Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CPA FAR Pensions Taxes
Hochgeladen von
jklein2588Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CPA FAR Pensions Taxes
Hochgeladen von
jklein2588Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Financial 6 (Pensions, Contingencies and Income Tax)
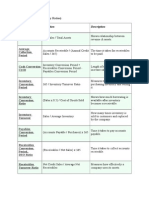
PENSION PLANS Types of plans: Defined Contribution Plan (401k) o The periodic amount of contributions to the plan and the way the contributions should be allocated to employees Defined Benefit Plan o Defines the benefits to be paid to employees at retirement (computed by future benefit payments) Definitions Accum. Benefit Obligation (ABO) use current salary o Present value of benefits attributed on current and past compensation Project Benefit Obligation (PBO) use (guess) future salary o Present value of all benefits attributed for services rendered prior to that date Assume future compensation levels I/S Accounting
Unamort.
AOCI
Current Service Cost PV of all benefits earned in the current period Interest Cost (discount rate) -
(Return on Plan Assets) offset pension exp by: Actual return on plan assets
or
expected return on assets
Amort. Of Unrecognized Prior Service Cost AOCI (Gains) & Losses AOCI Diff between the expected and actual return (use when expected returns used) o Earn more on plan than expected = gain (actual return > expected return) o Employees are expected to live longer after retire = bad (more retirement payments) Corridor Approach
Amort. of Existing Net Obligation or Net Asset at Implementation AOCI Funded status of the pension plan (FV plan asset PBO)
B/S Accounting Fund the pension Pension plan contribution: o Fund Status: FV of plan asset PBO = Fund Status o 1) Increases pension plan asset (overfunded) - ALWAYS noncurrent (FV of plan asset > PBO) o 2) Decreases pension plan liability (underfunded) current, noncurrent or both (FV of plan asset < PBO) Report current to the extent that can be payable within 12 mos. up to FV of plan Prior Service Cost & Pension Losses (deferred tax setup) Amortization Occurs
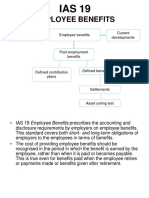
Defined Benefit Pension Plan Financial Statements Pension plan and sponsoring company are 2 separate legal entities o F/S for Pension Plan itself Statement of Net Assets Available for Benefits (B/S) Statement of Changes in Net Assets Available for Benefits (I/S) Statement of Accum Plan Benefits Statement of Changes in Accum Plan Benefits Disclosures 1) MORE is BETTER! 2) Disclose EVERYTHING! POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS OTHER THAN PENSIONS Note: accting for postretirement benefits mirrors pension accting under both IFRS & GAAP Accrual requirements cost of retiree health and other postretirement benefits must be ac accrued if: Obligation is attributable to employee services already rendered LIABILITY Employee rights accumulate or vest Payment is probable CO CONTIN CONTINGENCY RULES Amount of benefits can be reasonably estimated Definitions Accum. Postretirement Benefit Obligation (APBO) use discount rate o PV of future benefits that have vested as of the measurement date Expected Postretirement Benefit Obligation (EPBO) o PV of all future benefits expected to be paid as of the measurement date Amort. Or Expense of the Transition Obligation 2 big differences to Pension Plans
o o
1) Option to expense 2) 20 year (min)
OTHER DEFERRED COMPENSATION AND BENEFITS Types of Postemployment Benefits Salary & fringe benefits continuation, severance benefits Liability recognition accrue is ALL of the following are met Obligation is attributable to employee services already rendered LIABILITY Employee rights accumulate or vest Payment is probable CO CONTIN CONTINGENCY RULES Amount of benefits can be reasonably estimated Dr: Severance Expense Cr: Severance Liability Note: Footnote disclosure is required if all four criteria are not met CONTINGENCIES Loss Contingencies Loss is probably and can be reasonably estimated Record J/E (Likely to occur) o Record when probable and amount can be reasonably estimated o Use min. value if given range (i.e. 100,000 to 150,000 use 100,000 to record lose) IFRS use midpoint in range Loss is reasonably possible Disclose (More than remote, but less than likely) o If one of the two requirements above cannot be met, DISCLOSE Loss is remote Ignore (Slight change of occurring) unless guarantee type remote loss Debts of others guaranteed (officers/related parties) Obligations of commercial banks under standby letters of credit Guarantees to repurchase receivables that have been sold or reassigned Under IFRS, probable (>50%) =more likely than not to occur and possible = probably will not occur Gain Contingencies wait Avoid misleading implications as to the likelihood of realization Rule of conservatism
SUBSEQUENT EVENTS An event or transaction that occurs after B/S date but before the F/S are issued or available to be issued Recognize Subsequent Events record & disclose
o Conditions that existed at the B/S date Non-recognize Subsequent Events disclose o Conditions that occurred after the B/S date and did not exist at the B/S date
ACCOUNTING FOR INCOME TAXES Comprehensive Interperiod Tax Allocation Current Year taxes: Payable (liab.) or Refundable (asset) Future Year taxes: Deferred tax liab. or Deferred tax asset / benefit Differences 1. Permanent Differences affect current / not deferred Interest income, municipal obligations, dividends received deductions 2. Temporary Differences affect current & deferred Depreciation Deferred tax liabilities and assets recognition DTL Future tax accounting income > Future financial accounting income o Tax deductible first / F/S expense later o F/S income first / taxable income later
DTA o
Future tax accounting income < Future financial accounting income Amount of taxes paid in the current period exceeds the amount of income tax expense in the current period
Under IFRS, all DTA & DTL are netted and the net amount is reported as NON-CURRENT on the B/S
Operating losses Operating loss carry back (back 2 forward 20)
Operating loss carry forward o Tax effects are recognized to the extent that the tax benefit is more likely than not to be realized
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 655 Week 12 Notes PDFDokument63 Seiten655 Week 12 Notes PDFsanaha786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 & 10 Financial (FAR) NotesDokument7 SeitenChapter 9 & 10 Financial (FAR) NotesFutureMsCPANoch keine Bewertungen
- REG NotesDokument41 SeitenREG NotesNick Huynh75% (4)
- 2020 - Far SampleDokument21 Seiten2020 - Far SamplesuryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPA Exam REG - S-Corporation Taxation.Dokument2 SeitenCPA Exam REG - S-Corporation Taxation.Manny MarroquinNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEC NotesDokument17 SeitenBEC NotescsugroupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 16 PDFDokument5 SeitenForm 16 PDFJoshua Hicks100% (1)
- Activity Ratios and Key Financial Metrics ExplainedDokument7 SeitenActivity Ratios and Key Financial Metrics ExplainedSUBIR100% (1)
- BEC Study Guide 4-19-2013Dokument220 SeitenBEC Study Guide 4-19-2013Valerie Readhimer100% (1)
- RA 10963 TRAIN Law SummaryDokument74 SeitenRA 10963 TRAIN Law Summaryrandyblanza2014100% (5)
- Microeconomics and Financial FormulasDokument20 SeitenMicroeconomics and Financial FormulassasyedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prep M51C R1601 W01.note.gDokument56 SeitenPrep M51C R1601 W01.note.galghazalianNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEC 1 Outline Corporate Governance and Operations ManagementDokument4 SeitenBEC 1 Outline Corporate Governance and Operations ManagementGabriel100% (1)
- Tata Steel Company LimitedDokument24 SeitenTata Steel Company LimitedDivyarameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPA BEC 1 - Corporate GovernanceDokument3 SeitenCPA BEC 1 - Corporate GovernanceGabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEC 3 Outline - 2015 Becker CPA ReviewDokument4 SeitenBEC 3 Outline - 2015 Becker CPA ReviewGabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 FAR CPA NotesDokument4 SeitenChapter 2 FAR CPA Notesjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revenue Law and TaxationDokument33 SeitenRevenue Law and TaxationLUKWAGO GERALD100% (3)
- 05-Introduction To Payroll PDFDokument32 Seiten05-Introduction To Payroll PDFHetinawati HarahapNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPA FAR F-1 NotesDokument25 SeitenCPA FAR F-1 NotesRob Ricco100% (4)
- Formula Sheet Mini Test FARDokument26 SeitenFormula Sheet Mini Test FARcpacfa92% (13)
- Notes Chapter 9 FARDokument8 SeitenNotes Chapter 9 FARcpacfa100% (9)
- Chapter 7 CPA FAR NotesDokument5 SeitenChapter 7 CPA FAR Notesjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Appraisal Letter Salary IncrementDokument2 SeitenAppraisal Letter Salary Incrementmitendra pratap singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Northern CPAR: Taxation - Fringe Benefit Taxation: Rex B. Banggawan, Cpa, MbaDokument7 SeitenNorthern CPAR: Taxation - Fringe Benefit Taxation: Rex B. Banggawan, Cpa, MbaLouiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- RSM430 Final Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteRSM430 Final Cheat SheethappyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heads of Income Tax Under Income Tax Act, 1961Dokument15 SeitenHeads of Income Tax Under Income Tax Act, 1961Rahul Lahre100% (1)
- Motivational Strategies SumegaDokument74 SeitenMotivational Strategies Sumegakumar4243Noch keine Bewertungen
- 126687Dokument2 Seiten126687DiptiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conceptual Framework for Financial ReportingDokument11 SeitenConceptual Framework for Financial ReportingAnne NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Compensation and Benefits Package of ACI LimitedDokument48 SeitenEmployee Compensation and Benefits Package of ACI LimitedSaifur Rahman Steve50% (2)
- Notes Chapter 2 FARDokument5 SeitenNotes Chapter 2 FARcpacfa100% (16)
- Milk Plant Vita-1Dokument46 SeitenMilk Plant Vita-1o p chhabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet Mini Test REGDokument11 SeitenFormula Sheet Mini Test REGcpacfa100% (9)
- FAR Notes CH1: Revenue Recognition 1.0 (Becker 2017)Dokument12 SeitenFAR Notes CH1: Revenue Recognition 1.0 (Becker 2017)charlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAR Notes CH1: Standards & Framework 1.0 (Becker 2017)Dokument4 SeitenFAR Notes CH1: Standards & Framework 1.0 (Becker 2017)charlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPA Chapter 4 FAR Notes Inventories & CA/CLDokument5 SeitenCPA Chapter 4 FAR Notes Inventories & CA/CLjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- FAR Notes CH1: Comprehensive Income Statement 1.0 (Becker 2017)Dokument2 SeitenFAR Notes CH1: Comprehensive Income Statement 1.0 (Becker 2017)charlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAR Notes CH1: Income Statement & Balance Sheet & Discontinued Operations 1.0 (Becker 2017)Dokument7 SeitenFAR Notes CH1: Income Statement & Balance Sheet & Discontinued Operations 1.0 (Becker 2017)charles100% (1)
- Beta, Correlation and CovarianceDokument1 SeiteBeta, Correlation and CovariancecpacfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAR Notes Chapter 3Dokument3 SeitenFAR Notes Chapter 3jklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business Combinations - ASPEDokument3 SeitenBusiness Combinations - ASPEShariful HoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Study Guide PDFDokument8 SeitenAccounting Study Guide PDFgetasewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Chapter 7 FARDokument6 SeitenNotes Chapter 7 FARcpacfa100% (4)
- Financial 5 (Leases, Liabilities and Bond) : Present Value and Annuities Ordinary Annuity vs. Annuity DueDokument4 SeitenFinancial 5 (Leases, Liabilities and Bond) : Present Value and Annuities Ordinary Annuity vs. Annuity Duejklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Accounting Principles: 10 Basic ConceptsDokument9 SeitenIntroduction to Accounting Principles: 10 Basic ConceptsCaren Que ViniegraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 FARDokument4 SeitenChapter 3 FARZee DrakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEC Demo CompanionDokument23 SeitenBEC Demo Companionalik711698100% (1)
- ACG2001 Accounting Test 3 ReviewDokument48 SeitenACG2001 Accounting Test 3 ReviewElizabeth Koch100% (1)
- Statement of Cash Flows: HOSP 2110 (Management Acct) Learning CentreDokument6 SeitenStatement of Cash Flows: HOSP 2110 (Management Acct) Learning CentrePrima Rosita AriniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPA Regulation Notes - ChapDokument23 SeitenCPA Regulation Notes - ChapSteve DolphNoch keine Bewertungen
- REG Exam Format - CPADokument1 SeiteREG Exam Format - CPAgavkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Chapter 5 FARDokument6 SeitenNotes Chapter 5 FARcpacfa100% (10)
- Written Communications Memo on IFRS BenefitsDokument9 SeitenWritten Communications Memo on IFRS Benefitscpa2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Accountancy Notes PDFDokument11 SeitenAccountancy Notes PDFSantosh ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reg Notes CPADokument1 SeiteReg Notes CPAAdam JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Exploration EssayDokument4 SeitenAccounting Exploration Essayapi-253310608Noch keine Bewertungen
- BEC Formula Sheet Mini TestDokument7 SeitenBEC Formula Sheet Mini Testcpacfa73% (11)
- FAR Review NotesDokument2 SeitenFAR Review NotesFutureMsCPANoch keine Bewertungen
- BEC CPA Notes Chapter 48 Partnership SummaryDokument48 SeitenBEC CPA Notes Chapter 48 Partnership SummaryJame NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Chapter 6 FARDokument5 SeitenNotes Chapter 6 FARcpacfa100% (6)
- Advanced Financial Accounting and ReportingDokument15 SeitenAdvanced Financial Accounting and ReportingAcain RolienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Cost Accounting StandardsDokument2 SeitenSummary of Cost Accounting Standardsmanishchoudhary0412Noch keine Bewertungen
- Far Final ReviewDokument13 SeitenFar Final ReviewFutureMsCPA100% (1)
- IAS 19 - Employee BenefitsDokument1 SeiteIAS 19 - Employee BenefitsClarize R. MabiogNoch keine Bewertungen
- IAS 19 Employee Benefits ExplainedDokument40 SeitenIAS 19 Employee Benefits ExplainedYI WEI CHANGNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1FU491 Employee BenefitsDokument14 Seiten1FU491 Employee BenefitsEmil DavtyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pension Plans ExplainedDokument21 SeitenPension Plans ExplainedMichael NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- LKAS 19 2021 UploadDokument31 SeitenLKAS 19 2021 Uploadpriyantha dasanayake100% (1)
- IAS 19 Employee BenefitsDokument32 SeitenIAS 19 Employee BenefitsTamirat Eshetu WoldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Benefits: Cruz, Jerica May A. CBET-01-501EDokument21 SeitenEmployee Benefits: Cruz, Jerica May A. CBET-01-501Eclara san miguelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oregon ObjectionDokument40 SeitenOregon Objectionjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative NantasketDokument6 SeitenNarrative Nantasketjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Opioid Lawsuit Carr v. Manufacturers and DistributorsDokument114 SeitenOpioid Lawsuit Carr v. Manufacturers and DistributorsepraetorianNoch keine Bewertungen
- PS 2 Fall 2009 SolutionsDokument9 SeitenPS 2 Fall 2009 Solutionsjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bismarck NarrativeDokument2 SeitenBismarck Narrativejklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- SGA NarrativeDokument1 SeiteSGA Narrativejklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Team Practice Questions For Exam #3Dokument2 SeitenTeam Practice Questions For Exam #3jklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- VivianFashion FAC I Acquisitions Cycle TDokument1 SeiteVivianFashion FAC I Acquisitions Cycle Tjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Exam 2 Vocab Problems Acc Dep Impairment Loss GoodwillDokument1 SeiteSample Exam 2 Vocab Problems Acc Dep Impairment Loss Goodwilljklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 BBA Pre-Screen Case PDFDokument3 Seiten2008 BBA Pre-Screen Case PDFjklein25880% (1)
- Itm MemoDokument2 SeitenItm Memojklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- ACC/490 Weekly Overview: Week One: Auditing and AssuranceDokument2 SeitenACC/490 Weekly Overview: Week One: Auditing and Assurancejklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Personality Tests Are No Substitute For Interviews: Business WeekDokument1 SeitePersonality Tests Are No Substitute For Interviews: Business Weekjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capacity ManagementDokument4 SeitenCapacity Managementjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Quiz CH 12-2Dokument4 SeitenSample Quiz CH 12-2jklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Noreen 1 e Exam 04Dokument4 SeitenNoreen 1 e Exam 04jklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test 3BDokument11 SeitenTest 3Bjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm 1 AnsDokument3 SeitenMidterm 1 Ansjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- D. All of These Answers Are TrueDokument2 SeitenD. All of These Answers Are Truejklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Test Answers 2-3Dokument1 SeiteEnvironmental Test Answers 2-3jklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-1.teamwork - Wall Street JournalDokument2 Seiten2-1.teamwork - Wall Street Journaljklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- 305 Samp Ex 2 Keys 07Dokument1 Seite305 Samp Ex 2 Keys 07jklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- FLIGHTDokument3 SeitenFLIGHTjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Talking PlantsDokument7 SeitenTalking Plantsjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Accounting Chapter 5 Practice Exam SolutionsDokument4 SeitenManagerial Accounting Chapter 5 Practice Exam Solutionsjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Membership Application: (Please Print)Dokument2 SeitenMembership Application: (Please Print)jklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Directions From San FranciscoDokument1 SeiteDirections From San Franciscojklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Insect Vectored Disease Position Paper Rubric FS 08Dokument1 SeiteInsect Vectored Disease Position Paper Rubric FS 08jklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- BZZZZZZZZDokument3 SeitenBZZZZZZZZjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- How the Sacred Lotus Flower Generates Heat Like MammalsDokument1 SeiteHow the Sacred Lotus Flower Generates Heat Like Mammalsjklein2588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Appraisal at UfoneDokument16 SeitenPerformance Appraisal at UfoneMuhammad Amjad0% (1)
- Offer Letter For Women's Wrestling CoachDokument4 SeitenOffer Letter For Women's Wrestling CoachA.W. CarrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Rev FGHDokument2 SeitenTax Rev FGHDenardConwiBesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Gonzalez Contract FinalDokument4 SeitenAc Gonzalez Contract FinalEric NicholsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Benefits and Its Effect On Employee ProductivityDokument16 SeitenEmployee Benefits and Its Effect On Employee ProductivityJay Bags100% (1)
- Implementing a private company retirement plan under the Retirement Pay LawDokument18 SeitenImplementing a private company retirement plan under the Retirement Pay LawNFNLNoch keine Bewertungen
- MWP & KeymanDokument11 SeitenMWP & KeymanEnnsignn Advisory Services P LtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAPFlex Ben FAQs 2018Dokument13 SeitenSAPFlex Ben FAQs 2018Mukesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxation - Income TaxDokument158 SeitenTaxation - Income Taxnaren197667% (6)
- August 2016Dokument92 SeitenAugust 2016Cleaner MagazineNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCH 501 Lesson PlanDokument17 SeitenBCH 501 Lesson PlansdddNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Payee Disclosure Report - Saskatchewan GovernmentDokument252 Seiten2012 Payee Disclosure Report - Saskatchewan GovernmentAnishinabe100% (1)
- Complete Book P4 UDCDokument145 SeitenComplete Book P4 UDCshubham0% (1)
- Post Retirement BenefitsDokument4 SeitenPost Retirement BenefitsWill Emmanuel A PinoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Income From SalaryDokument16 SeitenIncome From SalaryGurpreet Singh100% (1)
- HI6028 Taxation Theory, Practice & Law: Student Name: Student NumberDokument12 SeitenHI6028 Taxation Theory, Practice & Law: Student Name: Student NumberMah Noor FastNUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Most Important - Income TaxDokument97 SeitenMost Important - Income TaxAkhil BaijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Labor: Blue BookDokument242 SeitenDepartment of Labor: Blue BookUSA_DepartmentOfLaborNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoint Slides by R. Dennis Middlemist, Professor of Management, Colorado State UniversityDokument60 SeitenPowerpoint Slides by R. Dennis Middlemist, Professor of Management, Colorado State UniversityPriyanka KulshresthaNoch keine Bewertungen