Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Marketing Analysis Paper
Hochgeladen von
hotirishcreamerCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Marketing Analysis Paper
Hochgeladen von
hotirishcreamerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Running head: MARKETING ANALYSIS PAPER
Marketing Analysis Paper Amber Landis MKT 498 November 30, 2012 Heather Teague
MARKETING ANALYSIS PAPER
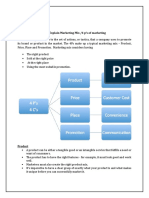
Marketing Analysis Paper It takes a lot of hard work and dedication to create the image of a company, brand, or products in any given market and be noticed by the target market. Whether it be marketing a piece of merchandise, a service, company, or even an individual positioning is crucial the success of any product. The positioning of that product is determined by how one gets into the mind of the prospective customer. When it comes to positioning the product one will want the prospect to recognize that the product is created to meet their needs. Different types of analysis used by marketers Product Positioning The positioning of a product can be expedited by using a graphical technique call perceptual mapping, and other survey techniques. Statistical techniques such as factor analysis, multi dimensional scaling, logic analysis, and conjoint analysis also determine position of a product in a market (Evans, et. al, 2004). Positioning is the process of designing an image so that the consumers within the target segment understand what the company or brand stands for. By doing this the organization is sending a message to the consumers and try to establish a competitive advantage that in hopes will appeal to the consumers in the target segment. When detailed marketing research is done then methodological problems can arise. If the company needs to collect some quantitative information, for instance opinion or facts through a researcher administered survey; interview or questionnaire. Surveys are very effective of collecting information and they are standardized, so they are free from any errors. While on the other hand, there are few disadvantages of surveys, like depending on subjects and the reasons for an action cannot be known; they dont give full sense of social processes making the analysis
MARKETING ANALYSIS PAPER
superficial; structured surveys with close ended questions have low validity when affective variables are researched. To evaluate the product, in factor analysis, the features of product can be used. Also quantitative marketing research techniques can be used. Quantitative research is about quantifying relationships between variables. From marketing prospective, quantitative research is most useful in gathering measurable information that can be tracked over time. This is helpful to the marketer because the comparisons help delineate not only the advantages and disadvantages but also the applications most appropriate for various research purposes. Factor analysis is inexpensive and accurate. Multidimensional scaling (MDS) and other statistical techniques can be used in marketing and social sciences. It can be used to build perceptual maps. These procedures involve algorithms that start with measures of similarity between pairs of products and try to find a geometric representation of the brands in the product category. These techniques position products that are perceived as similar close to one another and locate dissimilar products far apart. Dimensions of perceptual maps are not named by the multidimensional scaling programs. Researchers have to interpret the dimensions themselves based on the geometric representation. Additional information may be gathered from consumers to name the dimensions. The attributes that are the most important in consumers perceptions of a product category can be determined from survey research. In this way, positioning is not actually something that is done to the product; rather it is something that marketers do to the minds of consumers. It relates to how consumers perceive the
MARKETING ANALYSIS PAPER
product in terms of relative to competing offerings. Company needs to be careful in positioning their product as it is challenging to attempt to change that perception later on. Competitive positioning The competitive positioning paradigm, drawing largely on the work of Porter (1980, 1985), dominated strategic management in the 1980s. It emphasized the idea of strategic fit between the organization and its environment so as to achieve competitive advantage, referring to this as competitive positioning. When the prospective market can clearly see how the company's product differs from the others, it will be easier for the company to guide them to purchase the product. A key element of the positioning strategy is the value proposition (Campbell, et. al. 2002). In order to analyze competitor positioning, a competitor array is the most useful and common technique to use. A two dimensional matrix that shows a list of competitors, benefits expected by customers, the industry, the overall strength of each competitor in relation to one another as well as the rating of each competitor based on the key success factors and each is used to display it. Its usefulness depends on its capability to give the company the information it needs to know. Competitor profiling, a technique that gives more information about the companies and competitors, is also used by those that believe knowledge about the competitors is a very important intrinsic part of corporate strategy and also that the value of a customer is defined as relative to what the rival companies may offer. Core competence, which is a must for a successful competition, is gained by companies that practice advanced and systematic competitor profiling. Another way to gain more insight into what a competitor believes about their target market and marketing is media scanning. The
MARKETING ANALYSIS PAPER
changes they do as well as their ad's reveal a competitor's new strategic direction, new pricing strategy, new value migration, branding strategy, problems with previous positions, new positioning strategy or upcoming product offerings. The targeting and segmentation strategy, budget allocation, focus and selectivity can also be revealed due to the media strategy of a competitor. Therefore, a manager is able to execute his own media plan based on how he/she analyzes the changes or the behavior that have been observed from the competitor(s) so that his/her media plan does not share similarities with his/her competitors. Other than analyzing the current competitors, it is also important to estimate future competitive threats by taking into consideration the companies which are having high profit margins and are fairly new in the market, has future growth potential and competing with a related market/product. Customers Perceptions The image or picture a customer develops by considering various types of promotional inputs from the company about their services or products is referred to as the customers' perception. Assessing the customers' perceptions is vital because customers buy services and/or products based on their own expectation derived from the media/promotions or other sources such as word-of-mouth. If the product or service meets the customers' expectations, they will be satisfied; however, if they don't, then the customers will complain. Expectations are drawn from perceptions and, taking this into careful consideration, companies will need to understand the perceptions of their respective customers in order to facilitate sales and advertising promotional efforts towards a more pleasing bargain. A way of determining customers' perceptions is by using a questionnaire survey (for example, self-administrated questionnaires) to collect information.
MARKETING ANALYSIS PAPER
The measure of respondents' perceptions can also be measured using the Parasuman, Zeithaml and Berry's SERVQUAL instrument which have a customers' expectation section that may be filled out by the employees of the company. Another approach that may be used to analyze customers' perception is the MDS approach. In order to identify the fundamental dimensions underlying the original items of service quality is factor analysis. It is vital for a company to assess their customers' service quality perceptions first and then educate their staff on the way the customers define good service quality and to align those definitions with the company's definition. Distribution Channels How the product reaches the customers is ultimately determined by the distribution channels. Existing distribution channels may be well developed but they may be already dominated by incumbents while new entrants may get the advantage of promoting their own emerging channels as being more efficient than the emerging channels. The product or service must reach the appropriate customers at the appropriate times for the product to be effective. Determining what the target market is and how they behave as well as studying their consumption patterns are important when deciding what channel to use. By the target consumer, what level of service is desired? This usually boils down to the implications of warehouse and discount stores which show the willingness of customers to accept lower service outputs as long as it costs them lower prices. The importance of the product for the business as well as the size of the business is also a main factor that may help in determining the distribution channel that should be used. The variations in the nature of the product are also worth mentioning when deciding on the appropriate channel of distribution to use. A number of other factors that prevent a company from operating its own distribution channel, e.g., most marketers enter into a level of
MARKETING ANALYSIS PAPER
channel partnership; those who don't use the resellers need to assist the other parts of the distribution process (such as using parcel post shippers); creating their own shipping companies and transportation systems. Product positioning is a good way to create an impact by positioning the offerings of the company in ways that appeal to the targeted customers so that customers' perception is built on the target market which can help them guide in their purchasing decision (Nykiel, 2007). Competitive positioning and product positioning shows how product compares with its competitors and can help the organizations to become profitable. Customers perception and distribution channels are very important and helpful to understand quality and creating good impression of the company service by delivering products on time and also maintain the quality of products.
MARKETING ANALYSIS PAPER
References Campbell, D.; Stonehouse, G.; Houston, B. (2002), Business strategy: an introduction. Retrieved from Google books. Evans, M.; OMalley, L.; Patterson, M. (2004), Exploring direct and relationship marketing. Retrieved from EBSCOhost online database. Nykiel, R. A. (2007). Handbook of Marketing Research Methodologies. Retrieved from Google books.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Principles of Marketing WEEK 6Dokument6 SeitenPrinciples of Marketing WEEK 6JayMorales100% (1)
- Marketing Research Assignment FinalDokument14 SeitenMarketing Research Assignment FinalGaurav JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pepsi Vs Coke SurveyDokument2 SeitenPepsi Vs Coke SurveyShorelyn Suerte CapurasNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Market ResearchDokument13 SeitenWhat Is Market ResearchJudy Ann VicenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Marketing ResearchDokument22 SeitenApplication of Marketing ResearchVanisha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd-ModuleDokument33 Seiten3rd-ModuleRyan Paul BilgeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Research Assignment: Suraj Kumar - 21DM203Dokument9 SeitenMarket Research Assignment: Suraj Kumar - 21DM203SURAJ KUMAR-DM 21DM203Noch keine Bewertungen
- Customer-Centric Marketing IntroductionDokument90 SeitenCustomer-Centric Marketing IntroductionSanjib BeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of Good Marketing ResearchDokument18 SeitenCharacteristics of Good Marketing Researchsln5Noch keine Bewertungen
- VALUCA DUMITRU-Unit 03 Introduction To Marketing (Set-2)Dokument17 SeitenVALUCA DUMITRU-Unit 03 Introduction To Marketing (Set-2)Md. Helal MridhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Information Systems: A SummaryDokument5 SeitenMarketing Information Systems: A SummaryEYOBNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Topics of ManagementDokument8 Seiten3 Topics of ManagementaffanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Analytics: Sem Iii Dr. Uzma HasanDokument165 SeitenMarketing Analytics: Sem Iii Dr. Uzma HasanChalsee ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Salesmanship-Seatwork 6 - Sales ForecastingDokument6 SeitenProfessional Salesmanship-Seatwork 6 - Sales ForecastingGlenn BelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative Report - Marketing ProcessDokument5 SeitenNarrative Report - Marketing Processhlubuguin100% (1)
- Chapter Five Marketing ResearchDokument15 SeitenChapter Five Marketing ResearchTariku KolchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6 - Foundation For Market Strategy Selection and AnalysisDokument13 SeitenModule 6 - Foundation For Market Strategy Selection and Analysisalma agnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market ResearchDokument5 SeitenMarket ResearchLokamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market ResearchDokument9 SeitenMarket ResearchAnkit G SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avi Okok-2Dokument83 SeitenAvi Okok-2Avinash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- LouieDokument3 SeitenLouielephuthanh02Noch keine Bewertungen
- MKTG RSCH INSGHTDokument20 SeitenMKTG RSCH INSGHTDilip YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRA NotesDokument13 SeitenMRA Notesraju prajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Uses of Marketing ResearchDokument3 SeitenWhat Are The Uses of Marketing ResearchVia B. BorrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Analytics: Meaning, Characteristics, Advantages, DisadvantagesDokument26 SeitenMarketing Analytics: Meaning, Characteristics, Advantages, Disadvantagesprabha etc100% (1)
- Market Research Applications and Techniques for Improving Marketing DecisionsDokument14 SeitenMarket Research Applications and Techniques for Improving Marketing DecisionsSendhil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Research NotesDokument8 SeitenMarketing Research NotesEmily100% (1)
- Chapter 1Dokument14 SeitenChapter 1Vikram VrmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ent Notes MARKETING Eng Sep 2023Dokument10 SeitenEnt Notes MARKETING Eng Sep 2023SIZA THE POETNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Refers To Activities A Company Undertakes ToDokument12 SeitenMarketing Refers To Activities A Company Undertakes ToBal Chandra PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Marketing ConceptsDokument67 SeitenIntroduction to Marketing ConceptsPiyush AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No 1: Marketing Research, Difference Between Consumer and B2B Marketing, Scope of B2B Marketing ResearchDokument14 SeitenAssignment No 1: Marketing Research, Difference Between Consumer and B2B Marketing, Scope of B2B Marketing Researchbadal23238Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis On Marketing Mix StrategiesDokument8 SeitenThesis On Marketing Mix Strategiesamberrodrigueznewhaven100% (1)
- Handout 1Dokument9 SeitenHandout 1Sumit SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Research vs. Marketing Research - VoxcoDokument4 SeitenMarket Research vs. Marketing Research - VoxcoZahid5391Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing PlanDokument15 SeitenMarketing PlanalkharashyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relevance of modern marketing conceptsDokument7 SeitenRelevance of modern marketing conceptsKirwa NickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment # 1: Name: Ali Ahmed MalikDokument4 SeitenAssignment # 1: Name: Ali Ahmed MalikAli MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research MethodologyDokument26 SeitenResearch Methodologyvaibhav100% (1)
- Unit 5Dokument13 SeitenUnit 5Jahnavi AkumallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MarketingDokument15 SeitenMarketingnaserbanipalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENTREPRENEURSHIPDokument5 SeitenENTREPRENEURSHIPTembo U KondwelaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mba Marketing StrategyDokument12 SeitenMba Marketing Strategymb baNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meaning and Importance OfresearchDokument19 SeitenMeaning and Importance Ofresearchraazoo19Noch keine Bewertungen
- MBM813 - Zara JamaicaDokument8 SeitenMBM813 - Zara JamaicaJamaica RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Plan & Research GuideDokument13 SeitenMarketing Plan & Research GuidemariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 25, Marketing OverviewVon EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 25, Marketing OverviewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Research JAIBBDokument10 SeitenMarketing Research JAIBBSUBRATA SUTRADHARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Analytics PDFDokument105 SeitenMarketing Analytics PDFMayank TyagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Management - 2Dokument5 SeitenMarketing Management - 2sandhyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STP Marketing: Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning AnalysisDokument18 SeitenSTP Marketing: Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning Analysisashwin moviesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Royal EnfieldDokument41 SeitenRoyal EnfieldAnonymous RV1TQseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salman ResearchDokument63 SeitenSalman ResearchSalman MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actividad en Ingles BenchmarkingDokument2 SeitenActividad en Ingles BenchmarkingLUIS FERNANDO HERNANDEZ PEREZNoch keine Bewertungen
- MR 1ST ChapDokument14 SeitenMR 1ST Chap丨么S H Ã D Ø W么丨Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection N EntrepDokument12 SeitenReflection N EntrepDaniela OrionNoch keine Bewertungen
- MM CHP 4 PDFDokument8 SeitenMM CHP 4 PDFWaqar HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing ResearchDokument30 SeitenMarketing ResearchStephen MarcuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Principles, Strategies, and Concepts ExplainedDokument2 SeitenMarketing Principles, Strategies, and Concepts ExplainedKRISHAN MAE GALLARDONoch keine Bewertungen
- EEM Question Bank Explains Marketing Mix and Demand Forecasting MethodsDokument11 SeitenEEM Question Bank Explains Marketing Mix and Demand Forecasting Methodsjimaerospace05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ensayo, Int de Negocios - The Purpose of Marketing ResearchDokument3 SeitenEnsayo, Int de Negocios - The Purpose of Marketing Researchcamila sanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRM - SelvaDokument14 SeitenBRM - SelvaGuru KandhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zaid Raqeeb AlqadhiDokument5 SeitenZaid Raqeeb AlqadhizaidalqadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Research Report on Amul Taaza Tetra Power PackDokument43 SeitenMarket Research Report on Amul Taaza Tetra Power PackRiddhi Kintan PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Failure As A Reoccurring Issue in Developing Countries PDFDokument20 SeitenProject Failure As A Reoccurring Issue in Developing Countries PDFKALKIDAN KASSAHUNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Windsor-Tecumseh By-Election PollDokument7 SeitenWindsor-Tecumseh By-Election PollwindsorstarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 BSMTDokument5 SeitenChapter 3 BSMTjmar0% (1)
- Marketing Plans: Saying How You'll Get SalesDokument32 SeitenMarketing Plans: Saying How You'll Get SalesMahmoud AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differences Between Applied Research and Fundamental (Basic) ResearchDokument8 SeitenDifferences Between Applied Research and Fundamental (Basic) ResearchRowemar P. CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipor Report v4Dokument193 SeitenIpor Report v4Muhammad Mudasar SarkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Gap and Theoretical FrameworkDokument14 SeitenResearch Gap and Theoretical FrameworkAbdul Moiz YousfaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sociology As A Scientific Discipline - EditedDokument5 SeitenSociology As A Scientific Discipline - EditedMunyao JustusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Development of Multi-Purpose Chair in Educational SettingDokument26 SeitenDesign and Development of Multi-Purpose Chair in Educational SettingVinze Jan Santos100% (2)
- Impact of Service Quality on Passenger Satisfaction in Sri Lankan AirlinesDokument11 SeitenImpact of Service Quality on Passenger Satisfaction in Sri Lankan AirlinesBuddhika GonagalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Teachers' Role As Curricularist in The 21 CenturyDokument6 SeitenThe Teachers' Role As Curricularist in The 21 CenturyIckie BalandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employability Report Work SampleDokument2 SeitenEmployability Report Work Sampleapi-356625141Noch keine Bewertungen
- AhpDokument10 SeitenAhpIAEME PublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coutinho Nascimento FA 2014 PHD ThesisDokument381 SeitenCoutinho Nascimento FA 2014 PHD ThesisErica SandersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Understanding Markets, Market Demand, and The Marketing EnvironmentDokument34 SeitenChapter 3 - Understanding Markets, Market Demand, and The Marketing EnvironmentArman100% (1)
- Bentuk Kebenaran - Keyakinan Atau Iman - Kesaksian Ahli - Perjanjian Sederhana - IlmuDokument8 SeitenBentuk Kebenaran - Keyakinan Atau Iman - Kesaksian Ahli - Perjanjian Sederhana - IlmuLaela Intan RamadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gudmundsdóttir, D. G. 2013. The Impact of Economic Crisis On HappinessDokument19 SeitenGudmundsdóttir, D. G. 2013. The Impact of Economic Crisis On HappinessAntonio Casado da RochaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enterprise DG Publication: A Manual For Evaluating The Quality Performance of Tourist Destinations and ServicesDokument52 SeitenEnterprise DG Publication: A Manual For Evaluating The Quality Performance of Tourist Destinations and ServicesPham Phuong TungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fenton (2012) - The Cost of Satisfaction - A National Study of Patient Satisfaction, Health Care Utilization, Expenditures, and MortalityDokument7 SeitenFenton (2012) - The Cost of Satisfaction - A National Study of Patient Satisfaction, Health Care Utilization, Expenditures, and Mortalityghcabsb87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Social Media Influences on Students' ConsumerismDokument23 SeitenSocial Media Influences on Students' ConsumerismLorielle PamaylaonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cjce 2013 0595 PDFDokument13 SeitenCjce 2013 0595 PDFaymannasserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Student Satisfaction and Self Confidence With High Fidelity Simulation at Arab American University - PalestineDokument9 SeitenNursing Student Satisfaction and Self Confidence With High Fidelity Simulation at Arab American University - PalestineGlobal Research and Development ServicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing ResearchDokument256 SeitenMarketing ResearchsrvarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 100 Most Eminent Psychologists of The 20th CenturyDokument14 SeitenThe 100 Most Eminent Psychologists of The 20th CenturyFábio Augusto CalóNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 5Dokument66 SeitenChapter 1 5Jennylyn BraceroNoch keine Bewertungen