Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
GEO 110 Lecture 1 RYERSON
Hochgeladen von
Amandeep SaharanCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GEO 110 Lecture 1 RYERSON
Hochgeladen von
Amandeep SaharanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture 1 Introduction: - 4.
6 billion years ago - Sun was formed when gravity pulled material towards the centre (swelling motion) - Accretion, small grains buildup to form fist sized planets (planet tesema) - Asteroids and comets occasionally collide into the Earth The Earths Four Spheres: Geosphere: solid earth: core( 6000 C ;fluid but solid), mantle (2900km contributes to the largest component of the Earth), crust - Outer layer compressing the core - Mantle: Inner (soft, plastic, and weak) & Outer (cooler, solid) 80% of the Earth - Asthenosphere: area between the outer mantle and the crust reason why we have tectonic plate activity - Lithosphere (mantle and crust collectively): thinnest layer Hydrosphere: water sources, riverine, lacustrines (collective lakes), palustrine (collective wetland, marshes), ocean - Other sources of water come from frozen ice (i.e. Greenland, Arctic & Antarctic circles 1.8% fresh water) - Rivers, lakes (fresh water) account for <1% - Aquifer: regions of subterarian water supply- underground layer of water (sandwiched btw 2 impermeable layers OR an overlying permeable layer and underlying permeable material) - Confined Aquifer and Unconfined aquifer o Confined: clay or rock (impermeable) o Unconfined: permeable, also referred to as water-table Atmosphere: gaseous layer: N (largest) O (21%) CO2, Ar, He etc.. - Heterosphere: outermost sphere (composition: begins in the exosphere extends to ~80km) hetro= not UNIFORM! - Lightest elements found here! (He) - Homoshpere (extended from 80km to the Earths surface) - ozone found here O3 - Thermoshpere: (heat zone w/in the earth) NOT HOT (less volume of air) vibrational energy causes HIGH temperatures (e- excited!!) - Mesosphere (50-80km): coldest b/c particles serve as condensation nuclear COLDEST ONE - Stratophere temperature inversion (warms up)~ absorption of greenhouse gases - Troposhere: Tropopause: (transition zome btw stratosphere and troposphere) temperature with altitude (-6.4 for ever 1000m rise); higher you go, cooler it becomes Biosphere: realms of living organisms, nutrient cycles - Made of complex organisms: vertebrate, invertebrate, microorganisms, plant material - Nutrient recycling within the biosphere interaction, interdependence, interconnection among different systems
very dynamic and self- sustaining (reciprocal relationship: give&take) Carbon Cycle and Nitrogen Cycle Carbon Cycle: - Photosynthesis (plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere thus, loose Carbon). - When trees die, decomposes and Carbon is released (thru pressure & extreme heating) into the Earth. - We can gain carbon into the atmosphere from the combustion of coal, forest fires etc. - The lakes and ocean also absorbs a lot of carbon over the years. Nitrogen Fixation Cycle The process which gaseous form of nitrogen is absorbed by bacteria that dwell in the roots of trees. Convert the gaseous form of nitrogen into ammonia and nitrite ions. It becomes part of the tissue of plants. Produce NO2 and NH4
Nitrogen Denitrification Cycle: Process by which nitrite is converted back into nitrogen gas. Must occur for fixation to occur Provide N2
Earth as a System A system: is an assemblage or a combination of interacting component Suprasystem & subsystem: both components needed for the survival of the system Causes a chain of reaction and changes to other spheres ( interconnected) i.e. emission of greenhouse gases can cause acid deposition & this causes changes in the pH of water in turn, death to fishes Humans interact with the environment o Size of system o System interact in complex ways o Energy and material cycle are essential for the study of earth systems
Time & Rates of Change in the Earth Science James Hutton Sandstones Geomorphology- changes in the earth Scottish, physician Principals:
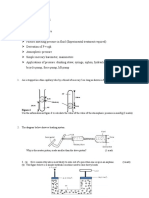
o Uniformitarianism/Gradualism: geologic changes occur over long period of time by a sequence of almost imperceptible event . Present is key to the past William Whewell Argued that geological change is sometimes rapid Catastrophism (paroxys): violent/ dramatic disasters contribute to changes in the Earth surface Threshold & Feedback Processes Threshold Effect Threshold: initial change slowly in response to small disturbance but after threshold is crossed, additional small changes cause RAPID dramatic changes. o Like the Tundra-reindeers Feedback: small disturbances in one area affects a another component of the earths system o Amplify original effect o Spreading o Example: High temperatures cause bacteria to flourish (2005, England) more food increased respiration increased CO2 Thus (France study 2003)- reduction of plant photosynthesis uptake of CO2 decreases Atmospheric CO2 increases
Energy Balance on the Earth Absorption & emission Photons= particles of light (Sun- Fusion (Hydrogen Helium)) Insolation o Measured on horizontal plate o Infrared- long wave radiation (reradiated energy) Refraction: disported, medium/ media, change in speed or direction o Rainbow effect/ highways (mirage) Reflection: solar radiation bounces directly back into space. o Angle of incident= angle of reflection o Albedo Power + texture of composition Forest= 50% of energy is reflected Desert= 35% Polar/ Greenlands= 80% Sky= 6-8% Reflection o radiation bounces directly back into space o angle of incident= angle of reflection Scattering: o Gases, pollen, dust, water droplets- disperse incoming sunlight o Inverse relationship between wavelength of energy and the amount of scattering
Shorter wavelength= more scattering Sky is blue- visible light (north) South- have both short/long wavelength- scattering by gases spreads light in both direction Longer wavelength= less scattering Absorption and emission o Molecules of matter o One form to another (photosynthesis) o Energy-isolation Radiation Balance: o Input + output of energy= net energy balance 1. Conduction: molecule to molecule, transfer by contact (pot and stove) 2. Convexion: movement of molecules from ONE location to ANOTHER (water vapor movement- equator to polor ends- HOT AIR BALLON, wind currents, hot air rises, cool air DROPS) 3. Advection: Horizontal movement of WIND FRICTION. land breeze/ sea breeze Thermo(heat)conveo(salt) o Land- opaque- cold faster o Sea- transparent- takes long time to warm up because of HIGH SUFRACE AREA What factors influence temperature conditions? o Location- Florida is on the same latitude as Russia o Wind system- Florida has different Wind system than Russia difference in Temperature (Russia-cold) (Wind affects temperature) o Land scapepavementsabsorb heatreradiated back into space o Curvature of earth-latitudinal o Cloud cover o Cold currents move towards the equator!!!
Cold Ocean Currents: Peru Benguelea W. Australia Canary Calforina Labrador E. Greenlands Oyashia
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- EarthSystem LatestpptxDokument55 SeitenEarthSystem LatestpptxFrances CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental ScienceDokument11 SeitenEnvironmental ScienceKimberly kate AlambraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explain The Earth Climatic Systems, Its Components and Their Interaction in DetailDokument16 SeitenExplain The Earth Climatic Systems, Its Components and Their Interaction in DetailAbdur RaufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate and Weather DifferencesDokument11 SeitenClimate and Weather DifferencesRitu RaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers To Critical Thinking and Review End of Chapter QuestionsDokument8 SeitenAnswers To Critical Thinking and Review End of Chapter QuestionsSalihin FhooziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions and Answers about: Planet EarthVon EverandQuestions and Answers about: Planet EarthBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Grade 10 Science Exam Notes / Study Guide SNC2D1Dokument2 SeitenGrade 10 Science Exam Notes / Study Guide SNC2D1NikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Earth SystemsDokument4 SeitenEarth and Earth SystemsMedicareMinstun ProjectNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Earth System 1Dokument43 SeitenThe Earth System 1CoachP7uck LoveDogAndFootballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geol-227 Ch-1 - A Changing PlanetDokument15 SeitenGeol-227 Ch-1 - A Changing Planetcelinaradwan16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Earth AstroDokument55 SeitenEarth AstroBel Esguerra CabillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frederick Liyo-LAS#2 Earth's SubsystemDokument7 SeitenFrederick Liyo-LAS#2 Earth's SubsystemFrederick Trafiero LiyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- THE EARTH SYSTEM: INTERCONNECTED SPHERESDokument32 SeitenTHE EARTH SYSTEM: INTERCONNECTED SPHERESJovic SasotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7:: Dynamic Planet: Earthquakes & VolcanoesDokument14 SeitenUnit 7:: Dynamic Planet: Earthquakes & VolcanoespringglesiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - Weather & Climate ChangeDokument3 SeitenUnit - Weather & Climate ChangeKareem AlhalabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AtmosphereDokument27 SeitenAtmosphereGus Edi100% (1)
- EAS 100 NotesDokument44 SeitenEAS 100 NotesJimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Science 2nd QuarterDokument11 SeitenEarth Science 2nd QuarterJhoana paola SugayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Systems Components and CyclesDokument8 SeitenEarth Systems Components and CyclesElleJay11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Earth's CLIMATE System: CLIMATE SYSTEM ELEMENTS (Part of Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, Geosphere, and Biosphere)Dokument4 SeitenEarth's CLIMATE System: CLIMATE SYSTEM ELEMENTS (Part of Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, Geosphere, and Biosphere)Kyla BaysaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth SystemDokument6 SeitenEarth SystemDwayne Ashley SilveniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Greenhouse Effect and Climate ChangeDokument37 SeitenThe Greenhouse Effect and Climate ChangeSwapnil RathodNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Template) Geography 2Dokument79 Seiten(Template) Geography 2Mia Mones Lunsayan BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components For ClimateDokument15 SeitenComponents For ClimateparijathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation: Directions: in Your Sheet of Paper. Write Only The Letter of The Correct AnswerDokument103 SeitenEvaluation: Directions: in Your Sheet of Paper. Write Only The Letter of The Correct AnswerAngelo RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmosphere HandoutDokument82 SeitenAtmosphere HandoutalyssaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Science (Finals)Dokument20 SeitenEnvironmental Science (Finals)jed.berdosNoch keine Bewertungen
- APES U2 L3 AtmosphereDokument45 SeitenAPES U2 L3 AtmosphereSohrab GhorbanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simsys HP PDFDokument31 SeitenSimsys HP PDFalexandra garciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecology Environmental SystemsDokument4 SeitenEcology Environmental SystemsfaustynNoch keine Bewertungen
- EarthsystemDokument23 SeitenEarthsystemapi-26963416Noch keine Bewertungen
- LEC - EarthsystemDokument28 SeitenLEC - EarthsystemLorie Mae ViloriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schematic of Earth System Components and Climate Governance (38 charactersDokument3 SeitenSchematic of Earth System Components and Climate Governance (38 charactersAbdur RaufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meteorology:: Atmospher and Ocean ClimateDokument28 SeitenMeteorology:: Atmospher and Ocean ClimateDanny Satria100% (1)
- Earth ScienceDokument2 SeitenEarth ScienceAelwenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate ChangeDokument9 SeitenClimate ChangeLeilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Systems SubsystemsDokument28 SeitenEarth Systems SubsystemsCyraRenMarquezTagarinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Systems Science: I) Ice Age Vs GlaciationDokument9 SeitenEarth Systems Science: I) Ice Age Vs Glaciationይቴ ስንሻዉNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVEN3501 Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteCVEN3501 Cheat Sheetangie_leo5374Noch keine Bewertungen
- Composition and Origin of The AtmosphereDokument71 SeitenComposition and Origin of The AtmosphereGutierrez KennethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lessson-3-Earths-SystemDokument25 SeitenLessson-3-Earths-Systemmizpehman12Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Ocean and Sea IceDokument5 SeitenThe Ocean and Sea IceAbdur RaufNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Basic Review of EarthDokument48 Seiten2.1 Basic Review of EarthPrabhat GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Earth SystemDokument46 SeitenChapter 3 Earth SystemAlma Dimaranan-AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biophysical Environments: The AtmosphereDokument5 SeitenBiophysical Environments: The AtmosphereAnanya UppalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Earth Science 2021 2022Dokument3 SeitenModule 2 Earth Science 2021 2022Razen SisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate Science Basics: Ian BeardsleyDokument19 SeitenClimate Science Basics: Ian BeardsleyIan BeardsleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Earth System: A Short OverviewDokument31 SeitenThe Earth System: A Short OverviewAngelica AmadeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS4652 Planetary Science: Lecture 4: Planetary Atmospheres LEE Man HoiDokument52 SeitenPHYS4652 Planetary Science: Lecture 4: Planetary Atmospheres LEE Man HoiYang Woo SeongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 NotesDokument4 SeitenChapter 1 NotesLena RobertsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planetary EnvironmentDokument38 SeitenPlanetary EnvironmentSHERRIE MAE BIJASANoch keine Bewertungen
- Env Sci1 PDFDokument54 SeitenEnv Sci1 PDFRolandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 - Earth SystemDokument16 SeitenModule 2 - Earth SystemB2 Frondozo, MarjorieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meteorology:: Atmospher and Ocean ClimateDokument33 SeitenMeteorology:: Atmospher and Ocean ClimateAgus Madatama PujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Four Subsystems of EarthDokument31 SeitenThe Four Subsystems of EarthGary SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate EmeDokument2 SeitenClimate EmeLouis Andre BarcelinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral SummaryDokument3 SeitenOral SummaryNatasha ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 Materials 2A FluidsDokument3 SeitenTopic 2 Materials 2A Fluidsmaram shbairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Engineering & Characterization: Dr. Ahmed Umar Munawar Office 321 Ahmed - Munawar@scme - Nust.edu - PKDokument19 SeitenSurface Engineering & Characterization: Dr. Ahmed Umar Munawar Office 321 Ahmed - Munawar@scme - Nust.edu - PKTayyab AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory NES713 Smoke Toxicity Index Test Chamber With Burning 100g SpecimenDokument3 SeitenLaboratory NES713 Smoke Toxicity Index Test Chamber With Burning 100g Specimenphoebe chanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scuttlers, Black Goo, and The Biogenic FieldDokument27 SeitenScuttlers, Black Goo, and The Biogenic FieldIan Beardsley100% (1)
- Artificial EvaporationDokument29 SeitenArtificial EvaporationMANISH PARDHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Annotated BibiliographyDokument4 SeitenFinal Annotated Bibiliographyapi-491166748Noch keine Bewertungen
- MDD of Soil TypesDokument119 SeitenMDD of Soil TypesThilan Senarathne100% (1)
- What Are Some Unbeilevably True Facts in The Vedas.Dokument6 SeitenWhat Are Some Unbeilevably True Facts in The Vedas.krishna iyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composites Today January 2023 PDFDokument36 SeitenComposites Today January 2023 PDFGautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydropower PosterDokument1 SeiteHydropower PosterfazarbadhushaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Kinetics of A Particle-Work and EnergyDokument65 SeitenModule 3 Kinetics of A Particle-Work and EnergyHuy VũNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method A7 The Determination of The Maximum Dry Density and Optimum Moisture Content of Gravel, Sand & SoilDokument11 SeitenMethod A7 The Determination of The Maximum Dry Density and Optimum Moisture Content of Gravel, Sand & SoilJohn PavlakisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical ScienceDokument3 SeitenPhysical ScienceShin NeulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nilai Serapan Karbon Hutan Pinus Di Desa 07f6bb5dDokument5 SeitenNilai Serapan Karbon Hutan Pinus Di Desa 07f6bb5dnia agusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ngày: outlook = sunny, temperature = cool, humidity = high, wind = strong => chơi tennis không 1. Xét trên toàn tập dữ liệu H (S) = * Nếu chọn outlook: Outlook: sunnyDokument4 SeitenNgày: outlook = sunny, temperature = cool, humidity = high, wind = strong => chơi tennis không 1. Xét trên toàn tập dữ liệu H (S) = * Nếu chọn outlook: Outlook: sunnyMinh Trí0% (1)
- Specific Objectives: Pressure QuestionsDokument6 SeitenSpecific Objectives: Pressure QuestionsBadmind JnrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repair and Maintenance of Window AcDokument16 SeitenRepair and Maintenance of Window AcAli Mehdi Maknojia0% (1)
- 325C1 2005Dokument9 Seiten325C1 2005Rajat SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: Class: Xi Target Jee 2022 DateDokument7 SeitenPhysics: Class: Xi Target Jee 2022 DateBhushanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResumeDokument5 SeitenResumeAllright ShitNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPT1 - Fundamental Principles & Methods-5th BatchDokument130 SeitenCPT1 - Fundamental Principles & Methods-5th BatchJohn Renzo GalinatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test BankDokument10 SeitenEarth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test Bankpanabase.trevat.puhh6e100% (19)
- Pearson Ib Chemistry Text Book AnswersDokument99 SeitenPearson Ib Chemistry Text Book Answersmohammad abdurehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRPMR Worksheet IDokument1 SeiteDRPMR Worksheet IArsela MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDCDokument67 SeitenEDCKiran VeesamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical CycleDokument39 SeitenBiochemical CycleShubhangi BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wilting PointDokument7 SeitenWilting Pointbunaladi.jhonNoch keine Bewertungen
- PXC XCXDokument23 SeitenPXC XCXKashif LiaqatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Amorphous Al2O3 1997 Physica B Condensed MatterDokument2 SeitenStructure of Amorphous Al2O3 1997 Physica B Condensed Matterkiller7470Noch keine Bewertungen