Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
DLD
Hochgeladen von
Sandy RonaldoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DLD
Hochgeladen von
Sandy RonaldoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SR INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
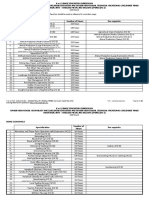
Rampally(V), Keesara(M), Ranga Reddy(Dist.) 501 301 Name of the faculty: Class: Class Hours UJWALA.B ECE 2nd BTECH 2 SEM 78
Lesson Plan of : __________________________________________ PULSE AND DIGITAL CIRCUITS Credit: 4 Total Number of Lectures Available:80 Total Number of Lecture According to Lesson Plan: 78 Lec No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 Date 17/12/12 to 22/12/12 Topic to be covered Linear wave shaping :Low pass RC circuits or sinusoidal input Step and pulse input Low pass response for ramp input Low pass response for square wave input Low pass circuit acts as an integrator High pass circuit for sinusoidal and step input Response for ramp input Response for square wave input attenuators RL and RLC circuits Ringing circuit NON-LINEAR WAVE SHAPING:Diode clippers Clipping at two independent levels Transistor clippers Comparators,applications of voltage comparators Clamping operation Clamping circuit taking source and diode resistance taking into account Clamping circuit theorem Practical clamping circuits Effect of diode characteristics on clamping voltage Synchronized clamping Switching characteristics of diodes :Diode as a switch Piecewise linear diode characteristics Diode switching times Transistor as a switch Breakdown voltages Transistor in saturation Temperature variation of saturation parameters Transistor switching times Silicon controlled switch circuits Multivibrators: Fixed Bias Bistable Multivibrator Problems on fixed bias multivibrator Reference T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3
24/12/12 to 29/12/12
31/12/12 to 05/01/13
07/01/13 to 12/01/13
16/01/13 to 22/01/13
23/01/13 to 29/01/13
30/01/13 to 05/01/13
33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76
30/01/13 to 05/01/13
06/01/13 to 10/01/13
14/02/13 to 20/02/13
21/02/13 to 27/02/13
28/02/13 to 06/03/13
07/03/13 to 13/03/13
14/03/13 to 20/03/13
21/03/13 to 27/03/13
28/03/13 to 03/04/13
04/04/13 to 10/04/13
A self biased transistor binary commutating capacitors A non saturating binary A direct connected binary the emmiter coupled binary the collector coupled monostable multivibrator the collector coupled monostable multivibrator emmiter coupled monostable multivibrator triggering the monostable multivibrator the collector coupled astable multivibrator the collector coupled astable multivibrator emmiter coupled astable multivibrator emmiter coupled astable multivibrator TIME BASE GENERATORS: methods of generating time base waveform Miller and Bootstrap time base generators basic principles Miller and Bootstrap time base generators basic principles Transistor miller time base generator Transistor Bootstrap time base generator Transistor Bootstrap time base generator Current time base generators Current time base generators Methods of linearity improvement. SAMPLING GATES: Basic operating principles of sampling gates Unidirectional sampling gates bidirectional sampling gates Four diode sampling gate Reduction of pedestal in gate circuits Six diode gate Applications of sampling gates. SYNCHRONIZATION AND FREQUENCY DIVISION: Pulse synchronization of Relaxation devices Freq uency division in sweep circuit Stability of relaxation devices Astable relaxation circuits Monostable relaxation circuits Synchronization of a sweep circuit with symmetrical signals Synchronization of a sweep circuit with symmetrical signals Sine wave frequency division with a sweep circuit Sine wave frequency division with a sweep circuit A sinusoidal divider using Regeneration and Modulation A sinusoidal divider using Regeneration and Modulation REALIZATION OF LOGIC GATES USING DIODES & TRANSISTORS: AND, OR and NOT gates using Diodes and transistors DCTL RTL DTL TTL
T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3
77 78
04/04/13 to 10/04/13
CML comparision
T1,R1,R3 T1,R1,R3
TEXT BOOKS : 1. 2. Pulse, Digital and Switching Waveforms - J. Millman and H. Taub, McGraw-Hill, 1991. Solid State Pulse circuits - David A. Bell, PHI, 4th Edn., 2002 .
REFERENCES : 1. 2. 3. Pulse and Digital Circuits - A. Anand Kumar, PHI, 2005. Wave Generation and Shaping - L. Strauss. Pulse, Digital Circuits and Computer Fundamentals - R.Venkataraman.
SR INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Rampally(V), Keesara(M), Ranga Reddy(Dist.) 501 301 Name of the faculty: Class: Class Hours UJWALA.B ECE II BTECH II SEM 50 mints
Lesson Plan of : __________________________________________ SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN Credit: 4 Total Number of Lectures Available: 80 Total Number of Lecture According to Lesson Plan: 82
LEC NO 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. DATE
TOPIC TO BE COVERED
BINARY SYSTEMS :Philosophy of number systems 17/12/12 Decimal and binary number system to octal and hexadecimal number systems 22/12/12 Conversions from 1 number system to other number system 1s and 2s complement representation of negative numbers and problems 9,s and 10,s complements and subtraction methods 24/12/12 Binary arithmetic: addition, subtraction, multiplication, to Binary codes, Gray code , XS-3 code and problems 29/12/12 BCD codes,BCD addition and subtraction error detecting codes,binary logic Error correcting codes,binary storage and registers BOOLEAN ALGEBRA AND LOGIC GATES :Fundamental 31/12/12 postulates of Boolean algebra to 05/01/13 Basic theorems and properties Reducing Boolean expressions Logic gates, universal logic gates Boolean functions and their representation 07/01/13 Canonical SOP,POS forms Standard SOP ,POS forms and problems to 12/01/13 Properties of XOR gates
REFERENC E T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3,R2 T2,T3
integrated circuits
GATE LEVEL MINIMIZATION :Introduction 16/01/13 Minimization of SOP and POS forms k-map for 2 and 3 variables to 22/01/13 k-map for 4 variables k-map for 5 variables Dont care combinations,Exclusive Or function 23/01/13 NAND and NOR implementation other Two-level implementnations, to 29/01/13 Hardward Description language (HDL). COMBINATIONAL LOGIC :Combinational Circuits
30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41.
Analysis procedure 30/01/13 Design procedure to Binary Adder 05/01/13 Binary Subtractor
Decimal Adder
T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3
Binary multiplier 06/01/13 magnitude comparator to magnitude comparator 10/01/13 Decoders Encoders Multiplexers
42.
43. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76.
14/02/13 problems to HDL for combinational circuits 20/02/13 HDL for combinational circuits SYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL LOGIC :Sequential circuits latches, Flip-Flops Analysis of clocked sequential circuits HDL for sequential circuits 28/02/13 HDL for sequential circuits State Reduction and Assignment to 06/03/13 State Reduction and Assignment
Design Procedure.
discussion 07/03/13 UNIT-6:Registers to shift Registers 13/03/13
SISO
SIPO 14/03/13 PISO,PIPO Ripple counters to 20/03/13 synchronous counters
other counters HDL for Registers 21/03/13 HDL for Registers
to HDL for counters 27/03/13 HDL for Registers discussion UNIT-7:Random-Access Memory Memory Decoding Error Detection & correction Read-only memory Programmable logic Array 04/04/13 programmable Array logic to 10/04/13
Sequential Programmable Devices.
77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82.
04/04/13 to ASYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL LOGIC :introduction 10/04/13
Analysis Procedure
T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3 T2,T3
Circuits with Latches
Design Procedure Reduciton of state and Flow Tables Hazards, Design Example. Race-Free state Assignment
TEXT BOOKS : 1. DIGITAL DESIGN Third Edition , M.Morris Mano, Pearson Education/PHI. 2. FUNDAMENTALS OF LOGIC DESIGN, Roth, 5th Edition,Thomson. REFERENCES : 1. Switching and Finite Automata Theory by Zvi. Kohavi, Tata McGraw Hill. 2. Switching and Logic Design, C.V.S. Rao, Pearson Education 3. Digital Principles and Design Donald D.Givone, Tata McGraw Hill, Edition. 4. Fundamentals of Digital Logic & Micro Computer Design , 5TH Edition, M. Rafiquzzaman John Wiley
Rafiquzzaman John Wiley
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Antenna em Modeling MatlabDokument284 SeitenAntenna em Modeling MatlabMarcelo Perotoni100% (3)
- 7 SegmentDokument1 Seite7 SegmentSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolarDokument9 SeitenSolarSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yogi 1Dokument7 SeitenYogi 1Sandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of MaerialsDokument45 SeitenStrength of MaerialsShivakumar PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuzzy With SVMDokument5 SeitenFuzzy With SVMSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AzliNing2003 ApplicationOfFuzzyLogic InAnOptimalDokument6 SeitenAzliNing2003 ApplicationOfFuzzyLogic InAnOptimalNur Aditya RizaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8051 Addressing ModesDokument1 Seite8051 Addressing ModesSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yogi 2Dokument17 SeitenYogi 2Sandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec2308: Microprocessors & Microcontrollers Lab Manual V Sem EceDokument99 SeitenEc2308: Microprocessors & Microcontrollers Lab Manual V Sem EceSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic Applications Lab NewDokument12 SeitenIc Applications Lab NewSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EdcDokument3 SeitenEdcSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- InTech-Bidirectional DC DC Converters For Energy Storage SystemsDokument19 SeitenInTech-Bidirectional DC DC Converters For Energy Storage SystemsSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EdcDokument3 SeitenEdcSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tools and Equipment of WorkshopDokument2 SeitenTools and Equipment of WorkshopSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01620561Dokument7 Seiten01620561Sandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sugeno-Type Fuzzy Logic Controller (SFLC) For A Modular Structured Multilevel Inverter (MSMI)Dokument5 SeitenSugeno-Type Fuzzy Logic Controller (SFLC) For A Modular Structured Multilevel Inverter (MSMI)Sandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Common Java CookbookDokument333 SeitenThe Common Java Cookbooktmo9d100% (20)
- A Brief Guide To TransferFunctions, Poles and ZeroesDokument11 SeitenA Brief Guide To TransferFunctions, Poles and ZeroesSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- State-Space Average Modelling of 6-And 12-Pulse Diode RectifiersDokument10 SeitenState-Space Average Modelling of 6-And 12-Pulse Diode RectifiersSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AzliNing2003 ApplicationOfFuzzyLogic InAnOptimalDokument6 SeitenAzliNing2003 ApplicationOfFuzzyLogic InAnOptimalNur Aditya RizaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuzzy With SVMDokument5 SeitenFuzzy With SVMSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling of Multi-Converter More Electric Ship Power Systems Using The Generalized State Space MethodDokument6 SeitenModeling of Multi-Converter More Electric Ship Power Systems Using The Generalized State Space MethodSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sea and UnderseaDokument8 SeitenSea and UnderseaSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oshaben Edward JDokument74 SeitenOshaben Edward JSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access: QualityDokument5 SeitenAccess: QualitySandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Power Electronic Converters Using The Generalized State-Space Averaging ApproachDokument4 SeitenAnalysis of Power Electronic Converters Using The Generalized State-Space Averaging ApproachSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZvsDokument29 SeitenZvsSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation in Fixed BWA Systems: ProceedingsDokument4 SeitenDynamic Bandwidth Allocation in Fixed BWA Systems: ProceedingsSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Transistor Equivalent Book 2sc2238Dokument31 SeitenTransistor Equivalent Book 2sc2238rsmy88% (32)
- Rotor-Gene 6000 ManualDokument143 SeitenRotor-Gene 6000 ManualamineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parker Hyd MotorDokument44 SeitenParker Hyd MotorUNIISCRIBDNoch keine Bewertungen
- New technologies transform vehicle design and materialsDokument145 SeitenNew technologies transform vehicle design and materialsHuy Nguyễn75% (4)
- Evolution of Microsoft Word VersionsDokument12 SeitenEvolution of Microsoft Word Versionsparminder_1993_21813100% (1)
- Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Kharagpur, West Bengal 721302Dokument28 SeitenIndian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Kharagpur, West Bengal 721302Bipradip BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- D 559 - 03 Standard Test Methods For Wetting and Drying Compacted Soil-Cement Mixtures PDFDokument7 SeitenD 559 - 03 Standard Test Methods For Wetting and Drying Compacted Soil-Cement Mixtures PDFРадо МицевNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpaceExplorationDebate ManualDokument14 SeitenSpaceExplorationDebate ManualCaren JasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Systems ReliabilityDokument27 SeitenPower Systems Reliabilityrprp2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- RS 485 25a ManDokument8 SeitenRS 485 25a MansitronixexNoch keine Bewertungen
- EX037 Report by Penny Taylor - Factual Report - September 2008 PDFDokument46 SeitenEX037 Report by Penny Taylor - Factual Report - September 2008 PDFagitentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Injection Molding - Fundamentals and Applications - Kamal Et AlDokument39 SeitenInjection Molding - Fundamentals and Applications - Kamal Et AlmohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument2 SeitenPDFrubenpatNoch keine Bewertungen
- B&E Brochure - ADC PDFDokument31 SeitenB&E Brochure - ADC PDFAbhishek VernekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROFIenergy WoL DOKU V16 en PDFDokument35 SeitenPROFIenergy WoL DOKU V16 en PDFfasgafdgsfdgsfdgafdNoch keine Bewertungen
- BO Web Intelligence XI Report Design QA210 Learner's GuideDokument374 SeitenBO Web Intelligence XI Report Design QA210 Learner's GuideTannoy78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cx31 Cat Transmission-Student HandoutDokument25 SeitenCx31 Cat Transmission-Student Handouteng_ebrahim_2000100% (4)
- 16th International Conference on Quality in Research (QiRDokument1 Seite16th International Conference on Quality in Research (QiRArifo Gunawan CahyanegoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Under The Waves, Above The Clouds. A History of The Pressure Suit.Dokument345 SeitenUnder The Waves, Above The Clouds. A History of The Pressure Suit.veence spenglerNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Elementary Lesson Plan TemplateDokument3 SeitenUNLV/Department of Teaching & Learning Elementary Lesson Plan Templateapi-454999501Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 15 - Adv CostDokument8 SeitenChapter 15 - Adv CostKIROJOHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flash Protection For Stellaris® MicrocontrollersDokument7 SeitenFlash Protection For Stellaris® MicrocontrollersTi MicrocontrollersNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABAP Test 1. Full Buffering Would Be Appropriate ForDokument9 SeitenABAP Test 1. Full Buffering Would Be Appropriate ForHemadri NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- K to 12 Guide on Shielded Metal Arc Welding CurriculumDokument26 SeitenK to 12 Guide on Shielded Metal Arc Welding CurriculumJoven Francisco100% (4)
- Literature Web RubricDokument1 SeiteLiterature Web RubricrfitzgeraldNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 - Transformer Protection Guide PDFDokument33 Seiten09 - Transformer Protection Guide PDFseshatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sulfur Recovery PDFDokument32 SeitenSulfur Recovery PDFShaho Abdulqader Mohamedali0% (1)
- Electricity Basics: Charges, Fields and CurrentsDokument17 SeitenElectricity Basics: Charges, Fields and CurrentsAyushJaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYTROL CT-3000 Transfer Manual Instruction ManualDokument12 SeitenHYTROL CT-3000 Transfer Manual Instruction Manualu2azovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recommendations For Layout, Design and Construction of Greenhouse StructuresDokument10 SeitenRecommendations For Layout, Design and Construction of Greenhouse StructuresCgpscAspirantNoch keine Bewertungen