Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tenses
Hochgeladen von
hadia23Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tenses
Hochgeladen von
hadia23Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
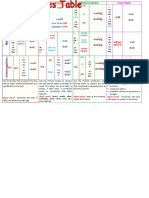
• Present simple • Present perfect
Used for action in the present, for things that are continuous/progressive
always true or that happen regularly, and for opinions Used for actions or events that started in the past
and beliefs but are still happening now, or for past actions which
I/we/you/they………. arrive (do not arrive) only recently finished and their effects are seen now
He/she/it………. arrives (does not arrive) I /you/we/they………. have been arriving (have
• Past simple not been arriving)
He/she/it………. has been arriving (has not been
Used for completed actions and events in the past
arriving)
I/we/you/they………. arrived (did not arrive)
He/she/it………. arrived (did not arrive) • Past perfect continuous/progressive
• Future simple Used for actions or events that happened for a
period of time but were completed before a particular
Used for actions and events in the future
time in the past
I/we/you/they………. will arrive (will not arrive)
I /you/we/they………. had been arriving (had not
He/she/it………. will arrive (will not arrive)
been arriving)
• Present perfect He/she/it………. had been arriving (had not been
Used to show that an event happened or an action arriving)
was completed at some time before the present • Future perfect
I/we/you/they………. have arrived (have not
arrived) continuous/progressive
He/she/it………. has arrived (has not arrived) Used for actions or events that will already be
happening at a particular time in the future
• Past perfect I /you/we/they………. will have been arriving
Used to show that an event happened or an action (will not have been arriving)
was completed before a particular time in the past He/she/it………. will have been arriving (will not
I/we/you/they………. had arrived (had not have been arriving)
arrived)
• Conditionals
He/she/it………. had arrived (had not arrived)
There are three main types of conditional
• Future perfect sentences. You can use these patterns to help you learn
Used to show that something will be completed them:
before a particular time in the future 1. If (present tense), ………. will + infinitive
I/we/you/they………. will have arrived (will not Use this pattern to talk about a possible condition
have arrived) and its likely result.
He/she/it………. will have arrived (will not have If she wins the next match, she'll be world
arrived) champion.
. Present continuous/progressive I'll go with him if he asks me.
Used for actions or events that are happening or 2. If (past tense), ………. would + infinitive
developing now, for future plans, or to show that an Use this pattern to talk about a situation that is
event is repeated imagined or not very likely.
I………. am arriving (am not arriving) If I was a millionaire, I'd sail around the world.
You/we/they………. are arriving (are not arriving) Formal: If I were a millionaire...
He/she/it………. is arriving (is not arriving) I'd be sick if I ate all that cake.
• Past continuous/progressive 3. If (past perfect),...would have+ past participle
Used for actions or events in the past that were not Use this pattern to talk about the possible result of
yet finished or that were interrupted an imagined situation in the past.
I………. was arriving (was not arriving) If John had asked for my advice, I would have
You/we/they………. were arriving (were not given it to him.
arriving) She would have seen us if she had looked
He/she/it………. was arriving (was not arriving)
• Future continuous/progressive
Used for actions or events that will continue into
the future
I /you/we/they………. will be arriving (will not
be arriving)
He/she/it………. will be arriving (will not be
arriving)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Become Your Higher SelfDokument142 SeitenBecome Your Higher Selfmhldcn100% (6)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Annotated Rockefeller Foundation Lockstep 2010Dokument54 SeitenThe Annotated Rockefeller Foundation Lockstep 2010Celso Miori100% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Earth's Forbidden Secrets - Searching For The PastDokument259 SeitenEarth's Forbidden Secrets - Searching For The PastSyncOrSwim100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Larry Niven THE THEORY AND PRACTICE OF TIME TRAVEL pt1Dokument4 SeitenLarry Niven THE THEORY AND PRACTICE OF TIME TRAVEL pt1J HalsteadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progressive Verb Tenses PowerpointDokument43 SeitenProgressive Verb Tenses PowerpointΑθηνουλα ΑθηναNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Best Year EverDokument13 SeitenYour Best Year EverFor You Language CenterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scenario Planning ToolDokument24 SeitenScenario Planning Toolmohamed.khalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Will Going To Present ContinuousDokument6 SeitenWill Going To Present Continuousilona1984Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nature of PlanningDokument2 SeitenNature of Planningjaanaan92% (24)
- BIG. Formgiving. An Architectural Future History - Exhibition Catalogues & Specific CollectionsDokument6 SeitenBIG. Formgiving. An Architectural Future History - Exhibition Catalogues & Specific Collectionsrikerita0% (5)
- The Isaiah Effect by Gregg BradenDokument8 SeitenThe Isaiah Effect by Gregg BradenKevin33% (3)
- Physics of A Breakthrough EnterpriseDokument10 SeitenPhysics of A Breakthrough EnterpriseSebastiao DuarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afirmative Sentence Negative Sentence Questions Shorts AnswersDokument9 SeitenAfirmative Sentence Negative Sentence Questions Shorts Answerspilarsilgado7174Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey On Futures Studies MethodsDokument10 SeitenA Survey On Futures Studies MethodsTawana MaditshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technological Forecasting & Social Change: Philippe Durance, Michel GodetDokument5 SeitenTechnological Forecasting & Social Change: Philippe Durance, Michel GodetSteeltonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Third Conditional 3Dokument2 SeitenThe Third Conditional 3John LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching For Hope - Walt WernerDokument9 SeitenTeaching For Hope - Walt Wernerapi-556600197Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic English Tenses Table GrammarDokument2 SeitenBasic English Tenses Table GrammarKatarina Vukičević VeljačaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herman de Vries PDFDokument120 SeitenHerman de Vries PDFNalkldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beckert & Suckert - The Future As Social FactDokument21 SeitenBeckert & Suckert - The Future As Social FactjohnhasslerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1: Section A Function Asking and Answering QuestionsDokument39 SeitenUnit 1: Section A Function Asking and Answering QuestionsZahid ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imam Khomeini, Ethics and Politics PDFDokument216 SeitenImam Khomeini, Ethics and Politics PDFkiyinjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purok 4, San Jose, Montevista, Davao de Oro: K To 12 Grade 6 Curriculum GuideDokument9 SeitenPurok 4, San Jose, Montevista, Davao de Oro: K To 12 Grade 6 Curriculum GuideAna Rose Colarte GlenogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles Lost Book of NostradamusDokument5 SeitenIngles Lost Book of NostradamusNibirutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alphonso Lingis - David Wood Deep TimeDokument5 SeitenAlphonso Lingis - David Wood Deep TimeTavarishNoch keine Bewertungen
- (E.dennis) - Resurrection of de Body and Transformation of The Universe Inthe Theology of RahnerDokument17 Seiten(E.dennis) - Resurrection of de Body and Transformation of The Universe Inthe Theology of RahnerFausto ZamboniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dosen Pengampuh: Abdi Nasrullah, S. PD., M.M., M.T (C)Dokument28 SeitenDosen Pengampuh: Abdi Nasrullah, S. PD., M.M., M.T (C)willyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spoken English Week 4Dokument5 SeitenSpoken English Week 4CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb Tenses - LectureDokument5 SeitenVerb Tenses - LectureAnne PatocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gatsby EssayDokument2 SeitenGatsby EssayMatúš NeczliNoch keine Bewertungen