Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
TRIGONOMETRY
Hochgeladen von
urfriend_jjn05Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TRIGONOMETRY
Hochgeladen von
urfriend_jjn05Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TRIGONOMETRY
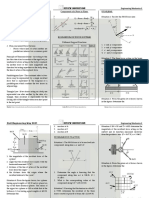
Trigonometry that branch of mathematics that deals with the study of triangles. Angle the figure formed by two half-lines (called rays) from a common point or origin (called vertex).. Its size is the amount of rotation from one of the rays (or sides) to the other. Kinds of Angles: Acute angle an angle which measures between 0o and 900. Right angle an angle formed by 2 perpendicular rays. It measures exactly 90o. Obtuse angle an angle which measures between 90o and 180o. Straight angle an angle formed by two rays extending in opposite directions. It measures exactly 180o. 5. Reflex angle an angle greater than 180o but less than 360o. 6. Perigon an angle measuring exactly 360o. 1. 2. 3. 4. Complementary angles angles whose sum is 90o. Supplementary angles - angles whose sum is 180o. Explementary angles - angles whose sum is 360o.
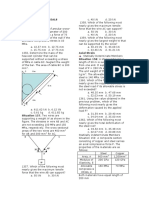
Triangle a polygon of three sides. One important property of a triangle is that the sum of two
of its sides is greater than the third side and their difference is less than the third side. Example: In triangle ABC, side AB = 8 m and side BC = 20 m. One possible dimension of side CA is
a. 13
b. 11
c. 9
d. 7
Solution: Since the difference of two sides of a triangle is less than the third side, then
BC AB < CA 20 8 < CA 12 < CA CA > 12
Kinds of Triangles (according to size of angles):
CA = 13
1. Right triangle a triangle with a right angle. 2. Oblique triangle - a triangle without a right angle. This is further classified into a. Acute triangle a triangle all of whose angles are acute. b. Obtuse triangle a triangle with one obtuse angle. Kinds of Triangles (according to relation of sides): 1. Scalene triangle a triangle with no equal sides. 2. Isosceles triangle - a triangle with two sides equal. 3. Equilateral triangle a triangle with all 3 sides equal. It is also equiangular. Similar triangles triangles where the corresponding angles are congruent and the corresponding sides are proportional. Given two similar triangles, the ratio of their areas is the square of the ratio of any two corresponding sides. Let A1 & A2 be area of smaller & bigger triangle, respectively.
b A1 a c = = = A2 x z y
2 2 2
Congruent triangles triangles that are identical.
The Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle, the sum of the squares of the legs is equal to the square of the hypotenuse. A set of three positive integers that satisfy the Pythagorean principle such as 3, 4 and 5 and 8, 15 and 17 constitute what is called a Pythagorean triple. Units for Measurement of Angles: 1. Degree a measure of an angle which is equal to 1/360 of a revolution. 2. Radian the measure of the central angle subtended by an arc of a circle which is equal in length to the radius of the circle. 1 revolution = 2 radians. 3. Mil - a measure of an angle which is equal to 1/6400 of a revolution. 4. Grad (or Gon) - a measure of an angle which is equal to 1/400 of a revolution. To convert from degrees to radians and vice-versa, we use the relation 180o = radians. Pairs of Cofunctions: 1. sine & cosine 2. tangent & cotangent 3. secant & cosecant Solution Of Right Triangles: A + B = 90o Pairs of Reciprocal Functions: 1. sine & cosecant 2. cosine & secant 3. tangent & cotangent
a2 + b2 = c2
sin =
opposite side hypotenuse adjacent side hypotenuse
opposite side adjacent side
csc =
hypotenuse opposite side hypotenuse adjacent side adjacent side opposite side
cos =
sec =
tan =
cot =
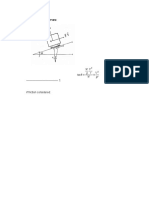
Special Right Triangles:
Solution of Oblique Triangles:
A + B + C = 180o
Law of Sines: In any triangle, the sides are proportional to the sines of the opposite angles, i.e.: a b c = = sin A sin B sin C Law of Cosines: In any triangle, the square of any side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides minus twice their product times the cosine of their included angle, i.e.
a 2 = b 2 + c 2 2bc cos A b 2 = a 2 + c 2 2ac cos B c 2 = a 2 + b 2 2ab cos C
Fundamental Trigonometric Identities: The Quotient Relations: tan = sin cos cot = cos sin
cos 2 + sin 2 = 1
The Pythagorean Relations: 1 + tan 2 = sec 2 cot 2 +1 = csc 2
cos( ) = cos cos sin sin sin ( ) = sin cos cos sin tan ( ) = tan tan 1 tan tan
Sum and Difference Formulas:
Double-Angle Formulas:
cos 2 = cos 2 sin 2 = 2 cos 2 1 = 1 2 sin 2 sin 2 = 2 sin cos 2 tan tan 2 = 1 tan 2
= 2 Half-Angle Formulas: sin = 2 tan = 2
cos
1 + cos 2 1 cos 2
or or
cos 2 = sin 2 =
1 + cos 2 2
1 cos 2 2
1 cos 1 cos sin = = 1 + cos sin 1 + cos
Functions of :
cos( ) = cos sin ( ) = sin tan ( ) = tan
Functions of Complementary Angles:
cos = sin ( 90 ) sin = cos( 90 ) tan = cot ( 90 ) cot = tan ( 90 ) sec = csc( 90 ) csc = sec( 90 )
Review Exercises in TRIGONOMETRY 1. Find the supplement of an angle whose compliment is 62o. a. 28o b. 118o c. 152o d. 162o
2. To find the angles of a triangle, given only the lengths of the sides, one would use a. law of tangents b. law of sines c. orthogonal functions d. law of cosines 3. Which is true regarding the signs of the natural functions for angles between 90o and 180o? a. cosine is negative b. sine is negative c. secant is positive d. tangent is positive 4. What is the value of that will satisfy the equation sin2 + 4 sin + 3 = 0 if 0 < 2? a. b. /4 c. 3/2 d. /2 5. Given a triangle with angle C = 28.7o, side a = 132 units and side b = 224 units. Solve for side c. a. 110 units b. 125.4 units c. 95 units d. 90 units 6. One radian is equivalent to a. 52o b. 45o c. 90o d. 57.3o
7. Given a right triangle where the hypotenuse is r, an acute angle , the side opposite is y and the adjacent side x. Which of the following relations does not apply? a. x2 + y2 = r2 b. cos 2 = 1 + 2 sin2 c. sin 2 = 2 sin cos d. 1 + tan2 = sec2 8. What do you call an angle whose terminal side coincides with either the x- or the yaxis? a. reflex angle b. quadrantal angle c. co-terminal angle d. right angle 9. For an object which is below the eye of an observer, the angle which the line of sight
to the object makes with the horizontal is called a. angle of depression b. angle of elevation c. bearing d. vertical angle 10. Two sides of a triangle measure 6 cm and 8 cm and their included angle is 40o. Find the third side. a. 5.144 cm b. 5.263 cm c. 4.256 cm d. 5.645 cm 11. The sum of the two interior angles of a triangle is equal to the third angle and the difference of the two angles is equal to 2/3 of the third angle. Find the third angle. a. 15o b. 75o c. 90o d. 120o 12. Two sides of a triangle are 50 m and 60 m long. The angle included between these sides is 30o. What is the interior angle opposite the longest side? a. 92.74o b. 93.74o c. 94.74o d. 91.74o 13. The measure of 1.5 revolutions counterclockwise is a. 540o b. 520o c. 90o 14. The product cot cos is also equivalent to a. cos b. csc sin c. sec cos d. 90o d. sin csc
15. If sin A = 3/7, where A is an acute angle, what is the exact value of tan A? a. 2 10 / 3 b. 3 10 / 20 c. 7 / 2 10 d. 7 10 / 20 16. Simplify: a. 2 cot2
csc csc + csc 1 csc + 1
b. 2 tan2
c. 2 csc2
d. 2 sec2
17. How many different values of x from 0o to 180o satisfies the equation (2 sin x 1)(cos x + 1) = 0? a. 3 b. 0 c. 1 d. 2 18. An obtuse angle is ______ than a right angle. a. lesser b. equal c. greater 19. Which of the following is equivalent to csc cos3 tan ? a. cos b. 1 sin2 c. sin2 d. oblique d. 1
20. What is the value of the angle whose tangent is equal to 1 and the sine of which is a negative quantity? a. 45o b. 90o c. 225o d. 315o 21. An angle more than radians but not less than 2 radians. a. straight angle b. obtuse angle c. reflex angle 22. Solve: cos2 + 2 sin + 1 = 0 given that 180o < < 270o. a. 227.058o b. 219.047o c. 132.942o d. vertical angle d. 255.036o
23. In general, for a triangle ABC, the equation (sin A)/a = (sin B)/b = (sin C)/c represents a. the law of cosines b. the law of sines c. the law of tangents d. the reciprocal of the law of sines 24. The difference of the squares of the secant and the tangent of an angle is equal to a. 2 b. 1 c. 0 d. 3 25. In the fourth quadrant, a. sin B > 0 and cos B < 0 c. sin B < 0 and cos B < 0 b. sin B > 0 and cos B > 0 d. sin B < 0 and cos B > 0 d. cos (2A B) d. II and IV d. cos d. 150o d. grad
26. Sin 2A cos B cos 2A sin B is equivalent to a. sin 2(A B) b. cos 2(A B) c. sin (2A B) 27. The cosecant function is negative in quadrants a. III and IV b. I and II c. I and III 28. Sin (270o + ) is equal to a. cos b. sin 29. If 0 < Arccot x <180o, then Arccot (-1/ a. 30o b. 60o c. sin
3)
is c. 120o
30. It is the measure of an angle equivalent to 1/400 of a revolution. a. mil b. degree c. radian
31. It is the measure of an angle equivalent to 1/6400 of a revolution. a. mil b. degree c. radian d. grad 32. 3200 mils is equal to how many degrees? a. 45o b. 90o 33. Express 45o in mils. a. 80 mils b. 800 mils c. 180o c. 8000 mils c. 2 d. 270o d. 80,000 mils d.
34. Evaluate: sec(Arccot 2) a. 5 b.
5/2
35. A triangle having three sides of unequal lengths is known as ______ triangle. a. right b. oblique c. scalene d. equilateral 36. The measure of 2.25 revolutions clockwise is a. 835o b. 805o c. 810o d. 810o
37. An angle greater than a straight angle and less than two straight angles is called a. right angle b. obtuse angle c. acute angle d. reflex angle 38. Which of the following statements is correct? a. All equilateral triangles are similar. b. All right triangles are similar.
c. All isosceles triangles are similar.
d. All rectangles are similar. d. 360o d. 15o d. 3/2
39. Explementary angles are angles whose sum is a. 90o b. 180o c. 270o 40. Solve for : = arccos (sin 2) a. 30o b. 45o 41. Solve for x: Arctan x + Arctan a. 1 b. c. 60o c. 2
2 x = 3 4
42. An observer found the angle of elevation of the top of a tree to be 27o. After moving 10 m closer (on the same vertical and horizontal plane as the tree), the angle of elevation becomes 54o. How high is the tree? a. 8.65 m b. 7.53 m c. 7.02 m d. 8.09 m 43. If x and y are complementary angles, find the value of P if P = cos (540o x) sin (540o y) + cos (90o x) sin (90o y) a. sin 2x b. cos 2y c. cos 2x d. cos 2y 44. A ladder 42 ft long is placed so that it will reach a window 30 ft high on one side of a street; if it is turned over, its foot being held in position, it will reach a window 25 ft high on the other side of the street. How wide is the street from building to building? a. 63.1 ft b. 65.4 ft c. 71.8 ft d. 82.5 ft 45. Each leg of an isosceles right triangle whose perimeter is 30 inches is _____ inches. a. 8.45 in. b. 8.79 in. c. 9.03 in. d. 9.72 in. 46. A person on a ship sailing due south at the rate of 15 miles an hour observes a lighthouse due west at 3 p.m. At 5 p.m. the lighthouse is 52o west of north. How far from the lighthouse was the ship at 4 p.m.? a. 38.4 mi. b. 48.73 mi. c. 41.22 mi. d. 45.75 mi. 47. Which of the following is true? a. cot (-) = cot b. cos (-) = - cos c. sec (-) = sec d. csc (-) = csc
48. From the top of a tower 63.2 ft high, the angles of depression of two objects situated in the same horizontal line with the base of the tower, and on the same side of the tower, are 31o16 and 46o28 respectively. Find the distance between the two objects. a. 104.08 ft b. 60.04 ft c. 52.06 ft d. 44.04 ft 49. Cos (A + B) cos A + sin (A + B) sin A is equal to a. sin B b. sin (2A + B) c. cos B d. cos (2A + B)
50. A vertical pole 35 ft high, standing on sloping ground, is braced by a wire which
extends from the top of the pole to a point on the ground 25 ft from the foot of the pole. If the pole subtends an angle of 30o at the point where the wire reaches the ground, how long is the wire? a. 54.3 ft b. 56.7 ft c. 50.8 ft d. 59.5 ft 51. The sides of a triangular lot are 130 m, 180 m and 190 m. What is the area of the lot? a. 11,260 m2 b. 11,225 m2 c. 10,250 m2 d. 14,586 m2
ANSWER KEY: 1. c 2. d 3. a 4. c 5. b 6. d 7. b 8. b 9. a 10. a 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. c b a b b d a c b c 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. c a b b d c a a c d 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. a c b b c c d a d a 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. b d b a b c c d c a 51. b
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Trigonometry: Angle MeasuresDokument36 SeitenTrigonometry: Angle MeasuresKiran Kumar100% (1)
- Trigonometry ReviewerDokument10 SeitenTrigonometry ReviewerNiko Ramarama100% (1)
- CE Board May 2021 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 1Dokument3 SeitenCE Board May 2021 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 1paul macasaetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Licensure Examination in Mathematics - November 1997Dokument3 SeitenLicensure Examination in Mathematics - November 1997Jeric PonterasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Math Refresher SetDokument4 SeitenAdvanced Math Refresher SetGracielle Nebres100% (1)
- Banking of Highway Curves:: W G V R W V GRDokument10 SeitenBanking of Highway Curves:: W G V R W V GRRetro GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigo and Anal GeomDokument37 SeitenTrigo and Anal GeomxaiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Footing DETAILDokument1 SeiteFooting DETAILjeff alcazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTN 5 Engineering Data and Analysis New OBE Format ReviewerDokument1 SeiteMTN 5 Engineering Data and Analysis New OBE Format ReviewerG BoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics - Problems - July 4Dokument7 SeitenFluid Mechanics - Problems - July 4John Paul JacalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Close Exam 7Dokument4 SeitenClose Exam 7sieged_rj3165Noch keine Bewertungen
- VTH Compre 1 by Perfecto Padilla JRDokument67 SeitenVTH Compre 1 by Perfecto Padilla JROwen Francis Arles MaongatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple ChoiceDokument61 SeitenMultiple ChoiceDenaiya Watton Leeh100% (7)
- CN Chap10 - Moments of InertiaDokument25 SeitenCN Chap10 - Moments of Inertiaengineer_atulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Const2Dokument101 SeitenDesign and Const2Sigue Ramel HinayasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bsce Quarantine Reviewer Diagnostic Exams PDFDokument27 SeitenBsce Quarantine Reviewer Diagnostic Exams PDFLaurence CervoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of MaterialsDokument1 SeiteStrength of MaterialsAnonymous P1iMibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials 1 PDFDokument3 SeitenStrength of Materials 1 PDFMaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm 20210405 SolutionDokument12 SeitenMidterm 20210405 SolutionSelf SevNoch keine Bewertungen
- DE Midterm ExaminationDokument3 SeitenDE Midterm ExaminationHades Vesarius RiegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock Board Examination in Mathematics A PDFDokument5 SeitenMock Board Examination in Mathematics A PDFVea ValcorzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry FinalDokument28 SeitenGeometry FinalVholts Villa VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part I - GeometryDokument4 SeitenPart I - GeometryMart Brevin Biton100% (1)
- Algebra ModuleDokument11 SeitenAlgebra ModuleGracielle Nebres100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Vector AnalysisDokument54 SeitenChapter 1 - Vector AnalysisandersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 2Dokument23 SeitenSet 2Sherwin Millares100% (1)
- Strength of Materials: de La Salle University - DasmariñasDokument5 SeitenStrength of Materials: de La Salle University - DasmariñasChynna Camille FortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Geometry 1Dokument4 SeitenAnalytic Geometry 1Mj AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity # 5: Solve The Following Problems. Show Clean and Complete Solutions For Each NumberDokument3 SeitenActivity # 5: Solve The Following Problems. Show Clean and Complete Solutions For Each NumberEurydiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials Compilation Team Malakas XD 1Dokument43 SeitenStrength of Materials Compilation Team Malakas XD 1Reiniel Cirujano AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Ball PresentationDokument18 SeitenCrystal Ball PresentationDruzmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Practice Problems Module 4Dokument9 SeitenMath Practice Problems Module 4Peejay OllabracNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eqe Reviewer With AnswerDokument16 SeitenEqe Reviewer With AnswerKirstie Alley San JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amplitude, Period, Phase Shift and FrequencyDokument19 SeitenAmplitude, Period, Phase Shift and FrequencyPaula FanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALGEBRA Board Exam ProblemsDokument9 SeitenALGEBRA Board Exam ProblemsAsagiri, Kishi D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diff Eq MidtermDokument28 SeitenDiff Eq MidtermThe Scam Gamer100% (1)
- Worksheet 6 Integral Calculus PDFDokument10 SeitenWorksheet 6 Integral Calculus PDFbenny bullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 Part 1Dokument1 SeiteAssignment 3 Part 1Student555Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz No 1Dokument2 SeitenQuiz No 1Tris ZackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra 3 KeyDokument2 SeitenAlgebra 3 KeyKim OrtuosteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upang Cea Common Bes025 p3Dokument69 SeitenUpang Cea Common Bes025 p3Jairo OntongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce Correl Solid GeometryDokument3 SeitenCe Correl Solid GeometryGlenn Frey LayugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Umay DesignDokument55 SeitenUmay DesignMhel CenidozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esplana SteelDesign2Dokument1 SeiteEsplana SteelDesign2Naigell SolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsDokument3 SeitenExcellence in Professional Engineering Review and Training SolutionsGlaiza Marie100% (1)
- GeometryDokument22 SeitenGeometrycharles gueta100% (1)
- Strength of MaterialsDokument10 SeitenStrength of MaterialsCaro Kan LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of MaterialsDokument11 SeitenStrength of Materialsjerold_arandiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-Inverse Laplace TransformsDokument25 Seiten4-Inverse Laplace TransformsADITYA THAKURNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of MetalsDokument26 SeitenMechanical Properties of MetalsIzzat IkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- 94 - Strength of Materials Refrehser SetDokument4 Seiten94 - Strength of Materials Refrehser SetJ O M A RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics PDFDokument6 SeitenAdvanced Engineering Mathematics PDFrenegadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems 1Dokument5 SeitenPractice Problems 1Lanz de la Cruz100% (1)
- MAT 171 ReviewDokument5 SeitenMAT 171 ReviewyveeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CalculusDokument16 SeitenCalculuscharles gueta100% (1)
- Module+5+ +Engg+Math+ +trigonometry+ (Part+3)Dokument14 SeitenModule+5+ +Engg+Math+ +trigonometry+ (Part+3)Satoru FujinumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14right Angle TrigonometryDokument12 Seiten14right Angle TrigonometryMhai MabantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry TipqcDokument62 SeitenTrigonometry TipqcMichael Damian50% (2)
- Polymer Carbon Black Composite Sensors in An Enose For Air Qual Monitoring Paper3Dokument6 SeitenPolymer Carbon Black Composite Sensors in An Enose For Air Qual Monitoring Paper3urfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quadrilateral - Always, Sometimes. Never (Answers)Dokument1 SeiteQuadrilateral - Always, Sometimes. Never (Answers)urfriend_jjn0580% (5)
- Sensors 2009, 9, 5099-5148 Doi:10.3390/s90705099Dokument50 SeitenSensors 2009, 9, 5099-5148 Doi:10.3390/s90705099Roshan AithalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung Cancer Detection Using An Enose IfpropDokument16 SeitenLung Cancer Detection Using An Enose Ifpropurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exhaled Breath Analysis in TB Case DetectionDokument2 SeitenExhaled Breath Analysis in TB Case Detectionurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Newton RaphsonDokument30 SeitenNewton Raphsonurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eee101 Expt3 PDFDokument4 SeitenEee101 Expt3 PDFurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet Opamp 741Dokument8 SeitenDatasheet Opamp 741phamvinh1102Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tach Circuit For V2.98 and Higher: Note This Was Tested With V2.98 Code and Bosch Solid-State Ignition - Peter FloranceDokument1 SeiteTach Circuit For V2.98 and Higher: Note This Was Tested With V2.98 Code and Bosch Solid-State Ignition - Peter Floranceurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1Dokument53 SeitenModule 1s.thrinadhraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euclid Pja 1116442375 PDFDokument6 SeitenEuclid Pja 1116442375 PDFurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- TRIGONOMETRYDokument8 SeitenTRIGONOMETRYurfriend_jjn05100% (1)
- OxygenSensorInstall PDFDokument3 SeitenOxygenSensorInstall PDFurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- PT ScriptDokument7 SeitenPT Scripturfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Review PDFDokument19 SeitenFinal Review PDFurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee105disc1 PDFDokument5 SeitenEe105disc1 PDFurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Tips On How To Answer Board Exam QuestionsDokument6 Seiten11 Tips On How To Answer Board Exam Questionsurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA3 Chap3 Practice TestanswersDokument6 SeitenCCNA3 Chap3 Practice Testanswersurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1986 Toyota 22RTE/RE EFI Wiring DiagramDokument3 Seiten1986 Toyota 22RTE/RE EFI Wiring DiagramGrant Dickerson100% (1)
- Eigrp & Rip CommandsDokument2 SeitenEigrp & Rip Commandsurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Probability HandoutsDokument11 SeitenProbability HandoutsChristian Antonio0% (1)
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsDokument24 SeitenCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsAllan Paul Lorenzo Abando76% (17)
- Nodal Mesh MethdDokument20 SeitenNodal Mesh MethdMurat GülerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3001 Coms SummaryDokument29 Seiten3001 Coms SummaryJeremiash ForondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Megasquirt 1Dokument52 SeitenMegasquirt 1urfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- INTEGRAL CALCULUS HandoutsDokument7 SeitenINTEGRAL CALCULUS Handoutsurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Smart Serial Male DTE To Male DCE 20ft Crossover CableDokument1 SeiteCisco Smart Serial Male DTE To Male DCE 20ft Crossover Cableurfriend_jjn05Noch keine Bewertungen
- AlgebraDokument18 SeitenAlgebraJhana Kimberly S. AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theorem: Using The Law of CosinesDokument8 SeitenTheorem: Using The Law of Cosinesjewish vanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cosine, Sine and Tangent of Multiple Angles (Recursive Formula)Dokument5 SeitenCosine, Sine and Tangent of Multiple Angles (Recursive Formula)Toyen BlakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiitjee Straight LineDokument3 SeitenFiitjee Straight LineMayank VatsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circle & Straight Line AssignmentDokument13 SeitenCircle & Straight Line AssignmentNdjskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Illustrate Congruent Triangle (M8GE-IIId-1) - Learning Activity SheetsDokument7 SeitenIllustrate Congruent Triangle (M8GE-IIId-1) - Learning Activity SheetsSheryl B. PresentacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM Pre Calculus Q2 M9 V2-DumoDokument19 SeitenLM Pre Calculus Q2 M9 V2-DumoTERESA N. DELOS SANTOS100% (1)
- Modul 10 - Solution of TriangleDokument21 SeitenModul 10 - Solution of Trianglehasnitajb100% (1)
- Disha Publication Rapid Shortcuts On Trigonometry. CB486988875 PDFDokument33 SeitenDisha Publication Rapid Shortcuts On Trigonometry. CB486988875 PDFShubham MoitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2 Holt Algebra 2 Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2Dokument27 SeitenWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2 Holt Algebra 2 Holt Mcdougal Algebra 2Rica MelchorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 13.2 (Solutions) : Question # 1Dokument6 SeitenExercise 13.2 (Solutions) : Question # 1faizankhan23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Class X Periodic Test II 40 Marks Sample Paper 02Dokument3 SeitenMaths Class X Periodic Test II 40 Marks Sample Paper 02hweta173Noch keine Bewertungen
- كراسة التمارين ١٢ ع فصل ثاني طبعة ثانيةDokument69 Seitenكراسة التمارين ١٢ ع فصل ثاني طبعة ثانيةAmani EbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry त्रिकोणमिति Extracted Previous year Latest QuestionsDokument16 SeitenTrigonometry त्रिकोणमिति Extracted Previous year Latest QuestionsSumit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- D 08 Poly Hedra TextDokument264 SeitenD 08 Poly Hedra Texteluucee81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Eq. and Ineq. - (SP, Step-1 To 3) - JEE-22-With Ref-30!9!20Dokument18 SeitenTrigonometric Eq. and Ineq. - (SP, Step-1 To 3) - JEE-22-With Ref-30!9!20Subrata KarmakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume of A PyramidDokument8 SeitenVolume of A PyramidAyeola RobertsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congruent Triangle ReviewDokument10 SeitenCongruent Triangle Reviewapi-283693756Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trig Functions of Special AnglesDokument23 SeitenTrig Functions of Special Anglesskitofu9114404Noch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Mathematics January 2015 P2 PDFDokument36 SeitenCSEC Mathematics January 2015 P2 PDFVanni xsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To The 2005 CMO: SolutionDokument9 SeitenSolutions To The 2005 CMO: Solutionshitaldr767Noch keine Bewertungen
- Proving Trigonometric IdentitiesDokument31 SeitenProving Trigonometric IdentitiesJedidah JongNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCSE Maths Equations To MemoriseDokument3 SeitenGCSE Maths Equations To MemoriseexxclaimNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIMO Sample Questions (ALL Groups) : 幼稚園組/ Kindergarten GroupDokument5 SeitenTIMO Sample Questions (ALL Groups) : 幼稚園組/ Kindergarten GroupSan KimSorngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 8 ClassDokument4 SeitenMathematics 8 ClassArooj BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Usemo 2022Dokument30 SeitenReport Usemo 2022au auNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 6-Q2-Theorems On SecantDokument2 SeitenWeek 6-Q2-Theorems On SecantLove Jen Bongon Estoque-AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triangles: On With Rational Altitudes, Angle Bisectors or MediansDokument123 SeitenTriangles: On With Rational Altitudes, Angle Bisectors or Medianskcassandra_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Sine Cosine and Tangent in Four QuadrantsDokument8 Seiten8 Sine Cosine and Tangent in Four Quadrantsapi-299265916Noch keine Bewertungen
- STD XTH Geometry Maharashtra BoardDokument35 SeitenSTD XTH Geometry Maharashtra Boardphanikumar50% (2)
- Geometry - Olympiad Material BY DR SHYAM SUNDAR AGRAWALDokument67 SeitenGeometry - Olympiad Material BY DR SHYAM SUNDAR AGRAWALdrssagrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tired of Being Tired: Receive God's Realistic Rest for Your Soul-Deep ExhaustionVon EverandTired of Being Tired: Receive God's Realistic Rest for Your Soul-Deep ExhaustionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Power Moves: Ignite Your Confidence and Become a ForceVon EverandPower Moves: Ignite Your Confidence and Become a ForceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Becoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonVon EverandBecoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1478)
- Son of Hamas: A Gripping Account of Terror, Betrayal, Political Intrigue, and Unthinkable ChoicesVon EverandSon of Hamas: A Gripping Account of Terror, Betrayal, Political Intrigue, and Unthinkable ChoicesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (497)
- How to Walk into a Room: The Art of Knowing When to Stay and When to Walk AwayVon EverandHow to Walk into a Room: The Art of Knowing When to Stay and When to Walk AwayBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- The False White Gospel: Rejecting Christian Nationalism, Reclaiming True Faith, and Refounding DemocracyVon EverandThe False White Gospel: Rejecting Christian Nationalism, Reclaiming True Faith, and Refounding DemocracyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- Out of the Dark: My Journey Through the Shadows to Find God's JoyVon EverandOut of the Dark: My Journey Through the Shadows to Find God's JoyBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (13)
- Bait of Satan: Living Free from the Deadly Trap of OffenseVon EverandBait of Satan: Living Free from the Deadly Trap of OffenseBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (311)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- The Freedom of Self-Forgetfulness: The Path to True Christian JoyVon EverandThe Freedom of Self-Forgetfulness: The Path to True Christian JoyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (192)
- Crazy Love, Revised and Updated: Overwhelmed by a Relentless GodVon EverandCrazy Love, Revised and Updated: Overwhelmed by a Relentless GodBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1001)
- Out of the Dark: My Journey Through the Shadows to Find God's JoyVon EverandOut of the Dark: My Journey Through the Shadows to Find God's JoyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- The Dangers of a Shallow Faith: Awakening From Spiritual LethargyVon EverandThe Dangers of a Shallow Faith: Awakening From Spiritual LethargyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (135)
- Now and Not Yet: Pressing in When You’re Waiting, Wanting, and Restless for MoreVon EverandNow and Not Yet: Pressing in When You’re Waiting, Wanting, and Restless for MoreBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Just Do Something: A Liberating Approach to Finding God's WillVon EverandJust Do Something: A Liberating Approach to Finding God's WillBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (98)
- Holy Bible in Audio - King James Version: The Complete Old & New TestamentVon EverandHoly Bible in Audio - King James Version: The Complete Old & New TestamentBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (105)
- Imagine the God of Heaven: Near-Death Experiences, God’s Revelation, and the Love You’ve Always WantedVon EverandImagine the God of Heaven: Near-Death Experiences, God’s Revelation, and the Love You’ve Always WantedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (30)
- Jesus and the Powers: Christian Political Witness in an Age of Totalitarian Terror and Dysfunctional DemocraciesVon EverandJesus and the Powers: Christian Political Witness in an Age of Totalitarian Terror and Dysfunctional DemocraciesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- The Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYVon EverandThe Secret Teachings Of All Ages: AN ENCYCLOPEDIC OUTLINE OF MASONIC, HERMETIC, QABBALISTIC AND ROSICRUCIAN SYMBOLICAL PHILOSOPHYBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryVon EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (44)