Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Dialysis
Hochgeladen von
Anusha VergheseCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dialysis
Hochgeladen von
Anusha VergheseCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
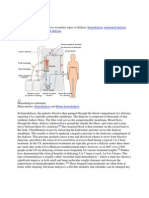
DEFINITION OF DIALYSIS: Dialysis treatment replaces the function of the kidneys, which normally serve as the body's natural
filtration system.
Through the use of a blood filter and a chemical solution known as dialysate, the treatment removes waste products and excess fluids from the bloodstream, while maintaining the proper chemical balance of the blood. Methods of therapy include 1. hemodialysis, 2. continuous renal replacement therapy and 3. various forms of peritoneal dialysis
NEED FOR DIALYSIS : The need for dialysis may be acute or chronic. Acute dialysis is indicated when there is a high and rising level of serum potassium, fluid overload, or
impending pulmonary edema, increasing acidosis, pericarditis, and severe confusion.
It may also be used to remove certain medications or other toxins(poisoning or medication overdose) from the blood.
Chronic or maintenance dialysis is indicated in chronic renal failure, known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), in the following instances: the presence of uremic signs and symptoms affecting all body systems nausea and vomiting, severe anorexia, increasing lethargy, mental confusion, hyperkalemia, fluid overload not responsive to diuretics and fluid restriction, and a general lack of well-being.
An urgent indication for dialysis in patients with chronic renal failure is pericardial friction rub. Patients with no renal function can be maintained by dialysis for years.
HEMODIALYSIS 1. Hemodialysis is performed to remove toxic wastes from the blood of patients in renal failure.
2. This potentially life-saving procedure removes blood from the body, circulates it through a purifying dialyzer and then returns the blood to the body. It is used for patients who are Acutely ill and Require short-term dialysis (days to weeks) and
For patients with ESRD who require long-term or permanent therapy.
A dialyzer (once referred to as an artificial kidney) serves as a synthetic semi permeable membrane, replacing the renal glomeruli and tubules as the filter for the impaired kidneys.
Patients receiving hemodialysis must undergo treatment for the rest of their lives or until they undergo a successful kidney transplant. Treatments usually occur three times a week for at least 3 to 4 hours per treatment
PRINCIPLES OF HEMODIALYSIS Diffusion, osmosis, and ultrafiltration are the principles on which hemo dialysis works COMPLICATIONS OF HEMODIALYSIS:
The patient is subject to a number of problems and complications.
One leading cause of death among patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis is 1. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Disturbances of lipid metabolism 2. Heart failure, 3. coronary heart disease and 4. anginal pain, 5. stroke, 6. peripheral vascular insufficiency 7. Anemia and fatigue contribute to diminished 8. physical and emotional well-being,
9. lack of energy and drive, and 10. loss of interest. 11. Gastric ulcers and other gastrointestinal problems 12. . Disturbed calcium metabolism leads to renal osteodystrophy that produces bone pain and fractures.
Other problemsinclude : 1. fluid overload associated with heart failure, malnutrition, 2. infection, 3. neuropathy, and 4. pruritus. 5. Up to 85% of people undergoing hemodialysis experience major sleep problems .
CONTINUOUS RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES: 1. Continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration (CAVH) 2. Continuous arteriovenous hemodialysis (CAVHD) 3. Continuous venovenous hemofiltration (CVVH) 4. Continuous venovenous hemodialysis (CVVHD)
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
1. The goals of peritoneal dialysis are to remove toxic substances and metabolic wastes and to re-establish normal fluid and electrolyte balance. 2. Peritoneal dialysis is the treatment of choice for patients with renal failure who are unable or unwilling to undergo hemodialysis or renal transplantation.
COMPLICATIONS OF PERITONNEAL DIALYSIS:
Peritonitis leakage of dialysate through the catheter site may occur bleeding
LONG-TERM COMPLICATIONS Hypertriglyceridemia, abdominal hernias (incisional, inguinal, diaphragmatic, and umbilical), It also aggravates symptoms of hiatal hernia and hemorrhoids. Low back pain and anorexia from fluid in the abdomen and constant sweet taste related to glucose absorption may also occur.
CONCLUSION: Dialysis treatment replaces the function of the kidneys, which normally serve as the body's natural filtration system. Through the use of a blood filter and a chemical solution known as dialysate, the treatment removes waste products and excess fluids from the bloodstream, while maintaining the proper chemical balance of the blood.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Renal Replacement Therapies Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisDokument86 SeitenRenal Replacement Therapies Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisSabita Tripathi100% (2)
- DIALYSISDokument6 SeitenDIALYSISJobelle AcenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DialysisDokument34 SeitenDialysisdaisy100% (2)
- Hemodialysi S: Ariane Jake C. Fernandez, RN, MSNDokument37 SeitenHemodialysi S: Ariane Jake C. Fernandez, RN, MSNMicah Alexis Candelario100% (3)
- Diabetes InsipidusDokument10 SeitenDiabetes InsipidusRahul K. JagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes Insipidus: Nitha K 2 Year MSC NursingDokument47 SeitenDiabetes Insipidus: Nitha K 2 Year MSC NursingNITHA K100% (1)
- Coronary Care Unit/ Cardiac Care Unit: Patient MonitorsDokument3 SeitenCoronary Care Unit/ Cardiac Care Unit: Patient MonitorsPhoebe Kyles Camma100% (1)
- Hemodialysis PDFDokument20 SeitenHemodialysis PDFGiri Siva71% (7)
- Heart BlockDokument10 SeitenHeart BlockEköw Santiago JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart Failure: Dr. J. SaravananDokument31 SeitenCongestive Heart Failure: Dr. J. Saravananpetervazhayil100% (1)
- Retinal DetachmentDokument6 SeitenRetinal DetachmentNader Smadi100% (3)
- TypesDokument3 SeitenTypesProser Faith TabaculdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Cardiomyopathy PPT NEWDokument62 SeitenA Cardiomyopathy PPT NEWShetal Sharma100% (1)
- Defibrillation TypedDokument8 SeitenDefibrillation TypedValarmathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care NursingDokument7 SeitenCritical Care NursingShilpa JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Transfusion TeachingDokument18 SeitenBlood Transfusion Teachingapi-277522722Noch keine Bewertungen
- Status Asthmaticus DefinitionDokument2 SeitenStatus Asthmaticus Definitionhemaanandhy0% (1)
- Nursing Management of The Critically Ill PatientDokument28 SeitenNursing Management of The Critically Ill PatientAtinder Sran100% (2)
- Acute Renal Failure TeoriDokument24 SeitenAcute Renal Failure TeoriVera Andri YaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse OximetryDokument3 SeitenPulse OximetryJanna Favila100% (3)
- Hepatic EncephalopathyDokument3 SeitenHepatic EncephalopathySuhas KandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Liver DiseaseDokument12 SeitenChronic Liver DiseaseamitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Liver CirrhosisDokument10 SeitenNotes Liver CirrhosisSanthu SuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dialyzer Reuse For DialysisDokument25 SeitenDialyzer Reuse For DialysisAndriKusuma100% (3)
- Assignment On Radiation TherapyDokument16 SeitenAssignment On Radiation TherapyAxsa AlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peritoneal DialysisDokument12 SeitenPeritoneal DialysisSheeba StephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Reconstructive & Cosmetic SurgeryDokument28 SeitenTypes of Reconstructive & Cosmetic SurgerySimon JosanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peritoneal Dialysis SeminarDokument25 SeitenPeritoneal Dialysis SeminardrresmiajithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument34 SeitenCase StudyBSNNursing101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Renal FailureDokument17 SeitenAcute Renal FailureDina Rasmita100% (1)
- Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary AngioplastyDokument22 SeitenPercutaneous Transluminal Coronary AngioplastyArya Gaunker100% (1)
- Peritoneal DialysisDokument3 SeitenPeritoneal DialysisSumit YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Block: BY DR - AriyalakshmiDokument26 SeitenHeart Block: BY DR - AriyalakshmiDiksha chaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HemodialysisDokument19 SeitenHemodialysisK.R.Raguram88% (26)
- Cardiovascular Assessment: Assessment Uses of CVS AssessmentDokument8 SeitenCardiovascular Assessment: Assessment Uses of CVS AssessmentKawaljit KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fulminant Hepatic FailureDokument50 SeitenFulminant Hepatic FailureSangeeta BSRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colostomy Care: Sital B Sharma MSC Nursing Part I Con, NBMCDokument39 SeitenColostomy Care: Sital B Sharma MSC Nursing Part I Con, NBMCShetal Sharma100% (1)
- 1 - Scope of Critical Care NursingDokument20 Seiten1 - Scope of Critical Care Nursinghanimozaghi100% (1)
- BPT GTT & Diabetes MellitusDokument25 SeitenBPT GTT & Diabetes MellitusBalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Mastectomy Exercises PPDokument11 SeitenPost Mastectomy Exercises PPLyrae Kaye Chio80% (5)
- Cardaic Emergency Drugs.Dokument13 SeitenCardaic Emergency Drugs.Alma SusanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of ComaDokument14 SeitenCare of ComaAhmed Fahmy100% (1)
- CirrhosisDokument54 SeitenCirrhosisYani86% (7)
- Emphysema: Presented By: Mis. M.K.Kaku Nursing TutorDokument10 SeitenEmphysema: Presented By: Mis. M.K.Kaku Nursing TutorKaku ManishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esophageal Stricture and ObstructionDokument11 SeitenEsophageal Stricture and ObstructionBibi Renu100% (6)
- TNAIDokument11 SeitenTNAISimran Josan100% (1)
- Critical Care NursingDokument2 SeitenCritical Care NursingJyoti KathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of A Bedridden Patient: Prepared by Jannet Reena PuraniDokument25 SeitenCare of A Bedridden Patient: Prepared by Jannet Reena PuraniAnn Merlin Jobin100% (1)
- Eye Banking OphthalmologyDokument21 SeitenEye Banking Ophthalmologyvivekrajbhilai5850100% (2)
- Tread Mill Test TMTDokument5 SeitenTread Mill Test TMTश्रीकृष्ण हेङ्गजू100% (1)
- HEMODIALYSISDokument7 SeitenHEMODIALYSISClarisse ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal CrisisDokument6 SeitenAdrenal CrisisSteven SetioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of Patients With Mechanical VentilatorDokument4 SeitenCare of Patients With Mechanical VentilatorIman Bee Sanayon0% (1)
- Perforated PeritonitisDokument5 SeitenPerforated PeritonitisDeepak singh ratheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fulminant Hepatic FailureDokument8 SeitenFulminant Hepatic Failuremiz uNoch keine Bewertungen
- Streptokinase GroupDokument16 SeitenStreptokinase GroupSuffocated LiveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cystometry "Cystometrogram" (CMG)Dokument7 SeitenCystometry "Cystometrogram" (CMG)Wendy EscalanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodialysis 1Dokument25 SeitenHemodialysis 1Jasmine KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide:: DialysisDokument13 SeitenStudy Guide:: DialysisDan Dan ManaoisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dialysis: Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisDokument38 SeitenDialysis: Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisNish Macadato BalindongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles For Successful Staff DevelopmentDokument3 SeitenPrinciples For Successful Staff DevelopmentAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Staff DevelopmentDokument2 SeitenTypes of Staff DevelopmentAnusha Verghese83% (6)
- GerentologyDokument17 SeitenGerentologyAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Staff-Development ProgramsDokument2 SeitenGuidelines For Staff-Development ProgramsAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Public RelationsDokument3 SeitenMethods of Public RelationsAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- Physiology of NewbornDokument3 SeitenPhysiology of NewbornAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public RelationsDokument5 SeitenPublic RelationsAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- Public RelationsDokument5 SeitenPublic RelationsAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- Principles For Successful Staff DevelopmentDokument3 SeitenPrinciples For Successful Staff DevelopmentAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occupational Health and SafetyDokument8 SeitenOccupational Health and SafetyAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public Relation in HospitalDokument6 SeitenPublic Relation in HospitalAnusha Verghese75% (4)
- Roles and Functions of Administrator in Staff DevelopmentDokument2 SeitenRoles and Functions of Administrator in Staff DevelopmentAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Types of Staff DevelopmentDokument2 SeitenTypes of Staff DevelopmentAnusha Verghese83% (6)
- Staff DevelopmentDokument3 SeitenStaff DevelopmentAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Nursing Superintendent Grade IIDokument2 SeitenNursing Superintendent Grade IIAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- Joint Director of NursingDokument2 SeitenJoint Director of NursingAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Tutor and Clinical InstructorsDokument2 SeitenNursing Tutor and Clinical InstructorsAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Organization of HospitalDokument29 SeitenOrganization of HospitalAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Superintendent Grade IDokument2 SeitenNursing Superintendent Grade IAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assistant Professor Nursing CollegeDokument3 SeitenAssistant Professor Nursing CollegeAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Staff Nurse Job DescriptionDokument4 SeitenStaff Nurse Job DescriptionAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group DynamicsDokument10 SeitenGroup DynamicsAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- PeplauDokument13 SeitenPeplauAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Principal CollegeDokument4 SeitenPrincipal CollegeAnusha Verghese50% (2)
- Senior Staff Nurse Job DescriptionDokument2 SeitenSenior Staff Nurse Job DescriptionAnusha Verghese70% (10)
- Consumer ActDokument13 SeitenConsumer ActAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professor CollegeDokument3 SeitenProfessor CollegeAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrincipalDokument3 SeitenPrincipalAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ved AnalysisDokument2 SeitenVed AnalysisAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Judgement MethodDokument17 SeitenProfessional Judgement MethodAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Sirosis PHDokument11 SeitenNon Sirosis PHHIstoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- FCPS Oct 2015-1Dokument9 SeitenFCPS Oct 2015-1Kahkashan HameedNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Causes EpilepsyDokument2 SeitenWhat Causes EpilepsyJames CollinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- My:optima Secure: HDFC ERGO General Insurance Company Limited ProspectusDokument18 SeitenMy:optima Secure: HDFC ERGO General Insurance Company Limited ProspectusManoj KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health 8 Quarter 1Dokument10 SeitenHealth 8 Quarter 1jayaaron.reyes.cNoch keine Bewertungen
- AFAA Personal Trainer CertificationDokument7 SeitenAFAA Personal Trainer CertificationubersteveNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIF - Version 9 FillableDokument3 SeitenCIF - Version 9 FillableCITY OF ILAGAN MEDICAL CENTERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular DiseaseDokument9 SeitenCardiovascular DiseaselizNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHLP Cum Learning Activity Sheets: Teacher's NoteDokument10 SeitenWHLP Cum Learning Activity Sheets: Teacher's NoteNeil BargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDC Salmonella FactsheetDokument2 SeitenCDC Salmonella FactsheetPanada SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garner 1511222Dokument17 SeitenGarner 1511222Bj LongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Denagard Amoxicillin MICs For Respiratory PathogensDokument2 SeitenDenagard Amoxicillin MICs For Respiratory Pathogensnick224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing Solutions/To Prevent Depression (2019) : Pavia National High School Evangelista ST., Pavia, IloiloDokument13 SeitenAssessing Solutions/To Prevent Depression (2019) : Pavia National High School Evangelista ST., Pavia, IloiloChimmy NochuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SURGERY - Complete 2nd EdDokument137 SeitenSURGERY - Complete 2nd Edlailatul husna100% (4)
- Brain WavesDokument6 SeitenBrain WavesDaniel MagurianuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment MnemonicsDokument23 SeitenAssessment MnemonicsAilene Ponce Fillon100% (1)
- Acute Renal FailureDokument4 SeitenAcute Renal FailurePerrilyn PereyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homocysteine and Markers of Coagulation and Endothelial Cell ActivationDokument7 SeitenHomocysteine and Markers of Coagulation and Endothelial Cell ActivationMaya RustamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension JDHHDDDokument5 SeitenHypertension JDHHDDabcxyz15021999Noch keine Bewertungen
- CRYPTOSPORIDIOSISDokument17 SeitenCRYPTOSPORIDIOSISOrakle mkhwanaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Counseling Depressed ElderlyDokument4 SeitenCounseling Depressed ElderlyLara Sabunod - PalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mupirocin OintmentDokument8 SeitenMupirocin Ointmentapi-3801331100% (1)
- Nejm Pcsk9 StudyDokument10 SeitenNejm Pcsk9 Studyherbertgur777Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHOLECYSTITISDokument4 SeitenCHOLECYSTITISMarcieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table For Cestodes and TrematodesDokument5 SeitenTable For Cestodes and TrematodesDawn WRein Legaspi100% (3)
- 1 4931693113845481676 PDFDokument590 Seiten1 4931693113845481676 PDFRene Cardozo100% (4)
- Dehydration - Background, Pathophysiology, EpidemiologyDokument4 SeitenDehydration - Background, Pathophysiology, EpidemiologyAri GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mcqs and Seqs of BiochemistryDokument6 SeitenMcqs and Seqs of BiochemistrymisbahnazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referat Malaria InovDokument29 SeitenReferat Malaria InovAssifa RidzkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Step-By-Step Guide To Performing A Complete Abdominal ExaminationDokument8 SeitenA Step-By-Step Guide To Performing A Complete Abdominal Examinationjojohnson250Noch keine Bewertungen