Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ESF Measurement Scope and Sequence August 2013
Hochgeladen von
Stu LoweOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ESF Measurement Scope and Sequence August 2013
Hochgeladen von
Stu LoweCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
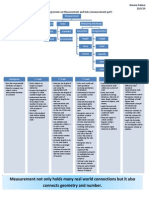
ESF Measurement
Phase 1 K1 K2 Year 1 Phase 2 Year 2 Year 3 Phase 3 Year 4 Year 5 Phase 4 Year 6
IBO Overall Expectation
Learners will develop an understanding of how measurement involves the comparison of objects and the ordering and sequencing of events. They will be able to identify, compare and describe attributes of real objects as well as describe and sequence familiar events in their daily routine.
Learners will understand that standard units allow us to have a common language to measure and describe objects and events, and that while estimation is a strategy that can be applied for approximate measurements, particular tools allow us to measure and describe attributes of objects and events with more accuracy. Learners will develop these understandings in relation to measurement involving length, mass, capacity, money, temperature and time. Standard units allow us to have a common language to identify, compare, order and sequence objects and events. We use tools to measure the attributes of objects and events. Estimation allows us to measure with different levels of accuracy.
Learners will continue to use standard units to measure objects, in particular developing their understanding of measuring perimeter, area and volume. They will select and use appropriate tools and units of measurement, and will be able to describe measures that fall between two numbers on a scale. The learners will be given the opportunity to construct meaning about the concept of an angle as a measure of rotation.
Learners will understand that a range of procedures exists to measure different attributes of objects and events, for example, the use of formulas for finding area, perimeter and volume. They will be able to decide on the level of accuracy required for measuring and using decimal and fraction notation when precise measurements are necessary. To demonstrate their understanding of angles as a measure of rotation, the learners will be able to measure and construct angles. Accuracy of measurements depends on the situation and the precision of the tool. Conversion of units and measurements allows us to make sense of the world we live in. A range of procedures exists to measure different attributes of objects and events.
IBO Conceptual Understanding
Measurement involves comparing objects and events. Objects have attributes that can be measured using non-standard units. Events can be ordered and sequenced.
Objects and events have attributes that can be measured using appropriate tools. Relationships exist between standard units that measure the same attributes.
Phase 1 K1 Compare and describe length, mass and capacity K2 Compare , describe and begin to measure the length, mass and capacity of objects using nonstandard units Year 1 Estimate, compare, describe and measure the length, mass and capacity of objects using nonstandard units
Phase 2 Year 2 Estimate, compare and measure the length with standard units Estimate, compare and measure mass, capacity and volume of objects using nonstandard units Year 3 Estimate, compare and measure objects using standard units of measurement: length, mass, volume and capacity Estimate, compare and measure area of objects nonstandard units
Phase 3 Year 4 Estimate, compare and measure objects using standard units of measurement: length, perimeter, area, mass, capacity, volume and temperature Year 5 Estimate, compare and measure objects using standard units of measurement: length, perimeter, mass, capacity, area, volume and temperature Calculate and develop rules for determining area and perimeter of rectangles Identify and describe the relationships between area and perimeter
Phase 4 Year 6 Estimate, compare and measure objects using standard units of measurement: length, perimeter, mass, capacity, area, volume and temperature Calculate and develop rules for determining area and perimeter of triangles Calculate and develop rules for determining volume of cubes and cuboids Identify and describe the relationships between area and volume, and between volume and capacity
Identify and describe relationships between units of measure (eg: 10mm is the same as 1cm)
Convert between units using whole numbers (e.g. 1 metre to 100 centimetres)
Convert between units using decimals to at least one place (e.g. change 2.6 kg to 2600 g)
Convert between units using decimals to at least two places (e.g. change 2.75 litres to 2750 ml, or vice versa)
Phase 1 K1 K2 Year 1
Phase 2 Year 2 Year 3
Phase 3 Year 4 Year 5
Phase 4 Year 6
Time
Identify, describe and sequence events in their daily routine, for example, before, after, bedtime, storytime, today, tomorrow
Identify, describe Read and write and sequence the time to the events in their hour weekly routine Name and order the days of the week Compare and order the duration of events using the every day language of time Connect days of the week to familiar events and actions
Read and write the time to the hour and half hour
Read and write the time to the quarterhour and 5 minute intervals (past, to)
Name and order the months of the year and seasons Describe duration using months, weeks, days, hours and minutes Connect months, dates and days to a calendar
Estimate and compare lengths of time: second, minute, hour, day, week, months and years Connect times to events in a day
Read and write the time to the minute and investigate the relationship between units of time
Read, write and compare 12 and 24 hour time systems and convert between them Connect 12 and 24 hour time to timetables Solve problems involving difference in time
Calculate time across time zones Solve problems involving difference in time
Convert between units of time
Describe time and duration using am and pm
Phase 1 K1 K2 Year 1
Phase 2 Year 2 Year 3 Identify angles as measures of turn and compare angle sizes in everyday situations
Phase 3 Year 4 Compare and classify angles using the language of right angle, acute and obtuse Year 5
Phase 4 Year 6
Estimate, compare, Estimate, compare, classify, measure and measure and construct angles construct angles within shapes Calculate and develop rules to find unknown angles within shapes, around a point and on a straight line
Angles
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankVon EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary School ‘KS1 (Key Stage 1) – Maths - Publications Guide – Ages 5-7’ eBookVon EverandPrimary School ‘KS1 (Key Stage 1) – Maths - Publications Guide – Ages 5-7’ eBookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement Ccss UnpackedDokument3 SeitenMeasurement Ccss Unpackedapi-256666476Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths FoundationDokument7 SeitenMaths FoundationvlorrawayNoch keine Bewertungen
- EKD Grade - Unit Plan #5 Unit Title: Perspectives: Overview of Unit: Transfer GoalDokument8 SeitenEKD Grade - Unit Plan #5 Unit Title: Perspectives: Overview of Unit: Transfer Goalapi-285442239Noch keine Bewertungen
- Term 3 Maths Unit PlanDokument7 SeitenTerm 3 Maths Unit Planapi-558132010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 4 MeasurementDokument40 SeitenGrade 4 Measurementapi-172041447Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matematika Bab 19Dokument62 SeitenMatematika Bab 19Liestiyono PrahadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math7 PDFDokument28 SeitenMath7 PDFShafika AidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Term 1 - North CoastDokument61 SeitenOpen Term 1 - North CoasternsteinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Denton ISD Blank Report CardDokument2 SeitenDenton ISD Blank Report CardlarrymmcbrideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 8Dokument3 SeitenWeek 8api-294626581Noch keine Bewertungen
- G9 Chemistry TG 2023 Web 38 75Dokument50 SeitenG9 Chemistry TG 2023 Web 38 75primhaile assefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ubd MeasurementDokument8 SeitenUbd Measurementapi-270795370Noch keine Bewertungen
- Num Planner Term 3 2015 - Number Problem SolvingDokument10 SeitenNum Planner Term 3 2015 - Number Problem Solvingapi-292761476Noch keine Bewertungen
- Units and MeasurementsDokument4 SeitenUnits and MeasurementsKizrah AragonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2/3 Maths - CapacityDokument2 SeitenYear 2/3 Maths - Capacitymbed2010100% (3)
- Mini-Unit of Study - Measurement-: Second GradeDokument27 SeitenMini-Unit of Study - Measurement-: Second Gradeapi-357504839Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Syllabus For Grade 11: Desktop/ Files Returned by Experts Sep. 2008 /physics Phy Grade 11Dokument37 SeitenPhysics Syllabus For Grade 11: Desktop/ Files Returned by Experts Sep. 2008 /physics Phy Grade 11lelisa kenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Students Need To Know and Understand About MeasurementDokument3 SeitenWhat Students Need To Know and Understand About MeasurementlelmriniNoch keine Bewertungen
- WK 5Dokument3 SeitenWK 5api-253610401Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 Physics SyllabusDokument26 SeitenGrade 9 Physics SyllabusMario ButlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Year 3Dokument1 SeiteTime Year 3Shamin GhazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 5 Prep NotesDokument1 SeiteWeek 5 Prep Notesapi-241619704Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch13 Zikmund Measurement and ScaleDokument31 SeitenCh13 Zikmund Measurement and Scalerohitoberoi1175% (4)
- Chapter 18 - SummaryDokument4 SeitenChapter 18 - SummaryMadisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Planner - MeasurementDokument11 SeitenMathematics Planner - Measurementapi-284217383Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Plan UploadDokument12 SeitenUnit Plan Uploadapi-382327019Noch keine Bewertungen
- Common Core GoalsDokument2 SeitenCommon Core Goalsapi-250859674Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 7 Prep NotesDokument1 SeiteWeek 7 Prep Notesapi-241619704Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit PlanDokument8 SeitenUnit Planapi-296218979Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ued 400 Gertis Brianna Ubd Unit PlansDokument12 SeitenUed 400 Gertis Brianna Ubd Unit Plansapi-427896234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 32 Lesson Plans Math 4-13-15 To 4-17-15Dokument9 SeitenWeek 32 Lesson Plans Math 4-13-15 To 4-17-15api-273233895Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes MTE3111 PDFDokument12 SeitenNotes MTE3111 PDFYeit Fong TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Year 4 MathsDokument7 SeitenAc Year 4 Mathsapi-230679736Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 2021 High School Entrance Exam Study GuidelinesDokument7 Seiten2020 2021 High School Entrance Exam Study GuidelinesSama AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Tool KitDokument16 SeitenMath Tool Kitapi-287683180Noch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument74 SeitenPhysicsYcarta Sleumas100% (1)
- Tep 522 Ubd Unit Plan Template - Allissa ArielDokument18 SeitenTep 522 Ubd Unit Plan Template - Allissa Arielapi-630269063Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Plan Overview: Students Will Be Able To Independently Use Their Learning ToDokument7 SeitenUnit Plan Overview: Students Will Be Able To Independently Use Their Learning Toapi-300681621Noch keine Bewertungen
- Units, Physical Quantities, Measurement, Errors and Uncertainties, Graphical Presentation, and Linear Fitting of DataDokument87 SeitenUnits, Physical Quantities, Measurement, Errors and Uncertainties, Graphical Presentation, and Linear Fitting of DataAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Geometry SyllabusDokument18 Seiten12 Geometry SyllabusSri KondabattulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Standard Year 11 Topic Guide MeasurementDokument12 SeitenMathematics Standard Year 11 Topic Guide MeasurementhritusahatutoringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time and DecimalDokument3 SeitenTime and DecimalNaDya NerdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math g2 m8 Full ModuleDokument244 SeitenMath g2 m8 Full ModuleRivka ShareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Parent TipsDokument2 SeitenModule 2 Parent Tipsapi-298601310Noch keine Bewertungen
- TT Yr6 Unit 3 Classroom Overview 2014Dokument2 SeitenTT Yr6 Unit 3 Classroom Overview 2014api-239475612Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ngec 9 Reflective 2Dokument2 SeitenNgec 9 Reflective 2simeon tayawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ngec 9 ReflectiveDokument2 SeitenNgec 9 Reflectivesimeon tayawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fraction and Decimal Unit of WorkDokument11 SeitenFraction and Decimal Unit of Workapi-270174865Noch keine Bewertungen
- g4 Area and Perimeter UnitDokument20 Seiteng4 Area and Perimeter Unitapi-249159678Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math Standards Adopted 1997 7Dokument6 SeitenMath Standards Adopted 1997 7establoid1169Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 5 Uoi 5 OverviewDokument2 SeitenYear 5 Uoi 5 Overviewapi-237523786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ued400 Biggs Crystal Stage 3 and Final Unit Design MathDokument7 SeitenUed400 Biggs Crystal Stage 3 and Final Unit Design Mathapi-539423238Noch keine Bewertungen
- ISUtrecht PYP Math SyllabusDokument8 SeitenISUtrecht PYP Math SyllabusRupak RakeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ued400 Moose Ashley Ubd Math Final UnitDokument6 SeitenUed400 Moose Ashley Ubd Math Final Unitapi-379324200Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Semester 2Dokument3 SeitenLesson Plan Semester 2api-643035312Noch keine Bewertungen
- ARTICULO SOBRE PERIMETRO Y AREA en-USDokument34 SeitenARTICULO SOBRE PERIMETRO Y AREA en-USNATHALIA ALEXANDRA CARRENO RODRIGUEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: What Are The Skills That Are Being Tested?Dokument11 SeitenPhysics: What Are The Skills That Are Being Tested?Devilpsn MakiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methodology: Tushar Sawant Rohit SinghaniaDokument26 SeitenResearch Methodology: Tushar Sawant Rohit SinghaniaAmruta ShetyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Policy - On - Drug - Adminstration (1) - Updated 22nd March 2011Dokument2 SeitenPolicy - On - Drug - Adminstration (1) - Updated 22nd March 2011Stu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESF Conference Program DAY1Dokument1 SeiteESF Conference Program DAY1Stu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESF Emerging Leaders Summit ProgramDokument3 SeitenESF Emerging Leaders Summit ProgramStu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESF Conference Program DAY2Dokument1 SeiteESF Conference Program DAY2Stu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPD Calendar A1posterterm One 2013 Finalart RevisedDokument1 SeiteCPD Calendar A1posterterm One 2013 Finalart RevisedStu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESF Shape and Space S&S August 2013Dokument4 SeitenESF Shape and Space S&S August 2013Stu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The ESF Mathematics Scope and SequenceDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To The ESF Mathematics Scope and SequenceStu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESF Reading Scope and SequenceDokument6 SeitenESF Reading Scope and SequenceStu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESF Pattern and Function S&S 2013Dokument3 SeitenESF Pattern and Function S&S 2013Stu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESF Number: K2 Year 2 Year 4 Year 6Dokument6 SeitenESF Number: K2 Year 2 Year 4 Year 6Stu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESF Data Handling August 2013Dokument3 SeitenESF Data Handling August 2013Stu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPD Calendar - 2012-13 - T3 - R1Dokument1 SeiteCPD Calendar - 2012-13 - T3 - R1Stu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- HomeworkDokument1 SeiteHomeworkStu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- UOI Information SheetDokument2 SeitenUOI Information SheetStu LoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Average TZDokument6 SeitenAverage TZvictor javier nuñezNoch keine Bewertungen
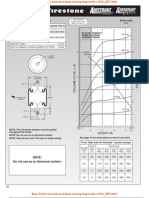
- Firestone Air Spring W02-358-3004Dokument29 SeitenFirestone Air Spring W02-358-3004MROstop.com100% (1)
- Exemplar Science Lesson Plan For Senior High School General Chemistry 1Dokument7 SeitenExemplar Science Lesson Plan For Senior High School General Chemistry 1Arnel MetilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths ProblemDokument28 SeitenMaths ProblemlaibaNoch keine Bewertungen
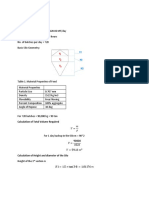
- Design Calculations For SiloDokument3 SeitenDesign Calculations For SiloLeera Gonzaga100% (2)
- Safe Lifting of Non-Cargo LoadsDokument52 SeitenSafe Lifting of Non-Cargo Loadsaveselov88100% (1)
- Model Exam 2019Dokument8 SeitenModel Exam 2019Tesfamichael FufaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (T3) Balloon QuestionDokument3 Seiten(T3) Balloon QuestionCretu NicolaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Computer LPG CalculationsDokument8 SeitenFlow Computer LPG CalculationsNurdeny PribadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equipment ProductivityDokument442 SeitenEquipment ProductivityLan Madrona100% (2)
- Optimizing Surface Area Using A Spreadsheet: InquireDokument3 SeitenOptimizing Surface Area Using A Spreadsheet: InquireAdam MikitzelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1 - Module2 - G7 - 8 - BPP - Mangaldan NHSDokument11 SeitenQ1 - Module2 - G7 - 8 - BPP - Mangaldan NHSElaeca AbenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Desimal CampuranDokument2 SeitenSoal Desimal CampuranMuhimatus Sa'diyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Mathematics, San Francisco State University Mission High School, Mr. Hsu Calculus ClassDokument1 SeiteDepartment of Mathematics, San Francisco State University Mission High School, Mr. Hsu Calculus Classalienboy97Noch keine Bewertungen
- DPP (1 TO) 13th PHYDokument37 SeitenDPP (1 TO) 13th PHYRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spheres and Cones QP Edexcel GcseDokument8 SeitenSpheres and Cones QP Edexcel GcseLOVE WITH MATHEMATICSNoch keine Bewertungen
- QSCDokument10 SeitenQSCShakti DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tribology BrochureDokument4 SeitenTribology BrochureLalo RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Related Rate ProblemDokument2 SeitenRelated Rate ProblemBaijan Balladares0% (1)
- ABE 315 - Module 2 - CoursepackDokument18 SeitenABE 315 - Module 2 - CoursepackRouge WintersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tricks For Producing Averaged Results For Surfaces or Volumes in ANSYS Mechanical - DRD TechnologyDokument4 SeitenTricks For Producing Averaged Results For Surfaces or Volumes in ANSYS Mechanical - DRD TechnologyCrismaru IonutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interactive PDF Y6 White Rose Maths Spring Block 5 Measurement Volume of A Cuboid T M 33921 1 - Ver - 1 PDFDokument1 SeiteInteractive PDF Y6 White Rose Maths Spring Block 5 Measurement Volume of A Cuboid T M 33921 1 - Ver - 1 PDFMohini KureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipeline BasicsDokument123 SeitenPipeline BasicsPN100% (6)
- Volume of Cuboid - Formula, Definition & Solved Questions - Grades 7-12Dokument11 SeitenVolume of Cuboid - Formula, Definition & Solved Questions - Grades 7-12Rahul SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volumes and Surface Area Homework 1Dokument9 SeitenVolumes and Surface Area Homework 1swati goelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMMT100 FT 7 2020 1Dokument9 SeitenPMMT100 FT 7 2020 1Kaoma MofyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement Second Quarter - Module 15: MathematicsDokument30 SeitenMeasurement Second Quarter - Module 15: MathematicsHe HeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation of Linear Momentum: - Newton's Second Law of Motion For A System IsDokument30 SeitenConservation of Linear Momentum: - Newton's Second Law of Motion For A System IsOmer AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- PST QuestionsDokument5 SeitenPST QuestionsPRIYANSH JNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Math DLP Year 1 2022-2023 by Rozayus AcademyDokument12 SeitenRPT Math DLP Year 1 2022-2023 by Rozayus Academyrphsekolahrendah100% (1)