A Comprehensive Guide to Exposure Therapy and Resilience-Building for Eating DisordersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiant Balance: A Comprehensive 90 Day Program to Improve Balance & Prevent FallsVon EverandRadiant Balance: A Comprehensive 90 Day Program to Improve Balance & Prevent FallsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Test For Gauging Recovery & Workout “Readiness” - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Ready For ActionVon EverandA Simple Test For Gauging Recovery & Workout “Readiness” - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Ready For ActionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain Breakthrough: The Art of Neurological Rehabilitation: Easy and Innovative Techniques, #1Von EverandBrain Breakthrough: The Art of Neurological Rehabilitation: Easy and Innovative Techniques, #1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDokument2 SeitenPa Tho PhysiologyhsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation S: "Pabalik-Balik Pa IndependentDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation S: "Pabalik-Balik Pa IndependenthsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient's ProfileDokument1 SeitePatient's ProfilehsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study of PneumoniaDokument13 SeitenA Case Study of PneumoniahsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salmonella Typhi (S. Typhi) - Common Worldwide, It Is Transmitted by The Fecal-Oral RouteDokument4 SeitenSalmonella Typhi (S. Typhi) - Common Worldwide, It Is Transmitted by The Fecal-Oral Routehsiria100% (1)
- NCP 2Dokument2 SeitenNCP 2hsiria100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDrug StudyhsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory and Diagnostic ExaminationsDokument2 SeitenLaboratory and Diagnostic ExaminationshsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument3 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyhsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenNCP Drug StudyhsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 1Dokument1 SeiteNCP 1hsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP-Drug Study 2Dokument4 SeitenNCP-Drug Study 2hsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVD) : School of Nursing and MidwiferyDokument13 SeitenA Case Study of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVD) : School of Nursing and Midwiferyhsiria100% (2)
- Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenDrug StudyhsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteDrug StudyhsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study of AmoebiasisDokument9 SeitenA Case Study of AmoebiasishsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biblio, NRSG and Medical MGTDokument4 SeitenBiblio, NRSG and Medical MGThsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 3Dokument3 SeitenNCP 3hsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument6 SeitenNCPhsiria100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationhsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationhsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenDrug StudyhsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSDokument25 SeitenCShsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CsDokument10 SeitenCshsiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRELIMS - NCMA216 TRANS - Nursing Process in PharmacologyDokument2 SeitenPRELIMS - NCMA216 TRANS - Nursing Process in Pharmacologybnancajas7602valNoch keine Bewertungen
- D Informatics Theory 1 2 PDFDokument40 SeitenD Informatics Theory 1 2 PDFkaycelyn jimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health &mental Illness PPT (1) - 2Dokument75 SeitenMental Health &mental Illness PPT (1) - 2N.a.s.r EbaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioeth Essay PalakpakanDokument5 SeitenBioeth Essay PalakpakanAngeline VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Submissions On IQNDokument37 SeitenAnalysis of Submissions On IQNAnne Utleg-JuyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection Essay English 1aDokument4 SeitenReflection Essay English 1aapi-294418947Noch keine Bewertungen
- Home Visiting in Community HealthDokument5 SeitenHome Visiting in Community Healthconradlin06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Theoretical Foundations in Nursing First Semester SY 2021 - 2022 Dr. Elena M. ValdezDokument36 SeitenTheoretical Foundations in Nursing First Semester SY 2021 - 2022 Dr. Elena M. ValdezRednax 0912Noch keine Bewertungen
- Family Focused Nursing Care 1st Edition Denham Eggenberger Young Krumwiede Test BankDokument36 SeitenFamily Focused Nursing Care 1st Edition Denham Eggenberger Young Krumwiede Test Bankkilter.murk0nj3mx100% (34)
- Funda OutlineDokument3 SeitenFunda OutlineMeeKo VideñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation in Nursing Practice, A New Nursing Trend in NursingDokument11 SeitenSimulation in Nursing Practice, A New Nursing Trend in NursingJelaine EllanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Checklist for Federal Hospital WardsDokument17 SeitenQuality Checklist for Federal Hospital WardsMohammed HamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Dilemma Essay 436 Benchmark RRDokument6 SeitenEthical Dilemma Essay 436 Benchmark RRapi-509517114Noch keine Bewertungen
- NURSE Criminal and Civil Case Research..Dokument7 SeitenNURSE Criminal and Civil Case Research..rjalavazo198950% (2)
- Paper: Nurse Duty in WardsDokument7 SeitenPaper: Nurse Duty in WardshafidhohNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Alleine PregnantDokument2 SeitenNCP Alleine PregnantAlleine YvethNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Framework For Pre-Qualifying Nurses To Build Leadership SkillsDokument7 SeitenA Framework For Pre-Qualifying Nurses To Build Leadership SkillsGauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Satisfaction in Healthcare OrganizationsDokument14 SeitenEmployee Satisfaction in Healthcare OrganizationsAntonette RayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- School Heath For CommunityDokument27 SeitenSchool Heath For Communityد.شيماءسعيدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micahfinney Resume UpdateDokument3 SeitenMicahfinney Resume Updateapi-255767391Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oprm 508 Ca 1Dokument7 SeitenOprm 508 Ca 1Nikhil VaishnawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of New Normal on Nursing Students' Clinical SkillsDokument32 SeitenEffects of New Normal on Nursing Students' Clinical SkillscarouselNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dona K Jose: Registered Nurse Mobile: +971 508840383, 050 199 0059Dokument1 SeiteDona K Jose: Registered Nurse Mobile: +971 508840383, 050 199 0059Jafar AP100% (2)
- M1: CDU-CN BSN Program Outcomes of The BSN CurriculumDokument8 SeitenM1: CDU-CN BSN Program Outcomes of The BSN CurriculumMeteor 858Noch keine Bewertungen
- SocallDokument266 SeitenSocallshawnpauly2Noch keine Bewertungen
- NovelDokument42 SeitenNovelJaison JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan CVADokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plan CVAessevyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word Form 3Dokument14 SeitenWord Form 3Nguyen Thuỳ AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Funda SummerDokument216 SeitenFunda SummerNom NomNoch keine Bewertungen