Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Termokimia Notes
Hochgeladen von
Sarah WongOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Termokimia Notes
Hochgeladen von
Sarah WongCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
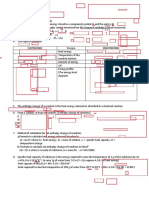
Chapter 12 : THERMOCHEMISTRY 4.1 The Changes Of Energy (E) in chemical reaction 1.
The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be ___________ or ____________. However, energy can be ___________ from one form to another. For example, chemical energy heat energy 2. Exothermic reaction the reaction which ____________ the heat energy ____ surroundings 3. Endothermic reaction the reaction which ___________ the heat energy ____ surroundings 4. The table below shows the differences between exothermic & endothermic reaction: Charateristics EXOTHERMIC ENDOTHERMIC 1.Heat energy 2.Thermometer 3.Changes of energy 4.Bonding 5.Energy Level Diagram 4.2 Calculation for the heat changes, H 1. H measured in ____________ unit 6.Examples - dissovels - dissovels concentrated acid ammonium salts in /alkali in water water - combustion - carbonate / nitrate - rusting of iron salts decomposes - acid reacts with metal by heat - neutralisation - acid reacts with - Haber process NaHCO3 & KHCO3 - Touch process - photosynthesis 2. H = mc m = the mass of reactant solution which immersed the thermometer c = heat capasity of water = 4.18 J g-1 C -1 = temperature change , T Chemical energy Heat energy
Reactant particles
Exothemic
Solution in Endothermic beaker = surroundings
5. Energy (E) - ability to do the works - measured in Joule (J) - 1000J = _____ KJ 6. Heat changes ( H) - the changes of heat during the chemical reaction - unit : _________ - ve value for ______________ - +ve value for ______________ - Hproducts-Hreactants
7. Heat energy will be absorbed in _____________ bonds(-ve) 8. Heat energy will be released in _____________ bonds(+ve)
3. Energy level diagram E H1 H = -ve H2 E H2 H1 H = +ve Endothermic H = H2 H1
5. Calculation of heat change in experiment
Exothermic
4.3
Heat of precipitation Diagram:
- Defination: - AgNO3 (ak) + NaCl (ak) Ionic equation : Ag+ (ak) + Cl- (ak) AgCl (p) + NaNO3 (ak) AgCl (p)
4. During the chemical reaction: Hx = heat change for reaction Hy = Heat absorbed to break the bonds (+ve) Hz = Heat realeased when bonds formed (-ve) Hx = Hy + Hz If Hy < Hz, If Hy > Hz, then then Hx ve (exo) Hx +ve (endo) CO (g) + H2 (g) ,Hx +ve
Heat realeased when bonds formed
-calculation: 1. 2. 3. 4.4 Heat of displacement Diagram:
Example: C (p) + H2O (ce) E
Heat absorbed to break the bonds
C (g) + 2H (g) + O (g)
Hz Hy
CO (g) + H2 (g)
Hx
Total heat change
Defination: Mg (p) + FeCl2 (ak) Fe (p) + MgCl2 (ak) ionic equation : Mg (p) + Fe2+(aq) Fe (p) + Mg2+ (aq)
C (s) + H2O (l)
4.5
Jisim bahan t/b & tidak diambil kira bahan t/b yg berlainan memberi haba penyesaran berlainan cth: haba t/b Zn dgn Fe2+ haba t/b Al dgn Fe2+
membakar bahan api (alkohol) sbyk jisim m1 & haba yg dibebaskan diguna utk memanaskan air pada V1. Perubahan suhu maksimum disukat haba pembakaran (KJmol-1)
Haba Peneutralan maksud: haba yang dibebaskan a/p satu mol ion H+ t/b dgn satu mol ion OH- utk menghasilkan satu mol air pada keadaan piawai Cth: HCl (ak) + NaOH (ak) Bilangan atom karbon per molekul alkohol Kesimpulan: Haba pembakaran semakin meningkat dgn pertambahan bil. atom C per molekul alkohol 4.7 Nilai Bahan Api 1. Bahan api : 2. Bahan api berbeza mempunyai haba pembakaran yang berlainan 3. Faktor pemilihan bahan api dalam kegunaan industri: a) b) c) d) menghasilkan tenaga haba yg byk mempunyai harga / kos yang rendah mudah diperoleh tidak mencemarkan alam sekitar
H2O (ce) + NaCl (ak) H = -x KJ mol-1 H2SO4 (ak) + Mg (OH)2 (ak) 2H2O (ce) + MgSO4 (ak) H = -2x KJ mol-1 + H (ak) + OH (ak) H2O (ce) - kaedah penentuan Haba Peneutralan - campurkan larutan asid M1 sbyk V1 dgn larutan alkali M2 sbyk V2 & perubahan suhu maksimum disukat Haba peneutralan antara asid kuat dgn alkali kuat adalah tetap, iaitu 57.3 KJ mol-1 Kerana semua asid & alkali kuat mengion secara lengkap Haba peneutralan antara asid lemah dgn alkali lemah < drpd -57.3 KJ mol-1 Kerana semua asid & alkali lemah mengion secara separa / tidak lengkap Maka sebahagian haba yg terbebas semasa proses peneutralan diserap utk memutuskan ikatan O-H dalam molekul asid lemah yg tidak mengion
4. Nilai bahan api: : utk membanding kos tenaga antara bahan api : unit KJg-1 5. Arang kok byk digunakan dalam industri Kelebihan: Keburukan: Sebab:- mengandungi bendasing seperti sulfur yang akan ditukar menjadi sulfur dioksida yang mengakibatkan hujan asid. Hujan asid memusnahkan hutan rimba, hidupan akuatik mati, struktur bangunan (logam / konkrit) terkakis.
4.6
Haba Pembakaran maksud: haba yang dibebaskan a/p satu mol bahan kimia terbakar dgn lengkap dalam oksigen pada keadaan piawai Cth: CH3OH (ce) + 3/2 O2 (g) kaedah penentuan Haba Pembakaran CO2 (g) + 2H2O (ce)
Persamaan: S (p) + O2 (g)
SO2 (g)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 2.experimental TechniquesDokument5 Seiten2.experimental TechniquesSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry Module 1Dokument9 SeitenThermochemistry Module 1PavithiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical EnergeticsDokument64 SeitenChemical Energeticsirnihafizan6812Noch keine Bewertungen
- ThermochemistryDokument31 SeitenThermochemistryDavidson ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 ThermochemistryDokument6 SeitenChapter 9 ThermochemistryMohammad AfifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8Dokument84 SeitenChapter 8Hafizszul FeyzulNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Thermochemistry (Semester 2)Dokument32 Seiten1 Thermochemistry (Semester 2)Esther NgiengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Enthalpy ChangesDokument14 SeitenEnthalpy ChangesBoodhonee AvinashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition Chem SPMDokument6 SeitenDefinition Chem SPMSarah Wong100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chapter 13 - ThermochemistryDokument22 SeitenChapter 13 - ThermochemistryvaogerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat of NeutralisationDokument4 SeitenHeat of NeutralisationZarith Hidayah IsmileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry Enthalpy H: Investice Do Rozvoje VzděláváníDokument7 SeitenThermochemistry Enthalpy H: Investice Do Rozvoje VzděláváníEva IndriyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - Termochemistry 55Dokument55 SeitenChapter 9 - Termochemistry 55ABC_Ais Batu CampurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5Dokument5 SeitenUnit 5billingsleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1Dokument19 SeitenChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1rhythm_no1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5studentDokument44 SeitenChapter 5studentDaniel ButenskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Chapter 4 ThermochemistryDokument6 SeitenForm 5 Chapter 4 ThermochemistryChee Jin TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo Test1Dokument3 SeitenThermo Test1Aman SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4 EnergeticsDokument12 Seiten1.4 EnergeticschwalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- GASEOUS STATE-03-Assignments (New)Dokument20 SeitenGASEOUS STATE-03-Assignments (New)Raju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Balances On Reactive Systems (Ch. 9)Dokument20 SeitenEnergy Balances On Reactive Systems (Ch. 9)Jessica BergerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Themochemistry HO1 and HO 2 CombustionDokument4 SeitenThemochemistry HO1 and HO 2 CombustionTAN CHONG HYEN MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnergrticsDokument31 SeitenEnergrticsnaeem mushtaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 - Chemical EnergeticsDokument51 SeitenModule 5 - Chemical Energeticspoopoodotcom23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 12. Reactive SystemsDokument9 SeitenLecture 12. Reactive SystemsHirun ManujayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPC Unit IvDokument50 SeitenCPC Unit IvJAVAGAR M 20CHR023Noch keine Bewertungen
- 14 ThermochemistryDokument6 Seiten14 ThermochemistryizabelNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnergeticsDokument11 SeitenEnergeticsMuhammadJahangirAlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Class Chapter 8 Chemistry Notes Sindh BoardDokument5 Seiten9th Class Chapter 8 Chemistry Notes Sindh BoardmotivonovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample ChapterDokument7 SeitenSample ChapterhugeamountNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionDokument11 Seiten1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionThanabalan MunuswamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry Cha4 Form5Dokument75 SeitenThermochemistry Cha4 Form5Azmi IsaacNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Uther Mokin WsDokument11 Seiten4 Uther Mokin WsCarlos ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 8 NotesDokument12 Seiten2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 8 NotesZa Evolution ClanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04combustion TechnologyDokument70 Seiten04combustion TechnologySheensky V. SalasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 3 ThermochemistryDokument43 SeitenCHAPTER 3 Thermochemistrykisan singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-Unit 7 Chemical EnergeticsDokument5 SeitenLecture-Unit 7 Chemical EnergeticsKemoy FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11: Thermochemistry - Heat and Chemical Changes Part 1 - Notes: Enthalpy and Bond EnergiesDokument11 SeitenChapter 11: Thermochemistry - Heat and Chemical Changes Part 1 - Notes: Enthalpy and Bond EnergiesSarthakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Module Sk025: Chemistry Semester 2 Chapter 2.0: Thermochemistry Unit 2.1: Concept of EnthalpyDokument7 SeitenTutorial Module Sk025: Chemistry Semester 2 Chapter 2.0: Thermochemistry Unit 2.1: Concept of EnthalpyMUHAMMAD IMRONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 9 Thermochemistry-1415 AznitaDokument84 SeitenChap 9 Thermochemistry-1415 Aznita黄麒安Noch keine Bewertungen
- H For This Reaction From The Following Data: H +177.4 KJ H - 191.2 KJ H - 241.8 KJ H - 43.8 KJDokument4 SeitenH For This Reaction From The Following Data: H +177.4 KJ H - 191.2 KJ H - 241.8 KJ H - 43.8 KJSaddy KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 12 Review - EnergyDokument4 SeitenUnit 12 Review - EnergyZachary NeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry TeacherDokument20 SeitenThermochemistry TeacherjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Revision WorksheetDokument26 SeitenFinal Revision Worksheetawash0takuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5a (AS-Level) : Chemical EnergeticsDokument12 SeitenChapter 5a (AS-Level) : Chemical EnergeticsMohamed AkkashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Che 320 Part ADokument41 SeitenChe 320 Part AFreddie UzokweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry-Jeemain GuruDokument20 SeitenThermochemistry-Jeemain Gurushalini singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 2Dokument5 SeitenProblem Set 2UnitedNationsAveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Change in Chemical Reaction Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherDokument8 SeitenEnergy Change in Chemical Reaction Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherMunshi LazimuzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4 EnergeticsDokument35 SeitenCH 4 Energeticsthat guyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Chemical Energetics Part I SolutionsDokument20 SeitenTutorial Chemical Energetics Part I SolutionsDarren LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matriculation Chemistry ThermochemistryDokument54 SeitenMatriculation Chemistry ThermochemistryzeemboyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionDokument11 Seiten1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionPrema RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energetics and ThermochemistryDokument60 SeitenEnergetics and ThermochemistryIsadora ThibauNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB CHEM 1-4 WorksheetsDokument7 SeitenIB CHEM 1-4 WorksheetsChung Khanh VUUNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 10Dokument4 SeitenCH 10Muizzudin AzaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionDokument11 Seiten1 Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionIEyra ShaHeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry PracticeDokument5 SeitenThermochemistry PracticemariajoticaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE1010 Tutorial Sheet 6Dokument4 SeitenCHE1010 Tutorial Sheet 6Chimuka Onson MapikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry Worksheet 1Dokument7 SeitenThermochemistry Worksheet 1Bennett BongNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIST OF DEFINITION (Template) IN CHEMISTRY F5Dokument7 SeitenLIST OF DEFINITION (Template) IN CHEMISTRY F5Sarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redox Electrolysis and Chemical Cell PDFDokument2 SeitenRedox Electrolysis and Chemical Cell PDFSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Analysis Past Year and Ramalan 2018Dokument5 SeitenChemistry Analysis Past Year and Ramalan 2018Sarah Wong0% (1)
- Redox Reaction Quick Notes: No Experiment Diagram Oxidation Half Equation Reduction Half Equation 1Dokument2 SeitenRedox Reaction Quick Notes: No Experiment Diagram Oxidation Half Equation Reduction Half Equation 1Sarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIST OF DEFINITION (Template) IN CHEMISTRY F4Dokument7 SeitenLIST OF DEFINITION (Template) IN CHEMISTRY F4Sarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pecutan Akhir Kimia BHGN B & C 2018 + Skema PDFDokument53 SeitenPecutan Akhir Kimia BHGN B & C 2018 + Skema PDFSyarfa FurzanneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action Word in ProceduresDokument1 SeiteAction Word in ProceduresSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry F4 Topic 4 - 5Dokument16 SeitenChemistry F4 Topic 4 - 5Sarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic TableDokument8 SeitenPeriodic TableKhairiyah AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry F4 Topic 7Dokument11 SeitenChemistry F4 Topic 7Sarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3: Chemical Formulas & EquationsDokument10 SeitenChapter 3: Chemical Formulas & EquationsSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry F4 Topic 6Dokument21 SeitenChemistry F4 Topic 6Sarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 3 Chemical Formulae & EquationsDokument1 SeiteCHAPTER 3 Chemical Formulae & EquationsSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic StructureDokument3 SeitenAtomic StructureSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- F4 Chapter 1Dokument10 SeitenF4 Chapter 1Sarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fats and Rubber NotesDokument5 SeitenFats and Rubber NotesSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of 4 Thermo ExpDokument4 SeitenComparison of 4 Thermo ExpSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4s Holiday ModuleDokument1 Seite4s Holiday ModuleSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Equation NotesDokument2 SeitenChemical Equation NotesSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- f4 - Chapter 7 PDP WorksheetDokument27 Seitenf4 - Chapter 7 PDP WorksheetSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bengkel 1 - Chemical EquationDokument5 SeitenBengkel 1 - Chemical EquationSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Number of Mole and EquationsDokument32 SeitenChemistry Number of Mole and EquationsSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Command Words in Chemistry Paper 2Dokument37 SeitenCommand Words in Chemistry Paper 2Sarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4s Holiday ModuleDokument1 Seite4s Holiday ModuleSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of PEKA ExperimentsDokument1 SeiteList of PEKA ExperimentsSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quote ExamDokument6 SeitenQuote ExamSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flower PotDokument1 SeiteFlower PotSarah WongNoch keine Bewertungen