Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
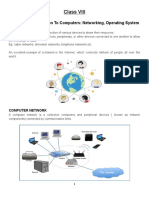
MODULE 1 Introduction To Network
Hochgeladen von
Chiew Hui LooOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MODULE 1 Introduction To Network
Hochgeladen von
Chiew Hui LooCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
N NN N N NN NE EE E E EE ET TT T T TT TW WW W W WW WO OO O O OO OR RR R R RR RK KK K K KK K
K KK K K KK KE EE E E EE EM MM M M MM ME EE E E EE EN NN N N NN NT TT T T TT TE EE E E EE ER RR R R RR RI II I I II IA AA A A AA AN NN N N NN N P PP P P PP PE EE E E EE EL LL L L LL LA AA A A AA AJ JJ J J JJ JA AA A A AA AR RR R R RR RA AA A A AA AN NN N N NN N M MM M M MM MA AA A A AA AL LL L L LL LA AA A A AA AY YY Y Y YY YS SS S S SS SI II I I II IA AA A A AA A
S SS S S SS Se ee e e ee eI II I I II If ff f f ff f A AA A A AA Ac cc c c cc cc cc c c cc ce ee e e ee es ss s s ss ss ss s s ss s L LL L L LL Le ee e e ee ea aa a a aa ar rr r r rr rn nn n n nn ni ii i i ii in nn n n nn ng gg g g gg g M MM M M MM Mo oo o o oo od dd d d dd du uu u u uu uI II I I II Ie ee e e ee e
Curriculum Development Centre
Ministry of Education
l
llt
tt1
11 l
lll
llI
II0
00l
ll
t
tt)
)) l
ll0
00l
ll
0
00t
tt0
00
0
00
l
ll)
))
t
tth
hh0
000
00I
II
F FF F
F FF FF FF Fl ll l
l ll ll ll l0 00 0
0 00 00 00 0j jj j
j jj jj jj jl ll l
l ll ll ll l
N NN N
N NN NN NN NN NN N
N NN NN NN N0 00 0
0 00 00 00 0
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
1
MODULE 1
I IN NT TR RO OD DU UC CT TI IO ON N T TO O N NE ET TW WO OR RK KS S
Curriculum Development Centre
Ministry of Education
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
2
1. Name of Module: Introduction to Networks
2. Learning Outcomes: Students should be able to:
a. define networks
b. list benefits of computer networks
c. identify the devices needed in computer networks
d. list types of computer networks
e. differentiate types of computer networks
f. state types of network topology (LAN, WAN, MAN)
g. explain current technology in computer networks
3. Knowledge and Skills
a. Network definitions
b. Benefits of sharing devices, data and information and internet access
c. Recognize devices for computer networks
d. List and differentiate the types of computer networks
e. List Types of network topology
f. Discuss and gather information on the current technology in computer
networks
4. Module Summary:
At the end of the module, students should be able to define networks, list the benefits and
the types of computer networks as well as network topology. They should be able to identify
the devices needed in computer networks and explain the current technology used in
computer networks.
This module contain 4 activities
Activity 1: Introduction to Networks
Activity 2: Type of Computer Networks
Activity 3: Network Topology
Activity 4: Current Technology in Computer Networks
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
3
Activity 1: Introduction to Networks
(a) Networks Definition
A network consists of two or more computers that are linked in order to share resources
(such as printers and CD-ROMs), exchange files, and allow electronic communications. The
computers on a network may be linked through cables, telephone lines, radio waves,
satellites or infrared light beams.
(b) Benefits of Computer Networks
1. File Sharing - Network file sharing between computers gives you more flexibility
rather than using floppy drives or Zip drives. you can use the network to save
copies of your important data on a different computer, examples share photos,
music files and documents.
2. Sharing Devices. Sharing devices is another benefit in which a network exceeds
stand-alone computers. For example laser printers, fax machines, modems,
scanners and CD-ROM players, when these peripherals are added to a network,
they can be shared by many users.
3. Sharing Internet Access. In computer network, students can access the internet
simultaneously.
4. Speed. Using a network is faster way for sharing and transferring files. Without a
network, files are shared by copying them to floppy disk.
5. Cost. Networkable versions of many popular software programmes are available
at considerable savings compared to buying individual licensed copies. Its allows
easier upgrading of the program.
6. Security. Files and programmes on a network are more secure as the users do
not have to worry about illegal copying of programmes. Passwords can be
applied for specific directories to restrict access to unauthorized users.
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
4
7. Centralized Software Management. One of the greatest benefits of installing a
school network is the fact that all of the software can be loaded on one computer
(the server). This saves time and energy when installing updates and tracking
files.
8. Electronic Mail. A network that provides the hardware necessary to install an e-
mail system. E-mails help in personal and professional communication for all
school personnel as it enables the spread of general information to the entire
school staff. Example, electronic mail on LAN (Local Area Network) enables
students to communicate with teachers and peers at their own school when
connected to the Internet, it enables users to communicate with others.
9. Flexible Access. School networks allow students to access their files from
computers throughout the school. Some schools provide public access to
students to begin an assignment in the computer lab and save then access the
file when they are at a cyber caf or home.
(c) Devices Needed in Computer Networks.
Hub
A central device that provides a common connection point
for nodes on a network.
Network Interface Card
A NIC (network interface card) is a piece of computer
hardware designed to allow computers to communicate
over a computer network.
Router
A device that forwards data packets along networks. A
router is connected to at least, two networks, commonly
two LANs or WANs or a LAN and its ISPs network.
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
5
Connector
Short for Registered Jack-45, an eight-wire connector used
commonly to connect computers onto a local-area network
(LAN), especially Ethernets. RJ-45 connectors look similar
to RJ-11 connectors used for connecting telephone
equipment.
Modem
Short for modulator-demodulator. A modem is a device or
program that enables a computer to transmit data over
telephone or cable lines. Computer information are stored
digitally, whereas information transmitted over telephone
lines are transmitted in a form of analogue waves. A
modem converts between these two forms.
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
6
Activity 2: Types of Computer Networks:
(a) Local Area Network (LAN)
Local Area Network are groups of computers and network devices connected together,
usually within the same building. The simplest form of LAN is to connect two computers
together.
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
7
(b) Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
MAN is a network that interconnect users with computer resources in a geographic area or
region larger than that covered by a local area network (LAN) but smaller than the area
covered by wide area network (WAN)
(c) Wide Area Network (WAN)
Wide Area Network is defined as a group of computers and network devices connected
across a large physical areas such as states or countries. Computers connected to a Wide
Area Network are often connected through the telephone system. They can also be
connected through leased lines or satellites. The largest WAN in existence is the Internet.
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
8
(d) Differences between Types of Computer Networks
Criteria LAN MAN WAN
Cost Low High Higher
Network Size Small Larger Largest
Speed Fastest Faster Fast
Transmission
Media Type
Twisted-Pair
Twisted-Pair and
Fibre-Optic
Fibre-Optic, radio
wave and satellite
Number of
computer
Smallest Large Largest
Activity 3: Types Of Network Topology :
(a) Star Network
A star network is also known as star topology. A star network is designed with each node
(file server, workstations, and peripherals) connected directly to a central network hub. The
hub will control the flow of communication in the network. If one of the nodes fails, the star
network will still function as long as the hub is working.
Star Network
Nodes
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
9
(b) Ring Network
Ring network is also known as ring topology. A ring network consists of all computers and
other devices that are connected in a loop. In a ring network, each node connects directly to
the neighbouring nodes. If the device on a ring network fails, all the devices before the failed
device are unaffected but those after the failed device will not function.
Ring Network
(c) Bus Network
A bus network is also known as a bus topology. A bus network consists of a single cable to
which all the computers and other devices are connected. It must have a common backbone
(the central cable) to connect all the devices. If one of the nodes fails, the bus network will
still function.
Bus Network
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
10
Activity 4: Current Technology in Computer Networks
(a) Wi-Fi
Official Wi-Fi logo
Wi-Fi (wireless fidelity) is a set of standards that refers to the Wireless Local Area Network
(WLAN) that applies IEEE 802.11 specification. Currently in
Some of the advantages of using Wi-Fi are as follows:
Simplicity. You can connect computers anywhere in your home or school without
the use for wires. Computers connected to the network using radio signals and
computers can be up to 30 meters or so apart.
Cost Wireless Networks are easy to set up and are inexpensive.
Easy Access Wi-Fi supports
1
roaming by moving your computers from one access
point to another as you move around a
2
hot spot. Wi-Fi works like a two-way radio
communication.
A computers wireless adapter translates data into a radio signal and transmits it using an
3
antenna. A wireless router receives the signal and
4
decodes it. It sends the information to
the internet using a physical, wired Ethernet connection.
To receive the signal, the router will receive data from the Internet, translating it into a radio
signal and sending it back to the wireless adapter.
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
11
(b) Bluetooth
Bluetooth logo Bluetooth Headset
Bluetooth is a network standard, specifically a protocol that defines how two Bluetooth
devices use short-range radio waves to transmit data. The data transfers between the
devices at a rate of up to 2 Mbps. To communicate with each other, Bluetooth devices must
be within 10 metres but can be extended to 100 metres with additional equipment.
A Bluetooth device contains a small chip that allows it to communicate with another
Bluetooth device. Examples of Bluetooth-enabled devices are desktop computers, notebook
computers, handheld computers, PDAs, smart phones, headset, microphones, digital
cameras, fax machines and printers.
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
12
For computers and devices that are not Bluetooth-enabled, you can purchase a Bluetooth
wireless port adapter that will convert an existing USB port or serial port into a Bluetooth
port. For example, Windows XP has a built-in Bluetooth support that allows users to easily
configure Bluetooth communications.
Are Wi-Fi and Bluetooth competing technologies?
Bluetooth is designed for limited data transfer between two devices, one of which is usually a
mobile device (e.g. a notebook computer and a printer, a digital camera and a desktop
computer and between two PDAs). However Wi-Fi which supports data transfer at faster
rates allow users to network many computers and devices together wirelessly.
GLOSSARY
1
roaming the ability to move from one coverage area to another without interruption
in service or lost in connectivity.
2
hot spot a geographic area that is covered by a wireless network so that internet
access is made available to any device with a wireless card.
3
antenna a component of a radio device that radiates radio waves from the source
and also receives signals from other transmitters.
4
decodes the conversion of encoded data back to its original form.
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
13
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
http://www.seniortechcenter.org/hardware_and_software/network_benefits.php
http://compnetworking.about.com/cs/wireless/f/whywirelesslan.htm
http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/sDefinition/0,,sid7_gci214083,00.html
http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/W/wide_area_network_WAN.html
http://www.the-itleader.com/glossary/wireless-fidelity.html
http://www.bethamir.com/MAN.gif
lCTL ron SccoNoAnY ScHooL - NcTwonKs ANo THc lNTcnNcT
14
Title : Network
Module 1 Introduction to Network
Students Name : ______________________________________________
Class : _______________________________________________________
At the end of the lesson pupil have learn the following skills :
Please tick ( ) one of the check box
SKILLS
DONT
KNOW
A LITTLE AVERAGE GOOD EXCELLENT
Define networks
List benefits of computer
networks
Identify the devices needed
in a computer Networks
List types of computer
networks
Differentiate types of
computer Networks
State types of network
topology
Explain current technology in
computer networks
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Module1-Introduction To NetworkDokument14 SeitenModule1-Introduction To NetworkUsop AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 8 Ch-1 Computer Network NotesDokument13 SeitenClass 8 Ch-1 Computer Network NotesHaresh NathaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network For Class 8 IcseDokument6 SeitenNetwork For Class 8 IcseGAMING WITH MaDMAN100% (1)
- Sir Gavs - Chapter 11Dokument11 SeitenSir Gavs - Chapter 11Jel MCNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.0 NetworkDokument24 Seiten2.0 NetworkChinta QaishyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network Concepts Week 2Dokument16 SeitenComputer Network Concepts Week 2emerson rebibisNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS - WEEK 1 2nd QTRDokument14 SeitenLAS - WEEK 1 2nd QTRarlyn villanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M08 Hand ToolsDokument38 SeitenM08 Hand Toolsgashaw mekonnenNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Based Networks BasicDokument14 SeitenIP Based Networks BasicAbi AnnunNoch keine Bewertungen
- LO 1 NewDokument52 SeitenLO 1 NewEdgar BatistianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLE ICT 10 Q4 INC Week1 4Dokument22 SeitenTLE ICT 10 Q4 INC Week1 4roland james lacabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Activity Sheet In: Computer Systems ServicingDokument12 SeitenLearning Activity Sheet In: Computer Systems ServicingCarvalds 0315Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 1 Week 4 Module 4: Computer Systems Servicing Ncii (TVL-ICT)Dokument14 SeitenQuarter 1 Week 4 Module 4: Computer Systems Servicing Ncii (TVL-ICT)PRESIDENT ELPIDIO QUIRINO NHSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Internet TechnologiesDokument15 SeitenIntroduction to Internet Technologiesfreedom mutepfeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Computer NetworksDokument21 SeitenUnderstanding Computer Networkssasi_17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year4 2nd Semester Computer Science EducationDokument48 SeitenYear4 2nd Semester Computer Science Educationzhwv64bdhtNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUTORIAL SHEET-1 (Solution) : Kcs-603: Computer NetworksDokument8 SeitenTUTORIAL SHEET-1 (Solution) : Kcs-603: Computer NetworksANAMIKA SRIVASTAVANoch keine Bewertungen
- TLE ICT 10 Q4 INC Week1 8Dokument40 SeitenTLE ICT 10 Q4 INC Week1 8LADY ANN GRACE LAGAS100% (2)
- Hawassa University Institute of Technology Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Stream Internship ProjectDokument20 SeitenHawassa University Institute of Technology Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Stream Internship ProjectmigadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 803 Web Application Class XI 1Dokument254 Seiten803 Web Application Class XI 1Naina KanojiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TVL Ict Computer Systems Servicing Ncii q1 Module 4 Passed 1Dokument21 SeitenTVL Ict Computer Systems Servicing Ncii q1 Module 4 Passed 1Leo LugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Marks QuestionsDokument58 Seiten2 Marks QuestionsPrashanth Kannan100% (1)
- On Computer Networking and SecurityDokument14 SeitenOn Computer Networking and SecurityshitaltadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pan/ I (W Rvilk Oi Data CDokument2 SeitenPan/ I (W Rvilk Oi Data CpaarveshNoch keine Bewertungen
- NGÂN HÀ BTEC-CO1 - LUẬN VĂNDokument23 SeitenNGÂN HÀ BTEC-CO1 - LUẬN VĂNNgân HàNoch keine Bewertungen
- (SUCN) : Set Up Computer NetworkDokument44 Seiten(SUCN) : Set Up Computer NetworkarkieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Project ReportDokument49 SeitenFinal Project ReportAllen NagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks (2-3)Dokument17 SeitenComputer Networks (2-3)younas125Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1: Introduction To NetworkingDokument12 SeitenModule 1: Introduction To NetworkingKihxan Poi Alonzo PaduaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OHS Safety Precautions PC ConfigurationDokument6 SeitenOHS Safety Precautions PC ConfigurationDakila Chea BetacheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 1Dokument18 SeitenPractical 1Harsh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adminstrate Network and Hardware PeripherialsDokument18 SeitenAdminstrate Network and Hardware PeripherialsDark KnightNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Teacher Will Show Students Some Picture of Network DevicesDokument3 SeitenThe Teacher Will Show Students Some Picture of Network DevicesJeruNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS2302 Computer Networks Anna University Engineering Question Bank 4 UDokument48 SeitenCS2302 Computer Networks Anna University Engineering Question Bank 4 UkuttymythuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network and The InternetDokument44 SeitenComputer Network and The InternetCj AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking and InternetDokument34 SeitenNetworking and InternetsangeethapanditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Networking TopologiesDokument26 SeitenWireless Networking TopologiesTamilarasan DeenathayalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilovepdf MergedDokument9 SeitenIlovepdf Mergedade ApriliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- It FastrackDokument97 SeitenIt FastrackAanand SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Assignment in CnsDokument7 SeitenFirst Assignment in CnsAlcala, John Paul P.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class8 Networking ConceptsDokument3 SeitenClass8 Networking ConceptsDiva75% (8)
- NetworkingDokument41 SeitenNetworkingBINS THOMASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking: A Survey: September 2015Dokument6 SeitenComputer Networking: A Survey: September 2015Mahatab RickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Guide Grade 7 - ICT 1Dokument8 SeitenLearning Guide Grade 7 - ICT 1Cabeyverse T3ELLYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 13Dokument11 SeitenUnit 13Luis Norbert SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking: A SurveyDokument6 SeitenComputer Networking: A SurveyAnuragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 25 Network FundamentalsDokument5 SeitenLesson 25 Network FundamentalsAssumpta Minette BurgosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1 IntroductionDokument36 SeitenLec 1 IntroductionShima NafieNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS2302-Computer Networks - Anna University Engineering Question Bank 4 UDokument49 SeitenCS2302-Computer Networks - Anna University Engineering Question Bank 4 UsamlawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer NetworkDokument19 SeitenComputer NetworkDeepti SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix FDokument118 SeitenAppendix FAmey KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking: A Survey: September 2015Dokument6 SeitenComputer Networking: A Survey: September 2015VaradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication CSE 225/233Dokument35 SeitenData Communication CSE 225/233Mamun Ahmed joyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key to All About Computers 8 - Progress PublishersDokument48 SeitenKey to All About Computers 8 - Progress PublishersPranay verma 7BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adama Poly Technique Colleg1Dokument32 SeitenAdama Poly Technique Colleg1Mahdi ZeynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Area Networks: An Introduction to the TechnologyVon EverandLocal Area Networks: An Introduction to the TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking Beginners Guide: An Introduction on Wireless Technology and Systems Security to Pass CCNA Exam, With a Hint of Linux Programming and Command LineVon EverandComputer Networking Beginners Guide: An Introduction on Wireless Technology and Systems Security to Pass CCNA Exam, With a Hint of Linux Programming and Command LineNoch keine Bewertungen
- CheckDokument3 SeitenCheckChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssessmentDokument13 SeitenAssessmentchobits_nemesisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pusat Perkembangan Kurikulum Kementerian Pelajaran MalaysiaDokument21 SeitenPusat Perkembangan Kurikulum Kementerian Pelajaran MalaysiaChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet Applications ModuleDokument13 SeitenInternet Applications ModuleChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Netiquette NotesDokument5 SeitenModule 3 Netiquette NotesChiew Hui Loo100% (1)
- MODULE 3 Sharing HardwareDokument12 SeitenMODULE 3 Sharing HardwareChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 3 Sharing HardwareDokument12 SeitenMODULE 3 Sharing HardwareChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharing Documents Over a NetworkDokument16 SeitenSharing Documents Over a NetworkChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Intro InternetDokument7 SeitenModule 1 - Intro InternetChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICTL ProgramDokument22 SeitenICTL ProgramChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- EthicsDokument1 SeiteEthicsSahidaNur IedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyber LawDokument9 SeitenCyber LawChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering DrawingDokument34 SeitenEngineering DrawingChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete The Crossword With The Simple Past Forms of The Irregular VerbsDokument2 SeitenComplete The Crossword With The Simple Past Forms of The Irregular VerbsChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete The Crossword With The Simple Past Forms of The Irregular VerbsDokument2 SeitenComplete The Crossword With The Simple Past Forms of The Irregular VerbsChiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 - Geometrical Constructions (P2) .Dokument7 Seiten13 - Geometrical Constructions (P2) .Chiew Hui LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost and Benefit Analysis of Outsourcing From The Perspective of Datapath LTDDokument59 SeitenCost and Benefit Analysis of Outsourcing From The Perspective of Datapath LTDranzlorenzoo100% (1)
- PExam 2020Dokument126 SeitenPExam 2020Omama MaazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vsip - Info - Ga16de Ecu Pinout PDF FreeDokument4 SeitenVsip - Info - Ga16de Ecu Pinout PDF FreeCameron VeldmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benedict - Ethnic Stereotypes and Colonized Peoples at World's Fairs - Fair RepresentationsDokument16 SeitenBenedict - Ethnic Stereotypes and Colonized Peoples at World's Fairs - Fair RepresentationsVeronica UribeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finding My Voice in ChinatownDokument5 SeitenFinding My Voice in ChinatownMagalí MainumbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Escalado / PLC - 1 (CPU 1214C AC/DC/Rly) / Program BlocksDokument2 SeitenEscalado / PLC - 1 (CPU 1214C AC/DC/Rly) / Program BlocksSegundo Angel Vasquez HuamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BC Planning EvenDokument5 SeitenBC Planning EvenRuth KeziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why study operating systems and how they workDokument12 SeitenWhy study operating systems and how they workMario ManihurukNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Yield Pics For STEP 2 CKDokument24 SeitenHigh Yield Pics For STEP 2 CKKinan Alhalabi96% (28)
- Mathematics Specimen Papers and Mark Schemes UG013054Dokument102 SeitenMathematics Specimen Papers and Mark Schemes UG013054minnie murphy86% (7)
- EVS XT2+ Tech Ref Software Manual v10.03 PDFDokument80 SeitenEVS XT2+ Tech Ref Software Manual v10.03 PDFgibonulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tipolo WH Gantt ChartDokument15 SeitenTipolo WH Gantt ChartMayeterisk RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Footprints 080311 For All Basic IcsDokument18 SeitenFootprints 080311 For All Basic IcsAmit PujarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory SafetyDokument4 SeitenLaboratory SafetyLey DoydoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Picco Tac 1095 N Hydrocarbon ResinDokument2 SeitenPicco Tac 1095 N Hydrocarbon ResindevanandamqaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NetworkingDokument1 SeiteNetworkingSherly YuvitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adventures in PioneeringDokument202 SeitenAdventures in PioneeringShawn GuttmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenatal AssessmentDokument9 SeitenAntenatal Assessmentjyoti singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mpce 24Dokument39 SeitenMpce 24Sachin Mehla0% (1)
- Asian Games African Games: Beach VolleyballDokument5 SeitenAsian Games African Games: Beach VolleyballJessan Ybañez JoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land-Use PlanningDokument15 SeitenLand-Use PlanningCiara MaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educating The PosthumanDokument50 SeitenEducating The PosthumanCatherine BrugelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ES1 Work Panel DatasheetDokument3 SeitenES1 Work Panel DatasheetGerardo Alberto Navarro LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressing and Finishing (Latest)Dokument8 SeitenPressing and Finishing (Latest)Imran TexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan ElementaryDokument3 SeitenSemi Detailed Lesson Plan ElementaryJinky JunioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 Diesel TOYOTA Jun11Dokument90 Seiten2018 Diesel TOYOTA Jun11eko sulistyo75% (4)
- Big Band EraDokument248 SeitenBig Band Erashiloh32575% (4)
- Literature Revisited: Understanding Key Concepts and Applying Analytical SkillsDokument31 SeitenLiterature Revisited: Understanding Key Concepts and Applying Analytical SkillsMuhammad Furqan Aslam Awan100% (2)
- JC Metcalfe - The Power of WeaknessDokument3 SeitenJC Metcalfe - The Power of Weaknesschopin23Noch keine Bewertungen
- List of SQAC DQAC SISC DISC 2019 20Dokument39 SeitenList of SQAC DQAC SISC DISC 2019 20Shweta jainNoch keine Bewertungen