Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mut.59.1.11.Satb.b (User Manual Insite Free)
Hochgeladen von
Lucien EponouOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mut.59.1.11.Satb.b (User Manual Insite Free)
Hochgeladen von
Lucien EponouCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Table of Content
1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6
GETTING STARTED Install the software Define hardware configuration Define software options Define frequency bands Define measurement parameters Define channels and carriers Define channels Define carriers
4 4 5 7 8 11 13 13 14 14 14 15 15 15 17 18 20 21 24 26
1.6.1 1.6.2 1.7 1.8 2 2.1 2.2 3 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 4
Define channel width Choose the attenuation mode STARTING A MEASUREMENT Launch a measurement Visualize data ANALYSIS/REMEASUREMENT Analysis in peaks mode Analysis in BCCH mode Re-measure in UMTS mode Additional functions for re-measurements INSITE Frees LEXICON
MUT.59.1.11.SATB.B
INSITE Free User manual
The INSITE Free software has been developped to perform selective RF measurements and to analyse measurements results with the adapted method, depending on the nature of the signal. 1 GETTING STARTED 1.1 Install the software
Before installing the software, check first the PC answers the following hardware requirements
HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS PC Pentium 500 MHz Cable link Operating system Memory Free space Spectrum analyser Application USB Port XP / WIN7 1GB RAM 200 MB free space on hard disc Serial Port, Ethernet or GPIB Microsoft Excel / OpenOffice Calc
Insert the software CD-ROM into the CD drive. Go to the folder and launch the application named setup.exe. Then, follow the instructions displayed on the screen. The INSITE Free software is ready to start
When opening the software, the following main window appears:
4/32
INSITE Free User manual Figure 1:
INSITE Free software main window
1.2
Define hardware configuration
In the main window, go to edit and select hardware configuration. The following window will appear:
Figure 2:
Hardware configuration window
STEP 1: Choose the Spectrum Analyser
Choose the spectrum analyser on the list Choose the port communication Click on check to verify that the communication is working
5/32
INSITE Free User manual
STEP 2: Choose UMTS scanner
Choose the UMTS scanner on the list Choose the port communication Click on check to verify that the communication is working
STEP 3: choose GPS
Choose the GPS device on the list Choose the port communication Click on check to verify that the communication is working
Antennessa supplies the probe, cable and switch and their corresponding calibration files for the INSITE Free software. Calibration files are ASCII files containing rows of data separated by tabulations. Example: 0.1 0.15 0.2 ... The first column contains the frequency in MHz. The next three columns contain the antenna factor of the probe or loss in dB of the cable for the selected way (the gain of each device is calculated using an affine function between the measured points). The switch has a somehow particular file, because it contains 7 columns for the lowest frequencies (below 30 MHz). The column 2, 3 and 4 correspond to the loss without amplifier and the three last ones to the gain of the amplifier. STEP 4: Choose the probe 0.002 0.003 0.003 0.002 0.002 0.004 0.003 0.003 0.003
Click on select probe and browse to select the calibration file (.probe)
STEP 5: Choose cable
Click on select cable and browse to select the calibration file (. cable)
STEP 6: Choose switch box
Click on select switch and browse to select the calibration file ( switch)
6/32
INSITE Free User manual
Click on check to verify that the communication is working 1.3 Define software options
In the main window, go to edit and select software configuration, the following window will appear:
Figure 3:
Software configuration window
The measurement results can be exported in an Excel or OpenOffice Calc file. These results are presented compared to an exposure limit. To choose the applying recommandation, click in the corresponding box.
The Custom standard recommendation permits to apply your own threshold recommandation, from a text file under the Standard
7/32
INSITE Free User manual
directory. It contains two columns. The first one corresponds to the frequency in MHz. The second one corresponds to the standard level in V/m. The two columns are separated by one tabulation. The extension file is .std.
Choose the maximum number of scan to be made per band, the type of scan for the first measure as well as the automatic peaks selection. Restrict users rights Click on save and exit to validate
Note 1: If one and only one report application (Excel / OpenOffice Cac) is installed on your PC, the Application Selection control is not displayed.
1.4
Define frequency bands
In the main window, go to the edit menu and select frequency bands. This window is made of three parts: Default band: for pre-defined band list. Measurement scenario: to select the bands to be measured. Select band information, to choose measurement parameters for each band. STEP 1: load default band list
Select load default bands list, a pop up window will appear with a selection of files. A default list of frequency bands are available, like for instance the france.def file.
Note 2: The default files are XML files. The files are usually named with the country name (e.g. france.def or uk.def).
Select one .def file in the scenarii subdirectory, the following window will appear:
8/32
INSITE Free User manual
Figure 4:
Frequency band configuration window
Note 3: The file path will be automatically saved and do not need to be specified again.
STEP 2: Select frequency band(s) to be measured In the default window are listed the available frequency bands.
Click on the wanted band(s), the following sign will appear at the bottom of the window: >> To select all the bands of the list, click on select all at the bottom of the window Click on the >> sign, the selected band(s) will appear in the measurement scenario list
STEP 3: Remove frequency band(s) to be measured
To remove a band, select it in the measurement scenario list, the following sign will appear at the bottom of the window: << To remove all the bands of the list, click on deselect all at the bottom of the window
9/32
INSITE Free User manual
Click on the << sign, the selected band(s) will be removed from the measurement scenario list
STEP 4: Create a new band
Click on new band at the bottom of the window to create a new band. Type the new band parameter in the selected band information window Define the band limits before trying to define carrier or channels
The new band will be listed in the measurement scenario list. It may be useful to use an explicit name that includes the band limits (e.g.: 47M60M.....my Band) .This will make further edition and researches easier.
STEP 5: Save the measurement scenario
Click on menu Save scenario as or Save and exit button to save the defined measurement scenario in .scn extension file.
Note 4: If you replace the extension .scn of a measurement scenario file, by the extension .def, it will be possible to reload the file as default band list.
10/32
INSITE Free User manual
1.5
Define measurement parameters
The measurement parameters can be defined in the measurement scenario list.
in the selected band
information window. This window becomes available, after clicking on a band
Figure 5:
Selected band information
Three types of post measurement analysis of the acquired data are available:
Standard (peaks) analysis: allows to select peaks and calculate the total field by adding the selected peaks BCCH Analysis: select some of the channels (this is done for a GSM or DCS band) that are BCCH (Broadcast Control Channels), re-measure them (if necessary) and associate them with a Trx. For each BCCH the field is then extrapolated by multiplying the field level by the square root of the Trx Number. The total field is processed by adding the selected extrapolated BCCH values
11/32
INSITE Free User manual
UMTS Analysis: when using an UMTS scanner, the scanner will do some measurements on some specified carriers, extract the scrambling codes and then extrapolate the maximum level
Note 5: The Level for automatic peaks selection (V/m) can be modified only if the Standard (peaks) analysis is selected. By default the level corresponds to the selected recommendation in the software configuration. This default level can be adjusted to a level just above the noise level for an automatic selection of the significant peaks. The Detection Mode and Measurement Mode can be selected. If the Max Hold, Min Hold or Average measurement modes are selected, the Temporal Measurement check box is displayed. Note 6: If Temporal Measurement check box is checked, duration in seconds must be filled. In this case, the three axes are scanned successively, during the indicated time. Then, the max, min or average field is calculated according to the selected measurement mode. Note 7: If the Temporal Measurement check box is not checked, in case of Max Hold or Min Hold measurement mode selection, the duration in seconds must be filled. This duration corresponds here to the duration of the scan for each axis. If Average measurement mode is selected, the number of samples must be filled. In the same way, this one is applied for each axis. Note 8: The Level for automatic peaks selection (V/m) can be modified only if the Standard (peaks) analysis is selected. By default the level corresponds to the selected recommendation in the software configuration. This default level can be adjusted to a level just above the noise level for an automatic selection of the significant peaks. Note 9: By default the most appropriate RBw/VBw available is chosen. Click in the Select RBw/VBw manually box, to choose another one.
12/32
INSITE Free User manual
1.6
Define channels and carriers
The channels function is available for the Standard (Peaks) and BCCH analysis modes. The carriers function is available for the Standard (Peaks) and UMTS analysis modes.
1.6.1
Define channels
In the frequency bands configuration window, go to the edit menu and select define channels, the following window will appear :
Figure 6:
Channels definition window
First channel freq: to select the centre frequency of the first channel in the band First channel number: this number will be associated with the first channel; the next ones will be numbered by adding 1, 2, and 3 to this number
Channel width : this is the bandwidth that will separate two consecutive channels. The chosen channel width will pre-define automatically the filter span used for peaks calculation.
Number of channels: total number of channels in the band: a control will be done to check that no channel is outside the bands limits.
13/32
INSITE Free User manual
1.6.2
Define carriers
In the frequency bands configuration window, go to the edit menu and select define carriers, the following window will appear:
Figure 7:
Define carriers window
Up to 20 carriers can be defined. In the re-measure screen, the carriers names will be displayed on the X axis instead of frequencies. In the peaks analysis mode, the peaks will be selected within the chosen carrier(s), if the level is above the defined threshold level.
1.7
Define channel width
The channel width represents the bandwidth occupied by every sender in the band. This information is used to determine the appropriate RBw and VBw and to check the quality of the measure. A minimum knowledge on the band is necessary to define its width. For example, it will be of 200 KHz in GSM but may rise to 8 MHz in TV.
1.8
Choose the attenuation mode
The following mode of attenuation are available: Maximum found on full scan: a first scan will be done for every session, the attenuation will be then defined depending on the maximum level found. This mode is recommended when little information on the scanned zone are available.
14/32
INSITE Free User manual
Attenuation checked on selected bands: a first scan will be done on every band defined in the scenario; this mode is recommended when a few bands only are scanned and the measurements are made close to a transmitter (frequency and types already known). Constant attenuation: the attenuation is constant and selected manually. This mode is recommended to perform many measurements in a restricted area, far from any transmitter. 2 STARTING A MEASUREMENT 2.1 Launch a measurement
In the main window, go to measurement and select launch measurement scenario. The software will then perform the measurement of all the bands defined in the scenario, starting from the lowest one. If the attenuation is not constant, there will be a first scan to determine the good value for it. When some bands are in the amplified zone, there will be another scan to check if the amplification can be used without any damage of the acquired data. 2.2 Visualize data
To visualize data, go to the file menu in the main software window and select open a session.
15/32
INSITE Free User manual
Figure 8:
Data visualization window for all chosen frequency bands
Standard Limit visualization The View Standard Limit permits the visualization of a black line
corresponding to the selectected threshold recommendation.
Zoom in/out Zoom in: drag an drop rightwards Zoom out: drag and drop leftwards
Figure 9:
Zoom in
Change display unit
16/32
INSITE Free User manual
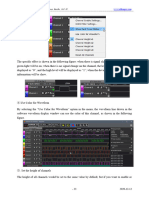
The menu at the bottom left of the window allows to change the display unit. The available choices are: dBV/m V/m A/m W/m2 mW/cm2
Change visualization mode Right from the display unit bottom, a menu allows to change the type of scale for the frequency axis. The available choices are: - Linear scale: make high bands visualization easier. - Logarithmic scale: make low bands visualization easier. - Distributed: all bands occupy the same width. Viewing elements properties Keep the mouse over a band area for a few second to view the name of the band Right click on the band cursor to view the element information and modify the analysis mode or the curve's colour. Auto peaks selection: if you have checked the Automatic peaks selection case in Software configuration, the Auto peaks selection button is visible. Click on it to select the peaks automatically according to the level defined for the band. Save a session: go to the file menu and select save session as. The session will be automatically saved in the session directory of the program. The sessions are saved as XML files (.ins file). XML is a standard of file syntax that is inspired by HTML and permits to save structured ASCII data.
ANALYSIS/REMEASUREMENT
The analysis mode has been chosen, when defining the frequency band to be measured. To access the analysis window, left click on the selected band in the main data visualization window for all chosen frequency bands.
17/32
INSITE Free User manual
3.1
Analysis in peaks mode
STEP 1: Define peaks (without channels or carriers) A peak can be defined in relation with a defined threshold and filter span: The level on this point is higher than the threshold And there is no higher point in the (filter span)-wide band centred on the point
Figure 10: Peaks definition
Click on threshold definition and left click on the graph: the threshold will be redefined to the Y-axis value of this point. The peaks will be represented with blue rectangles.
The filter span is the width of the chosen channel. By default the filter span corresponds to the chosen bandwidth. In this window, the filter span can be entered manually. There is a pre-control on the number of points used to determine if a point is a peak. The following equation is used for this assessment:
FilterSpan*NumberOfPointAnalyser/ (Fmax-Fmin)
< 1.3=> No peak selection.
If the entered filter span does not answer to this equation, a window will pop up, where you can enter manually a new filter span.
18/32
INSITE Free User manual
Note 10: If you have clicked on the auto peaks selection button in the main panel, when the panel Peak display and selection is displayed for the first time, some peaks are selected automatically in relation with the level defined in Frequency bands configuration. They do not take into account of threshold line.
STEP 2: Re-measure one peak In the selected peaks list or directly on the graph, left click on the selected peak Right click to open the re-measurement window.
STEP 3: Re-measure all peaks Select all the peaks to be re-measured in the selected peaks list. Go to measurement in the menu and select remeasure all selected peaks.
Figure 11: Re-measure one peak
19/32
INSITE Free User manual
In the selected peaks list, an indication is given on wether or not the RBw/VBw is proper. The mention OK, "usable" or Not OK appears. RBW/BandWith < 0.25 => Not OK RBW/BandWith < 0.5 RBW/BandWith > 0.5 => usable => OK
3.2
Analysis in BCCH mode
STEP 1: select channel The BCCH window displays the measured peak for each channel. To calculate the total field, click right on the selected channel: it will be displayed in the all BCCH channel list.
Figure 12: Select channel for BCCH analysis mode
STEP 2: Re-measure one channel Click on the chosen column with a left click Launch the re-measurement with a right click
20/32
INSITE Free User manual
Figure 13: Selection of channel for BCCH re-measurement mode
To extrapolate the electric field to the maximum, you can enter the number of TRX for each BCCH signal. STEP 3: Re-measure all chosen channels Go to the measurement menu and select remeasure all selected BCCH)
3.3
Re-measure in UMTS mode
STEP 1: Select Carrier Click right on the curve and validate the selection. The chosen carrier will appear in the carriers list.
21/32
INSITE Free User manual
Figure 14: Window for re-measurement in UMTS mode
STEP 2: re-measure one carrier Click left on the chosen carrier and launch the measurement with a right click. STEP 3: re-measure all the carriers (CPICH value) Go to the measurement menu and select remeasure all selected carriers STEP 4: view the scrambling code To view the information about the detected scrambling code, double click on the carrier. The scrambling code values are expressed in the unit selected in the UMTS processing panel.
22/32
INSITE Free User manual
Figure 15: Scrambling code information window
STEP 5: check the case Extrapolation Factor If you want to extrapolate the result, check the Extrapolation Factor case and indicate the extrapolation factor that you want to use. Extrapolated Level = SQRT (Extrapolation Factor) * Detected Level.
23/32
INSITE Free User manual
Figure 16: Extrapolated Level
3.4
Additional functions for re-measurements
Free scan: a free scan is available directly from the BCCH, peak and UMTS measurement window. Select the zone of the curve to be scanned and click on the free scan button. The following window will appears:
Figure 17: Pop up window for free scan re-measurement
The RBW/VBW can be changed at this stage manually or not. Validate to launch the scan.
24/32
INSITE Free User manual
Polarization: this function gives information on the field level repartition for each or a combination of the thee probe axis. To access this function from any of the re-measurement window, go to the menu measurement and select polarization analysis. A Excel report about the polarization can be generated. Generate Excel report: from each re-measurement window a Microsoft Excel or OpenOffice Calc report can be created. To access this function, go to the menu tools and select Generate report. Save Remeasurement data: click on File/Save Selected Carrier, BCCH or Peaks (depending on the chosen analysis) to save the remeasurement data. These remeasured data will be saved in the session file (*.iste).
Note 11: After selecting the Generate report menu, the report is opened and filled automatically. If you use OpenOffice Calc, please wait the following message before closing the document.
25/32
INSITE Free User manual
4 Session
INSITE Frees LEXICON
A session is a measurement on a fixed point that contains all the measured bands. It includes the initial measurement as well as the re-measurement(s). Band A band is composed of one measure and all the measurements for one frequency band (between two limits). It is associated with an analysis mode that will lead to a re-measurement screen. RBw The RBw (Resolution Bandwidth) represents the bandwidth of a filter that will be applied to the input signal. With a broader RBw, the signal will be higher, as it is taken on a wider bandwidth). If the RBw is to low compared to the channel width, the whole power in a channel may not be measured. This will lead to an underestimation of the field level. VBw The VBw (Video Bandwidth) is linked to the RBw. It's the bandwidth of a filter that may be seen as the inverse of an integration time for each point. The lower it is, the longer the scanning takes. The bigger it is, the more important are the variations. It is generally advised to respect this relation: VBw = RBw*3s Attenuation Attenuation is placed between RF Input of the analyser and the mixer to avoid damage on the mixer. It helps to measure high power signals and prevents the analyser to suffer damages (even if a band is not scanned). The attenuation should be constant for all the measurements. BCCH A BCCH (Broadcast Control Channel) is a fixed emitting channel with a constant level.
26/32
INSITE Free User manual
In GSM and DCS, it is a Downlink channel (from the base station to the mobile) that enables the base station to control the power emitted on traffic channels. Determining the maximum electro magnetic field level is difficult due to the very versatile emission levels of all the signals. The internationally accepted method is to identify the BCCH channels (the shape of their spectrum is specific, and their level is constant), get the power level in these channels and then extrapolate the BCCH level by multiplying the level by the square root of the number of Trx for this transmitter. The Trx number is the maximum number traffic channels that could be activated when the traffic is at its maximum state. It is an operator-owned data, which depends mainly on the population density of the area. When this information is unknown, the following table can be used: GSM High Density area (big station, fair) Large city (> 400k inh.) Small city (> 100k inh.) Countryside or small town (<100k inh) 6 4 3 3 DCS 8 8 6 3
27/32
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Tutorial: Harmonic AnalysisDokument9 SeitenTutorial: Harmonic AnalysisOmar ChacónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kitchen Zinc - Pimsleur French TranscriptsDokument3 SeitenKitchen Zinc - Pimsleur French TranscriptsRajesh20% (5)
- LibreOffice 7.0 Calc GuideDokument545 SeitenLibreOffice 7.0 Calc GuideFlavioRodolfoSeveroNoch keine Bewertungen
- FrontAccounting PDFDokument15 SeitenFrontAccounting PDFJon BgsnNoch keine Bewertungen
- TraceViewer GuideDokument5 SeitenTraceViewer GuideChange LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- TTL 2 CHAPTER 3 Productivity Software ApplicationTools For Teaching and Learning Rev. 2021Dokument45 SeitenTTL 2 CHAPTER 3 Productivity Software ApplicationTools For Teaching and Learning Rev. 2021Chloe Aravello67% (12)
- Activiy1 SofappDokument3 SeitenActiviy1 SofappGregoria Nituda100% (1)
- Omniscan Setup - Basic SetupDokument29 SeitenOmniscan Setup - Basic SetupVictor Antonio Diaz FaundezNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenOffice - Project-Management With Gantt-ChartsDokument27 SeitenOpenOffice - Project-Management With Gantt-ChartsQwertky100% (5)
- Omniscan Setup - Basic SetupDokument29 SeitenOmniscan Setup - Basic SetupcarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPO1 CALC Presentation LessonDokument21 SeitenCOMPO1 CALC Presentation LessonMark D. CalacalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Spectral Analysis MATLAB® Software User GuideVon EverandDigital Spectral Analysis MATLAB® Software User GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM Host Simulator User Manual V5-6Dokument23 SeitenASTM Host Simulator User Manual V5-6Rol PositivoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 RFA Application GuideDokument87 Seiten7 RFA Application GuideSuleman JahangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Successful VSA Analysis Using An OscilloscopeDokument18 SeitenSuccessful VSA Analysis Using An OscilloscopearinramNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 ECT Application GuideDokument67 Seiten4 ECT Application GuideSuleman JahangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB 1 Spectrum - FinalDokument15 SeitenLAB 1 Spectrum - FinalprerakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Sonics Radial Bond ServicesDokument31 SeitenComputer Sonics Radial Bond Servicesandy xuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 MFL Application GuideDokument56 Seiten10 MFL Application GuideSuleman JahangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 NFT Application GuideDokument57 Seiten8 NFT Application GuideSuleman JahangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 110758-W2-US LCR-Meter Operating Instructions enDokument13 Seiten110758-W2-US LCR-Meter Operating Instructions enadamatozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Noise LogDokument5 SeitenNoise Log087825550697Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operating The Coco-80X For FFT: Steps InvolvedDokument5 SeitenOperating The Coco-80X For FFT: Steps Involvedpalla mounicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uniden Bcd996xt Scanner User GuideDokument130 SeitenUniden Bcd996xt Scanner User GuideAnonymous ijZ3W6JxT9Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9 NFA Application GuideDokument60 Seiten9 NFA Application GuideSuleman JahangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Steps For Setup 2 - 0 SWDokument29 SeitenBasic Steps For Setup 2 - 0 SWnathaniel ekaikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PX 777 Programming Software InstructionsDokument7 SeitenPX 777 Programming Software InstructionsNei LobãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Windoas and DoasisDokument64 SeitenManual Windoas and DoasisAnonymous KvoezhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scan AnalysisDokument27 SeitenScan AnalysisNooruddin DeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Futronic MKII: Manager (PC Software) User ManualDokument14 SeitenFutronic MKII: Manager (PC Software) User ManualAl Nino AalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Book SW-U801Dokument22 SeitenManual Book SW-U801SersanassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diamond401 SW ManualDokument33 SeitenDiamond401 SW ManualMiranda HéctorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingst Virtual Instruments User Guide (v3.5)Dokument17 SeitenKingst Virtual Instruments User Guide (v3.5)Navid MohagheghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulate A WDM System With 8 Channels: Global ParametersDokument18 SeitenSimulate A WDM System With 8 Channels: Global ParametersIsabelAguirreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tracker Software Instructions: Cience OF EnsingDokument19 SeitenTracker Software Instructions: Cience OF EnsingOscar GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6. Examples: Frequency DomainDokument6 SeitenChapter 6. Examples: Frequency DomainblekstenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMM 8010 SW ManualDokument24 SeitenPMM 8010 SW ManualMarco Vinicio BazzottiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Signal ViewerDokument11 SeitenTest Signal ViewerIvailoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 70-1470 Programming ManualDokument29 Seiten70-1470 Programming ManualSebastiánUlloaQuezada100% (1)
- FCA Basic SetupDokument15 SeitenFCA Basic Setupliew99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atmospheric CorrectionDokument11 SeitenAtmospheric Correctionjrruiza19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Futronic MKII: Manager (PC Software) User ManualDokument15 SeitenFutronic MKII: Manager (PC Software) User ManualeminNoch keine Bewertungen
- BLI ManualDokument7 SeitenBLI ManualKURTNoch keine Bewertungen
- UT60A Computer Interface SoftwareEEEDokument4 SeitenUT60A Computer Interface SoftwareEEEEmanuel SepulvedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multipactor Manual 160Dokument35 SeitenMultipactor Manual 160Sergei_V_7521Noch keine Bewertungen
- FTIR University of TorontoDokument22 SeitenFTIR University of TorontoAlexandra OrzelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 DefHi Application GuideDokument60 Seiten5 DefHi Application GuideSuleman JahangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Vibration 2120Dokument27 SeitenBasic Vibration 2120jide.atolagbe3737Noch keine Bewertungen
- CARE, IIT Delhi CRP718 - 2015-16/1 Semester Experiment On PC Based Multi-Channel Data Acquisition. 1. ObjectivesDokument9 SeitenCARE, IIT Delhi CRP718 - 2015-16/1 Semester Experiment On PC Based Multi-Channel Data Acquisition. 1. ObjectivesPunitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Data-Streamer V1.3 - Usb and LPT Version: 1) Installing DatastreamerDokument8 SeitenManual Data-Streamer V1.3 - Usb and LPT Version: 1) Installing Datastreamerlong rangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual For The Sound Card Oscilloscope V1.32: 1 RequirementsDokument13 SeitenManual For The Sound Card Oscilloscope V1.32: 1 RequirementsMarian MarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADAP 2.0: Measurement and Analysis Software For Biochrom Anthos Microplate ReadersDokument44 SeitenADAP 2.0: Measurement and Analysis Software For Biochrom Anthos Microplate ReadersNETO95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Using The CX One Version 3 Data Trace FunctionDokument18 SeitenUsing The CX One Version 3 Data Trace FunctionEd CaranayNoch keine Bewertungen
- FWS ModuleDokument35 SeitenFWS ModuleWahyu Sutrisno0% (1)
- Monitor Spectrum: (Revision 3, July 2007)Dokument8 SeitenMonitor Spectrum: (Revision 3, July 2007)nogueiramnsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Futronic MKLL Manager Software ManualDokument15 SeitenFutronic MKLL Manager Software ManualTom MaboetieNoch keine Bewertungen
- UVwin7 Software Operating ManualDokument16 SeitenUVwin7 Software Operating ManualAngelica AmorasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual PocketVNADokument48 SeitenManual PocketVNARey Rustan YbeightisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TraceViewer HelpDokument5 SeitenTraceViewer HelpChange LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- OMA SW ManualDokument57 SeitenOMA SW ManualKoyi KabutoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kronos Processor GuideDokument11 SeitenKronos Processor GuideFaris MusyaffaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Ansoft High Frequency Structure SimulatorDokument31 SeitenStudy of Ansoft High Frequency Structure Simulatorshiva prasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Software para GillDokument34 SeitenManual Software para GillsoldadouniverNoch keine Bewertungen
- M WinSASDokument23 SeitenM WinSASTOS CCLNoch keine Bewertungen
- GM950 Programming ManualDokument101 SeitenGM950 Programming Manualrfsq100% (1)
- 3.2.2.6 Frame For Rotor Temperature Alarm Value SetupDokument51 Seiten3.2.2.6 Frame For Rotor Temperature Alarm Value SetupClip nhungcaunoihayNoch keine Bewertungen
- JCA/JDBC Driver: General NotesDokument32 SeitenJCA/JDBC Driver: General NotesvalmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- LibreOffice Suite Calc 6.3 Participant CertificateDokument10 SeitenLibreOffice Suite Calc 6.3 Participant CertificateHarsheen KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Spreadsheet Notes-1Dokument10 Seiten2021 Spreadsheet Notes-1Arieana MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traducao Via Val Daily - 02-05-12Dokument30 SeitenTraducao Via Val Daily - 02-05-12Val IvonicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Docmosis Template Guide: Create Documents and Reports Fast From TemplatesDokument65 SeitenDocmosis Template Guide: Create Documents and Reports Fast From TemplatesSandra Saky KapetanovNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS Office PDFDokument56 SeitenMS Office PDFsachin15j82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 9 Chapter 7 Word Processing Tool: Openoffice WriterDokument7 SeitenClass 9 Chapter 7 Word Processing Tool: Openoffice WriterMohan ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AndrewMacro OdtDokument428 SeitenAndrewMacro OdtAlperen AkçaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class-9 IT-WSDokument4 SeitenClass-9 IT-WSGauri MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Software Applications For Authors For Writing.9Dokument6 SeitenFree Software Applications For Authors For Writing.9stone heartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empowerment Technology ReviewerDokument4 SeitenEmpowerment Technology ReviewerJericko Allen ResusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drawing Basic Shapes: Draw GuideDokument16 SeitenDrawing Basic Shapes: Draw GuideAkash SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Setting Up Open Office For AlfrescoDokument4 SeitenSetting Up Open Office For AlfrescoSreenivas IyyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Libreoffice?: Writer (Word Processor)Dokument15 SeitenWhat Is Libreoffice?: Writer (Word Processor)Neuer FamilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filr InstDokument186 SeitenFilr InstsimonjeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Office 365 Product Key Ebaywaccz PDFDokument1 SeiteMicrosoft Office 365 Product Key Ebaywaccz PDFBlaabjergBlaabjerg15100% (1)
- LibreOffice - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument14 SeitenLibreOffice - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJuan Carlos Moreno HenaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cadette TrackerDokument317 SeitenCadette TrackerKjgrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apache OpenOfficeDokument5 SeitenApache OpenOfficeGwenjean Arce Velasco0% (1)
- Data Pilot 4290 Operating InstructionsDokument42 SeitenData Pilot 4290 Operating Instructionsenamicul50Noch keine Bewertungen
- Questions: Single/masterDokument2 SeitenQuestions: Single/masterPS1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction and Advantages of Libre OfficeDokument3 SeitenIntroduction and Advantages of Libre OfficeprakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP Lab ManualDokument101 SeitenCP Lab ManualmiraclesureshNoch keine Bewertungen