Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A Study On Credit Appraisal
Hochgeladen von
Mallik ArjunOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A Study On Credit Appraisal
Hochgeladen von
Mallik ArjunCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A study on credit appraisal
MEANING OF FINANCE Finance is also the science and art of determining if the funds of an organization are being used properly. Through financial analysis, companies and businesses can take decisions and corrective actions towards the sources of income and the expenses and investments that need to be made in order to stay competitive. Finance is the life blood of business. It flows in mostly from scale of goods and services. It flows out for meeting various types of expenditure. The activating element in any business which may be on industrial or commercial undertaking is the finance. Business finance has been defined as those activities which have to do with the provision and management of funds for the satisfactory conduct of a business. Business finance is defined as that business activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting the financial needs and overall objectives of business enterprises. So we can say business finance is mainly developed around three major objectives. Firstly, to obtain an adequate supply of capital for the needs of the business, Secondly, to conserve and increase the capital through better management, Thirdly, to make profit from the use of funds this is an overall objective of a business enterprise.
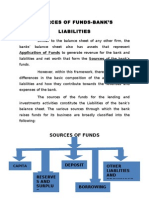
INDIAN FINANCIAL SYSTEM The financial system or the financial sector of any country consists of specialized and nonspecialized financial institutions of organized and unorganized financial markets of financial instruments and services, which facilitate transfer of funds procedures and practises adopted in the markets and financial interrelationship, are also part of the system. The structure of a financial system in any economy is as follows:
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 1
A study on credit appraisal
UNORGANISED MARKETS In these markets consist of many lenders, indigenous bankers, transfers and private chit funds etc. whose activities are not controlled by RBI. Recently the RBI has taken steps to bring private function companies and chit funds its strict control but using non banking financial companies directions in 1998. ORGANISED MARKETS In these markets there are standardized rules and regulations by Reserve Bank of India or other regulatory bodies. The organized markets can be further classified into two. They are: 1) Capital market. 2) Money market. CAPITAL MARKET: It is a market for long term funds which have a long or indefinite maturity. Capital market further divided into three mainly: a) Industrial Security market: It is a market for industry security namely equity shares or ordinary shares, preference share, debentures or bonds. It is a market where industrial concern raises their capital or debt by assuring appropriate instruments. It can be further subdivided into two. They are:
Primary market: It is a market for new issue or new financial claims. Secondary market: It is a market for existing securities and those already issued and quoted in stock exchange.
b) Government Securities Market: It is also called gilt-edged securities market. It is a market where government securities are traded (long term securities)
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 2
A study on credit appraisal
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS A financial instrument refers to these documents which represent financial claims on assets. Financial instrument can also be called financial securities. These instruments are classified into a) PRIMARY SECURITIES: Shares and debentures issued directly to Public.
b) SECONDARY SECURITIES: These securities issued by some intermediaries ex; UTI and Mutual fund again these securities may be classified on the basis of duration as follows. Short Term Securities: Within one year ex; bills of exchange. Medium Term Security: Maturity period between 1-5 years ex; debentures. Long Term Securities: Maturity period more than 5 years ex; Gilts.
FINANCIAL SERVICES a) MERCHANT BANKING: A merchant banker is a financial intermediary who helps to transfer capital from those it to those who need it. b) LOAN SYNDICATION: Much number of banks joins together and forms a syndicate to provide loan as big sum to corporate. c) LEASING: A lease is an agreement under which a company acquires a right to make use of capital assets like machinery for agreed period in return for periodic payment of rentals. d) HIRE PURCHASE: It is an agreement relating to transaction in which goods are let on hire. e) FACTORING: It is an agreement under which a financial intermediary assumes the credit risk in the collection of book debt passes for its client. f) VENTURE CAPITAL: A venture capitalist finances a project based on the potentialities of new innovative projects for new entrepreneurs. g) MUTUAL FUND: A mutual fund refers to a fund raised by a financial services company by pooling the savings of the public.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 3
A study on credit appraisal
MEANING OF BANK Banking is one of the most important sectors of business and finance that assists the world of commerce to keep on running. Without banks and the banking services that they provide, commerce and trade would collapse and credit would become virtually extinct. As the decades progress many new concepts are being introduced into banking. At their most basic, banks hold money on behalf of customers, which is payable to the customer on demand, either by appearing at the bank for a withdrawal or by writing a check to a third party. Banks use the money they hold to finance loans, which they make to businesses and individuals to pay for operations, mortgages, education expenses, and any number of other things. DEFINITION OF BANK An organization, usually a corporation, chartered by a state or federal government, which does most or all of the following: receives demand deposits and time deposits, honours instruments drawn on them, and pays interest on them; discounts notes, makes loans, and invests in securities; collects checks, drafts, and notes; certifies depositor's checks; and issues drafts and cashier's checks. CLASSIFICATION OF BANK Banks are classified into various types based on the function they perform. They are as follows: 1. COMMERCIAL BANK: Commercial banks perform all the business transactions of a typical bank. They accept saving bank deposits, fixed deposits and current deposits which are repayable on demand or on short notice. Likewise, they lend or invest only for short durations. They provide funds only for short term needs of trade and commerce. These banks cannot invest credits and overdrafts as they are expected to meet the immediate requirement of depositors. The commercial banks provide a vital service to its customers, a simple means of medium of exchange called cheques. They also perform a large number of agency functions to their customers for which they charge a commission.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 4
A study on credit appraisal
2. INDUSTRIAL/ INVESTMENTS BANKS: Investment banks, also called industrial banks, are those banks which provide funds on a long for industries. They are specialized in providing long term loans to industries with a view to buy plant, machineries, etc. These banks obtain funds through share capital, debenture and long term deposits from the public. The bank floats bonds for the sake of mobilizing funds to provide funds for big industrial corporations. They also underwrite or issue new shares and debenture of industrial companies. They also purchase entire issue of new securities of company and later sell them to public at higher prices. 3. EXCHANGE BANKS: Exchange banks are known as foreign banks or foreign exchange banks. These banks also provide foreign exchange for import trade. Their main function is to make international payment through the purchase and sale of exchange bills. The exchange bank provides assistance in the conversion of currencies. They discount foreign exchange bills which are used in foreign trade. 4. CO-OPERATIVE BANKS: Co-operative banks are performed to meet the meet the banking requirements of consumers. They are established in urban as well as rural areas. In rural areas, the bank provides finance to agriculture and in urban area it provides finance to buy consumer goods. These banks function like commercial banks receiving deposits and lending money. They provide short and medium term loans. As they are formed on cooperative principles, they are more service oriented rather than profit. The bank provides credit at lower rates of interest to people of small means like small cultivators, artisans, petty shop-keepers etc. They have been classified into land development banks or land mortgage banks and urban credit-oriented banks. 5. SAVINGS BANK: Savings banks are specialized financial institution establishment to mobilize savings from the people. They pool the savings of the small incomes of the community. The savings banks
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 5
A study on credit appraisal
accounts have been provided by all commercial and co-operative banks and even post offices. Saving bank business has become more prominent than others forms of accounts as it provide various facilities like frequent withdrawals, attractive rate of interest, the use of cheques etc. 6. CENTRAL BANK (RBI): Central bank is an apex bank in the country. It brings the entire banking system unified, controlled and regulated. It is the main source of an efficient banking system in the country. The monetary policy of a country is formulated and enforced by the central bank. It is responsible for monetary stability in the country. The expansion and contraction of note issue are managed by the central bank. It functions as a banker to the government and commercial banks. It assists the government in the implementation of various economies policies. FUNCTIONS OF BANKS Prof. Sayers in his book Modern Banking has described the functions of a modern bank in the following words: Ordinary banking business consists of changing cash from bank deposits and bank deposits for cash, transferring bank deposits for cash, transferring bank deposits from one person to another and giving bank deposits in exchange of bills of exchange, government bonds, the secured promises of businessmen to repay and so forth. The various functions of a modern bank are as follows:
1. Accepting deposits from public:
The major function of the commercial banks is accepting various types of deposits such as fixed deposits, current deposits and savings deposits. People want to keep their cash balances safe for which they deposit it with a bank. The commercial bank protects the cash of the customers and provides a convenient method of transferring funds through the use of cheques. It is the obligation of bank to honour cheques drawn upon the bank, making payment across the counter on demand by the customers to the extent of money available at the credit of customers account.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 6
A study on credit appraisal
Fixed deposits: A fixed deposit is one where a customer keeps a certain amount of money in a bank for a specific period. It may be 6months, 1 year, 2 years 3 years or 5 years. The fixed deposit is not expected to be withdrawn before the expiry of the period. Saving deposits: Saving deposits are those deposits on which the bank pays a certain conditions. The customers are expected to maintain a minimum balance in the account. Current deposits: Current deposits are those deposits which can be withdrawn at any time by means of cheques. The bank does not pay interest on current deposit. A customer who opens a current account has to maintain a minimum credit balance of Rs. 500. At the same time current holders has to pay service charge.
2. Making loans and advances:
The second main function of the commercial banks is to provide loans and advances out of the money the bank receives by the way of deposits. The bank receives deposits in order to lend the same. It is this function of a bankers activities which is the largest contributor to the banks profit. Commercial banks provide various types of loans such as direct loans, cash credit, bills discounted and overdrafts etc. Direct loans and advances are provided to all types of persons against the security of movable properties.
3. Agency services:
Another important function of a banker is the services offered by them as an agent. The commercial banks render a significant service by providing to its customers a simple means of medium of exchange called cheques. The cheque system is considered to be the most developed type of credit instrument. The banks perform miscellaneous functions such as undertaking the payment subscriptions, insurance premium, rent, etc. On the behalf of the customers they collect cheques, bills, salaries, pensions, dividends,
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 7
A study on credit appraisal
interests, etc that belongs to the respective accounts of the customers. The banks perform these functions as per the instructions given by the customers and make payments as and when directed. For these services they charge a certain amount of fee by means of commission.
4. General utility servicesA banker performs many general utility personal or miscellaneous services for his customers. The general utility services include the safe- keeping of valuables and documents, the issue of credit instrument for easy transfer of funds, collection of credit information regarding the customers, transaction in foreign exchange and provision of specialized advisory services to the customers.
EVOLUTION OF BANKING Banking is an ancient business with its history dated back to the 13 th century. When the first bill of exchange was used as money in the medieval trade. Banking in India has its origin as early as the Vedic period. During the days of east India Company, it was the turn of the agency house to carry out the banking business. The general bank of India was the first joint stock bank to be established in the year of 1886. The others that followed are the Bank of Hindustan and the Bengal Bank. In 1891 the first purely Indian Bank that is United Commercial Bank came into being. The setting up of Punjab National Bank in 1894 followed it. In 1920, three bank namely Bank of Bengal (1809), Bank of Bombay (1840), Bank of Madras (1843) was amalgamated and a new bank, Imperial Bank of India was established. The Reserve Bank of India, which is the Central bank, was created in 1935, with the passing Reserve Bank of India act in 1934. Later with the passing of State Bank of India in 1955 the undertaking of Imperial Bank of India was taken over by newly constituted State Bank of India. In the wake of Swadeshi Movement in 1905 no. of Bank with Indian Management were established in the country namely Punjab National Bank Ltd. The Bank of Baroda (1908), Bank of India (1906) Canara Bank Ltd. Indian Bank Ltd, Central Bank of India Ltd.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 8
A study on credit appraisal
(1911). ON July 19th 1969, 14 major Banks of the country were nationalized and on 15 th April 1980 six more Commercial Private Banks were also taken over by the government of India. Banking Industry has achieved a tremendous progress during the past few years; many Banks and Financial Institution have entered into the market and have made a rapid growth towards achieving the ultimate object of attaining leadership in Banking Industry. BANKING PROFILE: The Indian Banking System can be broadly classified into: 1) Nationalized (Government Owned) 2) Private Banks 3) Specialized Banking Institutions The RBI as a centralized body monitoring any discrepancies and short coming in the system. Private Banks has been fast on the uptake and are reorienting their strategies using the internet as the medium. BANKING SECTOR REFORMS: A radical re-structuring of the economic system consisting of industrial deregulation. Liberalization of policies relating to Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), Public Enterprise Reforms, of taxation system, trade liberalization and financial sector has been initiated in 1992-93. Financial sector reforms in the area of commercial banking, capital markets and non-banking finance companies have been undertaken. Improving financial sounds and credibility of banks is a part of banking reforms undertaken by the RBI, a regulatory and supervisory agency over commercial banks under the Banking companies Regulation Act 1949. In the areas of capital markets of SEBI was set up in 1992 to protect the interest of the investors in the securities and to promote development and regulation of security market. In regard to non-banking finance companies the RBI has issued several measures aimed at encouraging disciplined NBFCs, which run on sound business principles. The economic reforms also aimed at improved financial viability and institutional strengthening, to improve the effective
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 9
A study on credit appraisal
implementation of monetary policy, linkages among money anf foreign exchange markets have been enforced. THE ROLE OF BANKS IN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT Commercial Banks are playing a crucial role in the economic development of the country. In fact, without the development of commercial banking in 18th and 19th centuries. In the modern economy, banks considered not only merely as dealers in money but also as reservoirs of resources necessary for the economic development. Banks provide short-term loans which serve as a capital for industrial establishment. Banks also create credit, which enables the industry and commerce to expand economic activities. Banks are contributing very significantly for the expansion of industrialization. Expansion will provide more funds for the entrepreneurs to start new industries, which results in more employment and income generation. A very important service that banks render to the community is the creation of demand deposits in exchange of debts of short-term and long-term securities. Banks promote capital by means of pooling of savings from people. These are the important services rendered by the bank. FOUNDATION OF MODERN BANKING After the nationalization of some big commercial banks in India, there has been an immense growth in banking industry with the establishment of more number of banking offices. Today the banking business has become very competitive. Various types of banks provide large number of services not only on national but international ground as well. The growing trade and commerce has made banks to modernize their operations in order to satisfy the customers. Indian banks have also felt the need for modernization of their operations like their counterparts in western countries. This was very essential as well to deal with extremely increased volume of business in an appropriate and efficient manner and to do effective business. Modern banking institutions have sought to automation like introduction of computers and other equipments as well as the wealth of information technology. Today more and more number of business functions is
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 10
A study on credit appraisal
entrusted on banks. They provide their services to labourers, petty wage earners, small traders, etc. With the appearance of modern banking system, the rural credit system with the money lender nearly collapsed. The modern banks have developed strategies to meet the requirements of common men in achieving economic and social development. NATIONALIZATION OF 14 MAJOR COMMERCIAL BANKS In the history of commercial banking, the nationalization of the Imperial Bank of India was a great achievement. In February 1969, the social control of commercial banks came into force. The government made suitable organizational changes in order to implement the provisions of the Amended Act. The banks were directed to grant loans to agriculture, small scale industries and self employment in an increasing manner. The boards of managements of bank were reconstituted. Yet the industrialists who were on the Board of management continued to exert their influence on the lending policies of the big banks. The Reserve Bank of India started exercising its power to direct the banks when necessary to adopt new regulations. In fact, the social control was in stage of infancy. The government felt that that the social control was not sufficient in a planned economy. The government further said that under the private ownership, social objectives cannot be achieved. Therefore on 19th July 1969, the government announced the nationalization of 14 major banks, whose deposits were not less than 50 crores, through an ordinance. The 14 banks controlled 72 percent of total scheduled bank deposits. The banks that were nationalized are as follows: The Central Bank of India, Ltd. The Bank of India, Ltd. The Punjab National Bank, Ltd The Bank of Baroda, Ltd The United Commercial Bank, Ltd.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 11
A study on credit appraisal
Canara Bank, Ltd. United Bank of India, Ltd. Dena Bank, Ltd. Syndicate Bank of India, Ltd. The Union Bank of India, Ltd Allahabad Bank, Ltd. The Indian Bank, Ltd. The Bank of Maharashtra, Ltd. The Indian Overseas Bank, Ltd. Objectives of Nationalization As stated in the Act, the objective of nationalization is to control the heights of the economy and to meet gradually and enhance the needs of other development of the economy with respect to National Policy and the objectives. Except this main objective, other specific objectives were: Removal of the control of banks by a few persons Provision of adequate credit for agriculture Small scale industry and exports Professional outlook to bank management Encouragement of new classes of entrepreneurs Provide adequate training to staff
The government said that nationalization is a major step in the process of public control over the principal institution. This would mobilize the peoples savings and direct it towards
productive purposes. After the nationalization the banks will be more focused on the serving farmers, promoting agricultural production and developing rural sectors. Public ownership of banking will utilize the credit facility towards speculative and other unproductive purposes.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 12
A study on credit appraisal
Nationalization will also bring right atmosphere for the development of an adequate amount of professional management in the field of banking. Nationalization of six more banks in 1980 Continuing the policy of nationalization, in 1980 the government nationalized six more banks. They were The Andhra Bank, The Corporation Bank, The New Bank of India, The Oriental Bank of Commerce, The Punjab and Sind Bank and The Vijaya Bank. By nationalization of these banks, the government has been able to exercise control over 91 percent of the resources of the entire banking system. Remaining 9 percent is held by foreign banks and private sector banks. Achievements: After nationalization, the government introduced suitable administrative changes to implement the objectives enshrined in the Act. The banks started diversifying lending policies. Government set up different department to handle the proposals. Training centres were established to train the staff. Field officers were recruited to make contact with the prospective customers. Since nationalization, the performance of banking system is outstanding in a lot of respects. RESERVE BANK OF INDIA The RBI was established on 1st April 1935 under the reserve bank of India act, which was passed in the year 1934. The reserve bank of India is the central bank of our country. The RBI was started originally as a scheduled bank and its paid up capital was Rs.5 crores. When RBI was established, it took over the function of currency issue. The reserve bank of India was nationalized in the year 1948. The instruments used by reserve bank of India are. Bank rate Open market operations Variable cash reserve requirements.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 13
A study on credit appraisal
Functions of RBI: The reserve banks of India issues and regulates the issue of currency in India. The RBI acts as banker to government. The RBI looks after the derent financial transactions of the government and manages the public debt of government The RBI acts as banker to the commercial bank. Commercial banks keep and maintain their accounts with the reserve bank of India. Commercial bank keep deposits with RBI and they borrow money from RBI when necessary. RBI acts as lender to last resort to commercial banks. The RBI exercises the control over the volume of credit created by the commercial banks in order to ensure price stability
The Reserve Bank of India and Its Promotional Role: The RBI established the bill market scheme in 1952. The RBI has tried to help the establishment of financial corporation to provide credit to the agricultural sector of the economy. The RBI has promoted regional rural banks with the help of commercial banks to extend banking facilities to rural areas. The RBI has taken steps to enable the commercial banks to open branch in foreign countries. The RBI encourages and provides research in areas of banking.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 14
A study on credit appraisal
INTRODUCTION TO CREDIT APPRAISAL
CREDIT APPRAISAL Credit appraisal is the process by which the lender assesses the credit worthiness of the borrower. It revolves around character, collateral capability and capacity. It takes into account various factors like income of the applicants, number of dependents, monthly expenditure, repayment capacity, employment history, number of years of service and other factors which affect credit rating of the borrower. Credit appraisal is a process to ascertain the risks associated with the extension of the credit facility. It is generally carried by the financial institutions which are involved in providing financial funding to its customers. Credit appraisal is a process to ascertain the risks associated with the extension of the credit facility. It is generally carried by the financial institutions which are involved in providing financial funding to its customers Credit risk is a risk related to non repayment of the credit obtained by the customer of the bank. Thus it is necessary to appraise the creditability of the customer in order to mitigate the credit risk. Proper evaluation of the customer is performed, which measures the financial condition and the ability of the customer to repay back the loan in future. Generally the credit facilities are extended against the security know as collateral. But even though the loans are backed by the collateral, banks are normally interested in the actual loan amount to be repaid along with the interest. Thus the customers cash flows are ascertained to ensure the timely payment of the principal and the interest. The product is designed to automate the entire lending process in a bank and provide credit portfolio managers with tools and reporting to assist them in decision making. Banks offers different types of credit facilities to the eligible borrowers. For this, there are several procedures, control and guidelines laid out. Credit appraisal, sanctions, monitoring and asset recovery management comprise the entire gamut of activities in the lending process of a bank.
Process of Credit appraisal: The credit appraisal is a holistic exercise which starts from the time a prospective borrower walks into the branch and culminates in credit delivery and monitoring with the objective of ensuring and maintaining the quality of lending and managing credit risk.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 15
A study on credit appraisal
The process of credit appraisal is multi-dimensional and includes: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Management appraisal Technical appraisal Commercial appraisal Financial appraisal Economic appraisal
Management appraisal has received lot of attention these days as it is one of the long term factors affecting the business of the concern. Technical appraisal emphasizes on the technical feasibility of the venture and also finds out the possible economic life period of the present technology. Commercial appraisal focuses on the commercial viability of the project. It tries to find matters regarding demand in market, the acceptance of product in market. It also focuses on the presence of other substitutes of the product in the market. Financial appraisal is done to find out whether the promoter is having the capacity to raise finance both own equity and debt? What are the sources of margin? Will the business generate sufficient funds to service the debt and other stakeholders? Is the capital structure optimal? Economic appraisal examines level of cost/benefit and IRR (internal rate of returns).
The scope of credit structure is incomplete without examination of credit proposal. Credit proposal has to be examined from the point of 6Cs viz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Character Capacity Capital Condition Collateral Cash Flow
The credit policy of bank of India has undergone changes to cope up with the environmental changes, tap the available opportunities, achieve their commercial objective, fulfill social
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 16
A study on credit appraisal
obligations and adhere to mandatory directed lending norms. The credit policy consists of both fund based credit exposure and fund based credit exposure.
The credit policy is studied under- coverage, clientele marketing. The bank has over the years designed and adopted the best practices code. This in effect represents the banks philosophy towards effective corporate governance.
Meaning It is the process of appraising the credit worthiness of a loan applicant. Factors like age, income, number of Dependants, nature of employment, continuity of employment, repayment capacity, previous loans, credit cards etc are taken into account while appraising the credit worthiness of a person. Every bank or lending institutions have its own panel of officials for this purpose.
Definition The process of evaluating an applicants loan request or a corporations debt issue in order to determine the likelihood that the borrower will live upto his/her obligations.
Salient Features: 1. Data download/upload: Ensures prompt and accurate data entry in the business borrower application (profile and CMA) through floppy or web interface. 2. Pre-appraisal stage Eliminates costly errors and ensures complete and correct (input check procedures) of the uploaded borrower profile, and CMA data in required parameters sable format. 3. Verification
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 17
A study on credit appraisal
Verification of previously rejected borrowers reapplying for loans through defaulter lists pf the Reserve Bank of India, Export Credit Guarantee Corporation and the bank itself.
Appraisal methodology Working capital computations: 1. CMA Based 2. Cash budgeting (especially for seasonal business lines) 3. Turnover methodology Term loans 4. Non banking financial companies 5. Infrastructure handling Appraisal Tools 1. Sensitivity analysis and projections for working capital and term loans 2. Comparison of previous CMAs, industry and peer group comparisons, linking to financial database of service providers such as CRISIL, CMIE and C -online. 3. Credit risk rating incorporation. 4. Term loans interest workouts, moratoriums, repayment schedules, sensitivity. 5. Computation of MPBF, facility wise maximum limits. 6. Proposal preparation. Post appraisal stage: 1. 2. 3. 4. Ensures the sanctions adequately covered by the policy guided terms and conditions. Accepted securities and documents linked to various facilities. Accepted terms and conditions linked to various facilities. Sanctions and follow-up methodologies, compliance of terms and conditions as charging of securities completed and sanctioning facilities as per set authority. 5. Auto generation of sanction letter with facility wise limits, terms and conditions. Monitoring Timely and standard review of credit extended 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Terms and conditions compliances; security documents compliance Securities charging compliance Review proposals Audit queries Stock statements QIS, MSOD
Page 18
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
A study on credit appraisal
Figure in congruencies through early warning signals to avoid non performing asset information. 1. Linkage of bank statements received from borrower, branches, etc. Recovery procedures 1. Recovery procedures and non performing asset management compromise proposal, BIFR, legal actions and write- offs. 2. Various statements- prompt and timely monitoring of activities to monitor document movement, appraisal, monitoring recoveries and soon.
Dimensions of credit appraisal: A lot of attention has to be paid to this area. This is one of the long term factors affecting the business of the concern. Does the management have enough experience in line? What is its track record? What are the antecedents? Introduced to us by whom? These are some of the questions that need to be answered before we can take up any kind of exposure. Technical appraisal: What is the status of technology used? Has a prototype been developed of the product? What could be the possible economic life period of the present technology? Is the venture technology feasible? Technical appraisal of the projects need to be carried out by all India financial institutions, PSU banks/other leading banks having expertise in the area and the same may be accepted for an appraisal purpose, after subjected to vetting by TAC/TAD. Exemption from fresh techno-economic appraisal shall be available in the following categories: 1. Where appraisal has been carried out by all India financial institutions, PSU banks/other leading banks having expertise in the area and the same may be accepted for an appraisal purpose, after subjected to vetting by TAC/TAD. 2. Where appraisal carried out by leader of WC consortium and the branch/sanctioning authority observing no serious differences with such appraisal. 3. In case of AAA/AA rated accounts with the other banks, where our purposes to join the
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 19
A study on credit appraisal
consortium and/ sanction limits under multiple banking arrangement for the existing activity of the company or firm. 4. In case of well conducted existing accounts with credit rating of AAA and AA where only additional working capital limits are sought and diversification of the project is not proposed. 5. In case of well conducted existing accounts with credit rating of AAA and AA term loan requirements upto Rs. 10Crores, provided expansion of is in same product line and without change in technology. Commercial appraisal: The business has to be commercially viable for us to proceed further. Is there enough demand in the market? Is the product accepted in market? How many substitute products are there? What about entry and exit barriers? Is there scope for further growth? The nature of product, demand for the same, the existing and perceived competition in the segment, ability of the proponents to withstand the same, government policies governing the industry, etc. need to be taken into consideration. The trade practices in respect of the product should be thoroughly understood.
Financial appraisal: Does the promoter is having the capacity to raise finance both own equity and debt? What are the sources of margin? Will the business generate sufficient funds to service the debt and other stakeholders? Is the capital structure optimal? Through scrutiny of the financial aspects of the request needs to be carried out. Apart from ascertaining the need based character of the limits requested for, the financial health of the proponents, ability to absorb unanticipated financial costs need to be looked into. Ascertaining the need based character of the limits would include scrutiny of the cost of the project, means of financing, financial projections etc. need to be within acceptable parameters for those industries/activities. Where higher limits are considered, detailed of the financial health would be made and the following ratios computed: 1. Current ratio 2. Total outstanding liabilities/equity ratio
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 20
A study on credit appraisal
3. 4. 5. 6. Profit before interest and taxes/interest ratio Profit before tax/net sales ratio Inventory + receivables /sales ratio DSCR if the borrower enjoys any term loans with any bank/FI even if no TL is being considered by our bank. Assessment of working capital credit requirement hinges normally on the projected sales and other financial figures.
All the above ratios would be complied for the past two/three years including the latest audited balance sheet. As the ratios would vary from industry to industry, services, trade etc. It is proposed not to stipulate any particular bench mark for the above ratios. Besides the above factors, bank need to reckon the existence, if any, of negative factors that may adversely affect the continued well being of a customer. Economic appraisal: What is the break even level? Will the business post positive net present value through its economic life? What is the level of cost/benefit? What is the internal rate of returns? Will the cost of funding and operations be well below the IRR? As a prudent banker the following areas need to be particularly looked into: Character Antecedents- introduced by whom- is it a take over account? In which case, what does the status report say? - Background educational professional socio-economic, politicalinitiative and drive.
Capacity Experience in the activity track record planning, budgeting and review handlingproduction capacity- capacity utilization professional capacity to handle men, materials, money and minutes capacities to handle contingencies and crises. Capital Extent of stake in business. Ability to raise finance both owned equity and debt Ability to inspire and sustain investor confidence Ability to absorb losses expected and unexpected Structuring and budgeting capital.
Page 21
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
A study on credit appraisal
Condition Condition of economy growing, stagnant or depressed Number of competitors Substitutes in the market Demand v/s supply Government policies and regulations Status of technology Availability of man power, material & other resources. Pollution control and effluent treatment. Collateral Risk perception and evaluation Financial parameters Debt / equity ratio Asset cover Interest cover DSCR Availability, suitability and charge-ability of security -MAST principle Cash flow Pattern of cash generation Liquidity risk Break even analysis DCFT technique NPV IRR PV Index
Stages of credit appraisal: 1. Interview with the proponent and attestation of application on bank's prescribed format. 2. Adherence of KYC norms stipulated by reserve bank of India. 3. Attestation and verification of documents/financial statements according to type of facilities required as per bank's norms. 4. Inspection:
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 22
A study on credit appraisal
Pre-sanction inspection is done by bank's official's viz. Inspection of borrowers residence, making inquiries from his area and collect market reports, inspection of proposed principle and collateral securities. 5. Preparation of credit proposal: The proposal contains the complete information about the proponents background, appraisal of financial and managerial status, technical and economic viability of the activity and future prospects. 6. Sanction of credit proposal: The sanctioning authority goes through the credit proposal and it is his responsibility to ascertain the facts of the proposal. 7. A sanction letter is given to the proponent: The sanction letter contains the type and size of facility and margin stipulated with all terms and conditions including rate of interest and charges, insurance of the proposed security and periodicity of inspections etc. which is duly acknowledged by the proponents. 8. If the proponent agrees the terms and conditions stipulated by the bank, he/authorized persons have to execute the security document before the bank's authorized officer and finally the accounts is opened to disburse the facility. 9. After disbursement post sanction inspections are carried out by the banks official from time to time to ascertain the utilization of funds, for safeguard of the advance and bank's interest in the security. Credit Rating: Based on changing scenario and the need to factor certain vital parameters like market risk, industry risk, management risk, etc. so that important elements of the rating process are given sufficient attention, a new rating model has been evolved. Even though the main purpose of the rating system is to decide on risk, credit rating is also used to price of product in a scientific and transparent manner. Hence, apart from analysing the various risks , due weight age has been given to factors such as volume of business, share of ancillary business, length of relationship with the bank, threat of loss of business due to competition, over all image /reputation of the customer / group, etc. to do decide the pricing. Credit ratings are carried out as under: Type of account Aggregate fund based /non fund based Limits over Rs. 2 Lakhs, but less than Rs. 1 Crore.
Page 23
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
A study on credit appraisal
Aggregate fund based/non fund based limits of Rs. 1Crore and above (Except traders) The software solution enables a bank to standardize the proceedings across banks and enables installing certain financial uniformity amongst the borrowers. The process by which a lender appraises the credit worthiness of the perspective borrower. This normally involves appraising the payment history and establishing the quality and sustainability of his income. The lender satisfies himself of the good intentions of the borrower, usually through an interview.
Before extending any loan or credit to you, lenders check things like how much money you earn, how long you have been using credit and whether you have made payments on time.
Credit Scoring System: Credit scoring is the statistical system used by lenders to determine applicants credit worthiness. Information about borrower and his credit experiences is collected from your loan application and his credit report. Using a statistical program, lenders compare this information to the credit performance of consumers with similar profiles. How long borrower been using credit and whether he has made payments on time. A credit scoring system awards points for each factor that helps predict who is most likely to repay the debt. A total number of points a credit score helps predict how credit worthy the borrower are, that is, how likely it is that you will repay a loan and make the payments when due. The points are distributed in various aspects of borrower profile such as: 1. Personal information: age, educational qualifications, number of dependents/children, spouses income. 2. Employment information: organization, designation, length of service, etc. 3. Income information: net income, instalment of other loans, other liabilities 4. Net worth information: owning a house, vehicle, credit cards, telephone, etc. 5. Previous relations with the lender: banking account, credit card, any other loan, etc from the same lender. Borrower level of education can give an indication to the lender whether it is a good risk to extended credit to him. Higher the education better is the credit score. A person with professional qualifications is given more points than a simple graduate.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 24
A study on credit appraisal
Need of credit scoring: Credit scoring is based on real data and statistics, so it usually is more reliable than subjective or judgemental methods. It treats all applicants objectively. Judgemental methods typically rely on criteria that are not systematically tested and can vary when applied by different individuals. Companies providing loans and credit do not disclose their credit appraisal criteria. Both the score and the statistics that go into it are top secret. There are certain things we do know , fewer credit cards are better than several cards. Paying on time is a must. Some of the things that weigh heavily are stability both at home and on the job and a good payment history. The scoring system looks at how close borrower are to the limits on his cards, what he spend money on and how much he ask for in cash advances.
Scoring models generally evaluate the following types of information in credit report: What is borrower outstanding debt? Many scoring models evaluated the total amount of debt that borrower has compared to his credit limits. If the amount that borrower owe is close to his credit limit that is likely to have a negative effect on his score. Have borrower paid his dues on time? Payment history typically is a significant factor. It is likely that borrower score will be affected negatively if he has paid his dues late. How long is borrower credit history? Generally, lenders prefer a seasoned credit history i.e, a credit track record of more than a year. An insufficient credit history may have an effect on borrower score, but that can be offset by other factors, such as timely payments, low balance and previous relationship with the lender. How many and what types of credit accounts do the borrower have? Although it is generally good to have established credit accounts, too many loans and credit card accounts may have a negative effect on borrower score. Scoring models may be based on more than just information in borrower application from and bank statements. For example, lenders may call borrower for one-to-one discussion; investigate his credit reputation by contacting their employer, friends or neighbours. Lenders also look at borrower spending behaviour. The model considers all these information for evaluation. Reliable of the credit scoring: Credit scoring system enable lenders to evaluate a number of applicants consistently and impartially on many different characteristics. There are pros and cons to the credit scoring
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 25
A study on credit appraisal
system. On the plus side, it eliminates discrimination because approval is based on raw numbers. Although borrower may think such a system is arbitrary or impersonal, it can help make decisions faster, more accurately. On the other hand, the scored dont take into account consumers who have exceptional circumstances. If the score is too slow , they're turned down. Still, borrower must understand how it works if he/she is going to get it to work for him.
Credit verification agencies: 1. Role of credit verification agencies: Credit verification agencies provide the professional service of verifying, validating and certifying vital details of credit information on individuals applying to banks for loans. Use of credit verification agencies is gaining increasing as a risk mitigating strategy in the retail loan segment within the banking industry. The agencies usually verify the following minimum details in respect of each loan application: Identity of the applicants. Address of the applicants. Veracity of employment/profession of the applicants. Cross verification of the income details declared by the applicant Confirmation of telephone numbers
However such verifications by agencies is generally available only in respect of retail loans.
2. Benefits of entrusting credit verification to specialist agencies are: The major benefits of entrusting credit verification to specialist agencies are: Since credit verification agencies operate locally and have a specialization in their domain, the verification conducted by them is generally reliable prompting many banks in the industry to use the services of specialist credit verification agencies.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 26
A study on credit appraisal
The mobility required of officers in public sector banks often requires that officers have to play the role of a branch head and do business in big cities without much knowledge of the local credit market. The availability of specialist assistance in getting loan application and assist the branch heads in expanding retail credit by improving the process of borrower selection. 3. Guidelines on enlisting the services of credit verification agencies: Considering the benefits involved it has been decide to enlist the services of professional agencies providing credit verification for engaging banking and housing loans. The guidelines on the policy and procedure evolved for engaging the services of credit verification agencies are given below: Credit verification to be restricted to personal banking and housing loans- enlisting the assistance of verification agencies empanelled by the bank for credit verification agencies shall presently be restricted to loan under our personal banking and housing loans schemes. Six major cities identified for introduction of verification 6 major cities identified for commencing credit verification through external agencies. Since enlisting the services of credit verification agencies represents a new initiative for the bank, it has been decided as a pilot measures to commence credit verification through accredited external agencies only at the following major metros/cities Delhi Mumbai Bangalore Chennai Kolkata Hyderabad
This would also be appropriate for the reason that the above 6 cities account for a bill of the banks exposure in value terms.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 27
A study on credit appraisal
Benchmarks finalized for empanelling credit verification agencies - Following are the benchmarks prescribed for short listing verification agencies: The credit verification agency should have been in operation for not less than 3 years. The agency should be on the approved list of atleast 2 public sector/old or new generation private sector banks or reputed multi national banks. Empanelment with cooperative bank shall not be taken into account for this purpose. Verification report of the agency shall invariably cover the following minimum details Identity of the applicant Address of the applicant Veracity of employment/profession of the applicant Cross verification of the income details declared by the applicant. Confirmation of telephone numbers. Verification standards The verification agency empanelled by the bank shall verify the loan application forms referred to them for completeness and enter and store the details there of as specified by the bank. The agencies shall establish the identity of the applicant, collect and verify the veracity and correctness of the vital details such as employment, profession, and residences data by making phone calls as may be required. This exercise referred to as contact point verification. The agency shall provide the credit information after verification collected on the applicants and or co-applicants in the prescribed format, including derogatory credit history within the turn around time specified by the bank. If the information furnished by the agency is later found to be stale, wrong, false, incorrect or inadequate fully or partially by the bank, the agreement with such agency is liable to be cancelled and a claim for damage would be instituted, if felt necessary. Ceiling prescribed on fees payable taking into account the current market practices, a ceiling of Rs.120 is prescribed as the maximum permissible fee that can be paid per
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 28
A study on credit appraisal
case. GMOs/ROs empanelling credit verification agencies shall negotiate for rates with an upper ceiling of Rs.120 per case. The verification fees shall be added to the processing charges and out of pocket expenses payable by the borrower. Legal framework for assurance of fidelity, secrecy and agency relationship in order to ensure that data/information confidentiality is protected, while entrusting verification function to outside agencies necessary legal framework has been created for binding the agency to fidelity and secrecy. Verification to be a fair practice compliant with a view to obtaining the consent of the borrower for the verification to be carried out and reimbursement of the related costs the following line shall be added in the loan application proposed to be subjected to credit verification: the particulars of addresses, telephone numbers etc. Procedure to be followed at the specified GMO/RO wherever names of agencies have already been recommended by the GMOs and ROs and such name have been approved by CO: Bangalore. They are separately communicated to the GMO/RO concerned. GMOs/ROs shall obtain the indemnity cum agreement format described above from those agencies. Verification to be at the discretion of the branch head verification exercise shall be at the discretion of the branch head applicable only to personal banking and housing loans. In other words branch head entrust only those cases where the need for credit verification is perceived. Accountability aspect whenever a loan account has been subject to pre sanction external credit verification, it shall be deemed that the processing officials and the sanctioning authority have relied on an expert opinion in relation to the aspects covered in the verification report submitted by an valuer. Powers to permit modifications/deviations the chairman and managing director/executive director shall be empowered to make/permit
modifications/deviations to all or any of the above described guidelines on enlisting of credit verification agencies including the maximum fee payable for verification, benchmarks for verification and amendments to the format of the indemnity.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 29
A study on credit appraisal
Research Design
Research: Research simply means a search for facts, answers to questions & solutions to problems. It is a purposive investigation. It is an organised enquiry. It seeks to find explanations to unexplained phenomenon. To clarify doubtful propositions and to correct the miss conveyed facts. Definition: According to kerlinger defines research as a systematic, controlled, empirical and critical investigation of propositions about the presumed relation among natural phenomena. Research Design INTRODUCTION: Research design here refers to the methods used to collect the required data for the survey. It is the outline of the total project. It contains the information stating the objectives of the study, scope of the study methodology of the study, tools and techniques used for the survey, methods of data collection, limitation of the study etc. in short research design is the chapter in which the blue print of the whole project is explained. The research design includes an outline of the study which was conducted at Rythara Seva Sahakara Bank. There are various types of products and a service offered by RSSB, and providing loans to people are one of the important functions of the bank does. As this research study is mainly based on these schemes, we will discuss more on the loan schemes provided by Rythara Seva Sahakara Bank.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 30
A study on credit appraisal
Definition: According to Claire selltiz, A research design is the arrangement of conditions for collection and analysis of data in a manner that aims to combine relevance to the research purpose with economy in procedure. NEED FOR RESEARCH DESIGN: Research design is essential because it facilitates the smooth sailing of the various activities of a research programme. It makes research as efficient as possible yielding maximum information with minimum of expenditure. It saves a lot of effort, time and money. 1. It provides the blue print. 2. It limits boundaries of research activity. 3. It enables investigation to anticipate potential problems. 4. Research can be conducted on scientific basis science advance designing providers precise guideline. 5. Wastage of time and money is minimised. 6. Optimum reliability is achieved. 7. Designing helps in giving useful conclusions. Title of the study A study on credit appraisal with special reference to the Rythara seva Sahakara bank, singanayakanahalli. Statement of Problem The particular topic credit appraisal is chosen because it plays an very important role in the lending of the banking sector. The bank will be in trouble if the borrower is do not pay the interest and the return the principle amount/loan. Due to non payment of principal and interest the provision of the bank adversely and as a result the bank may be in loose condition.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 31
A study on credit appraisal
Thus, it is necessary to appraise the credit ability of the customers in order to mitigate the credit risk. Objectives of the study To know the credit turnover of the bank To know the principle position of the bank. To know the credit requirements of the various sectors. To know the steps taken while granting the loan i.e. appraising the credit. To analyse the credit worthiness and efficiency of the bank. Scope of the study The scope of the study is confined to the detailed analysis of the credit appraisal of the Rythara Seva Sahakara Bank at singanayakanahalli branch, Bangalore north only and it includes: 1. Concept of the credit appraisal. 2. Process and appraisal methodology. 3. Dimensions of credit appraisal. 4. Credit rating and credit scoring. Sources of data collection: The two types of data collection methods used in my research work are- Primary data and secondary data. Primary sources of data Primary data are those data which are originally collected for the first time for the specific purpose by an investigator. They are collected directly from the people to whom enquiry is related. They are primary to the instruction which contact for the information they are secondary to all other institutions which report data. It is the method where the first hand information is collected from an organisation for the study.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 32
A study on credit appraisal
The primary data or information has collected through the personal contacts with managers of the bank; data was also collected through informal interviews conducted with banks executives 7 employees. Secondary sources of data: Besides, primary data collected for the study, secondary data was collected from annual reports of bank, journals & through internet. Further more information is relating to important definition and common meaning of the bank terms collected from reputed books such as, Bank journals Textbooks Internet
Method of data collection: There are various methods of data collection as concerned to the project; direct interview method has been followed in this study. Limitations of the study: The study is limited to Rythara seva Sahakara bank in Singnayakanahally branch, Bangalore only. Due to inadequate time and cost it was not possible for me to make an exhaustive study. It is limited to the facts and figures of the annual report provided for the periods 2009,2010 and 2011. Interpretation of the study is based on the assumption that the respondents have given correct information. This study does not provide any information other than credit appraisal.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 33
A study on credit appraisal
OVERVIEW OF THE REPORT
1. INTRODUCTION: The first chapter gives the detailed introduction on the credit appraisal . 2. RESEARCH OF THE STUDY: The second chapter states the objectives, scope, source of data and research methodology. 3. COMPANY PROFILE OF THE ORGANIZATION: The third chapter gives the profile of the organization where the project is conducted. It also explains about the future plans of the company. 4. ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION: The chapter gives detail regarding the analysis and interpretation of data after collection. It comprises of brief notes regarding analysis and various methods through which they may be carried out. It also consists of the data in form of tables, graphs and pie-charts and its interpretation. 5. SUMMARY OF FINDINGS, CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS: This chapter comprises of the findings and conclusion drawn from the analysed & interpreted data and even suggestions with respect to findings. 6. ANNEXURE: 7. BIBLIOGRAPHY:
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 34
A study on credit appraisal
COMPANY PROFILE
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 35
A study on credit appraisal
BRIEF HISTORY OF THE SOCIETY: WHERE THERE IS SERVICE THERE IS THE WAY OF LIFE Farmers service Co-Operative societies were organized in our country on the recommendation made by the National Commission on Agriculture with a main object of providing integrated credit and services to farmers. Syndicate Bank being pioneers in agricultural lending took keen interest in sponsoring Farmer Service Co-operative Societies in our state. RYTHARA SEVA SAHKARA SANGHA (N), SINGANAYAKANAHALLI is one such society sponsored by the Bank during 1976. 9 Weak Societies amalgamated to Singanayakanahalli Society. Weak Societies are not in a position to cater the needs of Farming community. Singanayakanahalli society commenced its Business in December, 1976. The Financing Bank provided required managerial expertise by deputing one of their officers to work as Managing Director of the society. Government of Karnataka provided the Services of Agriculture Department by Deputing one Technical Officer and two Agriculture Assistants to work in the Society. The Society started its operation in December 1976; accordingly a comprehensive survey is done in 48 villages to identify the members and registered them as members of the society. The Society is covering 1710 Hectares of area the jurisdiction of the society. The small farmers, agricultural labours, village Artisans are enrolled as members of the society. The farmers are engaged in agriculture only by rain water and tank water. During Kharif they grow Ragi, Paddy and Vegetable crops. Most of the small farmers had difficult economic conditions and they had to work as labours to sustain themselves. In 1976 society has opened one more branch in yelahanka. Agriculture loans, supply of inputs, field demonstrations, and training programs were carried out. The society also had drawn the support of University of Agricultural Science, IIHR Hesgaraghatta to create a revolution in
agriculture. Especially all the small and marginal farmers were provided with short term and medium term loans. The advanced technology was made available by digging Bore wells and open wells for irrigation which helped conversion of dry land in to cultivatable land.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 36
A study on credit appraisal
The society also supported land less labours to become economically self reliant by providing them Loans for sheep rearing, piggery, poultry, dairy loan etc. In 1978 with the support of all the Govt. Department the Bank organized a loan Mela headed by the Co-operative Minister at Harohalli village and on-spot registering membership, on-spot sanction, on-spot disbursal of loans which was highly appreciated by one and all. Agriculture loans to members, technical assistance, sale of agriculture inputs, training camps are the main objectives of the societies. With only 2215 members and 1.12 lacks share capital and Society was running under loss. Through constructive activities and focused execution by the Management gradually the society turned into a Model cooperative society. In 1982 the society started to provide members consumer durables goods at concession rates and in 1998 the society was converted in to a bank. Today fully developed society has 6 full pledged branches, own Buildings NCDC assisted Godowns and is carrying out banking activities. By implementing different deposit schemes with own investments became self sufficient. The society has not taken any loan from the financing bank for the last 10 years. On 26-07-2007 at the Centnary celebration of cooperative movement the society awarded Best Working Co-Operative Society. The president and Chief Executive were felicitated by Mr. G.T. Devegowda honourable minister for Co-Operation and Sri. N.C.Nanaiah, one of the pioneering personalities of the Co-operative movement. On 14-11-2007 at the 54th all India Co-operative Week Mrs. Vanishree Vishwanath our president was recognized and felicitated as Best Woman President in Co-Operative Societies. On 19-11-2008 on the occasion of 55th All India Co-Operative week Mrs. Vanishree Vishwanth our president has honoured The Best Women President and also Mr. K.Krishna Bhat was honoured The Best Secretary award. Every year the members loans are encouraged the repayment situation is also very healthy for the last 3 decades the members of the society have become economically strong able to give
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 37
A study on credit appraisal
better education to their children and have constructed own houses and living better livings, VIPs from different states and countries have visited the societies. Now a days the society has been disbursing loan for different activities like agricultural production loan horticulture, Sericulture, animal husbandry loans, jewel loans, tractor and power tillers, education loan, SHG Loans, Farm House Loans, Self Employment Loans, Consumer Loans, Solar Loans etc. society has got a mini lorry which helps farmers to avail cheap transport facility for their agriculture produce. The society has financed poor farmers, agricultural labours especially SC/ST Members by providing them subsidy loans under Govt. schemes like SJSY Subsidy, SCP Subsidy, Udyogini and Asare scheme for woman members. With the Cooperation of university of agriculture sciences, Kakkehalli village in Bangalore is adopted and all the members were given agricultural loans and other support also. Recent developments as per the directions of Govt of Karnataka Department of Co-operation 380 women self help groups are organized from the society and loans are disbursed Rs. 3 to 5 lakhs per group. Society has Financed Government Schemes like Udyogini & Asare, nearly 400 SHG Group women members financed with Government Subsidy for self employment. Society has provided 15 high-tech model Vegetable and fruit selling Cart Department of Horticulture provided Rs. 10000-00 subsidy for each Schedule Cast Members. Society has arranged women training programmes, tailoring, Sericulture Cocoons decorative art and also mushroom culture. Society has engaged itself in social objectives like rain water harvest re-energisation of failed bore wells. Society has organized health camps like Heart Checkup Camps, eye camps and animal health check-up camps. Society is engaged in honouring Prathibha puraskara for SSLC and PUC toppers from among members children our society with all branches are computerized. Our head office building is constructed recently on latest designs. The society is committed to realize Mahatma Gandhijis Dream of empowering villages and socio-economic upliftment of poor is possible only by the Cooperatives.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 38
A study on credit appraisal
Introduction to Rythara Seva Sahakara Bank The Rythara Seva Sahakara bank was established keeping in view of helping farmers to develop their lands & get more income. The head office is situated in hindupur. In 1976 according to suggestion of NATIONAL AGRICULTURE COMMISSION, Commercial banks are requested to provide financial help to co-operative societies in state. Likewise syndicate bank, yeshwanthpur branch was requested to give financial help to singanayakanahalli farmers through co-operative society in June 1976. For 48 villages, 9 co-operative societies were established. Society was not in a position to help the members because of its poor condition. These 9 co-operative societies joined hands with AGRICULTURE SERVICE CO-OPERATIVE SOCIETY. Authority officer was appointed from the syndicate bank to work as co-ordinating director. In this society 13 administrative directors, representing different department like agriculture, animal husbandry, rural development, co-operative department, etc... Government of Karnataka reserved an agriculture office and 2 rural services work for their society. Agricultural service co-operative society, singanayakanahalli has started its activity in December 1976. Thereafter they did survey in 48 villages. They identified members and joined them in the society. 1970 acres of land come under this society. Small landlords, agriculturists & rural craftsman situated in this place and they grow crops & other vegetables with the help of rain water & available water resources like tank or reservoir. In 1976 the society has opened another branch at yelahanka. They provided loans to farmers for performing agriculture & helped them to purchase agricultural equipments. They conducted farming programmes to motivate farmers to develop their agricultural lands. Bangalore agricultural university & Indian crafts institutions came forward to help the society in view of crating revolution in the field of agriculture. For every small zamindhar they provide short tern and long tern and medium term loans and with the help of special scientific methods. Other than this they helped in digging wheels, bore wells, in barren land, which can be used for agriculture purpose. They give loans for this part of farmers who are members in this society. Rural development has provided donation, with which the society give loans to buy cow, goats, hens, pigs who does own agriculture land, to improve the economic status of the members.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 39
A study on credit appraisal
In 1978 with the help of all departments, societies arranged loan exhibition and joining new members, Members registration, loan approval, loan collection are done because of it, society had enjoyed compliments from the society. Agriculture loan, technological support, sales of agricultural equipments & to arrange training centres for members, is the main objective of the society. In the beginning society started with 2215 members with 1.12 lakhs share capital running under losses, due to its work activities gradually developments taken place & become a model co-operative society. In 1982 to reach the members to provide durable goods in discount price through sales distribution centre. In 1998 this society converted as bank. Today this co-operative bank has expanded and has six branches, owned head office, with the help of N.C.D.C, it established own gowdons. Society is doing banking business. It is introducing new deposit schemes, through this succeeded. And at present it has its own capital & did not takes any loans from other banks. This society carrying out its activities with its own capital. Every year bank is providing loans to its members & they are repaying the loan amount based on the terms and conditions. During three decades bank gives financial support to rural members because of this financial support, members are living independently, bank also gives education to their members children and build their own house and living with people. Bank in its operational area provides loans to members like crop loan, jewellery pledge loan, security loan, tractor loan, power tiller loan, self help group loan, small traders loan, house construction loan, higher education loan for agriculturists childrens and other loans to purchase house, old goods ,for solar equipment installation are given, bank has its own mini lorry & it is useful not only for bank, also farmers because farmers are using this vehicle at discounted rate.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 40
A study on credit appraisal
Co-operative movement India is a agricultural country; above 70% of our country population depends upon agriculture for their livelihood. As there is no agency to supply credit, farmers are the ready victims of the money lenders and indigenous bankers who charge high rate of interest. In order to protect them from the economic evils and morale generation the co-operative movement in India was encouraged. The co-operative banks are institutions established with principle credit & to promote thrift and self help among the economically weaker sections of the society, like commercial banks, the cooperative banks also received deposits & lend money, but they lend money to their members and make incidental profits although their solely objective is not profit earning. The co-operative bank in indie has grown in size & volume. A special feature of co-operative banks in india is its federal structure. The units ranging from primary level to national level, cooperative banking in india can be divided into two important areas namely agriculture and non agriculture. Co-operative banks are primary co-operative banks of the village level, central cooperative banks at district level and the state co-operative at the state level. The commercial banks were nationalized with the primary idea of helping agriculture and industry, however, there has been a feeling among the public that the public sector banks were not meeting the expectation of the people, therefore in July 1975 the government of india appointed a study group headed by Mr.Narasimhan to study the problems of rural credit in the context of the 20 programmes, the working group pointed out the weakness of the commercial banks and co-operative banks in the sphere of rural credit and suggested for a new type of credit organization which is to be closely associated with rural folk combined with modern outlook as that are commercial banks. As recommendations of the working group, the government formulated the regional rural bank ordinance in September 1975; this was subsequently replaced by RRB acts 1976. The act empowers the central government to setup RRBs in places where it may consider necessary to start with. There were only 5 regional rural banks on 2 October 1975. With as authorized capital
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 41
A study on credit appraisal
of Rs. 1 crore each, every rural bank is expected to cover a population of 1 crore through about 100 branches, now there are 196 RRBs. The objective of establishing the RRB was to develop the rural economy by developing the agriculture, trade, commerce & industry and other productive activities in rural areas, a parts from this. The RRBs are expected to help the small and marginal farmers, agricultural labours, artisans and small entrepreneurs. The RRBs acts as agency to provide institutional credit in the areas and to replace the money lenders in course of time, at the same time the RRBs should supplement the activities of the co-operative banks. Co-operative banks are organised under the co-operative societies. Siddanna gowda patel of kanaginal; initially the co-operative society was started at dharwad. At present now there are over 32000 diffrent types of co-operative societies in Karnataka. Agriculture is an unorganized profession in the country. Its success and fai lure depends on climatic factors to a large extent. Still its alround development depends on the availability of finance. Credit or finance plays a very vital role in agricultural progresses. But, agriculture in india is facing serious credit problems. Farmers in india are very poor and the are grooming under the burden of indebtedness. The financial position of the farmer is very well brought out automatically. The Indian farmers are born in debt, lives in debt, dies in bequeath debt, and indebtedness is the only companion of farmer cradle to grave. Credit needs of the farmer: loans are required to purchase of seeds, fertilizers,marketing of agricultural produce,payment of wages to hired labours, for buying cattle,small agricultural implements, repairs and construction of wells. From December 1976 , Rythara seva Sahakara sangha,singanayakanahalli started functioning. It recognized families under its jurisdiction of 48 villages from few were selected as members. The main objective of the society includes sanctioning loans to farmers, providing technological assistance,conducting scientific farming training programmes and marketing of agricultural inputs.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 42
A study on credit appraisal
During 1978 in harohally, loan fare was conducted which included on the spot membership,loan sanctioning and spot payment of loans which was most appreciated deed of the society. In 1998, society recognized itself onto Rythara seva Sahakara bank. Visions of the bank 1. Taking credit services nearest to doorsteps of the members. 2. Multipurpose, viable purpose, primary agricultural co-operative societies. 3. To provide integrated credit packages for the graduated farmers also. 4. To spread co-operative educates through women graduates farmers clubs. 5. To be strongest organization in the rural.
Mission Statement To improve the economic development of the members of the society and also giving attention for lending loans to farmer also. Release them from the clutches of moneylenders through ,making available loans at a reasonable rate of interest with simple terms and conditions. Information Technology in Rythara Seva Sahakara Bank Information technology is very important. Today, every banking sector is the modern method of technology of different department, so this bank also use and implements new techniques in the field of finance and all over the management in the organization. Rythara seva Sahakara bank was implementing recording all documentations in computerized and also monitoring the legal cases with the help of computers. Finance Government of Karnataka extended financial support for establishing the farmer co-operative societies/banks in the rural areas. It provided the maximum loan facilities to the individual farmers, small business man and others to take the benefit from these banks.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 43
A study on credit appraisal
Bank extends short and medium term loans to the members. Loans are given only to the members who are not defaulters and who had shares in the society in prescribed proportion. Generally, loans are given for a period of six months or one years or five years. Loans are normally given for productive purpose i.e, agricultural operations. Loans are ordinarily given on the personal securities of the borrowers supported by the personal securities of another member. Loans are also given against mortgages. Loans given by these societies carry a low rate of interest. Usually 4% per annum. Presently banks have six branches, own office building, six own gowdons of 100tonnes of capacity, one mini lorry for transporting farm inputs & other material at concessional rates; It has got its own investment and its divide of any type of loans from sponsored banks and others. No member is allowed to hold more than 20% of their total number of shares of society. To become the member of the bank should belong to the jurisdiction of the bank, should be of 18years and must be a farmer or craft man. It has power to hold property; the members are given more than six crores loan from all the different branches of the society. Exemption from Income Tax Section 80P of income tax act empowers the central government to exempt the society from payment of income tax, stamp duty or registration fees. Various Loans Provided By the Rythara Seva Sahakara Bank 1. Agricultural loans-crops loans. 2. Loans provided by pledging jewellers. 3. Loans on insurance. 4. Loans for purchasing tractors, power tillers etc... 5. Loans for small business. 6. Housing loans. 7. Higher education loans.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 44
A study on credit appraisal
8. Loans for buying home articles/appliances etc... 9. Solar heater system installation loans. 10. Self employment loans. Bankers of Rythara Seva Sahakara Bank 1. SYNDICATE BANK. 2. KARNATAKA BANK LIMITED. 3. ALLAHABAD BANK. 4. GRAIN MERCHANT CO-OPERATIVE BANK. 5. BHARATH CO-OPERATIVE BANK. 6. KARNATAKA STATE APEX BANK.
Important acts of Rythara Seva Sahakara Bank Karnataka co-operative societies Act-1959 Karnataka co-operative societies Rules-1960 Department of parliamentary affairs and legislation-2000 Bye-law of co-operative societies.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 45
A study on credit appraisal
Board Activity Chart of Rythara Seva Shakara Bank
Planning
Organising
Staffing
Directing
Controlling
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 46
A study on credit appraisal
Organizational Structure of Rythara Seva Sahakara Bank Share holder Directors Manager Staff
Shareholders The person who holds the share of company is called a shareholder/member of the company. The capital of the company is usually divided into certain individual units of a fixed amount. These units are called share. Share means a definite portion of the capital of a company. A share is the interest of a shareholder in the company measured by a sum of money. Societies provided by three types of shareholders namely: a. Class Shareholder (Former). b. Class Shareholder (Government) c. Class Shareholder (Individual) Directors There are ten board of directors from the different departments. Directors of the Rythara Seva Sahakara Bank VANISHREE N.MURTHY K.NAGEGOWDA
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 47
A study on credit appraisal
S.K.NAGARAJ REDDY THIMMARAY GOWDA PADMANABH SHETTY CHANDRU SHASHANKA JANARDHAN PAI KRISHNA BATTA
Future Prospects/Growth All branches should become computerized branch with ATM facility Undertaking commercial activities. Increasing sales. Become a RBI clearing house member
AUDIT,ENQUIRY & INSPECTION Audit Under rule 51, Rythara Seva Sahakara bank should keep accounts of books and registers as prescribed by the registrar from time to time. In case fails to maintain and write the accounts up to date as prescribed by the registrar. He is given powers under rule 52 to direct the society to gets to these accounts. Auditor should audit the final accounts and other statements and they may direct returns as with in two months from the close of the co-operative year. Enquiry Whenever irregularities and mismanagement etc, occur in the co-operative societies. The act provide for enquiry by the registrar under section 64.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 48
A study on credit appraisal
It is obligatory on registrar to hold this enquiry if an application received from any co-operative society to which the society concerned affiliated or by majority of the committee members of the societies or by not less than of the total number of members of the society. Inspection Section 8(65) the act provides for inspection of books of co-operative societies to ascertain their financial position and financial management. The registrar is empowered to pass an order under section 8(65) to conduct inspection of books of co-operative society by inspection officers appointed under the order. Amendment of BYE-LAWS Whenever it is desirable in the interest of the development of co-operative society are to provide better services to its members are to bring the Bye-laws in conformity with the act and rules. The bye-laws of co-operative society should be changed by the process of amendment. The proposals for the amendment of the bye-laws of a co-operative society can be initiated either by the society itself of the registrar. Whenever a co-operative society initiates amendment to its bye-laws, it has to convey a general body of meeting and secure the approval of 2\3 members present and voting and send the proposals to registrar is made responsible to ensure that the proposed changes in the bye-laws are in the conformity with the act and will promote the economic interest of the members of the society and satisfy the economic viability of the co-operative society. If these conditions are satisfied he may register the amendments.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 49
A study on credit appraisal
Table:01 Equity Share Capital
Year 2009-10 2010-11 2011=12 Total
Amount 151.98 160.39 30.06 342.44
Percentage [%] 44.38 46.84 8.78 100
Analysis: The above table shows that there are changes in the equity share capital of the bank. It is 44.38% in 2009-10, 46.84% in 2010-11 and 8.78% in 2011-12.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 50
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-01 Equity Share Capital
50.00 44.38% 45.00 40.00 35.00 30.00 25.00 20.00 15.00
46.84%
8.78% 10.00 5.00 0.00 2009-10 2010-11 2011=12
Interpretation: The above graph represents the changes in equity share capital from one year to another year. In 201011 it has increased to some extent but it has been suddenly decreased to a large extent in 2011-12.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 51
A study on credit appraisal
Table-02 Net Profit
Year 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 Total
Amount 124.24 183.77 232.56 540.57
Percentage [%] 22.98 34.00 43.02 100
Analysis: The above table shows the net profit for three financial years which is increasing from one financial year to another financial year. The net profit was 124.24 lakhs in 2009-2010, 183.77 lakhs in 2010-2011 and 232.56 lakhs in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 52
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-02 Net Profit
22.98%
43.02% 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
34.00%
Interpretation: From the above graph we can interpret that net profit is increasing year by year i.e. from 22.98% in 2009-2010 to 43.02% in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 53
A study on credit appraisal
Table-03 Current Assets
Year 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 Total
Amount 160.71 186.08 182.73 529.52
Percentage [%] 30.35 35.14 34.51 100
Analysis From the above table we can analyse that the value of current assets increased in the year 2010-2011 and it has decreased in the financial year 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 54
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-03 Current Assets
36.00 35.14% 34.51% 34.00
35.00
33.00
32.00
31.00 30.35% 30.00
29.00
28.00
27.00 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
Interpretation: The above graph represents the change in the value of current assets. The value of current assets increased from 30.35% to 35.14% in the financial year 2009-2010 and it has been diminished to 34.51% in the financial year 2010-2011.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 55
A study on credit appraisal
Table-04 Current Liabilities
Year 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 Total
Amount 10.31 5.22 32.81 48.34
Percentage [%] 21.33 10.80 67.87 100
Analysis: From the above table it can be analysed that there are fluctuations in the value of current liabilities. The value of current liability was Rs.10.31 Lakhs in 2009-2010 and it was Rs.32.81 Lakhs in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 56
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-04 Current Liabilities
2011-12
67.87%
2010-11
10.80%
2009-10
21.33%
0.00
10.00
20.00
30.00
40.00
50.00
60.00
70.00
80.00
Interpretation: From the above graph we can interpret that the value of current liabilities has decreased from 21.33% in 2009-2010 to 10.80% in 2010-2011 and again the value of current liabilities increased to 67.87% in the financial year of 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 57
A study on credit appraisal
Table-05: Personal loan
Year
Amount( in lakhs)
Percentage (%)
2009 - 2010
105.92
34.70
2010 - 2011
83.38
27.32
2011 - 2012
115.92
37.98
Total
305.22
100
ANALYSIS: From the above table it is analysed that the amount outstanding with respect to personal loan is 105.92 lakhs with 34.70% in 2009-2010. The amount outstanding with respect to personal loan is 83.38 lakhs with 27.32% and the amount outstanding with respect to personal loan is 115.92 lakhs with 37.98% in 2011 - 2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 58
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-05 Personal loan
40
35
30
25
20 34.7 % 15 27.32%
37.98 %
10
0 2009 - 2010 2010 - 2011 2011 - 2012
INTERPRETATION: From the above graph it can be interpreted that there is a decline in the amount outstanding with respect to personal loan in the year 2010 2011 and again there is substantial growth in the year 2011-2012 in the matter of personal loans.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 59
A study on credit appraisal
Table -06 Housing finance
Year 2009 - 2010 2010 - 2011 2011 - 2012 Total
Amount (in Lakhs) 82.76 98.87 113.36 294.99
Percentage (%) 28 34 38 100
ANALYSIS: From the above table it is analysed that the outstanding amount of loan was 82.76 lakhs with 28% in 2009-2010, In the year 2010 2011 the amount was 98.87 lakhs with 34 % and in the year 2011 2012 it was 113.36 lakhs with 38%.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 60
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-06 Housing finance
28% 38% 2009-2010 2010-2011 2011-2012
34%
INTERPRETATION: From the above pie- chart it can be inferred that there is continuous growth every year in the housing finance segment. There is a noticeable growth in the home loan segment which is very profitable to the bank for their further financial improvement.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 61
A study on credit appraisal
Table -07 Educational loan
Year
Amount (in Lakhs)
Percentage (%)
2009 - 2010 2010 - 2011
1.06 1.10
6.91 7.17
2011 - 2012
13.18
85.92
Total
15.34
100
ANALYSIS: From the above table it is analysed that the amount outstanding with respect to educational loan is 1.06 lakhs with 6.91% in the financial year 2009-2010. The amount outstanding with respect to educational loan is 1.10 lakhs with 7.17% in 2010-2011. And it was 13.18 lakhs with 85.92% in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 62
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-07 Education Loan
6.91% 7.17%
2009 - 2010 2010 - 2011 2011 - 2012
85.92%
INTERPRETATION: From the above pie-chart it is seen that there is a substantial growth of education loan in the year 2010 2011 and there is a tremendous growth in the year 2011 2012 as compared to previous years. There is a noticeable growth in the education loan segment of Rythara seva Sahakara bank which plays a very important role in the development of bank.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 63
A study on credit appraisal
Table-08 Advances to SC/ST Priority Sector
Year 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 Total
Amount 5000.00 5000.00 5000.00 15000.00
Percentage [%] 33.33 33.33 33.33 100
Analysis: From the above table we can analyse that the value of the advances provided to SC/ST priority sector remains same in the last three financial years.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 64
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-08 Advances to SC/ST Priority sector
33.33%
33.33%
2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
33.33%
Interpretation: The above graph represents the change in the value of advances given to SC/ST priority sector. Hence the value of advances to SC/ST priority sector was stable for last three years i.e. 33.33%.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 65
A study on credit appraisal
Table-09 Domestic Credit
Year 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 Total
Amount 10.31 8.22 2.99 21.52
Percentage [%] 47.91 38.20 13.89 100
Analysis: From the above table we can ascertain that the value of the domestic credit was Rs.10.31 Lakhs in 20092010, Rs.8.22 lakhs in 2010-2011 and Rs.2.99 lakhs in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 66
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-09 Domestic Credit
50.00 45.00 40.00 35.00 30.00 25.00 20.00 15.00 10.00 5.00 0.00
47.91%
38.20%
13.89%
2009-10 2010-11 2011-12
Series1
Interpretation: From the above graph we can interpret the change in the value of domestic credit of Rythara seva Sahakara bank. Hence there is a diminishing strategy in the value of domestic credit i.e. from 47.91% in 2009-2010 to 13.89% in the financial year 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 67
A study on credit appraisal
Table-10 Domestic Deposit
Year 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 Total
Amount 3996.63 5593.95 21407.66 30998.24
Percentage [%] 12.89 18.05 69.06 100
Analysis: The above table shows the change in the value of domestic deposit. The value of domestic deposit was Rs.3996.63 lakhs in 2009-2010, Rs.5593.95 Lakhs in 2010-2011 and 21407.66 lakhs in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 68
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-10 Domestic Deposits
70.00 60.00 50.00 40.00 30.00 20.00 10.00 0.00 2009-10 2010-11 12.89% 18.05%
69.06%
2011-12
Interpretation: From the above graph we can conclude the change in the value of domestic deposits. The value of domestic deposits has increased from 12.89% in 2009-2010 to 18.05% in 2010-2011 and again it has increased to 69.06% in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 69
A study on credit appraisal
Table-11 Net NPA
Year 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 Total
Amount 30.64 48.02 54.56 133.22
Percentage [%] 23.00 36.05 40.95 100
Analysis: From the above table we can analyse the value of change in the net NPV. It was Rs.30.64 Lakhs in 20092010, Rs.48.02 Lakhs in 2010-2011 and Rs.54.56 Lakhs in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 70
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-11 Net NPA
45.00 40.00 35.00 30.00 25.00 20.00 15.00 10.00 5.00 0.00 2009-10 2010-11 23.00%
40.95% 36.05%
2011-12
Interpretation: The above graph represents the change in the value of net NPA. The net NPA increased from 23% in 2009-2010 to 36.05% in 2010-2011 and again it has increased to 40.95% in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 71
A study on credit appraisal
Table-12 Bank Deposits
Year 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 Total
Amount 1523.11 2477.59 2831.94 6832.64
Percentage [%] 22.29 36.26 41.45 100
Analysis: From the above table it can be analysed that the value of Bank deposits was Rs.1523.11 lakhs in 20092010, Rs.2477.59 lakhs in 2010-2011 and Rs.2831.94 lakhs in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 72
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-12 Bank Deposits
2011-12
41.45%
2010-11
36.26%
2009-10
22.29%
0.00
5.00
10.00
15.00
20.00
25.00
30.00
35.00
40.00
45.00
Interpretation: From the above graph we can interpret the change in the value of bank deposits from 2009-2012. The value of bank deposits was 22.29% in 2009-10 and it was 41.45% in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 73
A study on credit appraisal
Table-13 Current Deposits
Year 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 Total
Amount 3996.63 5593.95 293.13 9883.71
Percentage [%] 40.44 56.60 2.97 100
Analysis From the above table we can analyse that the value of current deposits was Rs.3996.63 lakhs in 2009.10, Rs.5593.95 lakhs in 2010-2011 and it was 293.13 lakhs in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 74
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-13 Current Deposits
2.97%
40.44% 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 56.60%
Interpretation: The above graph represents percentage of change in current deposits. The current deposits increased from 40.44% in 2009-2010 and it was 2.97% in 2011-2012. Hence, the current deposits has decreased to a great extent.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 75
A study on credit appraisal
Table-14 Fixed Deposits
Year 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 Total
Amount 1582.22 1988.16 2866.07 6436.45
Percentage [%] 24.58 30.89 44.53 100
Analysis: From the above table we can analyse that the value of Fixed deposits was Rs.1582.22 lakhs in 20092010, Rs.1988.16 lakhs in 2010-2011 and Rs,2866.07 lakhs in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 76
A study on credit appraisal
Graph-14 Fixed Deposits
2011-12
44.53%
2010-11
30.89%
2009-10
24.48%
0.00
5.00
10.00
15.00
20.00
25.00
30.00
35.00
40.00
45.00
50.00
Interpretation: The above graph represents the change in the value of fixed deposits. The value of fixed deposits was increased from 24.48% in 2009-2010 to 30,89% in 2020-2011 and again it has increased to 44.53% in 2011-2012.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 77
A study on credit appraisal
Table 15 Table showing source of awareness about Rythara seva Sahakara bank
Source
No. of respondent
Percentage (%)
RSSB employees
12.5
Friends
22
55
Television
7.5
Newspaper
10
25
Total
40
100
ANALYSIS: From the above table it can be analysed that the source of awareness for 5 respondents is through RSSB employees, the source of awareness for 22 respondents is through friends, the source of awareness for 3 respondents is through television & the source of awareness for 10 respondents is through news paper.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 78
A study on credit appraisal
Graph 15 Graph showing source of awareness of Rythara seva Sahakara bank.
60
55%
50
40
30
25%
20 12.5% 10 7.5%
0 RSSB employees Friends Television Newspaper
INTERPRETATION: It can be inferred that majority of the respondent came to know about the bank through friends, followed by news paper and finally the least came to know through television.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 79
A study on credit appraisal
Chapter: 06 Summary of findings, suggestions and conclusions
Findings: 1. The equity share capital of the bank is quite satisfactory it maintained a stable rate of percentage. 2. The net profit of the bank is increasing year by year is good indication for the bank that it is in a healthy position. 3. When compare the percentage of the current assets over the current liabilities it is satisfactory i.e., the value of current assets is higher than the current liabilities in all three years. 4. The housing loan and education loan is also increasing year by year this will help to the common people and students. 5. Advances lend under priority sector to various sections of people is stable in all three years. 6. Domestic credit is decreased year by year in turn domestic deposits increased year by year, it is also good for the bank that they can get the sources for their operations. 7. The net NPA of the bank is increasing year by year. 8. Bank deposits increased tremendously and current deposits were maintained stable. 9. The Fixed deposit is in its way of increasing year by year. 10. Overall by observing the growing scenario, in every aspect it is good for the bank for its long run survival.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 80
A study on credit appraisal
SUGGESTIONS: 1. First thing is the equity share capital stale in all three years. If the bank attracts or obtains more equity capital it is good for its efficient operation. 2. The bank should attract more customers related to current deposits by offering more benefits to them. 3. The NPA rate increasing year by year. The bank should reduce NPA gradually. 4. More importance is bank should take more intention relating to the careful appraisal of the proposed applicant. 5. The bank has to give more additional facilities to retain its present customers. 6. The bank operation in the village side should also have improved because they are not aware about the banking activities. 7. The bank should try satisfying the customers as they desire. 8. Through this the bank can improve and become younger than ever.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 81
A study on credit appraisal
CONCLUSIONS: Every bank has its own credit structure as per their convenience and the norms proposed by their head office. But this certainly does not mean that the basic layout of the credit structure changes from bank to bank. There are certain rules and regulations as set by RBI which is exemplary for every bank to follow. The bank cannot deviate from the already set norms but certain margins can be added or deducted by bank as per their requirements. Credit appraisal is a process of appraising the credit worthiness of loan applicants. The funds of the depositors i.e., general public are mobilized by means of such advancement / investment. Thus it is extremely important for lender bank to assess the risk associated with credit; thereby ensure the security for the funds deposited by the depositors. In UBI the credit appraisal is done by thorough study of project which involves following.
1. A detailed study about the promoters is carried out in order to ensure promoters are experienced in line of business and are capable to implement and run the project. 2. A detailed study about technical aspects is done to determine the technical soundness of the project. 3. A detailed study relating to financial viability of the project is done; thereby ensuring that project will generate sufficient surplus to repay the loan replacement and interest. 4. It determines the risk associated with the project this is done by performing a sensitivity analysis and credit rating. With sensitivity analysis the projects capacity to service debts under worsened conditions is determined. Credit ratings provides ratings for various parameters like management ,financial , market and so , thereby determine the credit worthiness of the borrower . 5. It is on the basis of credit risk level; collateral securities to be given by the borrower are determined. This shows bank of India has sound system for credit appraisal.
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 82
A study on credit appraisal
BIBLIOGRAPHY
References: Websites:
A Hand Book of Banking by N. S. Toor Ramman Finance management. Finance management and policies by James C. Van Horne. Management accounting principle and practises by R. K. Sharma. Accounting for managers S. P Jain and K.L. Narang. Research methodology by C.R. Kothori. Business Research Methods by Appannaiah Reddy and Ramnath
www.google.com www.rbi.org.in
www.wikipedia.com
Govt First Grade College, Yelahanka.
Page 83
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Credit AppraisalDokument94 SeitenCredit AppraisalpratikshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010-05-20 - MFR of Interview With Greg Lippmann of DBDokument13 Seiten2010-05-20 - MFR of Interview With Greg Lippmann of DBHcs RichardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Rating ProcessDokument36 SeitenCredit Rating ProcessBhuvi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit AppraisalDokument6 SeitenCredit AppraisalAnjali Angel ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Appraisal ProcessDokument19 SeitenCredit Appraisal ProcessVaishnavi khot100% (1)
- Credit Appraisal in MuthootDokument30 SeitenCredit Appraisal in MuthootNISHI1994100% (1)
- Credit Appraisal Process GRP 10Dokument18 SeitenCredit Appraisal Process GRP 10Priya JagtapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial ManagementDokument49 SeitenFinancial ManagementBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Questions: Company BackgroundDokument5 SeitenQuestions: Company BackgroundVia Samantha de AustriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drawing on Credit: Assessing CreditworthinessDokument24 SeitenDrawing on Credit: Assessing CreditworthinessJimuel Faigao100% (1)
- Credit ApprisalDokument74 SeitenCredit Apprisalpiupush100% (1)
- Loans and AdvancesDokument18 SeitenLoans and AdvancesAnupam RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Appraisal Process of Sbi: A Case Study of Branch of Sbi in HisarDokument1 SeiteCredit Appraisal Process of Sbi: A Case Study of Branch of Sbi in Hisarnbtamana4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Is An Information System That IdentifiesDokument5 SeitenAccounting Is An Information System That Identifiesniser88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment of Management of Working Capital: TopicDokument13 SeitenAssignment of Management of Working Capital: TopicDavinder Singh BanssNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Credit Appresal Process With Special Reference To Differnent Loans Offer by Indian BankDokument86 SeitenAn Overview of Credit Appresal Process With Special Reference To Differnent Loans Offer by Indian BankAbhinandan SahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Market Operations BookDokument282 SeitenSecurity Market Operations BookAbhishek AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Credit Appraisal System in India With Special Reference To South Indian BanksDokument5 SeitenA Study On Credit Appraisal System in India With Special Reference To South Indian BanksEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investment BankingDokument16 SeitenInvestment BankingSudarshan DhavejiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Report On KYC, NPA & FactoringDokument19 SeitenBanking Report On KYC, NPA & FactoringKaushal Patel100% (1)
- 6.sources of FundsDokument10 Seiten6.sources of FundsHafizullah AnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to NPAs in BankingDokument46 SeitenIntroduction to NPAs in BankingPiyushVarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 MGT of Equity CapitalDokument29 SeitenChapter 16 MGT of Equity CapitalRafiur Rahman100% (1)
- Credit MonitoringDokument15 SeitenCredit MonitoringTushar JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Credit Management of JanataDokument47 SeitenAnalysis of Credit Management of Janataprokash halderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment of Management of Working Capital: TopicDokument13 SeitenAssignment of Management of Working Capital: TopicDavinder Singh Banss0% (1)
- Credit MonitoringDokument5 SeitenCredit MonitoringAmit GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avi Thesis Final Credit Risk Management in Sonali Bank LTDDokument20 SeitenAvi Thesis Final Credit Risk Management in Sonali Bank LTDHAFIZA AKTHER KHANAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- BankingDokument110 SeitenBankingNarcity UzumakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final PPT of Concept of RRBsDokument27 SeitenFinal PPT of Concept of RRBsManali ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Report on Nawanagar BankDokument26 SeitenBanking Report on Nawanagar Bankkaran BorichaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit AppraisalDokument11 SeitenCredit AppraisalKunal GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Appraisal in SBIDokument123 SeitenCredit Appraisal in SBIvivekdudejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assess credit worthinessDokument14 SeitenAssess credit worthinessAsim MahatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCFS Cooperative Bank LTDDokument64 SeitenSCFS Cooperative Bank LTDLïkïth RäjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Term and Long Term Sources of Bank FundDokument9 SeitenShort Term and Long Term Sources of Bank FundPeal Ahamed ShantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Credit Appraisal in PNBDokument76 SeitenReport On Credit Appraisal in PNBSanchit GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retail Banking of Allahabad BankDokument50 SeitenRetail Banking of Allahabad Bankaru161112Noch keine Bewertungen
- Credit AppraisalDokument89 SeitenCredit AppraisalSkillpro KhammamNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA Finance Thesis Topics List PDF: Equity Analysis of BanksDokument4 SeitenMBA Finance Thesis Topics List PDF: Equity Analysis of BanksbagyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Appraisal of Term Loans by Financial Institutions Like BanksDokument4 SeitenCredit Appraisal of Term Loans by Financial Institutions Like BanksKunal GoldmedalistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit AppraisalDokument12 SeitenCredit AppraisalAishwarya KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study of Financial Analysis of Nepal SDokument22 SeitenA Case Study of Financial Analysis of Nepal SDiwesh Tamrakar100% (1)
- CAMELS Ratings Framework for Banking SupervisionDokument19 SeitenCAMELS Ratings Framework for Banking SupervisionVikas R GaddaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Project of Vijaya BankDokument103 SeitenMy Project of Vijaya Banktamizharasid100% (1)
- Financial ManagementDokument13 SeitenFinancial ManagementSunny KesarwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Appraisal at Central Bank of IndiaDokument23 SeitenCredit Appraisal at Central Bank of IndiaNimishaSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Report Is To Analysis Credit Risk Management of Eastern Bank LimitedDokument30 SeitenThis Report Is To Analysis Credit Risk Management of Eastern Bank Limitedশফিকুল ইসলাম লিপুNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDokument11 SeitenReserve Bank of IndiaHarshSuryavanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Sector ReformsDokument27 SeitenBanking Sector ReformsArghadeep ChandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Banking System - Structure and Other Details (With Diagrams)Dokument14 SeitenIndian Banking System - Structure and Other Details (With Diagrams)krunaldedehiya100% (1)
- Financial Performance Analysis On Dhaka Bank LTDDokument15 SeitenFinancial Performance Analysis On Dhaka Bank LTDনূরুল আলম শুভNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Risk Management-City BankDokument69 SeitenCredit Risk Management-City BankGobinda saha100% (1)
- A Study On Credit Management at District CoDokument86 SeitenA Study On Credit Management at District CoIMAM JAVOOR100% (2)
- Chapter On NPA - 13032020 PDFDokument105 SeitenChapter On NPA - 13032020 PDFs s singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit and Collections HandbookDokument9 SeitenCredit and Collections Handbook4gen_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Appraisal: by N.R.Trivedi Dy. Manager Credit Head Office, Saurashtra Gramin BankDokument13 SeitenCredit Appraisal: by N.R.Trivedi Dy. Manager Credit Head Office, Saurashtra Gramin Bankniravtrivedi72Noch keine Bewertungen
- MEANING AND TYPES OF FINANCEDokument93 SeitenMEANING AND TYPES OF FINANCEShobhit GoswamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of the NBFC Industry in India and its TypesDokument4 SeitenOverview of the NBFC Industry in India and its TypesSmike ToretoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian financial system componentsDokument8 SeitenIndian financial system componentsShivam KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5524 - Lesson Note Financial InstitutionsDokument4 Seiten5524 - Lesson Note Financial Institutionsramlabs400Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ombudsman's dismissal of behest loan caseDokument12 SeitenOmbudsman's dismissal of behest loan casePamela BalindanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dear Sir Request For Project Financing Amounting Rs. - FUNDED FACILITY RS. - & NON FUNDED FACITIY Rs.Dokument2 SeitenDear Sir Request For Project Financing Amounting Rs. - FUNDED FACILITY RS. - & NON FUNDED FACITIY Rs.adnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security AgreementDokument3 SeitenSecurity AgreementAmeer BachekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bill of Exchange DiscountingDokument14 SeitenBill of Exchange Discountingrida_fatima1067% (3)
- Landti Bar QsDokument5 SeitenLandti Bar QsMikkaEllaAnclaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBI Project Report on Loans and AdvancesDokument85 SeitenSBI Project Report on Loans and AdvancesshahidafzalsyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burhani Lace Sale Notice Terms and ConditionsDokument12 SeitenBurhani Lace Sale Notice Terms and ConditionsakshayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equity Trust Fork ChroniclesDokument134 SeitenEquity Trust Fork ChroniclesAmbrose YollahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-11 - Input Demand - The Capital Market and The Investment DecisionDokument46 SeitenCh-11 - Input Demand - The Capital Market and The Investment DecisionAnubhab KhanraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Investments in Debt SecuritiesDokument15 SeitenChapter 10 Investments in Debt SecuritiesGlydel B. MatayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 2 MiCparDokument21 SeitenGroup 2 MiCparCarlito B. BancilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 19 Business Finance Needs and SourcesDokument5 SeitenChapter 19 Business Finance Needs and SourcesSol CarvajalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin 254 Final AssignmentDokument19 SeitenFin 254 Final AssignmentFahmida FaizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Unit II - Part 2 - Structure of The Philippine Financial SystemDokument8 Seiten4 - Unit II - Part 2 - Structure of The Philippine Financial SystemAlexis Ann Angan AnganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dacquel v. Spouses Sotelo, G.R. No. 203946, (August 4, 2021)Dokument15 SeitenDacquel v. Spouses Sotelo, G.R. No. 203946, (August 4, 2021)Pastel Rose CloudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic Vs GrijaldoDokument3 SeitenRepublic Vs GrijaldozielalcantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature and extent of guaranty definedDokument5 SeitenNature and extent of guaranty definedMaria Divina Gracia D. MagtotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subsequent Measurement of Lease LiabilityDokument2 SeitenSubsequent Measurement of Lease LiabilityAvox EverdeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop Debt Securities STAFFDokument42 SeitenWorkshop Debt Securities STAFFIshan MalakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Brink - Inside The Race To Stop The Collapse of The Global Financial System by Henry PaulsonDokument21 SeitenOn The Brink - Inside The Race To Stop The Collapse of The Global Financial System by Henry PaulsonKitto IrvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PUREGOLD 1Q2019 NET INCOME UP 11.9Dokument81 SeitenPUREGOLD 1Q2019 NET INCOME UP 11.9hiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - I-REITDokument27 SeitenChapter 4 - I-REITNABILAH SYAHBUDINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loan Disbursement PDFDokument10 SeitenLoan Disbursement PDFGemechu GuduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invest (Essay)Dokument2 SeitenInvest (Essay)Jesika NursudindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISSUES IN BANK BRANCH AUDITDokument26 SeitenISSUES IN BANK BRANCH AUDITkarbalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heirs of Gregorio LopezDokument81 SeitenHeirs of Gregorio LopezdaryllNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMTDokument3 SeitenFMTZakhir Bello0% (1)
- Introductory Course Material For INF516 InvestmentsDokument238 SeitenIntroductory Course Material For INF516 InvestmentshuguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 15,16, & 17 IA Valix Sales Type LeaseDokument15 SeitenChapter 15,16, & 17 IA Valix Sales Type LeaseMiko ArniñoNoch keine Bewertungen