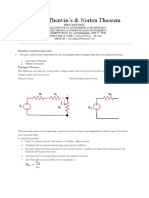
Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ECE Core Other Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
Pratyush ChauhanCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ECE Core Other Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
Pratyush ChauhanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
13B21EC211
Basic Telecommunications
(Core Course) Credits 4 Lectures 3 Tutorials 1 Practical 0
Pre-requisites: Semiconductor Physics Objective: The objectives are to study Semiconductor devices like diodes, Bipolar Junction Transistors, Field Effect Transistors, MOSFETs and their applications. To design and study amplifier circuits using BJTs, FETs and OPAMPs. To study Communication system and model. To study Modulation Techniques like Amplitude modulation and Angle modulation. To study basics of TDMA and FDMA. Course Assessment: Mid Term Test 30 End Term Test 45 Teacher Assessment (Based on Assignments, quizzes etc.) 25 Total 100 Course Outcomes: After studying this course the students would gain enough knowledge to analyze and design telecommunications circuits using semiconductor devices. Topics Covered: Introduction to telecommunications: Communications systems application and model. Concept and theory of base band and Carrier communication, spectra, BW and power analysis. Semiconductor Diodes: Introduction to semiconductors, PN junction with no bias forward bias, and reverse bias. V-I characteristics, Ideal diode, diode resistance, diode equation, Zener and avalanche breakdown, Diode as a switch. Diode circuits and applications: Performance of half wave and full wave rectifiers. Shunt capacitor filter, semiconductor photodiode, Light emitting diodes, modulator circuit, mixer circuit, envelope detector. Bipolar Junction transistor: Junction transistor, transistor current components, transistor construction, CB configuration, CE configuration, CE current gain, CC configuration. Need of biasing a transistor, selection and choice of operating point. Collector to base bias circuit, emitter feedback bias circuit, emitter bias circuit, voltage divider bias circuit. Field effect transistor: Junction FET, pinch off voltage, JFET Volt- Ampere characteristics, biasing the FET, the FET as a votage variable resistor, MOSFET, Digital MOSFET Circuits, Depletion MOSFET enhancement MOSFET, comparison of JFET, MOSFET and BJT. 1. Transistor Amplifier:
Meaning of amplification, frequency response of and RC coupled amplifier, Multistage amplifiers, need of Multistage amplifiers, selection of configuration of transistors in Multistage amplifiers, effect on bandwidth when stages are cascaded. Operational amplifiers: Ideal OPAMP , inverting amplifier, non inverting amplifier, adders, subtractors, voltage follower, OPAMP comparators, OPAMP for square, triangular and pulse generation. Peak detector, sample and hold circuits, difference amplifier configuration, voltage to current conversion. Modulation: Analogue modulation techniques, Amplitude, Angle modulation, generation, detection, Modulation Index, switching modulator, ring modulator, sampling and pulse modulation, Basics of TDMA, FDMA. Text Books 1. Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory by Robert Boyelsted and Louis Nashelsky. 2. Electronic Communication Systems by George Kennedy Reference Books 1. Electronic Communication Systems Fundamentals through Advanced by Tomasi.
13B21EC411
FUNDAMENTALS OF ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS
(Core Course)
Credits 4
Lectures 3 Tutorials 1 Practical 0 Pre-requisites: None Objective: The objectives are to study The basic mathematical tools to analyze signals, communication systems and their performance. The process of modulation, the different types of analog modulation/demodulation techniques, their analysis in the time and frequency domains and their implementation The performance of modulation systems in the presence of noise. Sampling theory and its analysis in time and frequency domain. Course Assessment: Mid Term Test 30 End Term Test 45 Teacher Assessment (Based on Assignments, quizzes etc.) 25 Total 100 Course Outcomes: Upon completion of this course, the students would have developed An understanding of the basic mathematical tools used in the study of communication systems. An understanding of analog transmission techniques, their performance and implementation. An understanding of sampling theory and sampling theorem. Topics Covered: Introduction: Fourier Transforms, Concept of Spectrum & Bandwidth, Basic mechanisms and application of modulation, Elements of communication point to point and broadcast, Wired and Wireless Communications, Signal propagation over different media Amplitude Modulation: Description, Time and Frequency domain analysis, Implementation. Variations of AM: DSB-SC, SSB, Hilbert Transformation, VSB. Implementation. Frequency Division Multiplexing Analysis, Application and Implementation Frequency Modulation: Time and Frequency domain analysis, Spectrum, Modulation and Demodulation implementation, FM system examples, Relationship between FM and PM Radio Communication: Transmitters, Homo/Hetero/Superheterodyne receivers, Mixer theory and implementation, Concept of Intermediate Frequency (IF): Direct detection, double IF
Phase Locked Loop (PLL): PLL Analysis and circuits, Application in FM demodulation, Concept of Synchronization in communication systems with PLL. Sampling Theory: Sampling Theorem time and frequency domain analysis, Baseband and Bandpass sampling, Samplers, Filtering, Signal recovery. Pulse Modulation Systems: Time and Frequency domain analysis of Pulse modulation systems, Modulation and Demodulation, Time Division Multiplexing Modulation systems in the presence of noise: Performance of Modulation systems in the presence of noise Review: Review of Probability theory and Random signals Text Books 1. A.B.Carlson, P.B. Crilly, J.C. Rutledge : Communication Systems, 4th edition, McGraw Hill 2. Kennedy, Davis : Electronic Communication Systems, 4 th edition, Tata McGraw Hill 3. D. Roddy, J. Coolen : Electronic Communications, 4th edition, Prentice Hall India. Reference books 1. H. Taub, D.L. Schilling 2. Simon Haykin : Principles of Communication Systems, , 2nd edition, Tata McGraw Hill. : Communication Systems, 4 th edition, Wiley
10B11EC514
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
(Core Course) Credits 4
Lectures 3 Tutorials 1 Practical 0
Pre-requisites: Signals and Systems Objective: The objectives are to study The essential components of communication systems. To understand the conceptual meaning of modulation and its need in communication, the various form of modulation like AM & its variants and Angle modulation. To study various methods of modulation and demodulation of AM and Angle modulation. To study sampling and sampling theorem and various pulse modulation schemes. To study some basic digital modulation schemes and their modulation and detection techniques. Course Assessment: Mid Term Test 30 End Term Test 45 Teacher Assessment (Based on Assignments, quizzes etc.) 25 Total 100 Course Outcomes: After studying this course the students would gain enough knowledge of analog communication, pulse modulation, digital communication. They can design any communication system for any given scenario. Topics Covered: Introduction: Elements of a communication system; Analog and digital signals, bandlimited signals and systems, bandwidth. Amplitude modulation: Introduction to Modulation; AM, AMSC, DSBSC, SSBSC, VSBSC communication. Detection of AM signals: Coherent detection, Envelope detection, Detection of DSBSC, SSBSC signals. Multiplexing Techniques. Angle modulation: Concepts of FM and PM, Narrowband and Wideband FM, Carsons rule, Direct and Indirect methods of FM generation, Detection of FM signals. Sampling and Pulse modulation techniques: Time and frequency domain sampling with aperture effects, Reconstruction of signals, PAM, PPM, PWM generation & demodulation methods. Speech Coding, Line Coding and Baseband Digital Transmission: Pulse Code modulation, PCM hierarchy, Line Codes: Unipolar-NRZ, polar-NRZ, Unipolar-RZ, BipolarRZ, Manchester Code, DPCM, DM, ADM, Bit rate and bandwidth of digital signals, Linear Predictive Coding (LPC). Digital Modulation Techniques: ASK, FSK ,PSK, QPSKs Modulation, Detection, Constellation diagrams, BER and their BW calculation. Mobile Communication: Overview of Mobile Communication, GSM Basics & Architecture of GSM.
Text Books 1. B P Lathi 2. Taub and Schilling Reference book 1. Simon Haykin : Modern Digital and Analog Communication, Oxford University Press. : Principles of Communication Systems, 2nd Edn. Tata McGraw Hill. : Communication Systems 4 th Edition, John Wiley.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ECE203 Modulation TechniquesDokument2 SeitenECE203 Modulation TechniquesSri MathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenDSS Custom ScriptingDokument8 SeitenOpenDSS Custom ScriptingHassan Ali Al SsadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symphony Maintenance and Technical Guide 1907555 PDFDokument36 SeitenSymphony Maintenance and Technical Guide 1907555 PDFRicha Potdar50% (4)
- Syllabus 2013 PDFDokument41 SeitenSyllabus 2013 PDFAbhay RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eeng360 Fall2010 2011 Course DescriptDokument2 SeitenEeng360 Fall2010 2011 Course DescriptEdmond NurellariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13.302 Signals & Systems (At) : L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credits: 4Dokument7 Seiten13.302 Signals & Systems (At) : L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credits: 4Surya TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Communications: Course Code:13EC1109 L TPC 4 0 0 3Dokument3 SeitenAnalog Communications: Course Code:13EC1109 L TPC 4 0 0 3NISHCHAY SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- M Tech Ec SyllabusDokument13 SeitenM Tech Ec SyllabusDhaval PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Semester SyllabusDokument5 Seiten4th Semester Syllabusdipupanda915Noch keine Bewertungen
- B.E. Electronics & Telecom. Engineering: Semester VIIDokument13 SeitenB.E. Electronics & Telecom. Engineering: Semester VIImahesh20moteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course OutlineDokument3 SeitenCourse OutlineIhsan ul HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Elective SyllabusDokument34 SeitenECE Elective SyllabusPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SYLLABUSDokument3 SeitenSYLLABUSArkajyoti SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Course Corrected 14 Nov. 2016Dokument12 SeitenECE Course Corrected 14 Nov. 2016Chaitanya BharathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic CommunicationDokument2 SeitenElectronic CommunicationHet PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENEE3309 OutlineDokument5 SeitenENEE3309 OutlineJLM SSNoch keine Bewertungen
- S. No. Topics Lectures: Dr. Tarun Kumar Rawat Course InstructorDokument1 SeiteS. No. Topics Lectures: Dr. Tarun Kumar Rawat Course InstructorDeepak SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credits Periods Exam Hrs. Sessional Marks Exam Marks Total Marks Theory Tutorial LabDokument7 SeitenCredits Periods Exam Hrs. Sessional Marks Exam Marks Total Marks Theory Tutorial Labpreethi priyamvadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credits Periods Exam Hrs. Sessional Marks Exam Marks Total Marks Theory Tutorial LabDokument7 SeitenCredits Periods Exam Hrs. Sessional Marks Exam Marks Total Marks Theory Tutorial Labpreethi priyamvadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pcs PDFDokument2 SeitenPcs PDFDisha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic of Analog Communication ES 202 FinalDokument3 SeitenBasic of Analog Communication ES 202 FinalKrishan GopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Tech. in Electronics & Communication Engineering / Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Syllabus of Paper - 1Dokument5 SeitenB.Tech. in Electronics & Communication Engineering / Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Syllabus of Paper - 1vishwas20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ec 321 RF & Micro Wave EngineeringDokument15 SeitenEc 321 RF & Micro Wave EngineeringHemanth ChimataNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Year SyllabusDokument17 Seiten4th Year Syllabusapi-350836154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sem 4Dokument16 SeitenSem 4BeawaredangerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semester-IV EC401 Analog Communication 3L:0T:0P 3 CreditsDokument15 SeitenSemester-IV EC401 Analog Communication 3L:0T:0P 3 CreditsChayan KoleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Introduction To Comm FINALDokument68 Seiten3 Introduction To Comm FINALDisha GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus PHD Even Semester Nov 2022 ECE WOCDokument2 SeitenSyllabus PHD Even Semester Nov 2022 ECE WOCsandeep_2262Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ece203 Modulation-Techniques Eth 1.20 Ac29 PDFDokument2 SeitenEce203 Modulation-Techniques Eth 1.20 Ac29 PDFRanjith KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC208 Analog Communication EngineeringDokument2 SeitenEC208 Analog Communication EngineeringtrismaheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposed Scheme For M.E. (Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering)Dokument9 SeitenProposed Scheme For M.E. (Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering)Prathamesh MestryNoch keine Bewertungen
- R18 B.TECH ECE II Year ADCDokument2 SeitenR18 B.TECH ECE II Year ADCPoongodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout - COM202 - Analog and Digital CommunicationDokument3 SeitenHandout - COM202 - Analog and Digital CommunicationBIsht NarendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACDokument26 SeitenACNandu0% (1)
- Bece304l Analog-Communication-Systems TH 1.0 71 Bece304l 66 AcpDokument2 SeitenBece304l Analog-Communication-Systems TH 1.0 71 Bece304l 66 AcpAakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC115 Analog Communication: L-T-P: 3-1-0 Total 42 LecturesDokument2 SeitenEC115 Analog Communication: L-T-P: 3-1-0 Total 42 LecturesNitish_Katal_9874Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analog and Digital CommunicationsDokument2 SeitenAnalog and Digital CommunicationsAparna LakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus For PHDFDokument2 SeitenSyllabus For PHDFchandravinitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE 4682 - Course SyllabusDokument2 SeitenEEE 4682 - Course Syllabuscharles chikwandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAE 101 Applied Mathematics LTPC 4 0 0 4 Module 1: Real Vector SpacesDokument8 SeitenMAE 101 Applied Mathematics LTPC 4 0 0 4 Module 1: Real Vector SpacesAswathy PaulnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Contents: Unit I Basic TelephonyDokument7 SeitenCourse Contents: Unit I Basic TelephonyKavita BurseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus For IES in Electronics&Communication PaperDokument4 SeitenSyllabus For IES in Electronics&Communication PaperRitesh Kumar BhadaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems EngineeringDokument3 SeitenCommunication Systems EngineeringR ChandrasekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRDO Syll (Ece)Dokument3 SeitenDRDO Syll (Ece)elisettynarendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Analog Integrated Circuits (TEC-502)Dokument13 SeitenI Analog Integrated Circuits (TEC-502)Suyash MaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entrance Exam Includes Questions From Following Subjects: Signals and Systems (15%)Dokument3 SeitenEntrance Exam Includes Questions From Following Subjects: Signals and Systems (15%)Krish RobertsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE3001 Analog Communication Systems NOV-2017Dokument3 SeitenECE3001 Analog Communication Systems NOV-2017Siva ShankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACS SYllabus Final 1Dokument2 SeitenACS SYllabus Final 1M RAVI KISHORENoch keine Bewertungen
- CDDokument5 SeitenCDSUNIL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Curriculum B.TECH. (EC) II-Year, IV-Semester Theory Paper I L T P Credits 3 1 0 4 EC-211: Analog Integrated Circuits Unit-1Dokument6 SeitenCourse Curriculum B.TECH. (EC) II-Year, IV-Semester Theory Paper I L T P Credits 3 1 0 4 EC-211: Analog Integrated Circuits Unit-1Dishant GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTech Digital Communication Syllabus Subject To Approval ofDokument5 SeitenMTech Digital Communication Syllabus Subject To Approval ofPuneet PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section-A: MDU B.Tech Syllabus (ECE) - II YearDokument2 SeitenSection-A: MDU B.Tech Syllabus (ECE) - II YearBindia HandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.E. Electronics, Electronics & Telecommunication) 2008 CourseDokument26 SeitenS.E. Electronics, Electronics & Telecommunication) 2008 CoursesanjuzadokarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.5.10 Electronics and Communication Engineering (EC) : Linear Algebra: CalculusDokument2 Seiten5.5.10 Electronics and Communication Engineering (EC) : Linear Algebra: CalculusMohan Kumar NNoch keine Bewertungen
- KTU Syllabus For S1 and S2 Basic ElectronicsDokument2 SeitenKTU Syllabus For S1 and S2 Basic ElectronicsAnand RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExtcDokument15 SeitenExtcapi-236544093Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics and Communication Engineering - EcDokument3 SeitenElectronics and Communication Engineering - EcSyedMuneerNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC734 RF Communication Circuits (3 0 0 3) : Course Learning OutcomeDokument1 SeiteEC734 RF Communication Circuits (3 0 0 3) : Course Learning OutcomeOla Gf OlamitNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF Analog Impairments Modeling for Communication Systems Simulation: Application to OFDM-based TransceiversVon EverandRF Analog Impairments Modeling for Communication Systems Simulation: Application to OFDM-based TransceiversNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiresolution Signal Decomposition: Transforms, Subbands, and WaveletsVon EverandMultiresolution Signal Decomposition: Transforms, Subbands, and WaveletsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationVon EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNoch keine Bewertungen
- HPFigs2013 14 A1bDokument24 SeitenHPFigs2013 14 A1bPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convocation Registration FormDokument2 SeitenConvocation Registration FormPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Registration and Orientation For New Entrants ACADEMIC YEAR 2015 16Dokument1 SeiteRegistration and Orientation For New Entrants ACADEMIC YEAR 2015 16Pratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Text Document Related To EEEDokument1 SeiteNew Text Document Related To EEEPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 - 1 - Advertisement No. 7 - 2014 (H.p. Administrative Combined Competitive Examination-2014)Dokument11 Seiten2015 - 1 - Advertisement No. 7 - 2014 (H.p. Administrative Combined Competitive Examination-2014)Pratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Himachal Pradesh Public Service Commission: General - (01) Pratyush ChauhanDokument1 SeiteHimachal Pradesh Public Service Commission: General - (01) Pratyush ChauhanPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lgec005 Code CDokument1 SeiteLgec005 Code CPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSPICE Tutorial 2Dokument25 SeitenPSPICE Tutorial 2Pratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Burn ProgramDokument2 SeitenHow To Burn ProgramPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFID Based Attandance Cum Security SystemDokument12 SeitenRFID Based Attandance Cum Security SystemAmit ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- REsumeDokument3 SeitenREsumePratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mathematics For GateDokument9 SeitenEngineering Mathematics For GateRishabh Jain0% (1)
- Pspice TutDokument20 SeitenPspice TutPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BillDesk Payment GatewayDokument1 SeiteBillDesk Payment GatewayPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payment ReceiptDokument1 SeitePayment ReceiptPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pspice Tutorial Stanford UniversityDokument4 SeitenPspice Tutorial Stanford UniversitySaif AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 - 1 - Advertisement No. 7 - 2014 (H.p. Administrative Combined Competitive Examination-2014)Dokument11 Seiten2015 - 1 - Advertisement No. 7 - 2014 (H.p. Administrative Combined Competitive Examination-2014)Pratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- About MeDokument1 SeiteAbout MePratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Directive Principles of State Policy-ADokument11 SeitenDirective Principles of State Policy-APratyush Chauhan50% (2)
- Science Lab PhysicsDokument1 SeiteScience Lab PhysicsPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- P 2700 Eyeblink Sensor in VehicleDokument25 SeitenP 2700 Eyeblink Sensor in Vehicle_imsandeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesDokument111 SeitenEce III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesGautam Sharma80% (10)
- B Tech ECE Courses NBADokument4 SeitenB Tech ECE Courses NBAPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Elective SyllabusDokument34 SeitenECE Elective SyllabusPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 3 Non Verbal CuesDokument35 SeitenLec 3 Non Verbal CuesPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limiting Power Transmission of Green Cellular Networks: Impact On Coverage and CapacityDokument6 SeitenLimiting Power Transmission of Green Cellular Networks: Impact On Coverage and CapacityPratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Storm Chasing and Weather DisastersDokument32 SeitenStorm Chasing and Weather DisasterspratyushchauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The CourseDokument10 SeitenIntroduction To The CoursePratyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Letter WritingDokument8 SeitenBusiness Letter WritingPratyush Chauhan0% (1)
- NORA-W10 DataSheet UBX-21036702Dokument36 SeitenNORA-W10 DataSheet UBX-21036702comercialNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCB, MCCB, Elcb, and RCCBDokument8 SeitenMCB, MCCB, Elcb, and RCCBMD SHAMSE ALAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-G TechnologyDokument18 Seiten4-G TechnologyClaudiu MădălinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum of Ms in Avionics EngineeringDokument34 SeitenCurriculum of Ms in Avionics EngineeringUfi70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phase Shift Keying (PSK) : July 2020Dokument11 SeitenPhase Shift Keying (PSK) : July 2020fares belNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Electrical Specification 2018Dokument54 SeitenGlobal Electrical Specification 2018ENRIQUENoch keine Bewertungen
- 27012472-MIMO Wall Mount Antenna DatasheetDokument1 Seite27012472-MIMO Wall Mount Antenna DatasheetСергей МирошниченкоNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.0.1 Electric CM 2000 E5Dokument41 Seiten3.0.1 Electric CM 2000 E5Nguyễn Duy HưngNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICOM RepetitorDokument22 SeitenICOM Repetitorrujanac100% (1)
- Shuvajit Paul (Ec 304)Dokument13 SeitenShuvajit Paul (Ec 304)Candy CrUshNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTU Catalogue - 4CAE001329 EN - A4 - WebDokument71 SeitenRTU Catalogue - 4CAE001329 EN - A4 - Webniyamei noomNoch keine Bewertungen
- STP100 110 60 IS XX 11Dokument230 SeitenSTP100 110 60 IS XX 11Monster LifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nec Tokin PDFDokument2 SeitenNec Tokin PDFAntero RafaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer DesignDokument112 SeitenTransformer DesignAshdeep SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- IK and IP Testing For Lighting ProductsDokument1 SeiteIK and IP Testing For Lighting ProductsvarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amarnath Sah Senior Technical Assistant NIELIT TezpurDokument17 SeitenAmarnath Sah Senior Technical Assistant NIELIT TezpurAmarnath SahNoch keine Bewertungen
- American Wire Gauge Chart and AWG Electrical Current Load Limits Table With Ampacities, Wire Sizes, Skin Depth Frequencies and Wire Breaking StrengthDokument3 SeitenAmerican Wire Gauge Chart and AWG Electrical Current Load Limits Table With Ampacities, Wire Sizes, Skin Depth Frequencies and Wire Breaking StrengthTsabitulKhairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relay Performance Testing: Jay Gosalia Vice President of Engineering and Marketing Doble Engineering Company, USADokument40 SeitenRelay Performance Testing: Jay Gosalia Vice President of Engineering and Marketing Doble Engineering Company, USArashid rahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MindConnect IoT2040 Product Sheet v1.0Dokument5 SeitenMindConnect IoT2040 Product Sheet v1.0TAENGKASEM K.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ab CableDokument23 SeitenAb CableJinto JacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data SSC-02Dokument2 SeitenData SSC-02dns19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Raw 3Dokument31 SeitenRaw 3Apik SubagyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tec Relay 52GDokument3 SeitenTec Relay 52Gimmer nainggolanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magel IsDokument40 SeitenMagel Iscacr_72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Theory ModifiedDokument83 SeitenGraph Theory ModifiedKrishna Reddy Y.VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Alarm Clock Using 8051Dokument14 SeitenDigital Alarm Clock Using 8051Akshat Sinha0% (2)
- XS5493 1900al Bro PDFDokument8 SeitenXS5493 1900al Bro PDFnurkovic_ele100% (1)
- Tems ParametersDokument15 SeitenTems Parametersganeshtomar880% (5)