Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Jona Quiz 3
Hochgeladen von
France John Evangelista TorresOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Jona Quiz 3
Hochgeladen von
France John Evangelista TorresCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
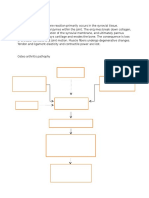
Quiz 3 Nursing Diagnosis: Acute (Chest) pain r/t myocardial ischemia resulting from coronary artery occlusion with
loss/restriction of blood flow to an area of the myocardium and the necrosis of the myocardium Short-term Goal: Within 1 hour of nursing intervention, the client will have improved comfort in chest Long-term Goal: Within 2 days of nursing intervention, the client will have improved feeling of control as evidenced by verbalizing a sense of control over present situation and future outcomes Cues Subjective: The client reports chest pain radiating to the left arm, neck and back Objective: Restlessness Facial grimacing Fatigue Peripheral cyanosis Weak pulse Cold and clammy skin Palpitations Shortness of breath Elevated temperature Pain scale of Nursing Problem Chest Pain Scientific Reason Coronary artery or one of its smaller branches is suddenly blocked. The part of the heart muscle supplied by this artery loses its blood (and oxygen) supply if the vessel is blocked. This part of the heart muscle is at risk of dying unless the blockage is quickly removed. Intervention 1. Assess characteristics of chest pain 2. Obtain history of previous cardiac pain and familial history of cardiac problems 3. Assess RR, PR, BP in episodes of chest pain 4. Maintain bed rest during chest pain, with comfortable position, maintain calm environment to promote relaxation 5. Prepare for administration of medications, and monitor response to therapy. Notify Rationale 1. Assisting the client in quantifying pain may differentiate preexisting and current pain patterns as well as identify complications 2. Provides information that may help to differentiate current pain from previous problems and complications 3. respirations may be increased as a result of pain and associate anxiety 4. to reduce oxygen consumption and demand, to reduce competing stimuli and reduces anxiety 5. pain control is apriority, as it indicates ischemia Evaluation Standard: the client had improved comfort in chest, as evidenced by: states a decrease in the rating of the chest pain, is able to rest, displays reduced tension, and sleeps comfortably, requires decrease analgesia or nitroglycerin Criteria: The clients chest pain was decreased to 4/10 and decreased in episodes
8/10
When a part physician if pain of the heart does not abate muscle is 6. Instruct patient in damaged it is NTG SL said to be administration after infarcted. The hospitalization. term Instruct patient in myocardial activity alterations infarction (MI) and limitations means 7. Instruct patient and damaged family in heart medications effects, muscle. contraindications, side effects and symptoms to report 8. Obtain a 12 lead ECG on admission, then each time chest pain recurs for evidence of further infarction as prescribed 9. Administer analgesics as ordered, such as morphine sulfate, meferidine 10. Administer beta blockers as ordered 11. Administer Calcium channel blockers as ordered
6. to decrease myocardial oxygen demand and workload on the heart 7. to promote knowledge and compliance with therapeutic regimen and to alleviate fear of unknown 8. serial ECG and stat ECGs record changes that can give evidence of further cardiac damage and location of MI 9. Morphine is the drug of choice to control MI pain, but other analgesics maybe used to reduce pain and reduce the workload on the heart 10. to block sympathetic stimulation, reduce heart rate and lowers myocardial demand 11. to increase coronary blood flow and collateral circulation which can decrease pain due to ischemia
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Scott Foresman Science Grade 4Dokument8 SeitenScott Foresman Science Grade 4rofi modiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HydrocortisoneDokument2 SeitenHydrocortisoneIvanne Hisoler100% (15)
- Advanced Tung Style Acupuncture Vol. 2 - Obstetrics & Gynecology PDFDokument556 SeitenAdvanced Tung Style Acupuncture Vol. 2 - Obstetrics & Gynecology PDFnhung_nguyen_12260% (5)
- Sample Nurse ResumeDokument1 SeiteSample Nurse ResumeEdgar Baliola Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- !XPSP 3Dokument105 Seiten!XPSP 3France John Evangelista TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Nurse ResumeDokument1 SeiteSample Nurse ResumeEdgar Baliola Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- EnglishDokument1 SeiteEnglishFrance John Evangelista TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scrooge Reaction PaperDokument2 SeitenScrooge Reaction PaperFrance John Evangelista TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Script: Scene#1:) : Look To Your KidsDokument1 SeiteScript: Scene#1:) : Look To Your KidsFrance John Evangelista TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dengue: Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever, Resulting in Bleeding, Low Levels of Blood Platelets andDokument5 SeitenDengue: Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever, Resulting in Bleeding, Low Levels of Blood Platelets andFrance John Evangelista TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- PathophyDokument1 SeitePathophyFrance John Evangelista TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Management SCIDokument3 SeitenMedical Management SCIFrance John Evangelista TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torres, France John E. Bsn3BDokument1 SeiteTorres, France John E. Bsn3BFrance John Evangelista TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching PlanDokument1 SeiteTeaching PlanFrance John Evangelista TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology2 RespiDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology2 RespiFrance John Evangelista TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids and Electrolytes NCM 101Dokument142 SeitenFluids and Electrolytes NCM 101France John Evangelista Torres100% (2)
- Fracture of HumerusDokument56 SeitenFracture of HumerusDr. Vinod Gupta100% (2)
- Scientific Career of Dr. Jaime Lagunez OteroDokument42 SeitenScientific Career of Dr. Jaime Lagunez OteroFrente CivicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6: Diagnostic Microbiology and Laboratory Methods - Pocket DentistryDokument9 Seiten6: Diagnostic Microbiology and Laboratory Methods - Pocket Dentistrykam LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng PDFDokument98 SeitenEng PDFMark Anthony MadridanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Harris Benedict and Mifflin ST Jeor Equations With Indirect Calorimetry in Evaluating Resting Energy ExpenditureDokument4 SeitenComparison of Harris Benedict and Mifflin ST Jeor Equations With Indirect Calorimetry in Evaluating Resting Energy ExpenditurephiliohallenNoch keine Bewertungen
- EasyOn PC ManualDokument120 SeitenEasyOn PC Manualasdfasdf87Noch keine Bewertungen
- 345-Article Text-1032-1-10-20180629Dokument4 Seiten345-Article Text-1032-1-10-20180629Regina AyediaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psoriasis & Psoriatic Arthritis: DR Prathibha J PDokument48 SeitenPsoriasis & Psoriatic Arthritis: DR Prathibha J PjefferyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lowdermilk: Maternity & Women's Health Care, 10th EditionDokument12 SeitenLowdermilk: Maternity & Women's Health Care, 10th Editionvanassa johnson100% (1)
- Hematologic EffectsDokument8 SeitenHematologic EffectsGiralph NikkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rapid Sequence Intubation: A Guide For AssistantsDokument6 SeitenRapid Sequence Intubation: A Guide For AssistantsjackyploesNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdrenalineDokument13 SeitenAdrenalineMobahil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resultados SaludDignaDokument2 SeitenResultados SaludDignaAdriana RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Types of StrabismusDokument9 SeitenCommon Types of Strabismustasya noerchaerunisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Freud and AnesthesiaDokument5 SeitenFreud and AnesthesiaRaluca LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aaha Avma Preventive Health Care GuidelinesDokument6 SeitenAaha Avma Preventive Health Care GuidelinesRox DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExodontiaDokument32 SeitenExodontiaahmed amerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roots and StuffDokument154 SeitenRoots and Stuffsean griffin100% (3)
- Crossectional Anatomy: Ahmed MohammedDokument26 SeitenCrossectional Anatomy: Ahmed Mohammedhawi adugnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal and Foetal Outcomes in Pregnancy With Gestational Thrombocytopenia: A Prospective Observational StudyDokument6 SeitenMaternal and Foetal Outcomes in Pregnancy With Gestational Thrombocytopenia: A Prospective Observational StudyIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Libros Transfusion PDFDokument44 SeitenCatalogo Libros Transfusion PDFmeds1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- 39.03.16 International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 87 405-414 PDFDokument10 Seiten39.03.16 International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 87 405-414 PDFNarendrakumar GopakumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scabies NotesDokument9 SeitenScabies NotesAvi eNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neo-Synephri Ne I Iot Ri Vi NDokument38 SeitenNeo-Synephri Ne I Iot Ri Vi NMarlo Dañez NorbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingkimmybapkiddingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Nursing Care Pacemaker Emil 2019Dokument5 Seiten11 Nursing Care Pacemaker Emil 2019ameliajamirusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adenomiosis CX ConservadoraDokument12 SeitenAdenomiosis CX Conservadorajuan carlos pradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pschology 2Dokument35 SeitenPschology 2Sarah Mae SaringanNoch keine Bewertungen