Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
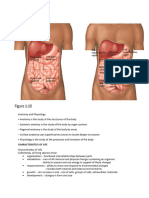
Anatomy and Physiology: The Cell-Is The Fundamental Unit of Life and The Body
Hochgeladen von
monster40lbsOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anatomy and Physiology: The Cell-Is The Fundamental Unit of Life and The Body
Hochgeladen von
monster40lbsCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 3: Anatomy and Physiology
The Cell- is the fundamental unit of Life and the Body. 7 Major functions of the cell Movement Conductivity Metabolic absorption Secretion Excretion respiration Reproduction Tissues- a group of cells that perform a similar function. Epithelial tissue- the protective tissue that lines internal and external body tissues. Ex; Skin, mucous membranes, the lining of the intestinal tract. Muscle tissue Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Skeletal muscle- is the most abundant muscle in the body. Connective tissue-is the most abundant tissue in the body. Nerve tissue- tissue that transmits electrical impulses throughout the body. Organs- a group of tissues functioning together. Ex; Heart, liver, brain, ovary, eye. Organ system- a group of organs that work together. Ex; cardiovascular system Homeostasis- the natural tendency of the body to maintain a steady and normal internal environment. Metabolism- is the term used to refer to the building up (anabolism) and breaking down (catabolism) of biochemical substances to produce energy. Hydration Body fluid components: o Intracellular fluid 75% of TBW (Total Body Water) o Extra cellular fluid 25% of TBW - Interstitial fluid 17.5% of TBW - Intravascular fluid 7.5% of TBW = 25% of Extra cellular fluid Causes of Dehydration Vomiting Diarrhea Perspiration Peritonitis Malnutrition Burns
Open wounds Electrolytes- a substance that, in water, separates into electrically charged particles. Ions- is a charged particle. Cation- an ion w/ a positive charge (+). Sodium (NA+)- is the most prevalent cation in the extracellular fluid. Hypernatremia- increase in NA+ Hyponatremia- decrease in NA+ Potassium (K+)- is the most prevalent cation in the intracellular fluid. Hyperkalemia Hypokalemia Calcium (CA++)- plays a major role in muscle contraction as well as nervous impulse transmission. Hypercalcemia Hypocalcemia Magnesium (Mg++)- is necessary for several biochemical processes that occur in the body and is closely associated w/ phosphate in many processes. Hypermagnesemia Hypomagnesemia Anion- an ion w/ a negative charge (-). Chloride (Cl-)- its negative charge balances the positive charge associated w/ the cations. It also plays a major role in fluid balance and renal function and has a close association w/ sodium (NaCl). Bicarbonate (HCO3-)- is the principle buffer of the body. It neutralizes the highly acidic H+. Phosphate (HPO4-)- is closely associated w/ magnesium in renal function.
Osmosis & Diffusion Isotonic- equal in concentration of solute molecules. Hypertonic- having a greater concentration of solute molecules. Hypotonic- having a lesser concentration of solute molecules Osmosis- is the (passive) passage of a solvent such as water through a membrane. Active transport- is the movement (requires energy) of a substance through a cell membrane against the osmotic gradient. Diffusion- is the movement of molecules through a membrane from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration. Facilitated diffusion- diffusion of a substance such as glucose through a cell membrane that requires the assistance of a helper or carrier protein. Acid-Base Balance PH- (Potential of Hydrogen). A measure of relative acidity or alkalinity.
Acid 0-------------------7.4-----------------14 Alkaline Normal pH = 7.35 - 7.45 a variation of .4 of this can be lethal.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Lymph Health: The Key to a Strong Immune SystemVon EverandLymph Health: The Key to a Strong Immune SystemBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Water Prescription: For Health, Vitality, and RejuvenationVon EverandThe Water Prescription: For Health, Vitality, and RejuvenationBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- F and e Imb .... Edu ..Dokument20 SeitenF and e Imb .... Edu ..esakkiammalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fe ConceptDokument177 SeitenFe ConceptIvan MaximusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDokument65 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte Imbalancesreenu100% (4)
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDokument9 SeitenFluid and Electrolytesfelicity tejadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Body FluidsDokument8 SeitenPhysiology of Body FluidsIvan Exekiel CabrillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDokument15 SeitenFluids and ElectrolytesDyanne Bautista100% (1)
- Electrolytes - P3 Oct3Dokument12 SeitenElectrolytes - P3 Oct3Edward Vladimir MoncayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolytes DisturbancesDokument8 SeitenFluid and Electrolytes DisturbancesRoselily Flores CoquillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDokument295 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte BalanceAnuchithra RadhakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eksu Lectures 2Dokument92 SeitenEksu Lectures 2Aina AdesolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis Is The Movement of Water Across Cell Membranes, From The Less ConcentratedDokument1 SeiteOsmosis Is The Movement of Water Across Cell Membranes, From The Less ConcentratedPraveen ThulasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mabes Fluid and ElectrolytesDokument9 SeitenMabes Fluid and ElectrolytesMabesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDokument8 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte BalanceSujatha AluguriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDokument7 SeitenFluids and ElectrolytessetanpikulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 - Fluid and Electrolyte Balance, Nursing Process, Fluid ImbalancesDokument23 SeitenPart 1 - Fluid and Electrolyte Balance, Nursing Process, Fluid Imbalancesfebie pacheco100% (1)
- Mid Exam LecturesDokument268 SeitenMid Exam LecturesTala IyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- HomeostasisDokument13 SeitenHomeostasisSanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rudaina Alelyani MEV Assignment3.Dokument15 SeitenRudaina Alelyani MEV Assignment3.Rudaina AlelyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceDokument14 SeitenFluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceShenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysiologyDokument84 SeitenPhysiologyWilliam BufNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Alterations in Fluid & Electrolyte BalanceDokument62 Seiten3 - Alterations in Fluid & Electrolyte Balancegeng gengNoch keine Bewertungen
- VTH93-TWTJW-PTTC7-8CP8X-2XV82: Total Body WaterDokument5 SeitenVTH93-TWTJW-PTTC7-8CP8X-2XV82: Total Body WatermharjemmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDokument68 SeitenFluid and ElectrolytesMara Jon Ocden CasibenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1Dokument7 SeitenLec 1dhoha alawsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Physiology: General Physiology The Cell HomeostasisDokument38 SeitenIntroduction To Physiology: General Physiology The Cell HomeostasisAnanta Subedi100% (1)
- Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalances FinalDokument142 SeitenFluid & Electrolyte Imbalances FinalPriyanka T100% (3)
- Fluids Balance: Tanto HDokument31 SeitenFluids Balance: Tanto HKamila JasmineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolytes Lecture NotesDokument85 SeitenFluid and Electrolytes Lecture NotesVince Peliño De MesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F and e ImbalanceDokument61 SeitenF and e ImbalancegoldamierNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPRE2Dokument13 SeitenCOMPRE2Rodrigo SeriozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To PhysiologyDokument20 SeitenIntroduction To PhysiologyVanessa Mae EncarnadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Capsule For SSC CGL by StudyIQDokument73 SeitenBiology Capsule For SSC CGL by StudyIQstudyiq83% (6)
- TransportDokument176 SeitenTransportbiologi88Noch keine Bewertungen
- University of Guyana H1Dokument58 SeitenUniversity of Guyana H1Aneesa A HenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid BalanceDokument50 SeitenFluid Balancesiti sarahdeazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceDokument50 SeitenFluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceBRI KUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology Module 2Dokument16 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Module 2JayR MendonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeostasis of Body FluidsDokument23 SeitenHomeostasis of Body FluidsJudy Ann L. CarpenterosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceDokument41 SeitenFluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceRn nadeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction - To - Physiology Slides of Doctor Mustafa ShehabatDokument30 SeitenIntroduction - To - Physiology Slides of Doctor Mustafa ShehabatAmmar SmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No. 1:: Mohammad NumanDokument11 SeitenAssignment No. 1:: Mohammad NumanUsama AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Questions in Anatomy and Physiology: Dr. Alona T. Badua Department of Animal ScienceDokument136 SeitenReview Questions in Anatomy and Physiology: Dr. Alona T. Badua Department of Animal Sciencewhin conayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology Lecture 2Dokument29 SeitenPhysiology Lecture 2Muhammad Khubaib AzeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asam Basa Dan ElektrolitDokument50 SeitenAsam Basa Dan ElektrolitDavid Ithu AgkhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Fluids and Fluid Compartments: Subject AboutDokument10 SeitenBody Fluids and Fluid Compartments: Subject AboutHareth mohammad mahmod NawajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Fluids 2022 StudentDokument36 SeitenBody Fluids 2022 Studentshavindrap2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology PPT Unit 1Dokument35 SeitenPhysiology PPT Unit 1vrindhasabu2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Parenteral SolutionsDokument55 SeitenFundamentals of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Parenteral SolutionsTri RachmadijantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Notes Week 1Dokument6 SeitenBiochem Notes Week 1Leah Mariz RocaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Biology Notes Updated April 2016Dokument94 SeitenIGCSE Biology Notes Updated April 2016Adi101010101010101100% (1)
- Module 1Dokument37 SeitenModule 1Sharanya BasakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Bio Semester 3Dokument11 SeitenAssignment Bio Semester 3api-317569592Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid & ElectrolytesDokument6 SeitenFluid & ElectrolyteskauragiousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan of Client With Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDokument28 SeitenNursing Care Plan of Client With Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceCj Aguilar50% (2)
- Revised Man As A Biological BeingDokument8 SeitenRevised Man As A Biological Beingapi-3832208Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid & ElectrolyteDokument18 SeitenFluid & Electrolytesaranya amuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument20 SeitenChapter 7criselledalipe12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology (NUR 190) Carmen Corder, MSN, RN Fluids and Electrolyte BalanceDokument17 SeitenPathophysiology (NUR 190) Carmen Corder, MSN, RN Fluids and Electrolyte BalanceSydney DeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psych 327 #15807 Sec 01 SchlussmanDokument6 SeitenPsych 327 #15807 Sec 01 Schlussmanmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development Through The Lifespan: Cognitive Development in Infancy and ToddlerhoodDokument48 SeitenDevelopment Through The Lifespan: Cognitive Development in Infancy and Toddlerhoodmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dishwasher: 24 Hours A Day, 7 Days A Week For LG Customer ServiceDokument48 SeitenDishwasher: 24 Hours A Day, 7 Days A Week For LG Customer Servicemonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development, Maturation, Aging, and Death: Lecture Presentation by Suzanne Long, Monroe Community CollegeDokument62 SeitenDevelopment, Maturation, Aging, and Death: Lecture Presentation by Suzanne Long, Monroe Community Collegemonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 07-IntelligenceDokument91 SeitenChapter 07-Intelligencemonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motivation and EmotionDokument56 SeitenMotivation and Emotionmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psych 327 #11955 Sec 02 Schnieder - 0001Dokument8 SeitenPsych 327 #11955 Sec 02 Schnieder - 0001monster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schizophrenia PowerpointDokument53 SeitenSchizophrenia Powerpointmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Memory: Reconstructing The Past The Biology of MemoryDokument60 Seiten10 Memory: Reconstructing The Past The Biology of Memorymonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurotransmitter ChartDokument1 SeiteNeurotransmitter Chartmonster40lbs100% (2)
- By: Margaret Wise Brown Adapted By: Jessie Moreau, M.Ed., NBCTDokument18 SeitenBy: Margaret Wise Brown Adapted By: Jessie Moreau, M.Ed., NBCTmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cook Handout AppendixDokument22 SeitenCook Handout Appendixmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Depression: WWW - Bradfordvts.co - UkDokument28 SeitenDepression: WWW - Bradfordvts.co - Ukmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.00 Exam 3 Notes: Please Pardon Any Spelling Errors or Typos!Dokument9 Seiten9.00 Exam 3 Notes: Please Pardon Any Spelling Errors or Typos!monster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cognition and Emotion: November 13-20, 2008Dokument90 SeitenCognition and Emotion: November 13-20, 2008monster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module3 - Psychology PowerpointDokument12 SeitenModule3 - Psychology Powerpointmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiological Mechanism of RegulationDokument11 SeitenPhysiological Mechanism of Regulationmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Powerpoint With Extra SlidesDokument111 SeitenChapter 5 Powerpoint With Extra Slidesmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Worksheet For 9 - 27Dokument2 SeitenLearning Worksheet For 9 - 27monster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Psychology: The Biological Basis of BehaviorDokument79 SeitenUnderstanding Psychology: The Biological Basis of Behaviormonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emotion RegulationDokument53 SeitenEmotion Regulationmonster40lbs100% (1)
- Visual Attention PartDokument3 SeitenVisual Attention Partmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 - Inductive and Deductive ReasoningDokument50 SeitenLecture 9 - Inductive and Deductive Reasoningmonster40lbs0% (1)
- L Basic Neuroscience Lecture 13Dokument17 SeitenL Basic Neuroscience Lecture 13monster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Bitter EndingDokument15 SeitenA Bitter Endingmonster40lbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis 1Dokument26 SeitenPathophysiology of Atherosclerosis 1jackNoch keine Bewertungen
- RLE Module 2M - Chest Physiotherapy, Postural Drainage, Nebulization, Chest Tube Drainage Systems, Blood TransfusionDokument57 SeitenRLE Module 2M - Chest Physiotherapy, Postural Drainage, Nebulization, Chest Tube Drainage Systems, Blood TransfusionAlexa GoteraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uworld - PSYCHIATRYDokument24 SeitenUworld - PSYCHIATRYNikxyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Article Yoda THD DM (Manuskrip)Dokument4 SeitenReview Article Yoda THD DM (Manuskrip)shafiyyah putri maulanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Atrophy System (MSA) Trust Caregiver's GuideDokument11 SeitenMultiple Atrophy System (MSA) Trust Caregiver's GuideThe Multiple System Atrophy CoalitionNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDF NAC ProtocolDokument247 SeitenCDF NAC ProtocolFrorefare LarcenerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Book Dyslipidemias PDFDokument525 Seiten2015 Book Dyslipidemias PDFvaleriaovando100% (1)
- Lucid Dreaming Tips OWDokument9 SeitenLucid Dreaming Tips OWarlikNoch keine Bewertungen
- DewormingDokument48 SeitenDewormingJulie Ann Escartin80% (5)
- IV. Recognizing National Issues and Concern - E-Substance Abuse EducationDokument9 SeitenIV. Recognizing National Issues and Concern - E-Substance Abuse EducationMicsjadeCastillo0% (1)
- Spirituality, Spiritual Well-Being, and Spiritual Coping in Advanced Heart FailureDokument18 SeitenSpirituality, Spiritual Well-Being, and Spiritual Coping in Advanced Heart FailurezakiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal MigrainDokument6 SeitenJurnal MigrainReksyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Punjab Cancer StatsDokument4 SeitenPunjab Cancer StatsPranjul SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caring For Injured Reptiles2004Dokument40 SeitenCaring For Injured Reptiles2004SujayJainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of Practice On: Workplace Safety and Health (WSH) Risk ManagementDokument51 SeitenCode of Practice On: Workplace Safety and Health (WSH) Risk Managementaminul islamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015-07-14 RASD Workshop-Discussion Paper ODE OCD FinalDokument30 Seiten2015-07-14 RASD Workshop-Discussion Paper ODE OCD FinalShayne JacobsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM2-CU10-Modification of Mendelian RatiosDokument17 SeitenCM2-CU10-Modification of Mendelian RatiosClaire GonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance Fluid Therapy in ChildrenDokument4 SeitenMaintenance Fluid Therapy in ChildrenNicole_0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bambang, Nueva VizcayaDokument19 SeitenInstructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bambang, Nueva VizcayaCJ M. Pablo100% (1)
- Legal Aid Society Complaint Re Homeless YouthDokument65 SeitenLegal Aid Society Complaint Re Homeless YouthPaul SchindlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perioperative Gyn Obs Fluid & Electrolytes ManagementDokument60 SeitenPerioperative Gyn Obs Fluid & Electrolytes Managementzamurd76100% (1)
- Pierre BudinDokument3 SeitenPierre BudinFer45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Selection TestDokument3 SeitenNursing Selection TestHarshita GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncma: Health AssessmentDokument25 SeitenNcma: Health AssessmentBb PrintsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuromuscular BlockersDokument25 SeitenNeuromuscular BlockersAbdelrahman GalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ludwig's AnginaDokument22 SeitenLudwig's AnginaDevavrat SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia in Adults 2019 PDFDokument22 SeitenAutoimmune Hemolytic Anemia in Adults 2019 PDFKevin Mora BañosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information MSQ KROK 2 Medicine 2007 2021 PEDIATRICSDokument112 SeitenInformation MSQ KROK 2 Medicine 2007 2021 PEDIATRICSReshma Shaji PnsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Article: Duplex Ultrasound Evaluation of Hemodialysis Access: A Detailed ProtocolDokument8 SeitenReview Article: Duplex Ultrasound Evaluation of Hemodialysis Access: A Detailed ProtocolRenov BaligeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereoatlas of Ophthalmic Pathology PDFDokument177 SeitenStereoatlas of Ophthalmic Pathology PDFMihai CrișanNoch keine Bewertungen